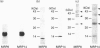Abstract
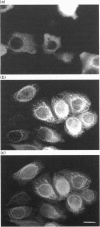
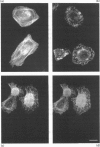
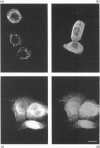
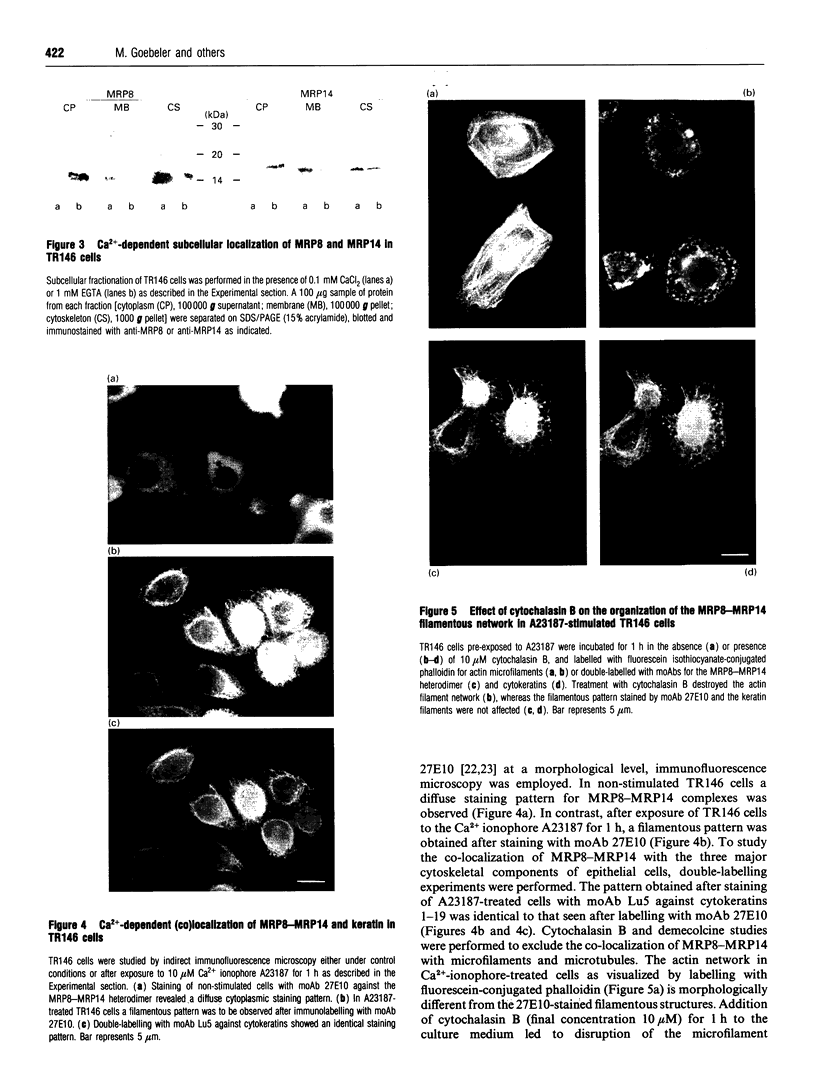
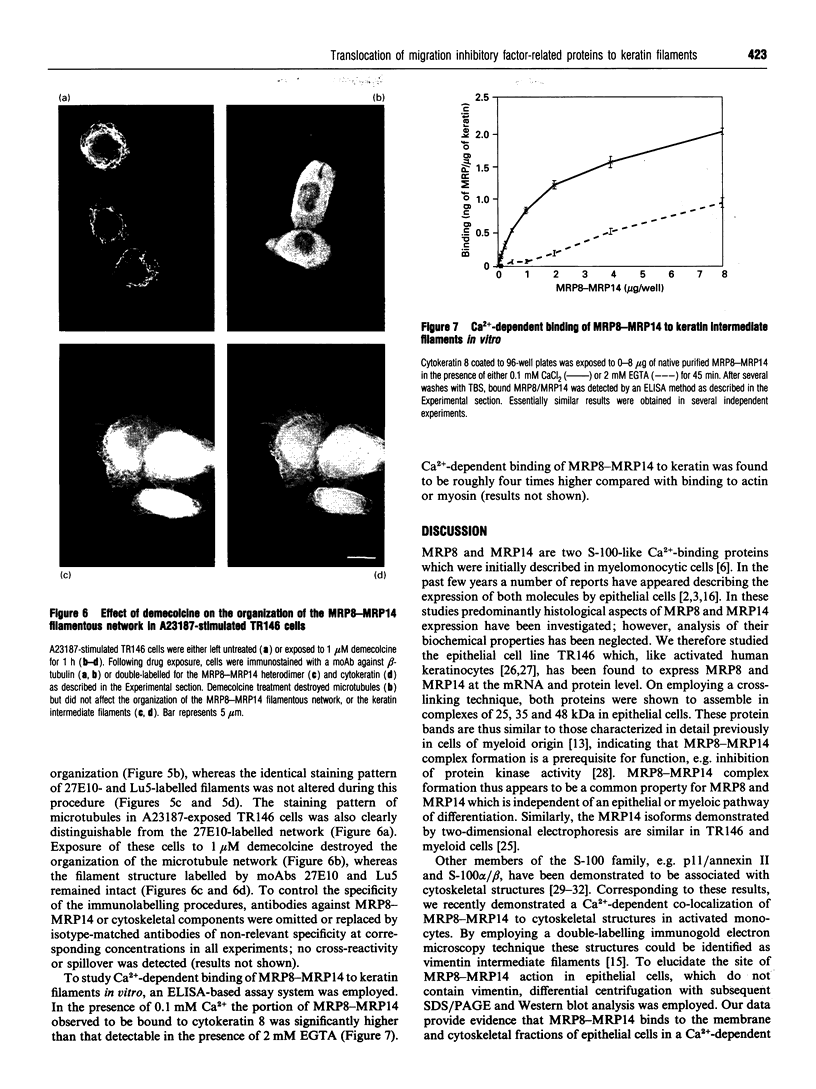
Migration inhibitory factor-related protein 8 (MRP8) and MRP14, two S-100-like Ca(2+)-binding proteins, have been described in cells of the epithelial lineage where they are either expressed constitutively (e.g. by mucosal squamous epithelium) or induced during disease (e.g. in keratinocytes during the course of psoriasis). Their biological function, however, is not yet clear. Recent studies have provided evidence that S-100-like proteins may interact with cytoskeletal components; we have therefore studied the biochemical properties and subcellular distribution of MRP8 and MRP14 in epithelial cells. TR146 human squamous carcinoma cells, which were found to express MRP8 and MRP14 in Northern and Western blot studies, were chosen for analysis. Cross-linking experiments using bis(sulphosuccinimidyl)suberate followed by SDS/PAGE and Western blot analysis revealed formation of heteromeric MRP8-MRP14 complexes. On subjecting TR146 cell lysates to two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and Western blotting, four distinct MRP14 isoforms could be identified resembling those described earlier in macrophages. A differential centrifugation technique revealed a Ca(2+)-dependent translocation of MRP8-MRP14 from the cytoplasm to the membrane and the Nonidet P40-insoluble cytoskeletal fraction. Double-label immunofluorescence microscopy of Ca2+ ionophore A23187-stimulated TR146 cells and cytochalasin B and demecolcine cytoskeleton disruption studies identified these structures as keratin intermediate filaments. Ca(2+)-dependent binding of MRP8-MRP14 to keratin filaments was additionally confirmed by an in vitro binding assay. In conclusion, our data suggest that MRP8 and MRP14 may be involved in Ca(2+)-dependent reorganization of cytoskeletal filaments in epithelial cells, which could be of importance for events associated with differentiation and inflammatory activation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baudier J., Cole R. D. Interactions between the microtubule-associated tau proteins and S100b regulate tau phosphorylation by the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5876–5883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudier J., Cole R. D. Reinvestigation of the sulfhydryl reactivity in bovine brain S100b (beta beta) protein and the microtubule-associated tau proteins. Ca2+ stimulates disulfide cross-linking between the S100b beta-subunit and the microtubule-associated tau(2) protein. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2728–2736. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj R. S., Zotz C., Zwadlo-Klarwasser G., Roth J., Goebeler M., Mahnke K., Falk M., Meinardus-Hager G., Sorg C. The calcium-binding proteins MRP8 and MRP14 form a membrane-associated heterodimer in a subset of monocytes/macrophages present in acute but absent in chronic inflammatory lesions. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jul;22(7):1891–1897. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi R., Giambanco I., Donato R. S-100 protein, but not calmodulin, binds to the glial fibrillary acidic protein and inhibits its polymerization in a Ca(2+)-dependent manner. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12669–12674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Dale I., Fagerhol M. K. Distribution of a formalin-resistant myelomonocytic antigen (L1) in human tissues. II. Normal and aberrant occurrence in various epithelia. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987 Jun;87(6):700–707. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/87.6.700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulombe P. A. The cellular and molecular biology of keratins: beginning a new era. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;5(1):17–29. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(05)80004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delabie J., de Wolf-Peeters C., van den Oord J. J., Desmet V. J. Differential expression of the calcium-binding proteins MRP8 and MRP14 in granulomatous conditions: an immunohistochemical study. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Jul;81(1):123–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05301.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgeworth J., Freemont P., Hogg N. Ionomycin-regulated phosphorylation of the myeloid calcium-binding protein p14. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):189–192. doi: 10.1038/342189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgeworth J., Gorman M., Bennett R., Freemont P., Hogg N. Identification of p8,14 as a highly abundant heterodimeric calcium binding protein complex of myeloid cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7706–7713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebeler M., Roth J., Burwinkel F., Vollmer E., Böcker W., Sorg C. Expression and complex formation of S100-like proteins MRP8 and MRP14 by macrophages during renal allograft rejection. Transplantation. 1994 Aug 15;58(3):355–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebeler M., Roth J., Henseleit U., Sunderkötter C., Sorg C. Expression and complex assembly of calcium-binding proteins MRP8 and MRP14 during differentiation of murine myelomonocytic cells. J Leukoc Biol. 1993 Jan;53(1):11–18. doi: 10.1002/jlb.53.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessian P. A., Edgeworth J., Hogg N. MRP-8 and MRP-14, two abundant Ca(2+)-binding proteins of neutrophils and monocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1993 Feb;53(2):197–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly S. E., Hunter J. A., Jones D. B., Clark B. R., Fleming S. Morphological evidence for calcium-dependent association of calgranulin with the epidermal cytoskeleton in inflammatory dermatoses. Br J Dermatol. 1991 May;124(5):403–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1991.tb00616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly S. E., Jones D. B., Fleming S. Calgranulin expression in inflammatory dermatoses. J Pathol. 1989 Sep;159(1):17–21. doi: 10.1002/path.1711590107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kligman D., Hilt D. C. The S100 protein family. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Nov;13(11):437–443. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunz M., Roth J., Sorg C., Kolde G. Epidermal expression of the calcium binding surface antigen 27E10 in inflammatory skin diseases. Arch Dermatol Res. 1992;284(7):386–390. doi: 10.1007/BF00372067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen P., Rasmussen H. H., Leffers H., Honoré B., Dejgaard K., Olsen E., Kiil J., Walbum E., Andersen A. H., Basse B. Molecular cloning, occurrence, and expression of a novel partially secreted protein "psoriasin" that is highly up-regulated in psoriatic skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Oct;97(4):701–712. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12484041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murao S., Collart F. R., Huberman E. A protein containing the cystic fibrosis antigen is an inhibitor of protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8356–8360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickoloff B. J., Turka L. A. Keratinocytes: key immunocytes of the integument. Am J Pathol. 1993 Aug;143(2):325–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odink K., Cerletti N., Brüggen J., Clerc R. G., Tarcsay L., Zwadlo G., Gerhards G., Schlegel R., Sorg C. Two calcium-binding proteins in infiltrate macrophages of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):80–82. doi: 10.1038/330080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omary M. B., Baxter G. T., Chou C. F., Riopel C. L., Lin W. Y., Strulovici B. PKC epsilon-related kinase associates with and phosphorylates cytokeratin 8 and 18. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(3):583–593. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Burwinkel F., van den Bos C., Goebeler M., Vollmer E., Sorg C. MRP8 and MRP14, S-100-like proteins associated with myeloid differentiation, are translocated to plasma membrane and intermediate filaments in a calcium-dependent manner. Blood. 1993 Sep 15;82(6):1875–1883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Goebeler M., van den Bos C., Sorg C. Expression of calcium-binding proteins MRP8 and MRP14 is associated with distinct monocytic differentiation pathways in HL-60 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Mar 15;191(2):565–570. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Sunderkötter C., Goebeler M., Gutwald J., Sorg C. Expression of the calcium-binding proteins MRP8 and MRP14 by early infiltrating cells in experimental contact dermatitis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1992;98(2):140–145. doi: 10.1159/000236177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupniak H. T., Rowlatt C., Lane E. B., Steele J. G., Trejdosiewicz L. K., Laskiewicz B., Povey S., Hill B. T. Characteristics of four new human cell lines derived from squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1985 Oct;75(4):621–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saintigny G., Schmidt R., Shroot B., Juhlin L., Reichert U., Michel S. Differential expression of calgranulin A and B in various epithelial cell lines and reconstructed epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Nov;99(5):639–644. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12668098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Roop D. R. Molecular and cellular biology of intermediate filaments. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:593–625. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M. Structure, function, and dynamics of keratin intermediate filaments. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Jun;100(6):729–734. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12475665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teigelkamp S., Bhardwaj R. S., Roth J., Meinardus-Hager G., Karas M., Sorg C. Calcium-dependent complex assembly of the myeloic differentiation proteins MRP-8 and MRP-14. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13462–13467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thewes M., Stadler R., Korge B., Mischke D. Normal psoriatic epidermis expression of hyperproliferation-associated keratins. Arch Dermatol Res. 1991;283(7):465–471. doi: 10.1007/BF00371784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. A., Eichner R., Sun T. T. Monoclonal antibody analysis of keratin expression in epidermal diseases: a 48- and 56-kdalton keratin as molecular markers for hyperproliferative keratinocytes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1397–1406. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamansky G. B., Nguyen U., Chou I. N. An immunofluorescence study of the calcium-induced coordinated reorganization of microfilaments, keratin intermediate filaments, and microtubules in cultured human epidermal keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Dec;97(6):985–994. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12491899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zokas L., Glenney J. R., Jr The calpactin light chain is tightly linked to the cytoskeletal form of calpactin I: studies using monoclonal antibodies to calpactin subunits. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):2111–2121. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.2111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwadlo G., Brüggen J., Gerhards G., Schlegel R., Sorg C. Two calcium-binding proteins associated with specific stages of myeloid cell differentiation are expressed by subsets of macrophages in inflammatory tissues. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Jun;72(3):510–515. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwadlo G., Schlegel R., Sorg C. A monoclonal antibody to a subset of human monocytes found only in the peripheral blood and inflammatory tissues. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 15;137(2):512–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Overbeck J., Stähli C., Gudat F., Carmann H., Lautenschlager C., Dürmüller U., Takacs B., Miggiano V., Staehelin T., Heitz P. U. Immunohistochemical characterization of an anti-epithelial monoclonal antibody (mAB lu-5). Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1985;407(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00701324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]