Abstract
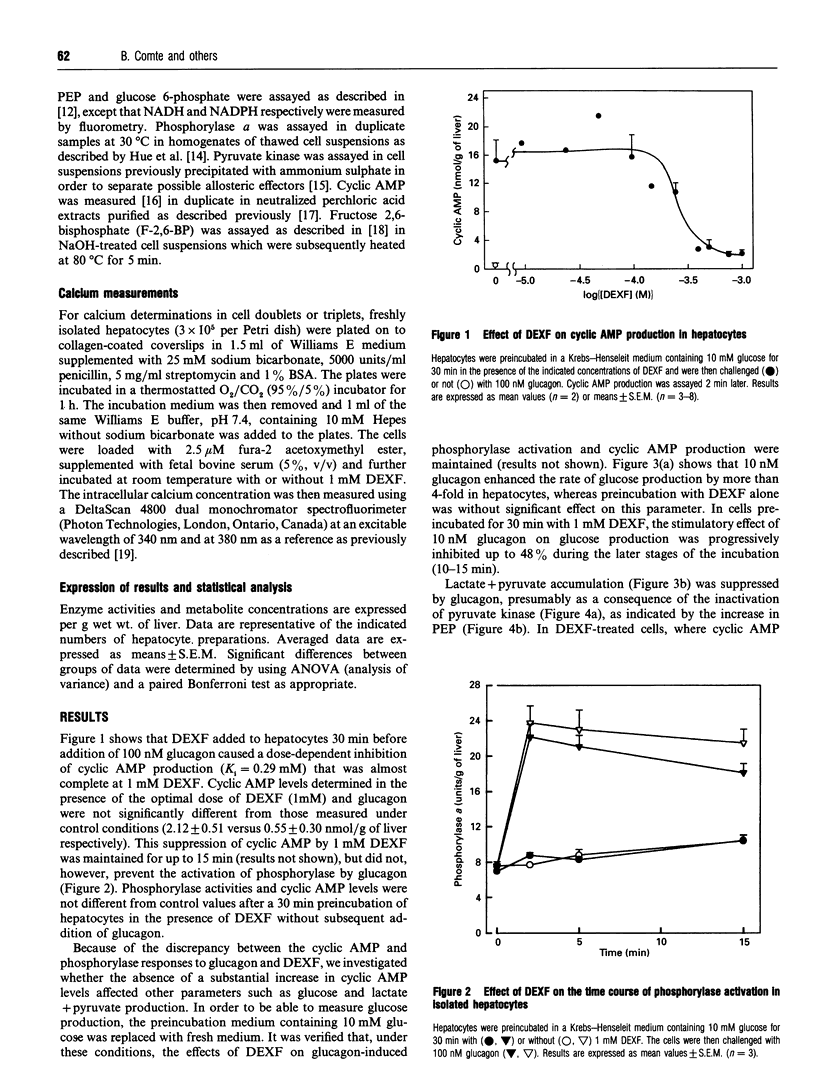
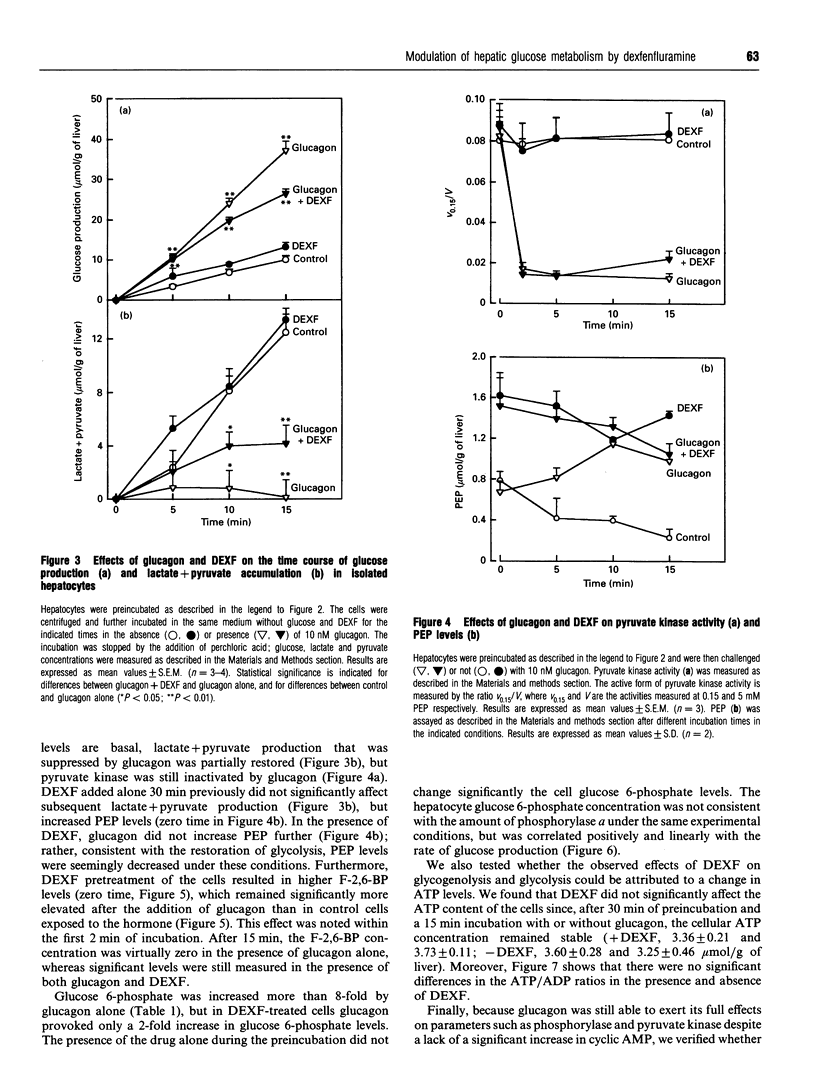
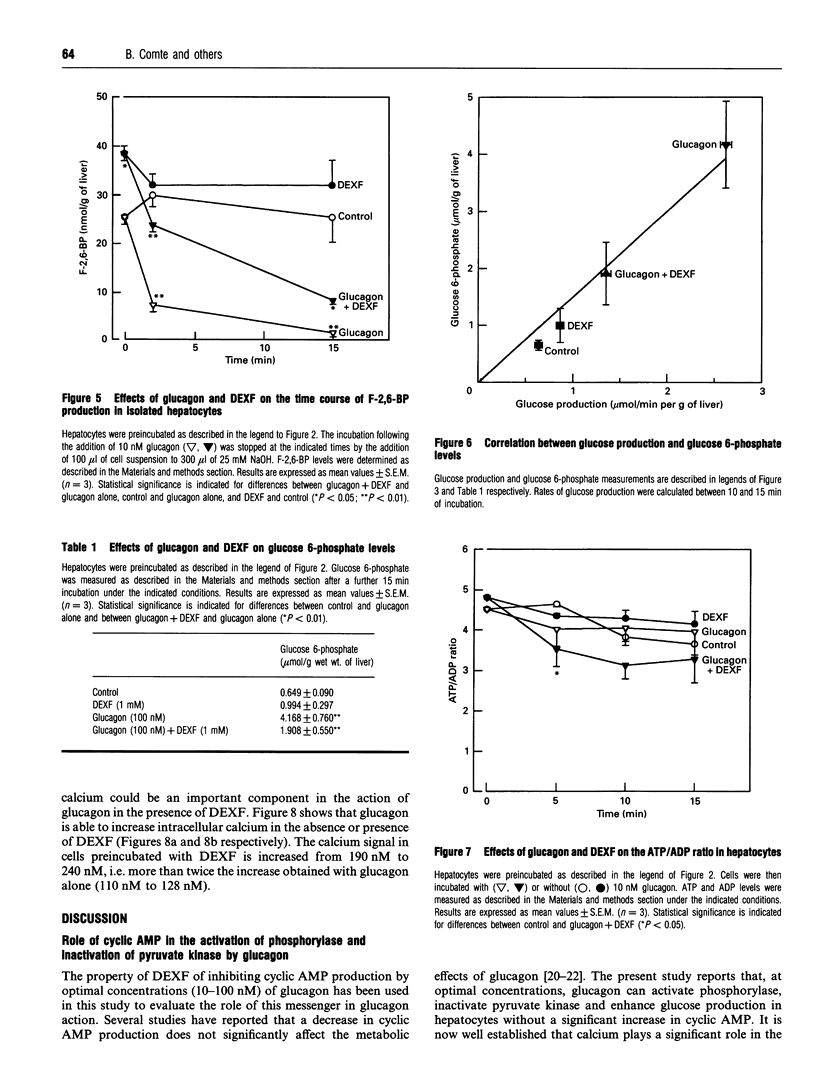
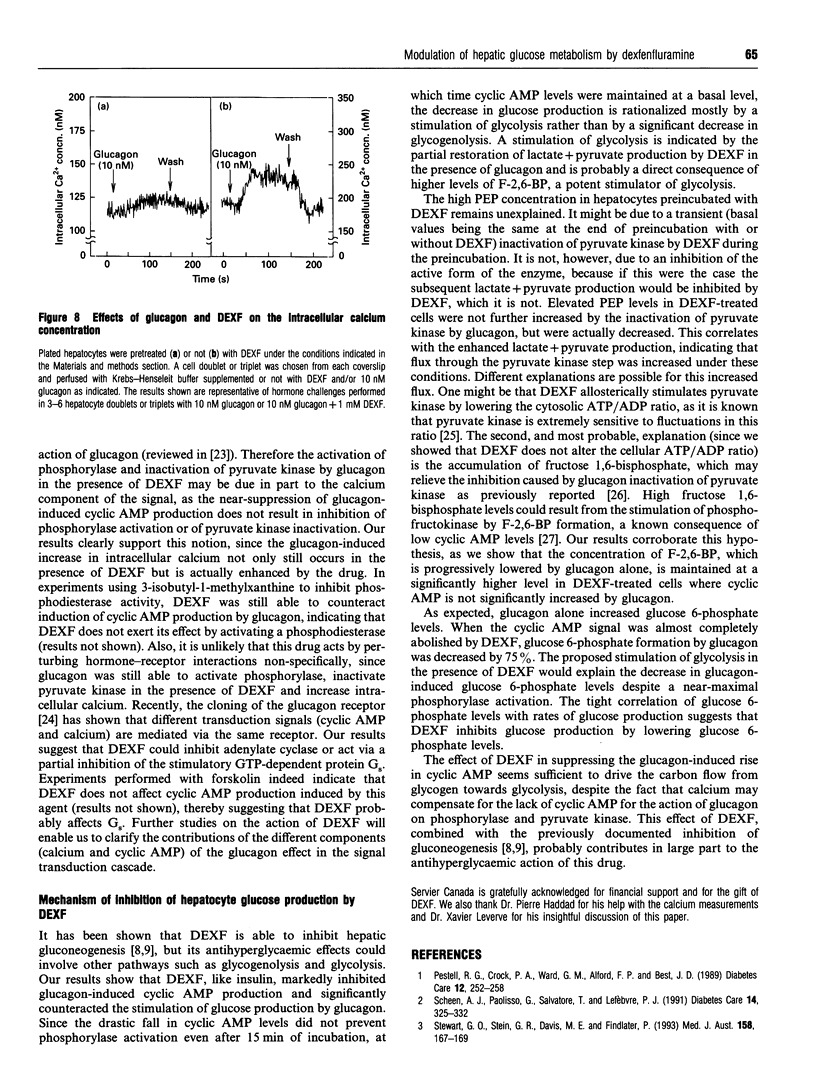
The mechanism of the antihyperglycaemic action of dexfenfluramine (DEXF) was investigated in isolated rat hepatocytes exposed to glucagon. Preincubation of hepatocytes with DEXF caused a dose-dependent inhibition of cyclic AMP formation by 100 nM glucagon (Ki = 0.29 mM) that was almost complete at 1 mM DEXF. Surprisingly, glucagon-induced phosphorylase activation was not affected by DEXF despite the significant drop in cyclic AMP levels. Glucose production stimulated by glucagon was inhibited by up to 48% by 1 mM DEXF, and the rate of glucose production correlated positively with the steady-state concentration of glucose 6-phosphate. DEXF also partially restored lactate + pyruvate production which was abolished by an optimal concentration of glucagon. Although DEXF was not able to prevent the inactivation of pyruvate kinase by glucagon, the lack of further accumulation of phosphoenolpyruvate in DEXF-treated cells supports the conclusion that the flux through pyruvate kinase is stimulated, probably via the increase in fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, thereby increasing glycolysis. Our results thus indicate that DEXF counteracts the inhibition of glycolysis by glucagon and that this property might contribute to the antihyperglycaemic effect of this drug. Furthermore, this study shows that, in the presence of the drug, glucagon caused phosphorylase activation and pyruvate kinase inactivation without a significant increase in cyclic AMP levels.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brindley D. N., Hales P., al-Sieni A. I., Russell J. C. Sustained decreases in weight and serum insulin, glucose, triacylglycerol and cholesterol in JCR:LA-corpulent rats treated with D-fenfluramine. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;105(3):679–685. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09038.