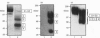Abstract
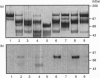
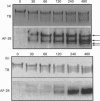
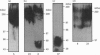
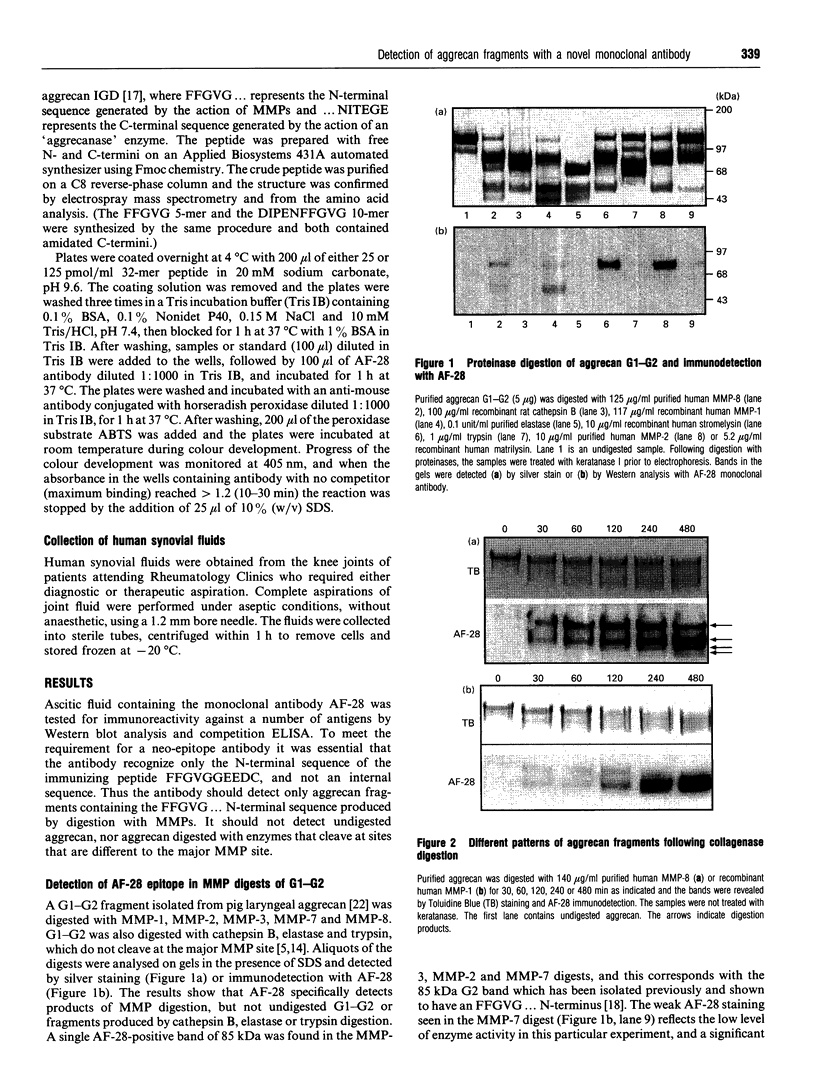
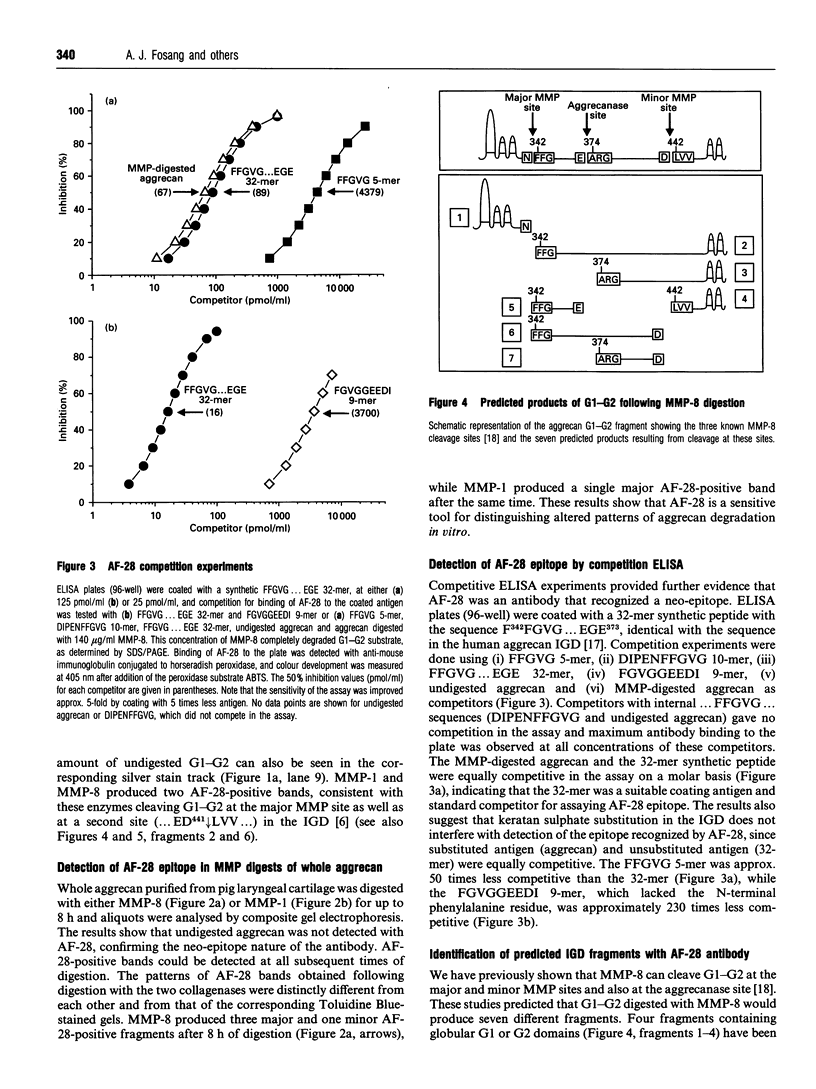
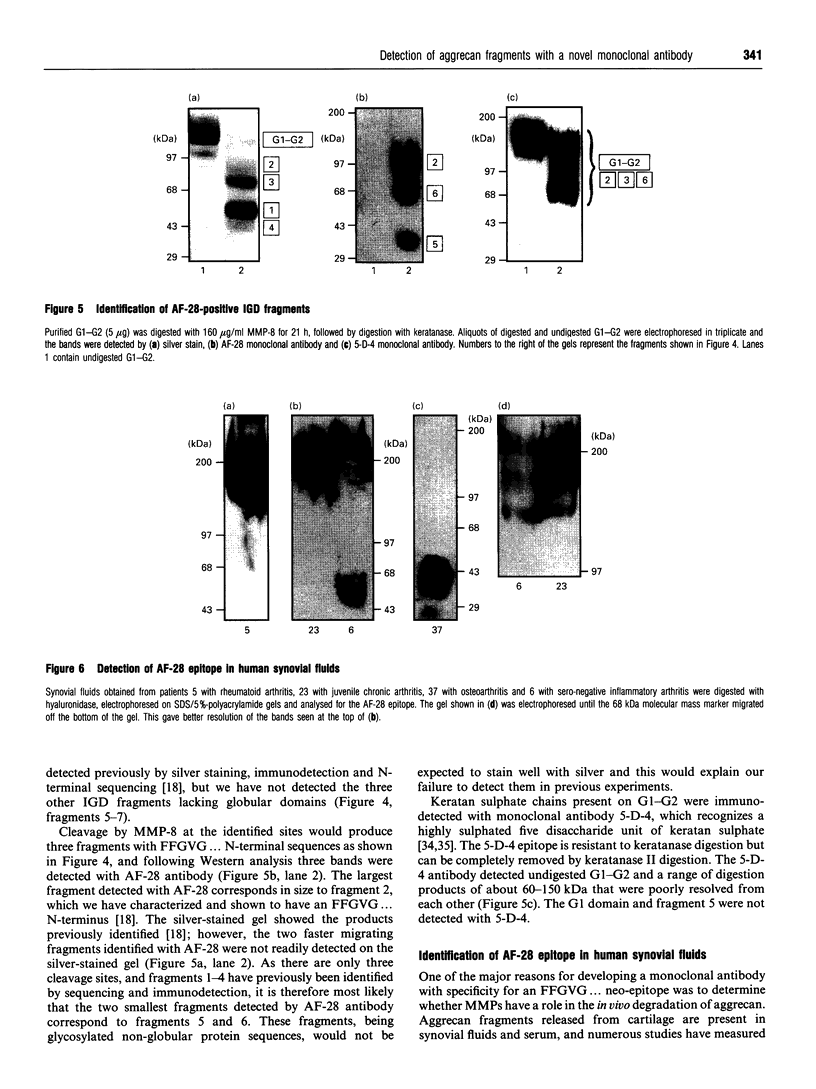
We have developed a monoclonal antibody AF-28 that specifically recognizes a neo-epitope on polypeptides with N-terminal FFGVG ... sequences. This sequence is found at the N-terminus of aggrecan fragments that have been digested with matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). By immunoblotting, monoclonal antibody AF-28 specifically detected G2 fragments derived from an aggrecan G1-G2 substrate digested with stromelysin, collagenase, gelatinase and matrilysin, but failed to detect G2 fragments obtained from elastase, trypsin or cathepsin B digests. Undigested G1-G2 was not detected. In addition, AF-28 antibody detected fragments derived from whole aggrecan and this detection did not require prior treatment with chondroitinase or keratanase. Competition experiments confirmed that peptides containing internal ... FFGVG ... sequences were not detected by the antibody, while native MMP-digested aggrecan fragments and a synthetic 32-mer peptide with FFGVG ... N-termini were equally competitive on a molar basis. An FFGVG 5-mer, and an FGVGGEEDI9-mer which lacked the N-terminal phenylalanine residue, were 50 times and 230 times respectively less competitive than the FFGVG ... 32-mer. Two fragments from the interglobular domain, F342-F373 and F342-D441, that are predicted products of G1-G2 digestion by neutrophil collagenase but have not previously been detected, could be detected with AF-28. The epitope recognized by AF-28 was also detected in human synovial fluids by Western blot analysis. A broad band of 100-200 kDa was detected in some patients and a dominant band of 40-60 kDa was found in two patients. The size of this small fragment corresponds with that seen for the porcine F342-E373 product and may represent the natural physiological product of aggrecan cleaved in vivo at both the MMP site (... DIPEN341 decreases F342FGVG ...) and the aggrecanase site (... ITEGE373 decreases A374RGSVI ...).
