Abstract
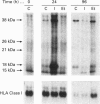
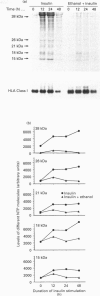
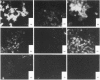
Neuronal thread proteins (NTPs) are molecules that accumulate in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease, and may play a key role in both normal and neurodegenerative neuritic sprouting. In this investigation we determined whether NTP expression is up-regulated by insulin, an important neurotrophic factor that stimulates differentiation-associated neurite outgrowth, and studied the effects of ethanol, a known inhibitor of growth factor receptor tyrosine phosphorylation, on NTP expression and insulin-mediated signal transduction cascade in neuronal [primitive neuroectodermal tumour cell line 2; (PNET2)] cells. PNET2 cells were treated with 50 m-units/ml insulin in the presence or absence of 100 mM ethanol for 0.2-96 h, and cell proliferation and expression of NTP molecules were investigated by metabolic labelling, immunoprecipitation and immunohistochemical staining. Insulin stimulation resulted in an immediate increase in the levels of three (38, 18 and 15 kDa) of five NTP species (the others were of 26 and 21 kDa), followed by a decline in expression within 120 min; however, studies performed up to 96 h of culture demonstrated up-regulation by insulin of all five NTP species. Ethanol either abolished or severely muted the short- and long-term insulin-mediated upregulation of NTP expression, and substantially reduced insulin-mediated neuronal differentiation. The effects of ethanol on NTP gene expression were associated with impaired insulin-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of both the insulin receptor beta subunit and the insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1), resulting in decreased association of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase with IRS-1. The findings suggest that ethanol may inhibit NTP expression associated with central nervous system neuronal differentiation by uncoupling the IRS-1-mediated insulin signal transduction pathway.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamo M. L., Shemer J., Roberts C. T., Jr, LeRoith D. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I induced phosphorylation in neurally derived cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Aug 27;692:113–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb26210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamo M., Raizada M. K., LeRoith D. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor receptors in the nervous system. Mol Neurobiol. 1989 Spring-Summer;3(1-2):71–100. doi: 10.1007/BF02935589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aizenman Y., de Vellis J. Brain neurons develop in a serum and glial free environment: effects of transferrin, insulin, insulin-like growth factor-I and thyroid hormone on neuronal survival, growth and differentiation. Brain Res. 1987 Mar 17;406(1-2):32–42. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90766-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander M. C., Lomanto M., Nasrin N., Ramaika C. Insulin stimulates glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene expression through cis-acting DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5092–5096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltensperger K., Kozma L. M., Cherniack A. D., Klarlund J. K., Chawla A., Banerjee U., Czech M. P. Binding of the Ras activator son of sevenless to insulin receptor substrate-1 signaling complexes. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1950–1952. doi: 10.1126/science.8391166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonthius D. J., West J. R. Acute and long-term neuronal deficits in the rat olfactory bulb following alcohol exposure during the brain growth spurt. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 1991 Nov-Dec;13(6):611–619. doi: 10.1016/0892-0362(91)90044-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borges S., Lewis P. D. The effect of ethanol on the cellular composition of the cerebellum. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1983 Jan-Feb;9(1):53–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1983.tb00323.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodie C., Vernadakis A. Ethanol increases cholinergic and decreases GABAergic neuronal expression in cultures derived from 8-day-old chick embryo cerebral hemispheres: interaction of ethanol and growth factors. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1992 Feb 21;65(2):253–257. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(92)90186-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess S. K., Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P., Sahyoun N. Characterization of a neuronal subtype of insulin-like growth factor I receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1618–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter E. A., Wands J. R. Ethanol inhibits hormone stimulated hepatocyte DNA synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 30;128(2):767–774. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90113-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter E. A., Wands J. R. Ethanol-induced inhibition of liver cell function: I. Effect of ethanol on hormone stimulated hepatocyte DNA synthesis and the role of ethanol metabolism. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1988 Aug;12(4):555–562. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1988.tb00241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarren S. K., Alvord E. C., Jr, Sumi S. M., Streissguth A. P., Smith D. W. Brain malformations related to prenatal exposure to ethanol. J Pediatr. 1978 Jan;92(1):64–67. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarren S. K., Smith D. W. The fetal alcohol syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1978 May 11;298(19):1063–1067. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197805112981906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M. Insulin signalling: search for the missing links. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):286–287. doi: 10.1038/348286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiCicco-Bloom E., Black I. B. Insulin growth factors regulate the mitotic cycle in cultured rat sympathetic neuroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4066–4070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diehl A. M., Thorgeirsson S. S., Steer C. J. Ethanol inhibits liver regeneration in rats without reducing transcripts of key protooncogenes. Gastroenterology. 