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bygrave F. L., Benedetti A. Calcium: its modulation in liver by cross-talk between the actions of glucagon and calcium-mobilizing agonists. Biochem J. 1993 Nov 15;296(Pt 1):1–14. doi: 10.1042/bj2960001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corvera S., Huerta-Bahena J., Pelton J. T., Hruby V. J., Trivedi D., García-Sáinz J. A. Metabolic effects and cyclic AMP levels produced by glucagon, (1-N alpha-Trinitrophenylhistidine,12-homoarginine)glucagon and forskolin in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Aug 17;804(4):434–441. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(84)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cárdenas-Tanús R. J., Huerta-Bahena J., García-Sáinz J. A. Angiotensin II inhibits the accumulation of cyclic AMP produced by glucagon but not its metabolic effects. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jun 21;143(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80259-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feliú J. E., Hue L., Hers H. G. Hormonal control of pyruvate kinase activity and of gluconeogenesis in isolated hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2762–2766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felíu J. E., Hue L., Hers H. G. Regulation in vitro and in vivo of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent inactivation of rat-liver pyruvate kinase type L. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Dec;81(3):609–617. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Sáinz J. A., Mendlovic F., Martínez-Olmedo M. A. Effects of phorbol esters on alpha 1-adrenergic-mediated and glucagon-mediated actions in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):277–280. doi: 10.1042/bj2280277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gascon-Barré M., Haddad P., Provencher S. J., Bilodeau S., Pecker F., Lotersztajn S., Vallières S. Chronic hypocalcemia of vitamin D deficiency leads to lower intracellular calcium concentrations in rat hepatocytes. J Clin Invest. 