Abstract
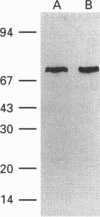
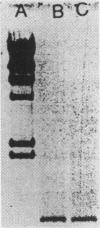
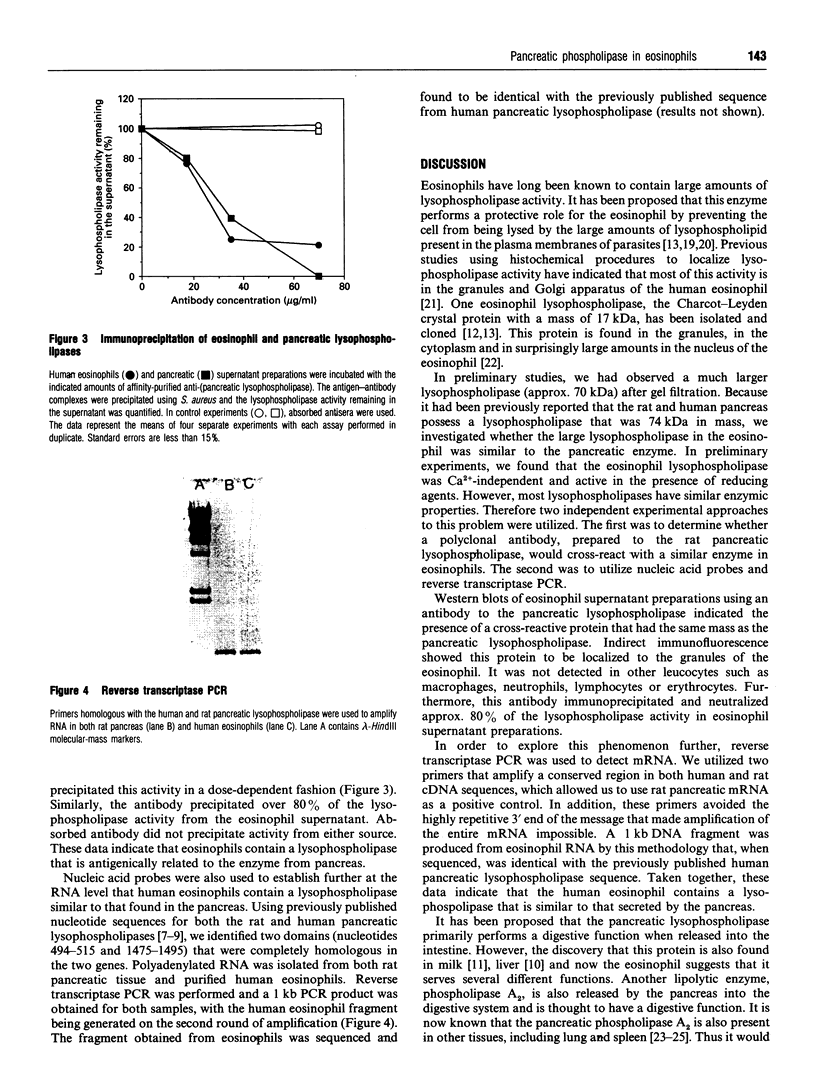
The supernatant fraction from lysed human eosinophils, when separated by gel-filtration chromatography, contains a protein with lysophospholipase activity of approximate molecular mass 74 kDa. This mass differs substantially from the 17 kDa of a previously cloned eosinophil lysophospholipase (Charcot-Leyden crystal protein), but is similar to that reported for a pancreatic enzyme. We have therefore further characterized this pancreatic-like lysophospholipase in human eosinophils. A rabbit polyclonal antibody was produced against a synthetic peptide consisting of amino acids 325-349 from the 74 kDa rat pancreatic lysophospholipase. Western-blot analysis of eosinophil extracts indicate that this antibody recognizes a single 74 kDa band in these preparations. Incubation of the supernatant fraction from sonified eosinophils with this antibody, followed by precipitation of antibody-antigen complexes with Protein A, removes the majority of the lysophospholipase activity. Indirect immunofluorescence examination with this antibody indicates this protein to be localized to granules of eosinophils and not in other leucocytes. Moreover, reverse transcriptase PCR of polyadenylated RNA from eosinophils and from rat pancreatic tissue with primers to rat pancreatic lysophospholipase resulted in readily detectable 1 kb DNA products in both samples. Sequencing revealed this DNA fragment to be identical with the human pancreatic lysophospholipase cDNA sequence. Taken together, these data indicate that eosinophils contain a lysophospholipase that is similar to the human pancreatic enzyme.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abouakil N., Rogalska E., Bonicel J., Lombardo D. Purification of pancreatic carboxylic-ester hydrolase by immunoaffinity and its application to the human bile-salt-stimulated lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Aug 12;961(3):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90077-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosner M. S., Gulick T., Riley D. J., Spilburg C. A., Lange L. G., 3rd Receptor-like function of heparin in the binding and uptake of neutral lipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7438–7442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. A., Conway T. M., Shorr R. G., Crooke S. T. Identification and isolation of a mammalian protein which is antigenically and functionally related to the phospholipase A2 stimulatory peptide melittin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4402–4406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer R., Dri P., Zabucchi G., Patriarca P. A simple and rapid method for isolation of eosinophilic granulocytes from human blood. J Leukoc Biol. 1992 Sep;52(3):331–336. doi: 10.1002/jlb.52.3.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Weller P. F., Monahan-Earley R. A., Letourneau L., Ackerman S. J. Ultrastructural localization of Charcot-Leyden crystal protein (lysophospholipase) and peroxidase in macrophages, eosinophils, and extracellular matrix of the skin in the hypereosinophilic syndrome. Lab Invest. 1990 May;62(5):590–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garsetti D. E., Ozgür L. E., Steiner M. R., Egan R. W., Clark M. A. Isolation and characterization of three lysophospholipases from the murine macrophage cell line WEHI 265.1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Dec 2;1165(2):229–238. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(92)90191-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garsetti D. E., Steiner M. R., Holtsberg F., Ozgür L. E., Egan R. W., Clark M. A. Comparison of six mammalian lysophospholipases. J Lipid Mediat. 1993 Mar-Apr;6(1-3):223–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garsetti D., Holtsberg F., Steiner M. R., Egan R. W., Clark M. A. Butyric acid-induced differentiation of HL-60 cells increases the expression of a single lysophospholipase. Biochem J. 1992 Dec 15;288(Pt 3):831–837. doi: 10.1042/bj2880831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goven A. J. Effect of anti-eosinophil serum on phospholipase B activity in mice infected with Trichinella spiralis. J Parasitol. 