Abstract
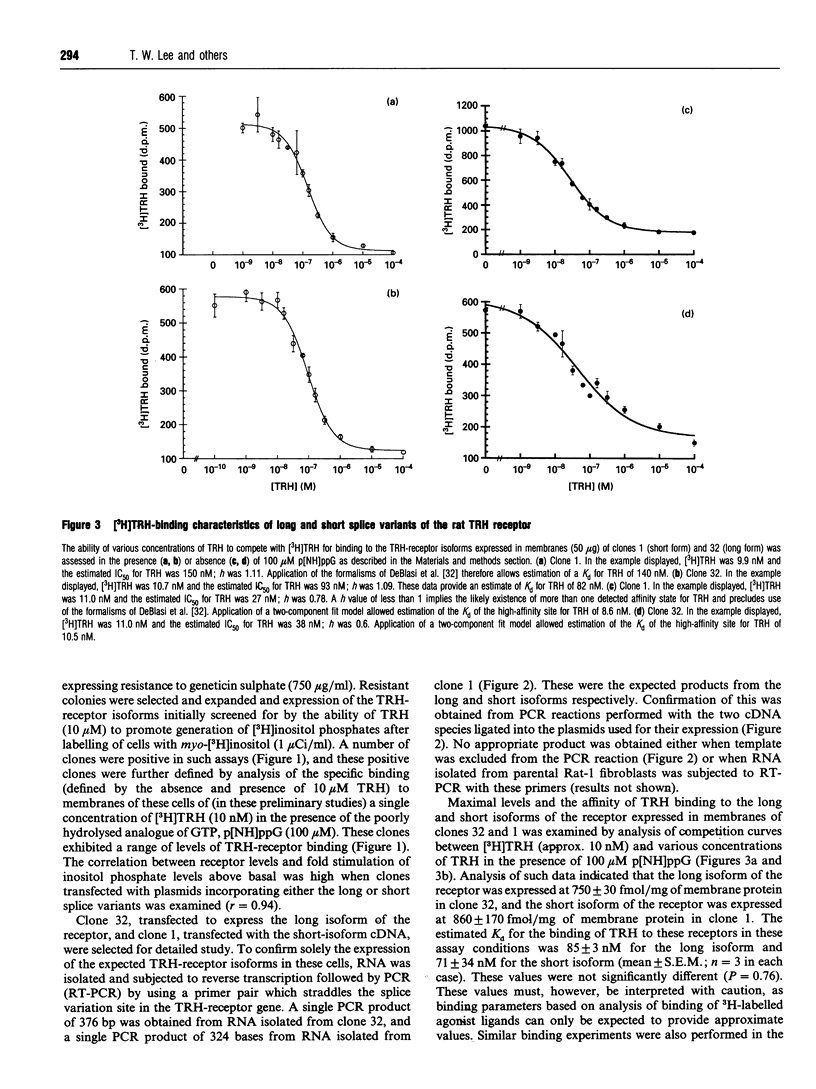
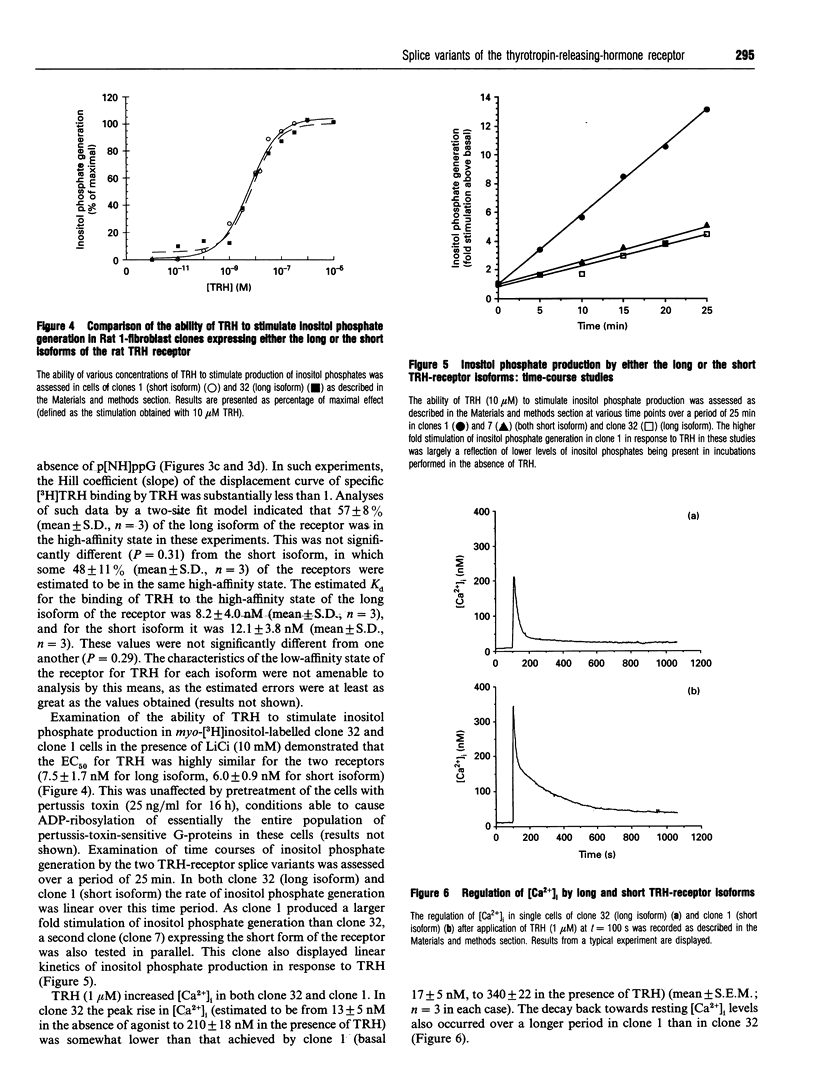
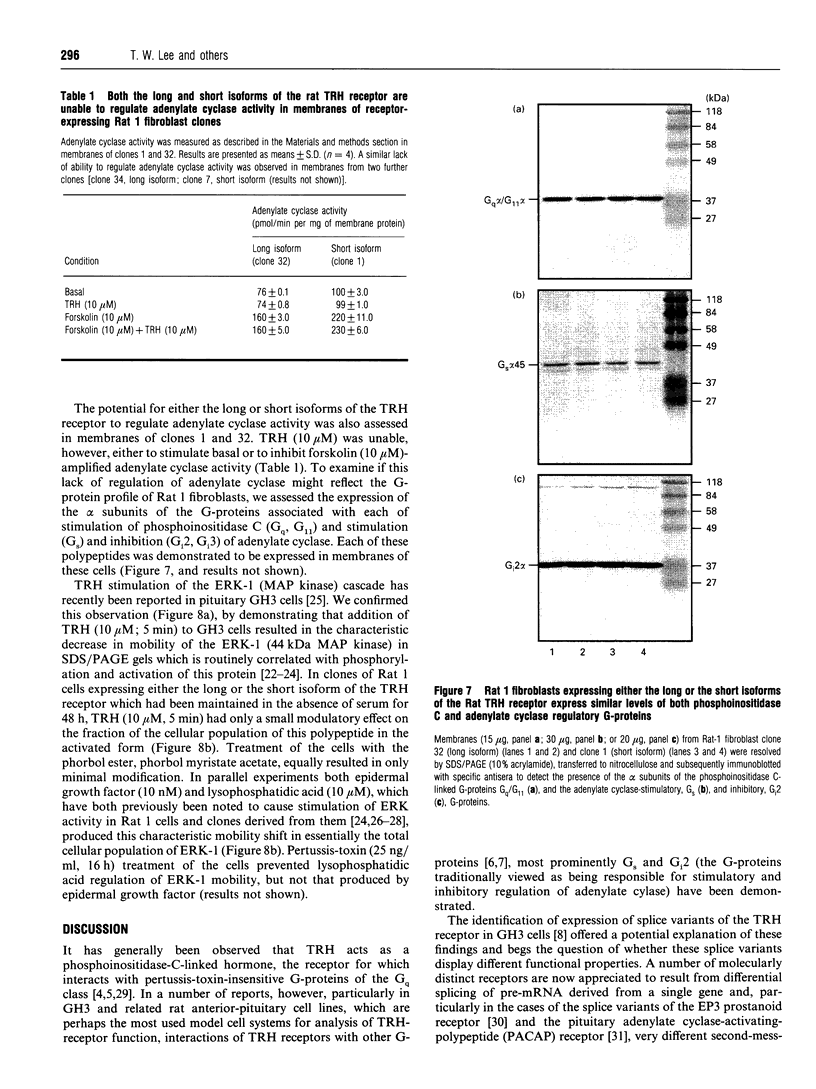
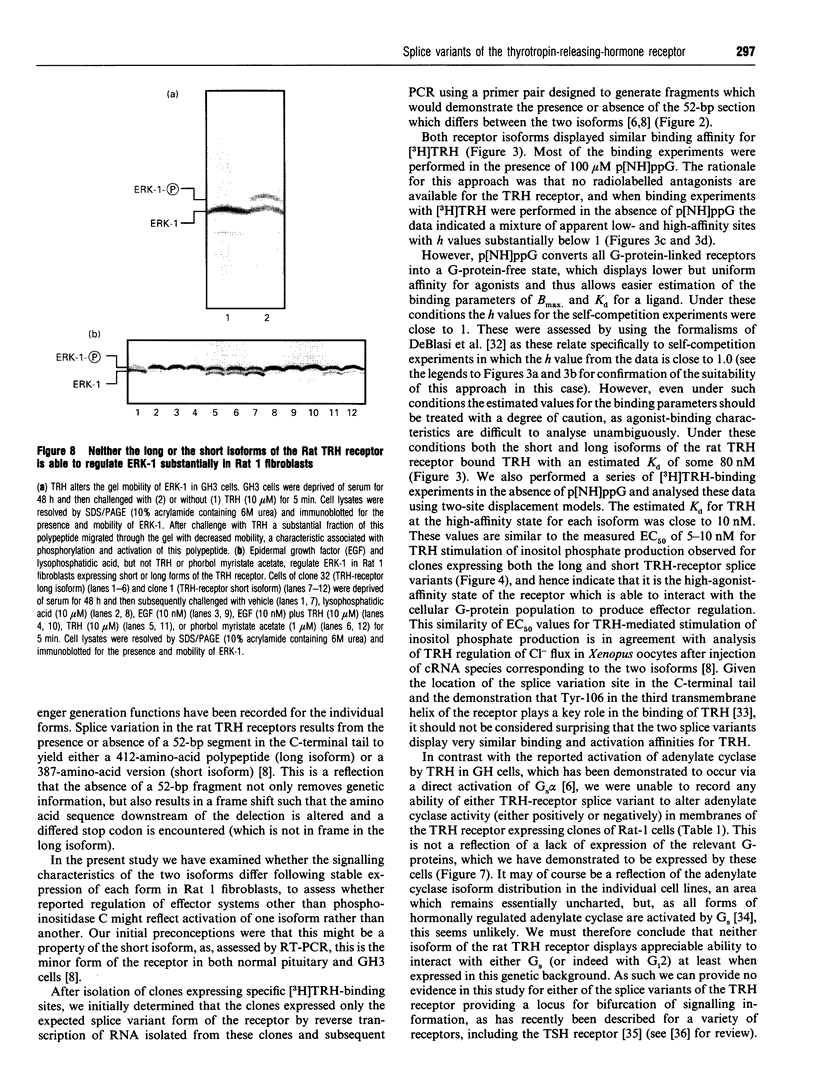
cDNA species encoding either the long or the short isoforms of the rat thyrotropin-releasing-hormone (TRH) receptor were expressed stably in Rat 1 fibroblasts, and clones expressing specific binding of [3H]TRH were detected and expanded. Clones expressing each of these receptors at levels up to 1 pmol/mg of membrane protein were selected for analysis. Reverse-transcriptase PCR on RNA isolated from these clones confirmed that each clone expressed only mRNA corresponding to the expected splice variant. Both receptor splice variants bound [3H]TRH with a Kd of some 80 nM when binding assays were performed in the presence of guanosine 5'-[beta gamma-imido]-triphosphate. In the presence of TRH, both receptor subtypes were able to cause stimulation of inositol phosphate generation in a pertussis-toxin-insensitive manner with similar EC50 values and to stimulate the mobilization of intracellular Ca2+, but, despite reports that TRH receptors can also interact with the G-proteins Gs and Gi2, neither receptor splice variant was able to modulate adenylate cyclase activity in either a positive or a negative manner. These data indicate that the long and short isoforms of the rat TRH receptor have similar affinities for TRH and display similar abilities to interact with the Gq-like G-proteins, but show no ability to regulate adenylate cyclase, at least when expressed in this genetic background.