1994 May;93(5):2159–2167. doi: 10.1172/JCI117212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geelen M. J. Effects of fenfluramine on hepatic intermediary metabolism. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Nov 15;32(22):3321–3324. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90357-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geelen M. J. Mechanisms responsible for the inhibitory effects of benfluorex on hepatic intermediary metabolism. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Jun 1;32(11):1765–1772. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90123-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hue L., Bontemps F., Hers H. The effects of glucose and of potassium ions on the interconversion of the two forms of glycogen phosphorylase and of glycogen synthetase in isolated rat liver preparations. Biochem J. 1975 Oct;152(1):105–114. doi: 10.1042/bj1520105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek L. J., Lok S., Rosenberg G. B., Smith R. A., Grant F. J., Biggs S., Bensch P. A., Kuijper J. L., Sheppard P. O., Sprecher C. A. Expression cloning and signaling properties of the rat glucagon receptor. Science. 1993 Mar 12;259(5101):1614–1616. doi: 10.1126/science.8384375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leverve X. M., Fontaine E., Putod-Paramelle F., Rigoulet M. Decrease in cytosolic ATP/ADP ratio and activation of pyruvate kinase after in vitro addition of almitrine in hepatocytes isolated from fasted rats. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Sep 15;224(3):967–974. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.00967.