Abstract
The widespread deposition of amyloid plaques is one of the hallmarks of Alzheimer disease (AD). A recently described component of amyloid plaques is the 35-residue peptide, non-A beta component of AD amyloid, which is derived from a larger intracellular neuronal constituent, alpha-synuclein. We demonstrate that transglutaminase catalyses the formation of the covalent non-A beta component of AD amyloid polymers in vitro as well as polymers with beta-amyloid peptide, the major constituent of AD plaques. The transglutaminase-reactive amino acid residues in the non-A beta component of AD amyloid were identified as Gln79 and Lys80. Lys80 is localized in a consensus motif Lys-Thr-Lys-Glu-Gly-Val, which is conserved in the synuclein gene family. Thus transglutaminase might be involved in the formation of insoluble amyloid deposits and participate in the modification of other members of the synuclein family.
Full text
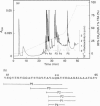
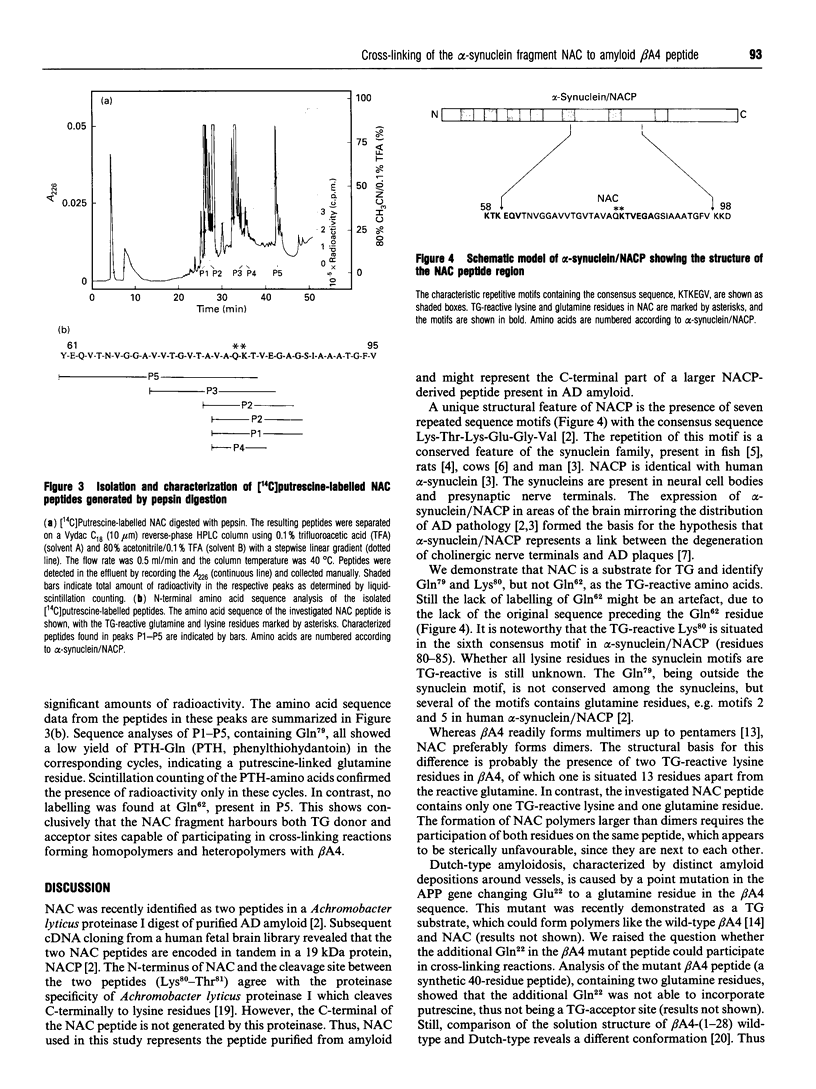
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aeschlimann D., Paulsson M. Transglutaminases: protein cross-linking enzymes in tissues and body fluids. Thromb Haemost. 1994 Apr;71(4):402–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashall F., Goate A. M. Role of the beta-amyloid precursor protein in Alzheimer's disease. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Jan;19(1):42–46. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90173-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookes A. J., St Clair D. Synuclein proteins and Alzheimer's disease. Trends Neurosci. 1994 Oct;17(10):404–405. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudek S. M., Johnson G. V. Transglutaminase catalyzes the formation of sodium dodecyl sulfate-insoluble, Alz-50-reactive polymers of tau. J Neurochem. 1993 Sep;61(3):1159–1162. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03636.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudek S. M., Johnson G. V. Transglutaminase facilitates the formation of polymers of the beta-amyloid peptide. Brain Res. 1994 Jul 18;651(1-2):129–133. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)90688-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eitan S., Schwartz M. A transglutaminase that converts interleukin-2 into a factor cytotoxic to oligodendrocytes. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):106–108. doi: 10.1126/science.8100369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich P., Fesus L., Tarcsa E., Czéh G. Protein cross-linking by transglutaminase induced in long-term potentiation in the Ca1 region of hippocampal slices. Neuroscience. 1991;43(2-3):331–334. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90297-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho G. J., Gregory E. J., Smirnova I. V., Zoubine M. N., Festoff B. W. Cross-linking of beta-amyloid protein precursor catalyzed by tissue transglutaminase. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jul 25;349(1):151–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00663-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikura K., Takahata K., Sasaki R. Cross-linking of a synthetic partial-length (1-28) peptide of the Alzheimer beta/A4 amyloid protein by transglutaminase. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jul 12;326(1-3):109–111. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81772-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakes R., Spillantini M. G., Goedert M. Identification of two distinct synucleins from human brain. FEBS Lett. 1994 May 23;345(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00395-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima S., Nara K., Rifkin D. B. Requirement for transglutaminase in the activation of latent transforming growth factor-beta in bovine endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;121(2):439–448. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.2.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Conrad S. M. Transglutaminases. Mol Cell Biochem. 1984;58(1-2):9–35. doi: 10.1007/BF00240602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Parameswaran K. N., Velasco P. T. Sorting-out of acceptor-donor relationships in the transglutaminase-catalyzed cross-linking of crystallins by the enzyme-directed labeling of potential sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):82–83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Yee A., Brewer H. B., Jr, Das S., Potter H. Amyloid-associated proteins alpha 1-antichymotrypsin and apolipoprotein E promote assembly of Alzheimer beta-protein into filaments. Nature. 1994 Nov 3;372(6501):92–94. doi: 10.1038/372092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroteaux L., Campanelli J. T., Scheller R. H. Synuclein: a neuron-specific protein localized to the nucleus and presynaptic nerve terminal. J Neurosci. 1988 Aug;8(8):2804–2815. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-08-02804.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroteaux L., Scheller R. H. The rat brain synucleins; family of proteins transiently associated with neuronal membrane. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Oct;11(3-4):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90043-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masaki T., Fujihashi T., Nakamura K., Soejima M. Studies on a new proteolytic enzyme from Achromobacter lyticus M497-1. II. specificity and inhibition studies of Achromobacter protease I. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 24;660(1):51–55. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90107-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajo S., Tsukada K., Omata K., Nakamura Y., Nakaya K. A new brain-specific 14-kDa protein is a phosphoprotein. Its complete amino acid sequence and evidence for phosphorylation. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Nov 1;217(3):1057–1063. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18337.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaoka H., Perez D. M., Baek K. J., Das T., Husain A., Misono K., Im M. J., Graham R. M. Gh: a GTP-binding protein with transglutaminase activity and receptor signaling function. Science. 1994 Jun 10;264(5165):1593–1596. doi: 10.1126/science.7911253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen L. K., Sørensen E. S., Petersen T. E., Gliemann J., Jensen P. H. Identification of glutamine and lysine residues in Alzheimer amyloid beta A4 peptide responsible for transglutaminase-catalysed homopolymerization and cross-linking to alpha 2M receptor. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jan 31;338(2):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80356-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Abraham C., Ihara Y. Brain transglutaminase: in vitro crosslinking of human neurofilament proteins into insoluble polymers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6070–6074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorimachi K., Craik D. J. Structure determination of extracellular fragments of amyloid proteins involved in Alzheimer's disease and Dutch-type hereditary cerebral haemorrhage with amyloidosis. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Jan 15;219(1-2):237–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb19935.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uéda K., Fukushima H., Masliah E., Xia Y., Iwai A., Yoshimoto M., Otero D. A., Kondo J., Ihara Y., Saitoh T. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding an unrecognized component of amyloid in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11282–11286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]