Abstract
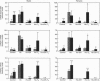
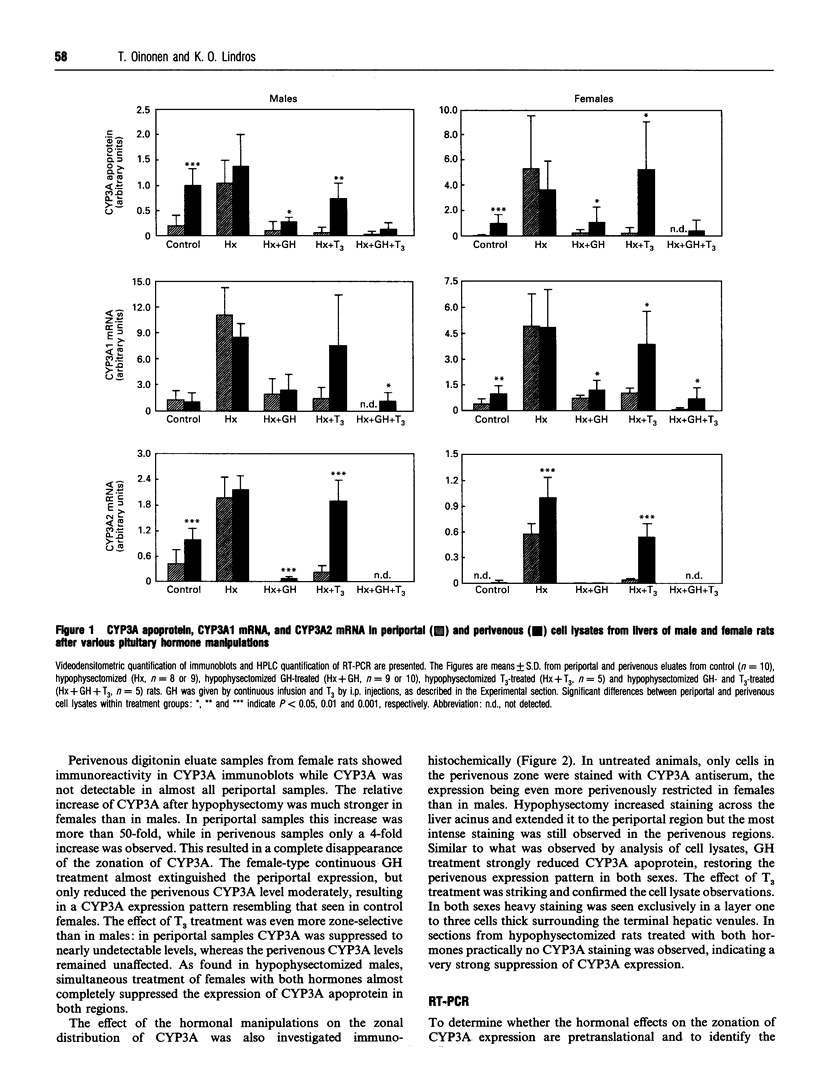
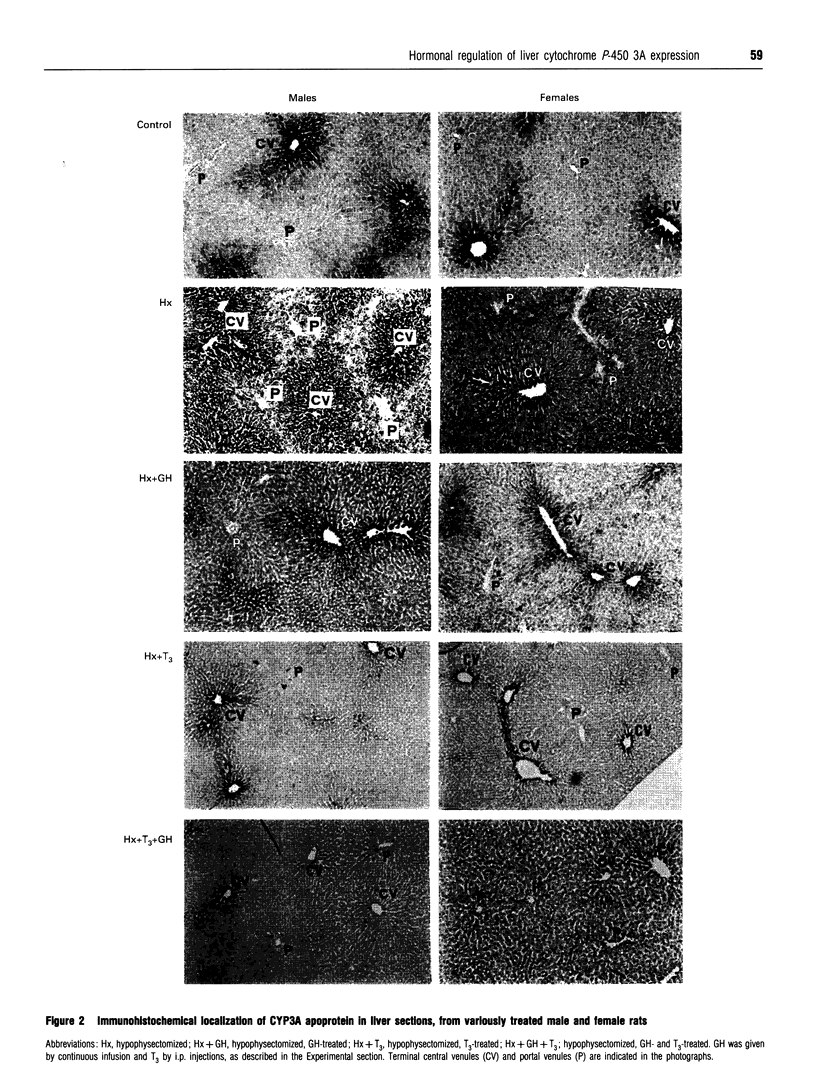
Most cytochrome P-450 enzymes are expressed characteristically in a zonated pattern in the liver. The factors responsible for this heterogenous expression are largely unknown. Here we report how growth hormone and tri-iodothyronine regulate the steroid-hydroxylating cytochrome P-450 (CYP) 3A forms, which are constitutively expressed mainly in the perivenous (downstream) liver region. By comparing cell lysates obtained from the periportal and perivenous acinar regions we observed that the elevated CYP3A expression observed after hypophysectomy was due mainly to a dramatic increase in the normally silent periportal region. This effect was particularly strong in females. Treatment with growth hormone re-established the perivenous expression pattern, a finding corroborated by immunohistochemical analysis of liver sections. Analysis of periportal and perivenous mRNA by reverse-transcriptase PCR demonstrated that in males the changes in CYP3A2 mRNA paralleled the changes at the protein level. In females, CYP3A2 mRNA was detected only after hypophysectomy, and the zonal protein changes seemed to be governed by changes in CYP3A1 mRNA levels. Treatment of hypophysectomized animals with tri-iodothyronine also suppressed the expression of CYP3A, both in males and females. However, this occurred almost exclusively in the periportal region. This was observed both at the protein level, as determined by immunoblotting and immunohistochemically, and at the CYP3A1 and 3A2 mRNA level. These results indicate that growth hormone and thyroid hormone regulate the expression of CYP3A genes zone-specifically by suppressing their transcription in the periportal (upstream) region of the liver.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron J., Redick J. A., Guengerich F. P. An immunohistochemical study on the localization and distributions of phenobarbital- and 3-methylcholanthrene-inducible cytochromes P-450 within the livers of untreated rats. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5931–5937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumbach W. R., Horner D. L., Logan J. S. The growth hormone-binding protein in rat serum is an alternatively spliced form of the rat growth hormone receptor. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1199–1205. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson G., Julkunen A., Penttilä K. E., Lindros K. O. Effect of phenobarbital on the distribution of drug metabolizing enzymes between periportal and perivenous rat hepatocytes prepared by digitonin-collagenase liver perfusion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Feb;240(2):663–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger H. J., Schuetz E. G., Schuetz J. D., Guzelian P. S. Divergent effects of cycloheximide on the induction of class II and class III cytochrome P450 mRNAs in cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Sep;281(2):204–211. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90433-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bühler R., Lindros K. O., Nordling A., Johansson I., Ingelman-Sundberg M. Zonation of cytochrome P450 isozyme expression and induction in rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Feb 15;204(1):407–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16650.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekberg S., Carlsson L., Carlsson B., Billig H., Jansson J. O. Plasma growth hormone pattern regulates epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor messenger ribonucleic acid levels and EGF binding in the rat liver. Endocrinology. 1989 Oct;125(4):2158–2166. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-4-2158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt R., Mecke D. Heterogeneous distribution of glutamine synthetase among rat liver parenchymal cells in situ and in primary culture. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):567–570. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt R. Metabolic zonation of the liver: regulation and implications for liver function. Pharmacol Ther. 1992;53(3):275–354. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(92)90055-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemzik B., Greenway D., Nevins C., Parkinson A. Regulation of two electrophoretically distinct proteins recognized by antibody against rat liver cytochrome P450 3A1. J Biochem Toxicol. 1992 Spring;7(1):43–52. doi: 10.1002/jbt.2570070109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J. Molecular genetics of the P-450 superfamily. Pharmacol Ther. 1990;45(1):1–38. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(90)90006-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Nebert D. W., Hardwick J. P., Kasper C. B. Complete cDNA and protein sequence of a pregnenolone 16 alpha-carbonitrile-induced cytochrome P-450. A representative of a new gene family. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7435–7441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Song B. J., Hardwick J. P. Pregnenolone 16 alpha-carbonitrile-inducible P-450 gene family: gene conversion and differential regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2969–2976. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gooding P. E., Chayen J., Sawyer B., Slater T. F. Cytochrome P-450 distribution in rat liver and the effect of sodium phenobarbitone administration. Chem Biol Interact. 1978 Mar;20(3):299–310. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(78)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpert J. R. Multiplicity of steroid-inducible cytochromes P-450 in rat liver microsomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 May 15;263(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingelman-Sundberg M., Johansson I., Penttilä K. E., Glaumann H., Lindros K. O. Centrilobular expression of ethanol-inducible cytochrome P-450 (IIE1) in rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 30;157(1):55–60. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz E. D., Dong M. W. Rapid analysis and purification of polymerase chain reaction products by high-performance liquid chromatography. Biotechniques. 1990 May;8(5):546–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirita S., Matsubara T. cDNA cloning and characterization of a novel member of steroid-induced cytochrome P450 3A in rats. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 Dec;307(2):253–258. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobie P. E., García-Aragón J., Wang B. S., Baumbach W. R., Waters M. J. Cellular localization of the growth hormone binding protein in the rat. Endocrinology. 1992 May;130(5):3057–3065. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.5.1374020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marti U., Gebhardt R. Acinar heterogeneity of the epidermal growth factor receptor in the liver of male rats. Eur J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;55(1):158–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendel C. M., Weisiger R. A., Jones A. L., Cavalieri R. R. Thyroid hormone-binding proteins in plasma facilitate uniform distribution of thyroxine within tissues: a perfused rat liver study. Endocrinology. 1987 May;120(5):1742–1749. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-5-1742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Gonzalez F. J., Yamazoe Y., Kato R. Purification and characterization of four catalytically active testosterone 6 beta-hydroxylase P-450s from rat liver microsomes: comparison of a novel form with three structurally and functionally related forms. J Biochem. 