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestell R. G., Crock P. A., Ward G. M., Alford F. P., Best J. D. Fenfluramine increases insulin action in patients with NIDDM. Diabetes Care. 1989 Apr;12(4):252–258. doi: 10.2337/diacare.12.4.252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheen A. J., Paolisso G., Salvatore T., Lefèbvre P. J. Improvement of insulin-induced glucose disposal in obese patients with NIDDM after 1-wk treatment with d-fenfluramine. Diabetes Care. 1991 Apr;14(4):325–332. doi: 10.2337/diacare.14.4.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. O., Stein G. R., Davis T. M., Findlater P. Dexfenfluramine in type II diabetes: effect on weight and diabetes control. Med J Aust. 1993 Feb 1;158(3):167–169. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1993.tb121695.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Hue L., Hers H. G. Control of the fructose-6-phosphate/fructose 1,6-bisphosphate cycle in isolated hepatocytes by glucose and glucagon. Role of a low-molecular-weight stimulator of phosphofructokinase. Biochem J. 1980 Dec 15;192(3):887–895. doi: 10.1042/bj1920887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Hue L., Hers H. G. Extracellular metabolites in suspensions of isolated hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 1;248(2):517–521. doi: 10.1042/bj2480517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Sieni A. I., Plested C. P., Rolland Y., Brindley D. N. Decreased incorporation of glucose into lipids and increased lactate production by adipose tissue after long-term treatment of rats with D-fenfluramine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Nov 1;38(21):3661–3667. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90569-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Werve G. Isolation and characteristics of hepatocytes. Toxicology. 1980;18(3):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(80)90062-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Werve G., Stalmans W., Hers H. G. The effect of insulin on the glycogenolytic cascade and on the activity of glycogen synthase in the liver of anaesthetized rabbits. Biochem J. 1977 Jan 15;162(1):143–146. doi: 10.1042/bj1620143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