1990 Oct;99(4):1105–1112. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90631-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diehl A. M., Yang S. Q., Cote P., Wand G. S. Chronic ethanol consumption disturbs G-protein expression and inhibits cyclic AMP-dependent signaling in regenerating rat liver. Hepatology. 1992 Nov;16(5):1212–1219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dow K. E., Riopelle R. J. Ethanol inhibits NMDA-stimulated neurite growth by sensory neurons in vitro. Neuroreport. 1990 Oct;1(2):111–114. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199010000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dow K. E., Riopelle R. J. Ethanol neurotoxicity: effects on neurite formation and neurotrophic factor production in vitro. Science. 1985 May 3;228(4699):591–593. doi: 10.1126/science.3983644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguay L., Coutu D., Hetu C., Joly J. G. Inhibition of liver regeneration by chronic alcohol administration. Gut. 1982 Jan;23(1):8–13. doi: 10.1136/gut.23.1.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammeltoft S., Ballotti R., Nielsen F. C., Kowalski A., Van Obberghen E. Receptors for insulin-like growth factors in the central nervous system: structure and function. Horm Metab Res. 1988 Jul;20(7):436–442. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1010854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girault J. A., Chamak B., Bertuzzi G., Tixier H., Wang J. K., Pang D. T., Greengard P. Protein phosphotyrosine in mouse brain: developmental changes and regulation by epidermal growth factor, type I insulin-like growth factor, and insulin. J Neurochem. 1992 Feb;58(2):518–528. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluckman P. D. Fetal growth: an endocrine perspective. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl. 1989;349:21–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1989.tb17162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gressens P., Lammens M., Picard J. J., Evrard P. Ethanol-induced disturbances of gliogenesis and neuronogenesis in the developing murine brain: an in vitro and in vivo immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study. Alcohol Alcohol. 1992 May;27(3):219–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross J., Carlson R. I., Brauer A. W., Margolies M. N., Warshaw A. L., Wands J. R. Isolation, characterization, and distribution of an unusual pancreatic human secretory protein. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2115–2126. doi: 10.1172/JCI112216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haystead C. M., Gregory P., Shirazi A., Fadden P., Mosse C., Dent P., Haystead T. A. Insulin activates a novel adipocyte mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase that shows rapid phasic kinetics and is distinct from c-Raf. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 29;269(17):12804–12808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich K. A. Insulin and IGF-I receptor signaling in cultured neurons. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Aug 27;692:72–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb26207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich K. A., Toledo S. P. Insulin receptors mediate growth effects in cultured fetal neurons. I. Rapid stimulation of protein synthesis. Endocrinology. 1989 Sep;125(3):1451–1457. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-3-1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich K. A., de Vellis G., Gilmore P. R. Functional properties of the subtype of insulin receptor found on neurons. J Neurochem. 1988 Sep;51(3):878–887. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01824.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii D. N., Recio-Pinto E., Spinelli W., Mill J. F., Sonnenfeld K. H. Neurite formation modulated by nerve growth factor, insulin, and tumor promoter receptors. Int J Neurosci. 1985 Apr;26(1-2):109–127. doi: 10.3109/00207458508985610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. L., Smith D. W. Recognition of the fetal alcohol syndrome in early infancy. Lancet. 1973 Nov 3;302(7836):999–1001. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao K. J., Cook D. J., Scornik J. C. Quantitative analysis of platelet surface HLA by W6/32 anti-HLA monoclonal antibody. Blood. 1986 Sep;68(3):627–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karns L. R., Ng S. C., Freeman J. A., Fishman M. C. Cloning of complementary DNA for GAP-43, a neuronal growth-related protein. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):597–600. doi: 10.1126/science.2437653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J., Siebel C. W., McCormick F., Roth R. A. Ras p21 as a potential mediator of insulin action in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):840–843. doi: 10.1126/science.3554510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozma L., Baltensperger K., Klarlund J., Porras A., Santos E., Czech M. P. The ras signaling pathway mimics insulin action on glucose transporter translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4460–4464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasserre C., Christa L., Simon M. T., Vernier P., Bréchot C. A novel gene (HIP) activated in human primary liver cancer. Cancer Res. 1992 Sep 15;52(18):5089–5095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenoir D., Honegger P. Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF I) stimulates DNA synthesis in fetal rat brain cell cultures. Brain Res. 1983 Apr;283(2-3):205–213. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(83)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li N., Batzer A., Daly R., Yajnik V., Skolnik E., Chardin P., Bar-Sagi D., Margolis B., Schlessinger J. Guanine-nucleotide-releasing factor hSos1 binds to Grb2 and links receptor tyrosine kinases to Ras signalling. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):85–88. doi: 10.1038/363085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters B. A., Raizada M. K. Insulin-like growth factor I receptors and IGF-I actions in neuronal cultures from the brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Aug 27;692:89–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb26208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F. Signal transduction. How receptors turn Ras on. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):15–16. doi: 10.1038/363015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee A. C., Kosik K. S., Kowall N. W. Neuritic pathology and dementia in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1991 Aug;30(2):156–165. doi: 10.1002/ana.410300206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medema R. H., de Laat W. L., Martin G. A., McCormick F., Bos J. L. GTPase-activating protein SH2-SH3 domains induce gene expression in a Ras-dependent fashion. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3425–3430. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messina J. L., Standaert M. L., Ishizuka T., Weinstock R. S., Farese R. V. Role of protein kinase C in insulin's regulation of c-fos transcription. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9223–9228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles M. F., Diaz J. E., DeGuzman V. Ethanol-responsive gene expression in neural cell cultures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Apr 14;1138(4):268–274. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(92)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. G., Jr, Backer J. M., Sun X. J., Shoelson S., Hu P., Schlessinger J., Yoakim M., Schaffhausen B., White M. F. IRS-1 activates phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase by associating with src homology 2 domains of p85. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10350–10354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. G., Jr, White M. F. The new elements of insulin signaling. Insulin receptor substrate-1 and proteins with SH2 domains. Diabetes. 1993 May;42(5):643–650. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.5.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama M., Wands J. R. Cloning and increased expression of an insulin receptor substrate-1-like gene in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Feb 28;183(1):280–285. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91640-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onorato M., Mulvihill P., Connolly J., Galloway P., Whitehouse P., Perry G. Alteration of neuritic cytoarchitecture in Alzheimer disease. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;317:781–789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski C. C., Chernausek S. D., Akeson R. Actions of insulin-like growth factor-I on the B104 neuronal cell line: effects on cell replication, receptor characteristics, and influence of secreted binding protein on ligand binding. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jun;139(3):469–476. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041390304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozturk M., de la Monte S. M., Gross J., Wands J. R. Elevated levels of an exocrine pancreatic secretory protein in Alzheimer disease brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):419–423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peiffer J., Majewski F., Fischbach H., Bierich J. R., Volk B. Alcohol embryo- and fetopathy. Neuropathology of 3 children and 3 fetuses. J Neurol Sci. 1979 Apr;41(2):125–137. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(79)90033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porras A., Nebreda A. R., Benito M., Santos E. Activation of Ras by insulin in 3T3 L1 cells does not involve GTPase-activating protein phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):21124–21131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Påhlman S., Meyerson G., Lindgren E., Schalling M., Johansson I. Insulin-like growth factor I shifts from promoting cell division to potentiating maturation during neuronal differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):9994–9998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.9994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recio-Pinto E., Ishii D. N. Effects of insulin, insulin-like growth factor-II and nerve growth factor on neurite outgrowth in cultured human neuroblastoma cells. Brain Res. 1984 Jun 8;302(2):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90246-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recio-Pinto E., Lang F. F., Ishii D. N. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor II permit nerve growth factor binding and the neurite formation response in cultured human neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2562–2566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recio-Pinto E., Rechler M. M., Ishii D. N. Effects of insulin, insulin-like growth factor-II, and nerve growth factor on neurite formation and survival in cultured sympathetic and sensory neurons. J Neurosci. 1986 May;6(5):1211–1219. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-05-01211.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnicoff M., Rubini M., Baserga R., Rubin R. Ethanol inhibits insulin-like growth factor-1-mediated signalling and proliferation of C6 rat glioblastoma cells. Lab Invest. 1994 Nov;71(5):657–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnicoff M., Sell C., Ambrose D., Baserga R., Rubin R. Ethanol inhibits the autophosphorylation of the insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) receptor and IGF-1-mediated proliferation of 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21777–21782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Rubin C. S., Cobb M. H., Smith C. J. Insulin stimulates the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in a cell-free system derived from 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3630–3633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki Y., Wands J. R. Ethanol impairs insulin receptor substrate-1 mediated signal transduction during rat liver regeneration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Feb 28;199(1):403–409. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki Y., Zhang X. F., Nishiyama M., Avruch J., Wands J. R. Expression and phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 during rat liver regeneration. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):3805–3808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheibel A. B., Tomiyasu U. Dendritic sprouting in Alzheimer's presenile dementia. Exp Neurol. 1978 May 15;60(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(78)90164-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shemer J., Raizada M. K., Masters B. A., Ota A., LeRoith D. Insulin-like growth factor I receptors in neuronal and glial cells. Characterization and biological effects in primary culture. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7693–7699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Margolis B., Mohammadi M., Lowenstein E., Fischer R., Drepps A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Cloning of PI3 kinase-associated p85 utilizing a novel method for expression/cloning of target proteins for receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90410-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. J., Rothenberg P., Kahn C. R., Backer J. M., Araki E., Wilden P. A., Cahill D. A., Goldstein B. J., White M. F. Structure of the insulin receptor substrate IRS-1 defines a unique signal transduction protein. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):73–77. doi: 10.1038/352073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung C. K., Sánchez-Margalet V., Goldfine I. D. Role of p85 subunit of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase as an adaptor molecule linking the insulin receptor, p62, and GTPase-activating protein. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 29;269(17):12503–12507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terazono K., Yamamoto H., Takasawa S., Shiga K., Yonemura Y., Tochino Y., Okamoto H. A novel gene activated in regenerating islets. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2111–2114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The I., Murthy A. E., Hannigan G. E., Jacoby L. B., Menon A. G., Gusella J. F., Bernards A. Neurofibromatosis type 1 gene mutations in neuroblastoma. Nat Genet. 1993 Jan;3(1):62–66. doi: 10.1038/ng0193-62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobe K., Matuoka K., Tamemoto H., Ueki K., Kaburagi Y., Asai S., Noguchi T., Matsuda M., Tanaka S., Hattori S. Insulin stimulates association of insulin receptor substrate-1 with the protein abundant Src homology/growth factor receptor-bound protein 2. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11167–11171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urso T., Gavaler J. S., Van Thiel D. H. Blood ethanol levels in sober alcohol users seen in an emergency room. Life Sci. 1981 Mar 2;28(9):1053–1056. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90752-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wands J. R., Carter E. A., Bucher N. L., Isselbacher K. J. Inhibition of hepatic regeneration in rats by acute and chronic ethanol intoxication. Gastroenterology. 1979 Sep;77(3):528–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. M., Myers M. G., Jr, Sun X. J., Aaronson S. A., White M., Pierce J. H. IRS-1: essential for insulin- and IL-4-stimulated mitogenesis in hematopoietic cells. Science. 1993 Sep 17;261(5128):1591–1594. doi: 10.1126/science.8372354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Yonekura H., Terazono K., Yamamoto H., Okamoto H. Complete nucleotide sequence of human reg gene and its expression in normal and tumoral tissues. The reg protein, pancreatic stone protein, and pancreatic thread protein are one and the same product of the gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7432–7439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Maron R., Kahn C. R. Insulin rapidly stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of a Mr-185,000 protein in intact cells. Nature. 1985 Nov 14;318(6042):183–186. doi: 10.1038/318183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. W., Sarnecki C., Roberts T. M., Blenis J. ras mediates nerve growth factor receptor modulation of three signal-transducing protein kinases: MAP kinase, Raf-1, and RSK. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1041–1050. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90076-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Y. Y., Wands J. R., de la Monte S. M. Characterization of thread proteins expressed in neuroectodermal tumors. Cancer Res. 1993 Aug 15;53(16):3823–3829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi K., Holt K., Pessin J. E. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase functions upstream of Ras and Raf in mediating insulin stimulation of c-fos transcription. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14597–14600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonezawa K., Ando A., Kaburagi Y., Yamamoto-Honda R., Kitamura T., Hara K., Nakafuku M., Okabayashi Y., Kadowaki T., Kaziro Y. Signal transduction pathways from insulin receptors to Ras. Analysis by mutant insulin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 11;269(6):4634–4640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Monte S. M., Bhavani K., Xu Y. Y., Puisieux A., Wands J. R. Modulation of p36 gene expression in human neuronal cells. J Neurol Sci. 1995 Feb;128(2):122–133. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(94)00218-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Monte S. M. Disproportionate atrophy of cerebral white matter in chronic alcoholics. Arch Neurol. 1988 Sep;45(9):990–992. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1988.00520330076013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Monte S. M., Ozturk M., Wands J. R. Enhanced expression of an exocrine pancreatic protein in Alzheimer's disease and the developing human brain. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):1004–1013. doi: 10.1172/JCI114762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Monte S. M., Volicer L., Hauser S. L., Wands J. R. Increased levels of neuronal thread protein in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1992 Dec;32(6):733–742. doi: 10.1002/ana.410320606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Monte S. M., Wands J. R. Neuronal thread protein over-expression in brains with Alzheimer's disease lesions. J Neurol Sci. 1992 Dec;113(2):152–164. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(92)90243-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]