1990 May;107(5):718–725. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Kamataki T., Waxman D. J., Guengerich F. P., Estabrook R. W., Feyereisen R., Gonzalez F. J., Coon M. J., Gunsalus I. C., Gotoh O. The P450 superfamily: update on new sequences, gene mapping, accession numbers, early trivial names of enzymes, and nomenclature. DNA Cell Biol. 1993 Jan-Feb;12(1):1–51. doi: 10.1089/dna.1993.12.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oinonen T., Nikkola E., Lindros K. O. Growth hormone mediates zone-specific gene expression in liver. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jul 26;327(2):237–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80176-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park S. S., Waxman D. J., Miller H., Robinson R., Attisano C., Guengerich F. P., Gelboin H. V. Preparation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to pregnenolone 16-alpha-carbonitrile inducible rat liver cytochrome P-450. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Sep 1;35(17):2859–2867. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90477-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quistorff B., Grunnet N. Dual-digitonin-pulse perfusion. Concurrent sampling of periportal and perivenous cytosol of rat liver for determination of metabolites and enzyme activities. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 1;243(1):87–95. doi: 10.1042/bj2430087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro V., Lechner M. C. Cloning and characterization of a novel CYP3A1 allelic variant: analysis of CYP3A1 and CYP3A2 sex-hormone-dependent expression reveals that the CYP3A2 gene is regulated by testosterone. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Feb 14;293(1):147–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90377-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saarinen J., Saarelainen R., Lindros K. O. A rapid method to study heterogeneous gene expression in liver by direct assay of messenger RNA from periportal and perivenous cell lysates. Hepatology. 1993 Mar;17(3):466–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada M., Nagata K., Murayama N., Yamazoe Y., Kato R. Role of growth hormone in modulating the constitutive and phenobarbital-induced levels of two P-450(6)beta (testosterone 6 beta-hydroxylase) mRNAs in rat livers. J Biochem. 1989 Dec;106(6):1030–1034. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosh D., Alberti K. G., Agius L. Hypophysectomy does not alter the acinar zonation of gluconeogenesis or the mitochondrial redox state in rat liver. Biochem J. 1989 May 15;260(1):183–187. doi: 10.1042/bj2600183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., LeBlanc G. A., Morrissey J. J., Staunton J., Lapenson D. P. Adult male-specific and neonatally programmed rat hepatic P-450 forms RLM2 and 2a are not dependent on pulsatile plasma growth hormone for expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11396–11406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Ram P. A., Notani G., LeBlanc G. A., Alberta J. A., Morrissey J. J., Sundseth S. S. Pituitary regulation of the male-specific steroid 6 beta-hydroxylase P-450 2a (gene product IIIA2) in adult rat liver. Suppressive influence of growth hormone and thyroxine acting at a pretranslational leve;. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;4(3):447–454. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. T., Simonet L. C. Effects of growth hormone on cytochrome P-450j. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 30;155(1):392–397. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazoe Y., Shimada M., Murayama N., Kawano S., Kato R. The regulation by growth hormone of microsomal testosterone 6 beta-hydroxylase in male rat livers. J Biochem. 1986 Oct;100(4):1095–1097. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]