1983 Feb;69(1):88–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groven A. J., Moore G. W. Phospholipase B activity in congenitally athymic (nude) mice infected with Trichinella spiralis. Z Parasitenkd. 1980;61(3):265–269. doi: 10.1007/BF00925517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J. H., Stratowa C., Rutter W. J. Isolation of full-length putative rat lysophospholipase cDNA using improved methods for mRNA isolation and cDNA cloning. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 24;26(6):1617–1625. doi: 10.1021/bi00380a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison E. H. Bile salt-dependent, neutral cholesteryl ester hydrolase of rat liver: possible relationship with pancreatic cholesteryl ester hydrolase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Nov 4;963(1):28–34. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90334-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissel J. A., Fontaine R. N., Turck C. W., Brockman H. L., Hui D. Y. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNA for rat pancreatic cholesterol esterase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Nov 28;1006(2):227–236. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90201-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda Y., Ogawa M., Shibata T., Nakaguchi K., Nishijima J., Wakasugi C., Mori T. Distribution of immunoreactive pancreatic phospholipase A2 (IPPL-2) in various human tissues. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1987 Nov;58(2):281–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirkle M. S., Goven A. J., Foster L. A., Kester A. S. Light and electron microscopic demonstration of phospholipase B activity in the mouse eosinophil. Histochemistry. 1988;88(2):181–185. doi: 10.1007/BF00493302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reue K., Zambaux J., Wong H., Lee G., Leete T. H., Ronk M., Shively J. E., Sternby B., Borgström B., Ameis D. cDNA cloning of carboxyl ester lipase from human pancreas reveals a unique proline-rich repeat unit. J Lipid Res. 1991 Feb;32(2):267–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seilhamer J. J., Randall T. L., Yamanaka M., Johnson L. K. Pancreatic phospholipase A2: isolation of the human gene and cDNAs from porcine pancreas and human lung. DNA. 1986 Dec;5(6):519–527. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1986.5.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhilber W., Dittié A., Lütcke H., Kern H. F., Tooze J. A lysophospholipase specific for exocrine pancreatic cells is stored in zymogen granules and secreted into pancreatic juice. Eur J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;51(2):242–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson F. J., Clark M. A. Purification of a lysophosphatidic acid-hydrolysing lysophospholipase from rat brain. Biochem J. 1994 Jun 1;300(Pt 2):457–461. doi: 10.1042/bj3000457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tojo H., Ono T., Kuramitsu S., Kagamiyama H., Okamoto M. A phospholipase A2 in the supernatant fraction of rat spleen. Its similarity to rat pancreatic phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5724–5731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller P. F., Bach D. S., Austen K. F. Biochemical characterization of human eosinophil Charcot-Leyden crystal protein (lysophospholipase). J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15100–15105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Z., Tenen D. G., Dvorak A. M., Ackerman S. J. The gene for human eosinophil Charcot-Leyden crystal protein directs expression of lysophospholipase activity and spontaneous crystallization in transiently transfected COS cells. J Leukoc Biol. 1992 Dec;52(6):588–595. doi: 10.1002/jlb.52.6.588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Bosch H., Aarsman A. J., de Jong J. G., van Deenem L. L. Studies on lysophospholipases. I. Purification and some properties of a lysophospholipase from beef pancreas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 19;296(1):94–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]