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry F. P., Gaw J. U., Young C. N., Neame P. J. Hyaluronan-binding region of aggrecan from pig laryngeal cartilage. Amino acid sequence, analysis of N-linked oligosaccharides and location of the keratan sulphate. Biochem J. 1992 Sep 15;286(Pt 3):761–769. doi: 10.1042/bj2860761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. K., Roughley P. J., Mort J. S. The action of human articular-cartilage metalloproteinase on proteoglycan and link protein. Similarities between products of degradation in situ and in vitro. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):117–122. doi: 10.1042/bj2370117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney S. L., Bayliss M. T., Collier J. M., Muir H. Electrophoresis of 35S-labeled proteoglycans on polyacrylamide-agarose composite gels and their visualization by fluorography. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jul;156(1):38–44. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty A. J., Murphy G. The tissue metalloproteinase family and the inhibitor TIMP: a study using cDNAs and recombinant proteins. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990 Jun;49 (Suppl 1):469–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doege K. J., Sasaki M., Kimura T., Yamada Y. Complete coding sequence and deduced primary structure of the human cartilage large aggregating proteoglycan, aggrecan. Human-specific repeats, and additional alternatively spliced forms. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):894–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flannery C. R., Lark M. W., Sandy J. D. Identification of a stromelysin cleavage site within the interglobular domain of human aggrecan. Evidence for proteolysis at this site in vivo in human articular cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1008–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosang A. J., Hardingham T. E. Isolation of the N-terminal globular protein domains from cartilage proteoglycans. Identification of G2 domain and its lack of interaction with hyaluronate and link protein. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 1;261(3):801–809. doi: 10.1042/bj2610801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosang A. J., Last K., Knäuper V., Neame P. J., Murphy G., Hardingham T. E., Tschesche H., Hamilton J. A. Fibroblast and neutrophil collagenases cleave at two sites in the cartilage aggrecan interglobular domain. Biochem J. 1993 Oct 1;295(Pt 1):273–276. doi: 10.1042/bj2950273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosang A. J., Last K., Neame P. J., Murphy G., Knäuper V., Tschesche H., Hughes C. E., Caterson B., Hardingham T. E. Neutrophil collagenase (MMP-8) cleaves at the aggrecanase site E373-A374 in the interglobular domain of cartilage aggrecan. Biochem J. 1994 Dec 1;304(Pt 2):347–351. doi: 10.1042/bj3040347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosang A. J., Neame P. J., Hardingham T. E., Murphy G., Hamilton J. A. Cleavage of cartilage proteoglycan between G1 and G2 domains by stromelysins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15579–15582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosang A. J., Neame P. J., Last K., Hardingham T. E., Murphy G., Hamilton J. A. The interglobular domain of cartilage aggrecan is cleaved by PUMP, gelatinases, and cathepsin B. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19470–19474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Fosang A. J. Proteoglycans: many forms and many functions. FASEB J. 1992 Feb 1;6(3):861–870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T., Bayliss M. Proteoglycans of articular cartilage: changes in aging and in joint disease. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Dec;20(3 Suppl 1):12–33. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(90)90044-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes C. E., Caterson B., Fosang A. J., Roughley P. J., Mort J. S. Monoclonal antibodies that specifically recognize neoepitope sequences generated by 'aggrecanase' and matrix metalloproteinase cleavage of aggrecan: application to catabolism in situ and in vitro. Biochem J. 1995 Feb 1;305(Pt 3):799–804. doi: 10.1042/bj3050799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes C. E., Caterson B., White R. J., Roughley P. J., Mort J. S. Monoclonal antibodies recognizing protease-generated neoepitopes from cartilage proteoglycan degradation. Application to studies of human link protein cleavage by stromelysin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16011–16014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilic M. Z., Handley C. J., Robinson H. C., Mok M. T. Mechanism of catabolism of aggrecan by articular cartilage. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Apr;294(1):115–122. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90144-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knäuper V., Krämer S., Reinke H., Tschesche H. Characterization and activation of procollagenase from human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. N-terminal sequence determination of the proenzyme and various proteolytically activated forms. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Apr 30;189(2):295–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koklitis P. A., Murphy G., Sutton C., Angal S. Purification of recombinant human prostromelysin. Studies on heat activation to give high-Mr and low-Mr active forms, and a comparison of recombinant with natural stromelysin activities. Biochem J. 1991 May 15;276(Pt 1):217–221. doi: 10.1042/bj2760217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lark M. W., Williams H., Hoernner L. A., Weidner J., Ayala J. M., Harper C. F., Christen A., Olszewski J., Konteatis Z., Webber R. Quantification of a matrix metalloproteinase-generated aggrecan G1 fragment using monospecific anti-peptide serum. Biochem J. 1995 Apr 1;307(Pt 1):245–252. doi: 10.1042/bj3070245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. C., Powell J. E., Tregear G. W., Niall H. D., Stevens V. C. A method for preparing beta-hCG COOH peptide-carrier conjugates of predictable composition. Mol Immunol. 1980 Jun;17(6):749–756. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90145-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee X., Ahmed F. R., Hirama T., Huber C. P., Rose D. R., To R., Hasnain S., Tam A., Mort J. S. Crystallization of recombinant rat cathepsin B. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):5950–5951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmander L. S., Neame P. J., Sandy J. D. The structure of aggrecan fragments in human synovial fluid. Evidence that aggrecanase mediates cartilage degradation in inflammatory joint disease, joint injury, and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Sep;36(9):1214–1222. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loulakis P., Shrikhande A., Davis G., Maniglia C. A. N-terminal sequence of proteoglycan fragments isolated from medium of interleukin-1-treated articular-cartilage cultures. Putative site(s) of enzymic cleavage. Biochem J. 1992 Jun 1;284(Pt 2):589–593. doi: 10.1042/bj2840589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehmet H., Scudder P., Tang P. W., Hounsell E. F., Caterson B., Feizi T. The antigenic determinants recognized by three monoclonal antibodies to keratan sulphate involve sulphated hepta- or larger oligosaccharides of the poly(N-acetyllactosamine) series. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jun 2;157(2):385–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09680.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mok M. T., Ilic M. Z., Handley C. J., Robinson H. C. Cleavage of proteoglycan aggregate by leucocyte elastase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Feb 1;292(2):442–447. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90014-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Allan J. A., Willenbrock F., Cockett M. I., O'Connell J. P., Docherty A. J. The role of the C-terminal domain in collagenase and stromelysin specificity. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9612–9618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Cockett M. I., Ward R. V., Docherty A. J. Matrix metalloproteinase degradation of elastin, type IV collagen and proteoglycan. A quantitative comparison of the activities of 95 kDa and 72 kDa gelatinases, stromelysins-1 and -2 and punctuated metalloproteinase (PUMP). Biochem J. 1991 Jul 1;277(Pt 1):277–279. doi: 10.1042/bj2770277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole A. R., Witter J., Roberts N., Roughley P. J., Webber C., Campbell I. Immunodetection and characterization of the degradation of cartilage proteoglycans in vitro and in vivo. J Rheumatol. 1987 May;14(Spec No):80–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandy J. D., Flannery C. R., Neame P. J., Lohmander L. S. The structure of aggrecan fragments in human synovial fluid. Evidence for the involvement in osteoarthritis of a novel proteinase which cleaves the Glu 373-Ala 374 bond of the interglobular domain. J Clin Invest. 1992 May;89(5):1512–1516. doi: 10.1172/JCI115742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandy J. D., Neame P. J., Boynton R. E., Flannery C. R. Catabolism of aggrecan in cartilage explants. Identification of a major cleavage site within the interglobular domain. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8683–8685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilim V., Fosang A. J. Proteoglycans isolated from dissociative extracts of differently aged human articular cartilage: characterization of naturally occurring hyaluronan-binding fragments of aggrecan. Biochem J. 1994 Dec 15;304(Pt 3):887–894. doi: 10.1042/bj3040887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. V., Hembry R. M., Reynolds J. J., Murphy G. The purification of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 from its 72 kDa progelatinase complex. Demonstration of the biochemical similarities of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1. Biochem J. 1991 Aug 15;278(Pt 1):179–187. doi: 10.1042/bj2780179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witter J., Roughley P. J., Webber C., Roberts N., Keystone E., Poole A. R. The immunologic detection and characterization of cartilage proteoglycan degradation products in synovial fluids of patients with arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 May;30(5):519–529. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]