Abstract
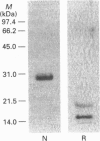
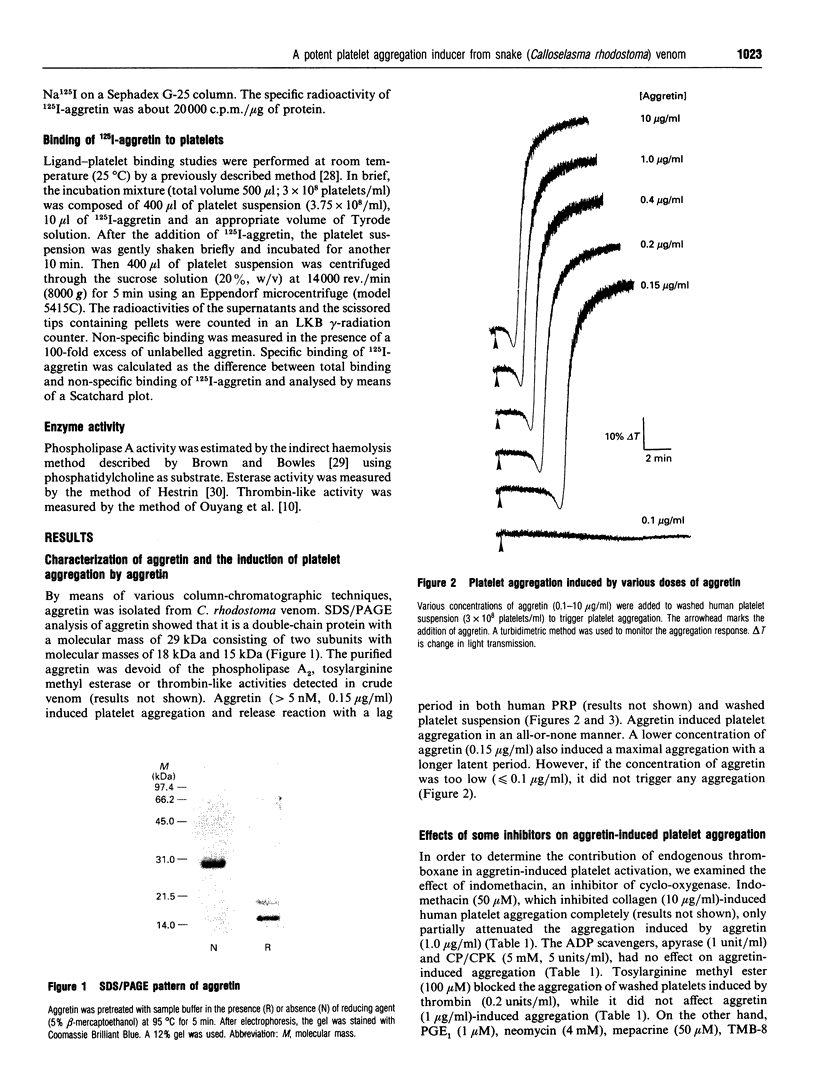
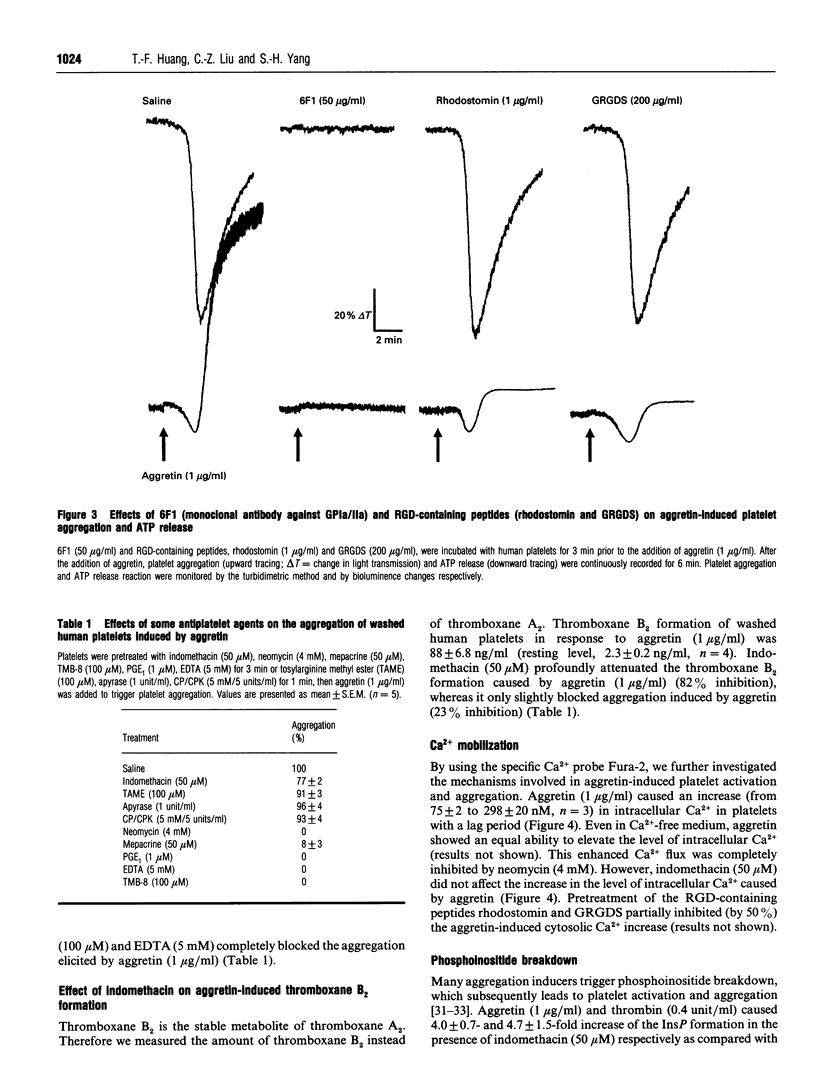
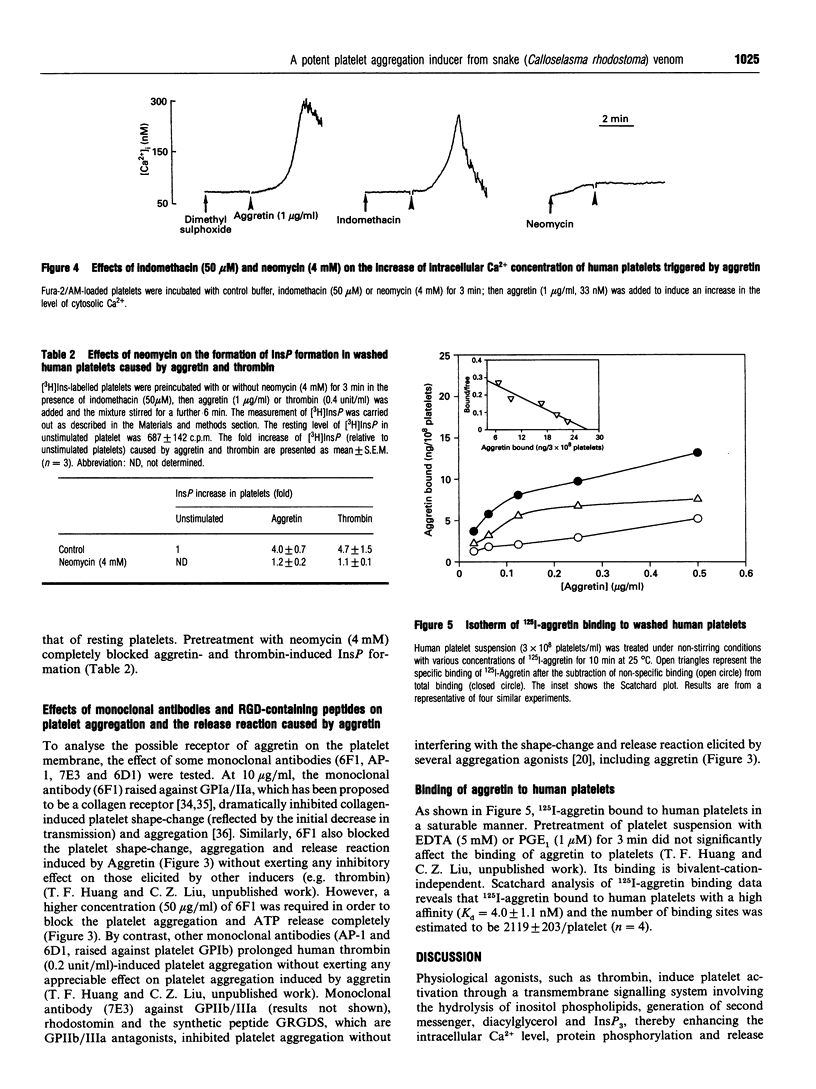
A potent platelet aggregation inducer, aggretin, was purified from Malayan-pit-viper (Calloselasma rhodostoma) venom by ionic-exchange chromatography, gel-filtration chromatography and HPLC. It is a heterodimeric protein (29 kDa) devoid of esterase, phospholipase A and thrombin-like activity. Aggretin (> 5 nM) elicited platelet aggregation with a lag period in both human platelet-rich plasma and washed platelet suspension. EDTA (5 mM), prostaglandin E1 (1 microM) and 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoic acid 8-(diethylamino)octyl ester ('TMB-8'; 100 microM) abolished its aggregating activity, indicating that exogenous bivalent cations and intracellular Ca2+ mobilization are essential for aggretin-induced platelet aggregation. Neomycin (4 mM) and mepacrine (50 microM) completely inhibited aggretin (33 nM)-induced aggregation; however, creatine phosphate/creatine phosphokinase (5 mM, 5 units/ml) and indomethacin (50 microM) did not significantly affect its aggregating activity. Aggretin caused a significant increase of [3H]InsP formation in [3H]Ins-loaded platelets, intracellular Ca2+ mobilization and thromboxane B2 formation. Neomycin, a phospholipase C inhibitor, completely inhibited both the increase of [3H]InsP and intracellular Ca2+ mobilization of platelets stimulated by aggretin. A monoclonal antibody (6F1) directed against glycoprotein Ia/IIa inhibited platelet shape change and aggregation induced by aggretin. 125I-aggretin bound to platelets with a high affinity (Kd = 4.0 +/- 1.1 nM), and the number of binding sites was estimated to be 2119 +/- 203 per platelet. It is concluded that aggretin may act as a glycoprotein Ia/IIa agonist to elicit platelet aggregation through the activation of endogenous phospholipase C, leading to hydrolysis of phosphoinositides and subsequent intracellular Ca2+ mobilization.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORN G. V., CROSS M. J. THE AGGREGATION OF BLOOD PLATELETS. J Physiol. 1963 Aug;168:178–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. L., Kennerly D. A., Stanford N., Majerus P. W. Diglyceride lipase: a pathway for arachidonate release from human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3238–3241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G. Formation of lysophosphatidylinositol in platelets stimulated with thrombin or ionophore A23187. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5196–5200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broekman M. J., Ward J. W., Marcus A. J. Phospholipid metabolism in stimulated human platelets. Changes in phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidic acid, and lysophospholipids. J Clin Invest. 