Abstract
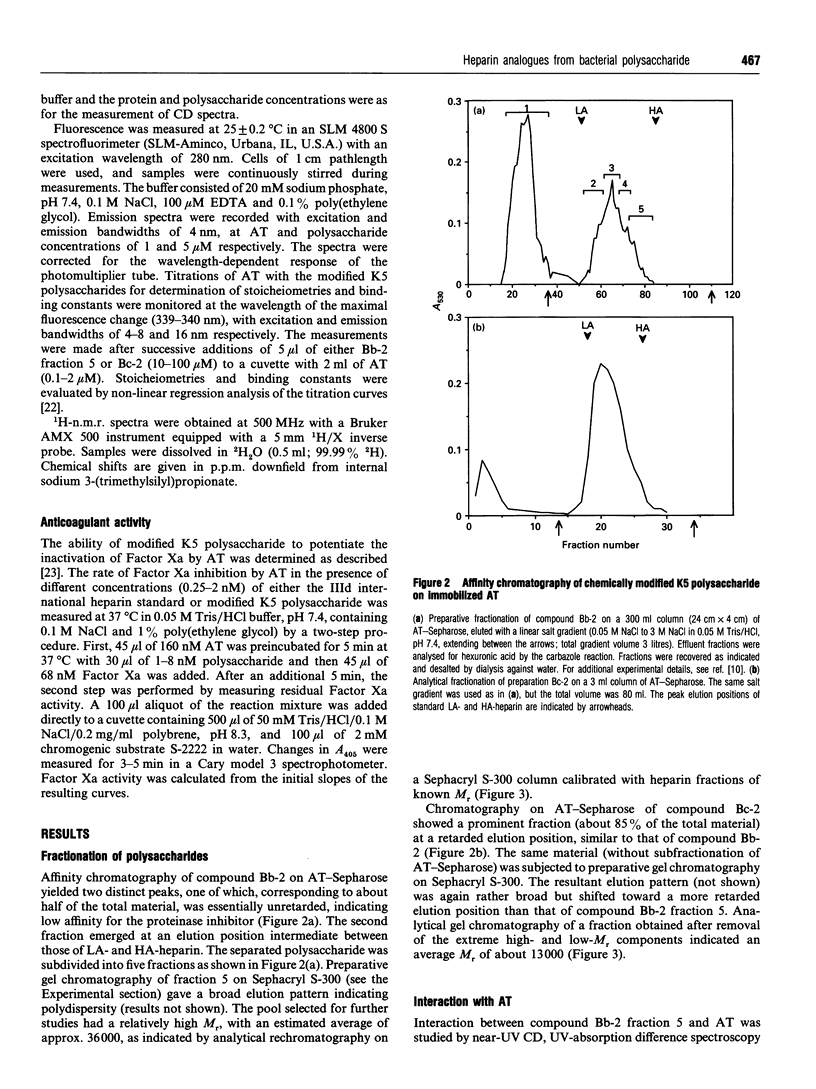
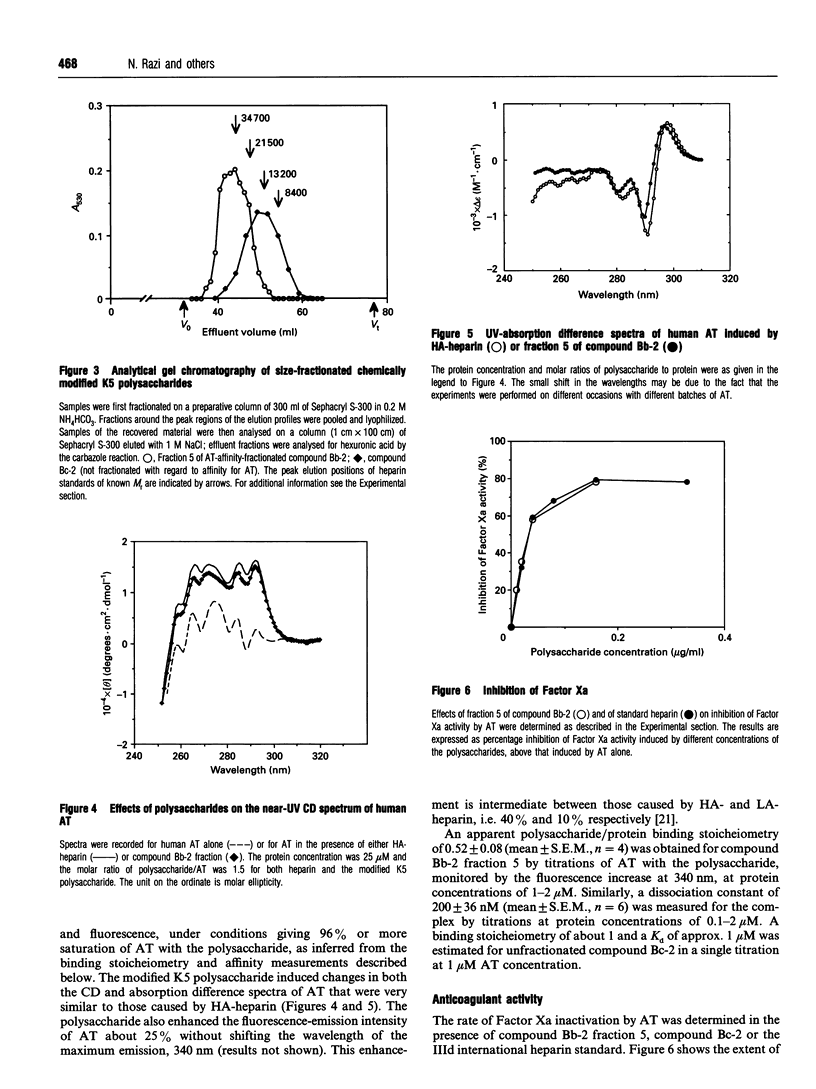
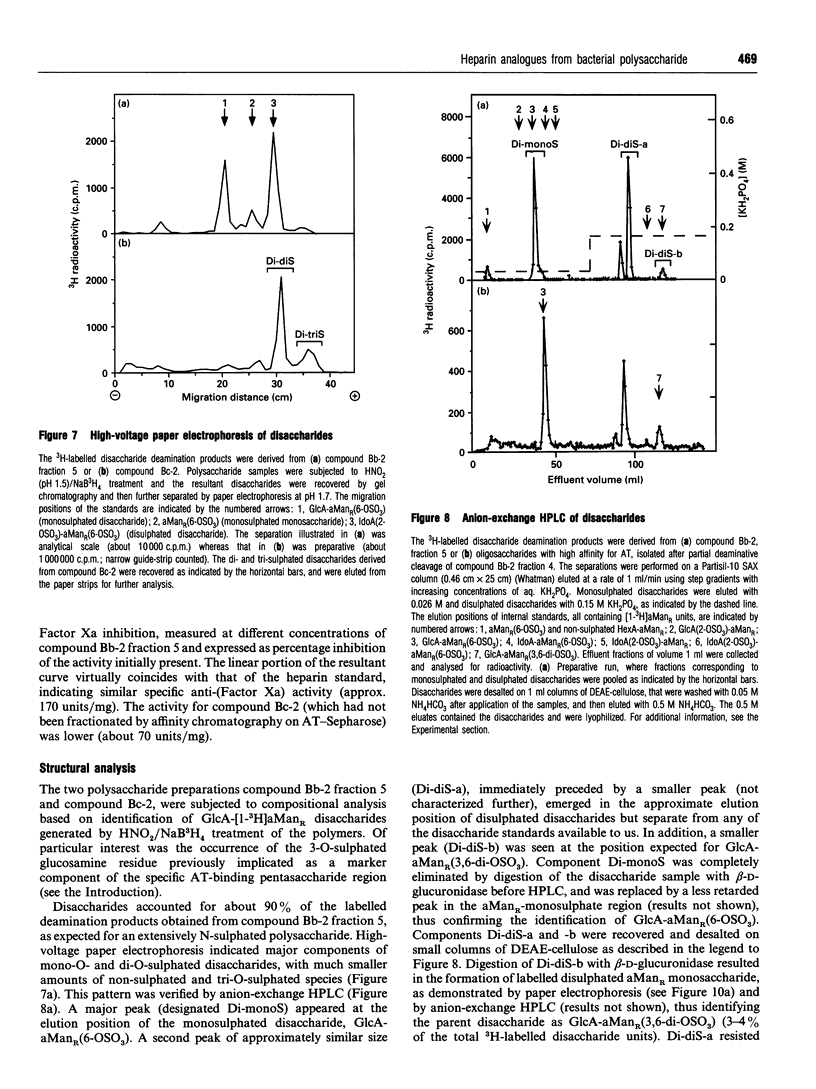
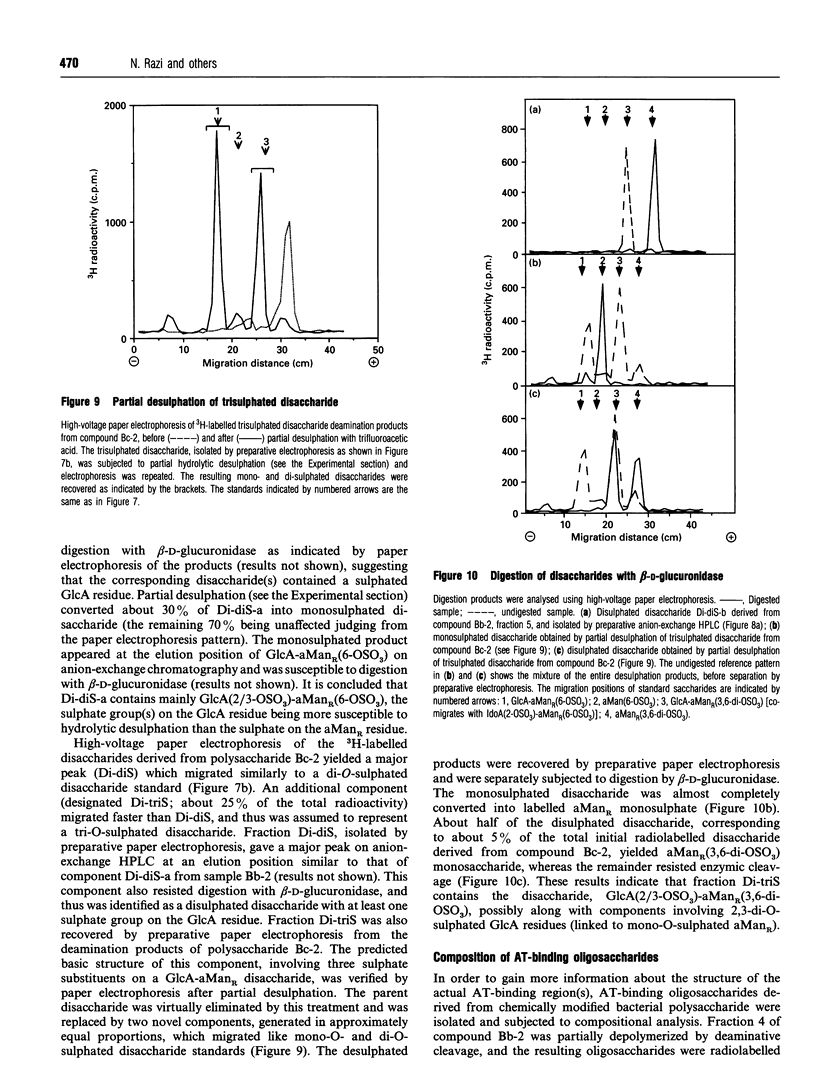
Capsular polysaccharide from Escherichia coli K5, with the basic structure (GlcA beta 1-4GlcNAc alpha 1-4)n, was chemically modified through N-deacetylation, N-sulphation and O-sulphation [Casu, Grazioli, Razi, Guerrini, Naggi, Torri, Oreste, Tursi, Zoppetti and Lindahl (1994) Carbohydr. Res. 263, 271-284]. Depending on the reaction conditions, the products showed different proportions of components with high affinity for antithrombin (AT). A high-affinity subfraction, M(r) approx. 36,000, was shown by near-UV CD, UV-absorption difference spectroscopy and fluorescence to cause conformational changes in the AT molecule very similar to those induced by high-affinity heparin. Fluorescence titrations demonstrated about two AT-binding sites per polysaccharide chain, each with a Kd of approx. 200 nM. The anti-(Factor Xa) activity was 170 units/mg, similar to that of the IIId international heparin standard and markedly higher than activities of previously described heparin analogues. Another preparation, M(r) approx. 13,000, of higher overall O-sulphate content, exhibited a single binding site per chain, with Kd approx. 1 microM, and an anti-(Factor Xa) activity of 70 units/mg. Compositional analysis of polysaccharide fractions revealed a correlation between the contents of -GlcA-GlcNSO3(3,6-di-OSO3)- disaccharide units and affinity for AT; the 3-O-sulphated GlcN unit has previously been identified as a marker component of the AT-binding pentasaccharide sequence in heparin. The abundance of the implicated disaccharide unit approximately equalled that of AT-binding sites in the 36,000-M(r) polysaccharide fraction, and approached one per high-affinity oligosaccharide (predominantly 10-12 monosaccharide units) isolated after partial depolymerization of AT-binding polysaccharide. These findings suggest that the modified bacterial polysaccharide interacts with AT and promotes its anticoagulant action in a manner similar to that of heparin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atha D. H., Lormeau J. C., Petitou M., Rosenberg R. D., Choay J. Contribution of monosaccharide residues in heparin binding to antithrombin III. Biochemistry. 