Abstract
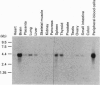
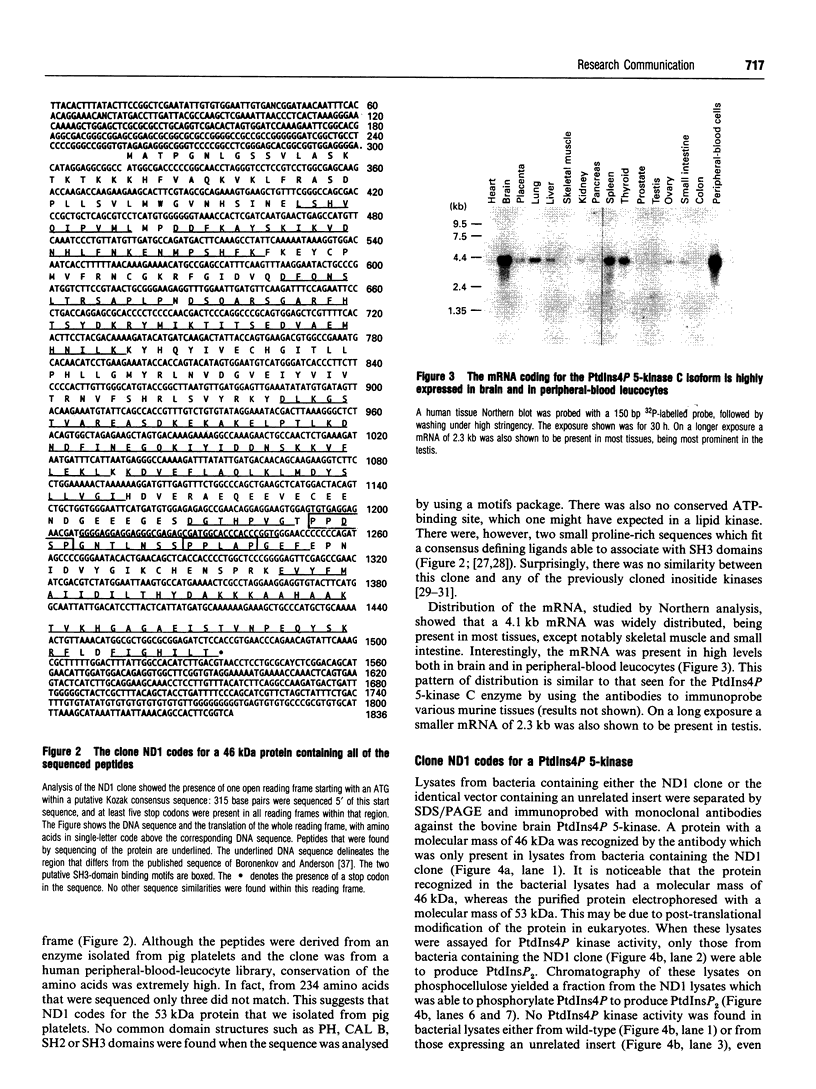
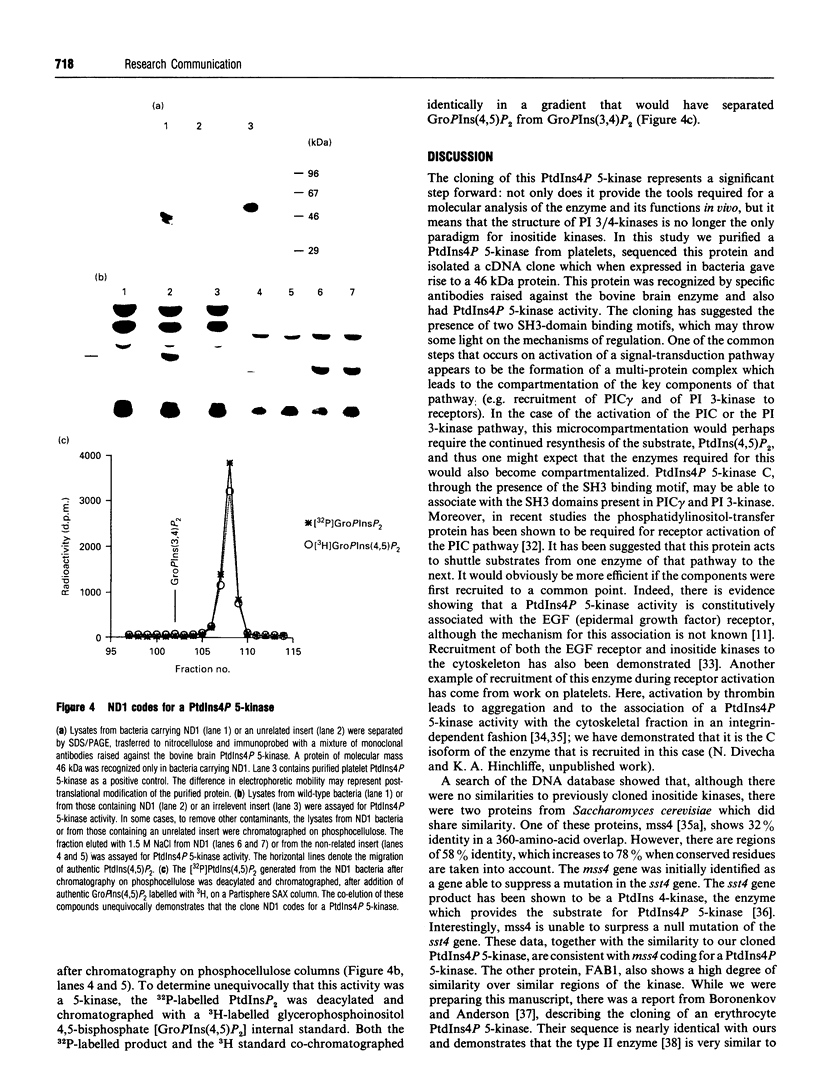
In this study we describe the purification and sequencing of the C isoform of platelet PtdIns4P 5-kinase. Subsequently a cDNA was isolated from a human circulating-leucocyte library, which when sequenced was shown to contain all of the peptides identified in the purified protein. In addition, expression of this cDNA in bacteria led to the production of a protein which was recognized by specific monoclonal antibodies raised to the bovine brain enzyme [Brooksbank, Hutchings, Butcher, Irvine and Divecha (1993) Biochem. J. 291, 77-82] and also led to the appearance of PtdIns4P 5-kinase activity in the bacterial lysates. Interestingly, the cDNA showed no similarity to any of the previously cloned inositide kinases. A search of the DNA databases showed that two proteins from Saccharomyces cerevisiae shared close similarity to this enzyme, one of which, the mss4 gene product, has been implicated in the yeast inositol lipid pathway. These data suggest that the PtdIns4P 5-kinases are a new family of inositide kinases unrelated to the previously cloned phosphoinositide 3/4-kinases.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bazenet C. E., Ruano A. R., Brockman J. L., Anderson R. A. The human erythrocyte contains two forms of phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase which are differentially active toward membranes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):18012–18022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boronenkov I. V., Anderson R. A. The sequence of phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase defines a novel family of lipid kinases. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 17;270(7):2881–2884. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.7.2881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooksbank C. E., Hutchings A., Butcher G. W., Irvine R. F., Divecha N. Monoclonal antibodies to phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase: distribution and intracellular localization of the C isoform. Biochem J. 1993 Apr 1;291(Pt 1):77–82. doi: 10.1042/bj2910077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Lactose genes fused to exogenous promoters in one step using a Mu-lac bacteriophage: in vivo probe for transcriptional control sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4530–4533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong L. D., Traynor-Kaplan A., Bokoch G. M., Schwartz M. A. The small GTP-binding protein Rho regulates a phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase in mammalian cells. Cell. 1994 Nov 4;79(3):507–513. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90259-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke N. G., Dawson R. M. Alkaline O leads to N-transacylation. A new method for the quantitative deacylation of phospholipids. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 1;195(1):301–306. doi: 10.1042/bj1950301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Filhol O., Payrastre B., Hunter T., Gill G. N. Interaction between the epidermal growth factor receptor and phosphoinositide kinases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):637–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen P. J., Dawson A. P., Irvine R. F. Purification and characterization of an Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 binding protein from pig platelets: possible identification of a novel non-neuronal Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 receptor. Biochem J. 1995 Jan 1;305(Pt 1):139–143. doi: 10.1042/bj3050139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen P. J., Patel Y., Kakkar V. V., Irvine R. F., Authi K. S. Specific binding sites for inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate are located predominantly in the plasma membranes of human platelets. Biochem J. 1994 Mar 15;298(Pt 3):739–742. doi: 10.1042/bj2980739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Divecha N., Brooksbank C. E., Irvine R. F. Purification and characterization of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinases. Biochem J. 1992 Dec 1;288(Pt 2):637–642. doi: 10.1042/bj2880637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan C. A., Schnieders E. A., Emerick A. W., Kunisawa R., Admon A., Thorner J. Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase: gene structure and requirement for yeast cell viability. Science. 1993 Nov 26;262(5138):1444–1448. doi: 10.1126/science.8248783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Bustos J. F., Marini F., Stevenson I., Frei C., Hall M. N. PIK1, an essential phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase associated with the yeast nucleus. EMBO J. 1994 May 15;13(10):2352–2361. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06519.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudette D. C., Holub B. J. Effect of genistein, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, on U46619-induced phosphoinositide phosphorylation in human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 16;170(1):238–242. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91265-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grondin P., Plantavid M., Sultan C., Breton M., Mauco G., Chap H. Interaction of pp60c-src, phospholipase C, inositol-lipid, and diacyglycerol kinases with the cytoskeletons of thrombin-stimulated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15705–15709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halenda S. P., Feinstein M. B. Phorbol myristate acetate stimulates formation of phosphatidyl inositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidyl inositol 4,5-bisphosphate in human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 30;124(2):507–513. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91583-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiles I. D., Otsu M., Volinia S., Fry M. J., Gout I., Dhand R., Panayotou G., Ruiz-Larrea F., Thompson A., Totty N. F. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: structure and expression of the 110 kd catalytic subunit. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):419–429. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90166-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janmey P. A. Phosphoinositides and calcium as regulators of cellular actin assembly and disassembly. Annu Rev Physiol. 1994;56:169–191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.56.030194.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins G. H., Fisette P. L., Anderson R. A. Type I phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase isoforms are specifically stimulated by phosphatidic acid. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11547–11554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Uno I., Ishikawa T., Takenawa T. Activation of phosphatidylinositol kinase and phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate kinase by cAMP in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3116–3121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim W. A., Richards F. M., Fox R. O. Structural determinants of peptide-binding orientation and of sequence specificity in SH3 domains. Nature. 1994 Nov 24;372(6504):375–379. doi: 10.1038/372375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Eck M. J. SH3 domains. Minding your p's and q's. Curr Biol. 1995 Apr 1;5(4):364–367. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moritz A., De Graan P. N., Gispen W. H., Wirtz K. W. Phosphatidic acid is a specific activator of phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7207–7210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahas N., Plantavid M., Mauco G., Chap H. Association of phosphatidylinositol kinase and phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate kinase activities with the cytoskeleton in human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 27;246(1-2):30–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payrastre B., Plantavid M., Breton M., Chambaz E., Chap H. Relationship between phosphoinositide kinase activities and protein tyrosine phosphorylation in plasma membranes from A431 cells. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 15;272(3):665–670. doi: 10.1042/bj2720665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payrastre B., van Bergen en Henegouwen P. M., Breton M., den Hartigh J. C., Plantavid M., Verkleij A. J., Boonstra J. Phosphoinositide kinase, diacylglycerol kinase, and phospholipase C activities associated to the cytoskeleton: effect of epidermal growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):121–128. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pertile P., Liscovitch M., Chalifa V., Cantley L. C. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate synthesis is required for activation of phospholipase D in U937 cells. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 10;270(10):5130–5135. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.10.5130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Chang K. J. Regulation of brain phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate kinase by GTP analogues. A potential role for guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3206–3210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Hughes K. T., Irvine R. F. Pathway of phosphatidylinositol(3,4,5)-trisphosphate synthesis in activated neutrophils. Nature. 1991 May 2;351(6321):33–39. doi: 10.1038/351033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L., Jackson T. R., Hawkins P. T. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate supply by agonists and non-hydrolysable GTP analogues. Biochem J. 1993 Dec 1;296(Pt 2):481–488. doi: 10.1042/bj2960481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. V., Metcalfe J. C., Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Moore J. P. Mitogens increase phosphorylation of phosphoinositides in thymocytes. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):462–465. doi: 10.1038/312462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. M., Cunningham E., Fensome A., Ball A., Totty N. F., Truong O., Hsuan J. J., Cockcroft S. An essential role for phosphatidylinositol transfer protein in phospholipase C-mediated inositol lipid signaling. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):919–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90471-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totty N. F., Waterfield M. D., Hsuan J. J. Accelerated high-sensitivity microsequencing of proteins and peptides using a miniature reaction cartridge. Protein Sci. 1992 Sep;1(9):1215–1224. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urumow T., Wieland O. H. A small G-protein involved in phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate kinase activation. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 9;263(1):15–17. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80694-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urumow T., Wieland O. H. Evidence for a cholera-toxin-sensitive G-protein involved in the regulation of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate kinase of rat liver membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Nov 18;972(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90121-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urumow T., Wieland O. H. Purification and partial characterization of phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate kinase from rat liver plasma membranes. Further evidence for a stimulatory G-protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 9;1052(1):152–158. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90070-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rooijen L. A., Rossowska M., Bazan N. G. Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate kinase by its product phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 16;126(1):150–155. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90584-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K., Cantley L. C. Cloning and characterization of a human phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 18;269(46):28878–28884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Ohya Y., Goebl M., Nakano A., Anraku Y. A novel gene, STT4, encodes a phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase in the PKC1 protein kinase pathway of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1166–1172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Ohya Y., Nakano A., Anraku Y. Genetic interactions among genes involved in the STT4-PKC1 pathway of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1994 Mar;242(6):631–640. doi: 10.1007/BF00283416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]