1980 Aug;66(2):275–283. doi: 10.1172/JCI109854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Bowles M. E. Studies on the phospholipase A activity of Crotalus atrox venom. Toxicon. 1966 Mar;3(3):205–212. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(66)90022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiou C. Y., Malagodi M. H. Studies on the mechanism of action of a new Ca-2+ antagonist, 8-(N,N-diethylamino)octyl 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate hydrochloride in smooth and skeletal muscles. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Feb;53(2):279–285. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07359.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S., Beer J. H., Scudder L. E., Steinberg M. H. Collagen-platelet interactions: evidence for a direct interaction of collagen with platelet GPIa/IIa and an indirect interaction with platelet GPIIb/IIIa mediated by adhesive proteins. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):182–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey M. G., Esnouf M. P. The isolation of a component of the venom of Trimeresurus okinavensis that causes the aggregation of blood platelets. Biochem J. 1969 Mar;111(5):733–743. doi: 10.1042/bj1110733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Michell R. H. The polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase of erythrocyte membranes. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 15;198(1):133–140. doi: 10.1042/bj1980133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emms H., Lewis G. P. The roles of prostaglandin endoperoxides, thromboxane A2 and adenosine diphosphate in collagen-induced aggregation in man and the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jan;87(1):109–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10162.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould R. J., Polokoff M. A., Friedman P. A., Huang T. F., Holt J. C., Cook J. J., Niewiarowski S. Disintegrins: a family of integrin inhibitory proteins from viper venoms. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1990 Nov;195(2):168–171. doi: 10.3181/00379727-195-43129b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann S. L., Prescott S. M., Majerus P. W. The effects of mepacrine and p-bromophenacyl bromide on arachidonic acid release in human platelets. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Apr 15;215(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90300-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. F., Holt J. C., Lukasiewicz H., Niewiarowski S. Trigramin. A low molecular weight peptide inhibiting fibrinogen interaction with platelet receptors expressed on glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16157–16163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunicki T. J., Nugent D. J., Staats S. J., Orchekowski R. P., Wayner E. A., Carter W. G. The human fibroblast class II extracellular matrix receptor mediates platelet adhesion to collagen and is identical to the platelet glycoprotein Ia-IIa complex. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4516–4519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Billah M. M., Cuatrecasas P. The initial action of thrombin on platelets. Conversion of phosphatidylinositol to phosphatidic acid preceding the production of arachidonic acid. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5037–5040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlas G. Purification and preliminary structure of a potent platelet aggregating glycoprotein isolated from the venom of Crotalus durissus cascavella. Toxicon. 1982;20(1):289–290. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(82)90228-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustard J. F., Perry D. W., Ardlie N. G., Packham M. A. Preparation of suspensions of washed platelets from humans. Br J Haematol. 1972 Feb;22(2):193–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb08800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neylon C. B., Summers R. J. Stimulation of alpha 1-adrenoceptors in rat kidney mediates increased inositol phospholipid hydrolysis. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun;91(2):367–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb10291.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke F. A., Halenda S. P., Zavoico G. B., Feinstein M. B. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate releases Ca2+ from a Ca2+-transporting membrane vesicle fraction derived from human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):956–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang C. H., Yeh H. I., Huang T. F. Purification and characterization of a platelet aggregation inducer from Calloselasma rhodostoma (Malayan pit viper) snake venom. Toxicon. 1986;24(7):633–643. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(86)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang C., Huang T. F. A potent platelet aggregation inducer from Trimeresurus gramineus snake venom. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 13;761(2):126–134. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90221-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang C., Teng C. M. The action mechanism of the purified platelet aggregation principle of Trimeresurus mucrosquamatus venom. Thromb Haemost. 1979 May 25;41(3):475–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang C., Wang J. P., Teng C. M. A potent platelet aggregation inducer purified from Trimeresurus mucrosquamatus snake venom. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 19;630(2):246–253. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pischel K. D., Bluestein H. G., Woods V. L., Jr Platelet glycoproteins Ia, Ic, and IIa are physicochemically indistinguishable from the very late activation antigens adhesion-related proteins of lymphocytes and other cell types. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):505–513. doi: 10.1172/JCI113348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock W. K., Rink T. J. Thrombin and ionomycin can raise platelet cytosolic Ca2+ to micromolar levels by discharge of internal Ca2+ stores: studies using fura-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 29;139(1):308–314. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80114-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott S. M., Majerus P. W. Characterization of 1,2-diacylglycerol hydrolysis in human platelets. Demonstration of an arachidonoyl-monoacylglycerol intermediate. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):764–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REID H. A., THEAN P. C., CHAN K. E., BAHAROM A. R. Clinical effects of bites by Malayan viper (Ancistrodon rhodostoma). Lancet. 1963 Mar 23;1(7282):617–621. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91268-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Sanchez A., Hallam T. J. Diacylglycerol and phorbol ester stimulate secretion without raising cytoplasmic free calcium in human platelets. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):317–319. doi: 10.1038/305317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W. Molecular mechanisms of platelet activation. Physiol Rev. 1989 Jan;69(1):58–178. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staatz W. D., Rajpara S. M., Wayner E. A., Carter W. G., Santoro S. A. The membrane glycoprotein Ia-IIa (VLA-2) complex mediates the Mg++-dependent adhesion of platelets to collagen. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1917–1924. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng C. M., Hung M. L., Huang T. F., Ouyang C. Triwaglerin: a potent platelet aggregation inducer purified from Trimeresurus wagleri snake venom. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Sep 15;992(3):258–264. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(89)90083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng C. M., Ko F. N., Tsai I. H., Hung M. L., Huang T. F. Trimucytin: a collagen-like aggregating inducer isolated from Trimeresurus mucrosquamatus snake venom. Thromb Haemost. 1993 Mar 1;69(3):286–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargaftig B. B., Prado-Franceschi J., Chignard M., Lefort J., Marlas G. Activation of guinea-pig platelets induced by convulxin, a substance extracted from the venom of Crotalus durissus cascavella. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Dec 19;68(4):451–464. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90420-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]