1985 Nov 5;24(23):6723–6729. doi: 10.1021/bi00344a063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BITTER T., MUIR H. M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:330–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourin M. C., Lindahl U. Glycosaminoglycans and the regulation of blood coagulation. Biochem J. 1993 Jan 15;289(Pt 2):313–330. doi: 10.1042/bj2890313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bäckström G., Hök M., Lindahl U., Feingold D. S., Malmström A., Rodén L., Jacobsson I. Biosynthesis of heparin. Assay and properties of the microsomal uronosyl C-5 epimerase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2975–2982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casu B., Grazioli G., Razi N., Guerrini M., Naggi A., Torri G., Oreste P., Tursi F., Zoppetti G., Lindahl U. Heparin-like compounds prepared by chemical modification of capsular polysaccharide from E. coli K5. Carbohydr Res. 1994 Oct 17;263(2):271–284. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(94)00172-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casu B., Oreste P., Torri G., Zoppetti G., Choay J., Lormeau J. C., Petitou M., Sinäy P. The structure of heparin oligosaccharide fragments with high anti-(factor Xa) activity containing the minimal antithrombin III-binding sequence. Chemical and 13C nuclear-magnetic-resonance studies. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 1;197(3):599–609. doi: 10.1042/bj1970599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casu B. Structure and biological activity of heparin. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1985;43:51–134. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60067-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson A., Björk I. Binding to antithrombin of heparin fractions with different molecular weights. Biochem J. 1981 Feb 1;193(2):427–433. doi: 10.1042/bj1930427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferro D. R., Provasoli A., Ragazzi M., Casu B., Torri G., Bossennec V., Perly B., Sinaÿ P., Petitou M., Choay J. Conformer populations of L-iduronic acid residues in glycosaminoglycan sequences. Carbohydr Res. 1990 Jan 15;195(2):157–167. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(90)84164-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hök M., Björk I., Hopwood J., Lindahl U. Anticoagulant activity of heparin: separation of high-activity and low-activity heparin species by affinity chromatography on immobilized antithrombin. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jul 1;66(1):90–93. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80592-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellén L., Lindahl U. Proteoglycans: structures and interactions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:443–475. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusche M., Bäckström G., Riesenfeld J., Petitou M., Choay J., Lindahl U. Biosynthesis of heparin. O-sulfation of the antithrombin-binding region. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15474–15484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusche M., Lindahl U. Biosynthesis of heparin. O-sulfation of D-glucuronic acid units. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15403–15409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusche M., Torri G., Casu B., Lindahl U. Biosynthesis of heparin. Availability of glucosaminyl 3-O-sulfation sites. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7292–7300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl U., Bäckström G., Thunberg L., Leder I. G. Evidence for a 3-O-sulfated D-glucosamine residue in the antithrombin-binding sequence of heparin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6551–6555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl U., Lidholt K., Spillmann D., Kjellén L. More to "heparin" than anticoagulation. Thromb Res. 1994 Jul 1;75(1):1–32. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(94)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl U., Thunberg L., Bäckström G., Riesenfeld J., Nordling K., Björk I. Extension and structural variability of the antithrombin-binding sequence in heparin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12368–12376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordenman B., Björk I. Binding of low-affinity and high-affinity heparin to antithrombin. Ultraviolet difference spectroscopy and circular dichroism studies. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 8;17(16):3339–3344. doi: 10.1021/bi00609a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordenman B., Björk I. Fractionation of heparin by chromatography on immobilized thrombin. Correlation between the anticoagulant activity of the fractions and their content of heparin with high affinity for antithrombin. 1980 Aug 15-Sep 1Thromb Res. 19(4-5):711–718. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90044-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordenman B., Danielsson A., Björk I. The binding of low-affinity and high-affinity heparin to antithrombin. Fluorescence studies. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Sep 15;90(1):1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson S. T., Björk I., Sheffer R., Craig P. A., Shore J. D., Choay J. Role of the antithrombin-binding pentasaccharide in heparin acceleration of antithrombin-proteinase reactions. Resolution of the antithrombin conformational change contribution to heparin rate enhancement. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12528–12538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pejler G., Danielsson A., Björk I., Lindahl U., Nader H. B., Dietrich C. P. Structure and antithrombin-binding properties of heparin isolated from the clams Anomalocardia brasiliana and Tivela mactroides. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11413–11421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragazzi M., Ferro D. R., Perly B., Sinaÿ P., Petitou M., Choay J. Conformation of the pentasaccharide corresponding to the binding site of heparin for antithrombin III. Carbohydr Res. 1990 Jan 15;195(2):169–185. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(90)84165-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaklee P. N., Conrad H. E. Hydrazinolysis of heparin and other glycosaminoglycans. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 1;217(1):187–197. doi: 10.1042/bj2170187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. E., Conrad H. E. Nearest neighbor analysis of heparin: identification and quantitation of the products formed by selective depolymerization procedures. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 7;15(18):3943–3950. doi: 10.1021/bi00663a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