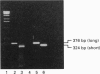
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alblas J., van Corven E. J., Hordijk P. L., Milligan G., Moolenaar W. H. Gi-mediated activation of the p21ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway by alpha 2-adrenergic receptors expressed in fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22235–22238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allgeier A., Offermanns S., Van Sande J., Spicher K., Schultz G., Dumont J. E. The human thyrotropin receptor activates G-proteins Gs and Gq/11. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):13733–13735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L., Hoyland J., Mason W. T., Eidne K. A. Characterization of the gonadotrophin-releasing hormone calcium response in single alpha T3-1 pituitary gonadotroph cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1992 Aug;86(3):167–175. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(92)90141-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. G., Milligan G. Regulation of p42 and p44 MAP kinase isoforms in Rat-1 fibroblasts stably transfected with alpha 2C10 adrenoreceptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 May 16;200(3):1529–1535. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aragay A. M., Katz A., Simon M. I. The G alpha q and G alpha 11 proteins couple the thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor to phospholipase C in GH3 rat pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):24983–24988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBlasi A., O'Reilly K., Motulsky H. J. Calculating receptor number from binding experiments using same compound as radioligand and competitor. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Jun;10(6):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90266-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollasch M., Kleuss C., Hescheler J., Wittig B., Schultz G. Gi2 and protein kinase C are required for thyrotropin-releasing hormone-induced stimulation of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels in rat pituitary GH3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6265–6269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A., Johnson J. L., Milligan G. Down-regulation of Gi sub-types by prolonged incubation of adipocytes with an A1 adenosine receptor agonist. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5206–5210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hordijk P. L., Verlaan I., van Corven E. J., Moolenaar W. H. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation induced by lysophosphatidic acid in Rat-1 fibroblasts. Evidence that phosphorylation of map kinase is mediated by the Gi-p21ras pathway. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):645–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh K. P., Martin T. F. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone and gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptors activate phospholipase C by coupling to the guanosine triphosphate-binding proteins Gq and G11. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Oct;6(10):1673–1681. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.10.1333052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim G. D., Carr I. C., Anderson L. A., Zabavnik J., Eidne K. A., Milligan G. The long isoform of the rat thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor down-regulates Gq proteins. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 5;269(31):19933–19940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leevers S. J., Marshall C. J. Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase, ERK2, by p21ras oncoprotein. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):569–574. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie F. R., Milligan G. Delta-opioid-receptor-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase is transduced specifically by the guanine-nucleotide-binding protein Gi2. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 15;267(2):391–398. doi: 10.1042/bj2670391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
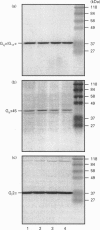
- Milligan G. Foetal-calf serum stimulates a pertussis-toxin-sensitive high-affinity GTPase activity in rat glioma C6 BU1 cells. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):501–505. doi: 10.1042/bj2450501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G. Mechanisms of multifunctional signalling by G protein-linked receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Jun;14(6):239–244. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90019-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Streaty R. A., Gierschik P., Spiegel A. M., Klee W. A. Development of opiate receptors and GTP-binding regulatory proteins in neonatal rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8626–8630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Unson C. G. Persistent activation of the alpha subunit of Gs promotes its removal from the plasma membrane. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 15;260(3):837–841. doi: 10.1042/bj2600837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell F. M., Mullaney I., Godfrey P. P., Arkinstall S. J., Wakelam M. J., Milligan G. Widespread distribution of Gq alpha/G11 alpha detected immunologically by an antipeptide antiserum directed against the predicted C-terminal decapeptide. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 5;287(1-2):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullaney I., Mitchell F. M., McCallum J. F., Buckley N. J., Milligan G. The human muscarinic M1 acetylcholine receptor, when express in CHO cells, activates and downregulates both Gq alpha and G11 alpha equally and non-selectively. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jun 14;324(2):241–245. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81401-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba T., Sugimoto Y., Negishi M., Irie A., Ushikubi F., Kakizuka A., Ito S., Ichikawa A., Narumiya S. Alternative splicing of C-terminal tail of prostaglandin E receptor subtype EP3 determines G-protein specificity. Nature. 1993 Sep 9;365(6442):166–170. doi: 10.1038/365166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmichi M., Sawada T., Kanda Y., Koike K., Hirota K., Miyake A., Saltiel A. R. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone stimulates MAP kinase activity in GH3 cells by divergent pathways. Evidence of a role for early tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3783–3788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulssen R. H., Paulssen E. J., Gautvik K. M., Gordeladze J. O. The thyroliberin receptor interacts directly with a stimulatory guanine-nucleotide-binding protein in the activation of adenylyl cyclase in GH3 rat pituitary tumour cells. Evidence obtained by the use of antisense RNA inhibition and immunoblocking of the stimulatory guanine-nucleotide-binding protein. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Feb 15;204(1):413–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16651.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman J. H., Thaw C. N., Laakkonen L., Bowers C. Y., Osman R., Gershengorn M. C. Hydrogen bonding interaction of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) with transmembrane tyrosine 106 of the TRH receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):1610–1613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plevin R., Palmer S., Gardner S. D., Wakelam M. J. Regulation of bombesin-stimulated inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate generation in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts by a guanine-nucleotide-binding protein. Biochem J. 1990 Jun 15;268(3):605–610. doi: 10.1042/bj2680605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellar R. E., Taylor P. L., Lamb R. F., Zabavnik J., Anderson L., Eidne K. A. Functional expression and molecular characterization of the thyrotrophin-releasing hormone receptor from the rat anterior pituitary gland. J Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Apr;10(2):199–206. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0100199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spengler D., Waeber C., Pantaloni C., Holsboer F., Bockaert J., Seeburg P. H., Journot L. Differential signal transduction by five splice variants of the PACAP receptor. Nature. 1993 Sep 9;365(6442):170–175. doi: 10.1038/365170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel M. C., Buckley N. J. Differential regulation of muscarinic receptor mRNA levels in neuroblastoma cells by chronic agonist exposure: a comparative polymerase chain reaction study. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 May;43(5):694–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann M., Simon M. I. G protein diversity: a distinct class of alpha subunits is present in vertebrates and invertebrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9113–9117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straub R. E., Frech G. C., Joho R. H., Gershengorn M. C. Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding the mouse pituitary thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9514–9518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang W. J., Gilman A. G. Adenylyl cyclases. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):869–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90236-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winitz S., Russell M., Qian N. X., Gardner A., Dwyer L., Johnson G. L. Involvement of Ras and Raf in the Gi-coupled acetylcholine muscarinic m2 receptor activation of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase kinase and MAP kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19196–19199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries-Smits A. M., Burgering B. M., Leevers S. J., Marshall C. J., Bos J. L. Involvement of p21ras in activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2. Nature. 1992 Jun 18;357(6379):602–604. doi: 10.1038/357602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Peña P., Delgado L. M., del Camino D., Barros F. Cloning and expression of the thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor from GH3 rat anterior pituitary cells. Biochem J. 1992 Jun 15;284(Pt 3):891–899. doi: 10.1042/bj2840891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Peña P., Delgado L. M., del Camino D., Barros F. Two isoforms of the thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor generated by alternative splicing have indistinguishable functional properties. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25703–25708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]