Abstract
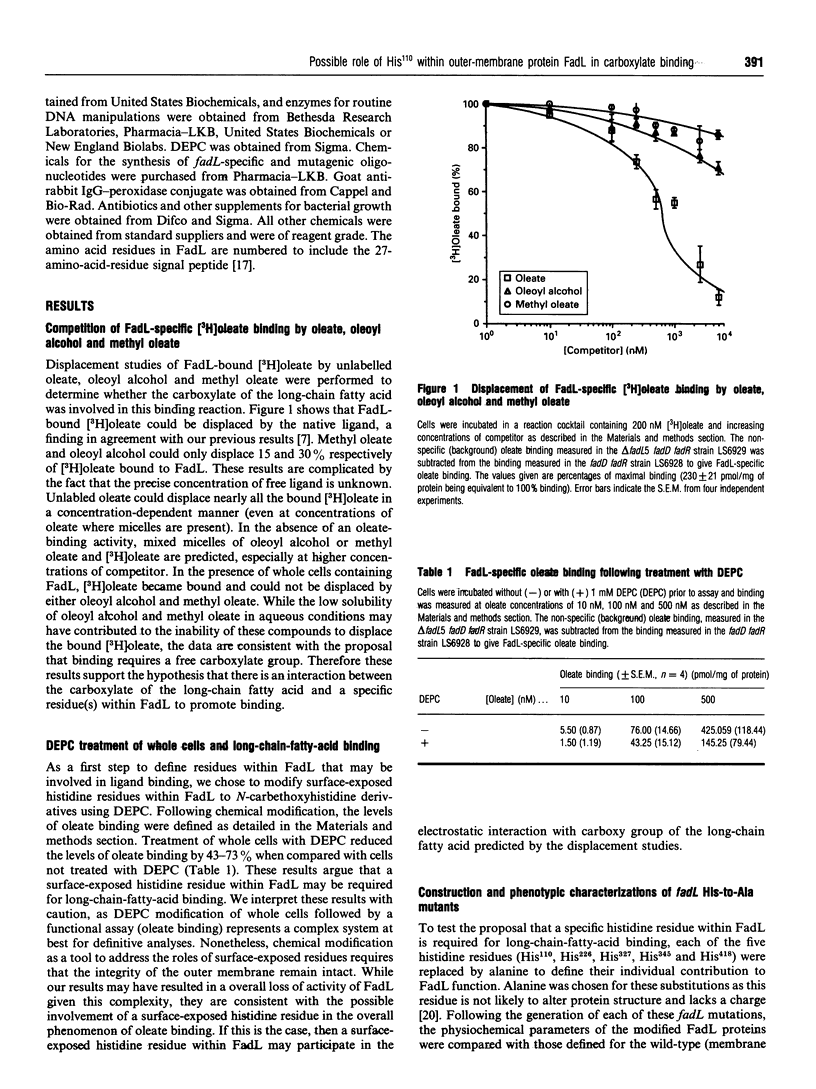
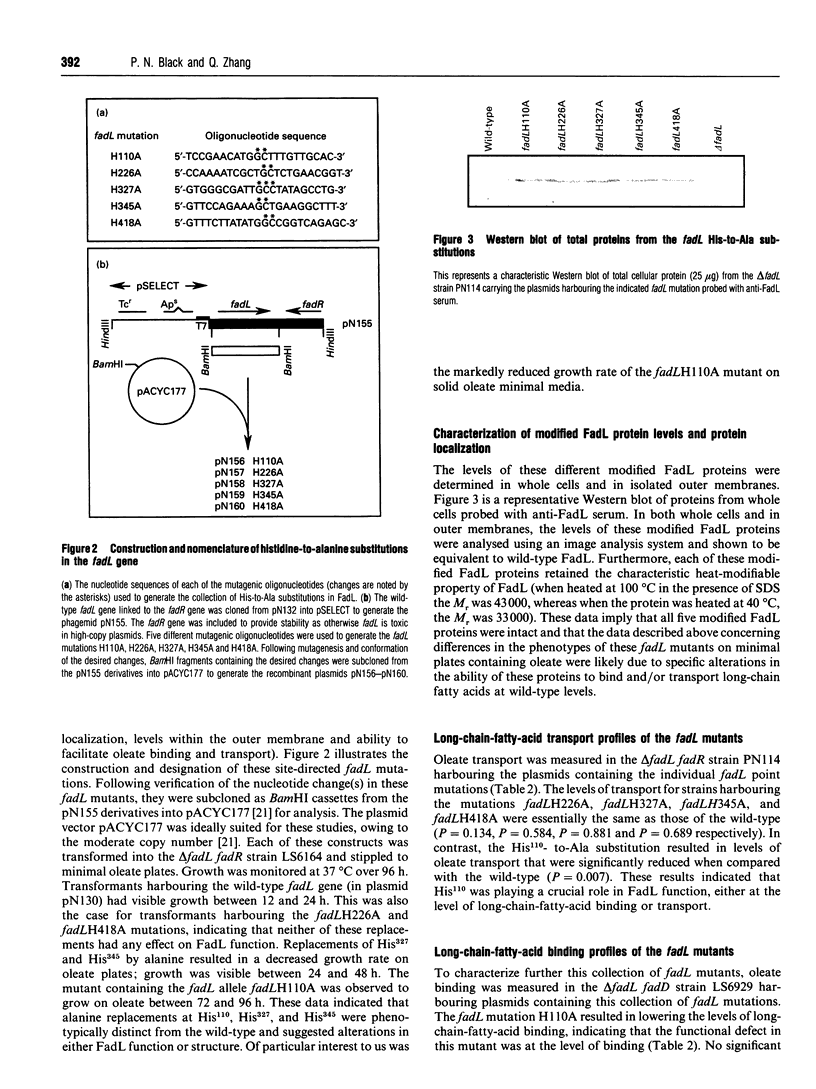
The binding of exogenous fatty acids to the outer-membrane protein FadL of Escherichia coli is specific for long-chain fatty acids (C14-C18). Oleoyl alcohol [(Z)-9-octadecen-1-ol] and methyl oleate were unable to displace FadL-specific binding of [3H]oleate (C18:1), suggesting that the carboxylate of the long-chain fatty acid was required for binding. Therefore the binding of exogenous fatty acids to FadL is governed, in part, by the carboxy group of the long-chain fatty acid. Treatment of whole cells with 1 mM diethyl pyrocarbonate (DEPC) depressed binding by 43-73% over the range of oleate concentrations used (10-500 nM). On the basis of these results and the notion that histidine residues often play a role involving proton transfer and charge-pairing, the five histidine residues within FadL (His110, His226, His327, His345 and His418) were replaced by alanine using site-directed mutagenesis. Altered FadL proteins were correctly localized in the outer membrane at wild-type levels and retained the heat-modifiable property characteristic of the wild-type protein. Initial screening of these fadL mutants revealed that the replacement of His110 by Ala resulted in a decreased growth rate on minimal oleate/agar plates. The rates of long-chain fatty acid transport for delta fadL strains harbouring each mutation on a plasmid, with the exception of fadLH110A, were the same, or nearly the same, as those for the wild-type. fadLH110A was also defective in binding, arguing that the functional effect of this mutation was at the level of long-chain-fatty-acid binding.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azizan A., Black P. N. Use of transposon TnphoA to identify genes for cell envelope proteins of Escherichia coli required for long-chain fatty acid transport: the periplasmic protein Tsp potentiates long-chain fatty acid transport. J Bacteriol. 1994 Nov;176(21):6653–6662. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.21.6653-6662.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black P. N. Characterization of FadL-specific fatty acid binding in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 28;1046(1):97–105. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(90)90099-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black P. N., DiRusso C. C. Molecular and biochemical analyses of fatty acid transport, metabolism, and gene regulation in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Jan 3;1210(2):123–145. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(94)90113-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black P. N. Primary sequence of the Escherichia coli fadL gene encoding an outer membrane protein required for long-chain fatty acid transport. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):435–442. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.435-442.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameda K. Partial purification and characterization of fatty acid binding protein(s) in Escherichia coli membranes and reconstitution of fatty acid transport system. Biochem Int. 1986 Aug;13(2):343–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameda K., Suzuki L. K., Imai Y. Transport of fatty acid is obligatory coupled with H+ entry in spheroplasts of Escherichia coli K12. Biochem Int. 1987 Feb;14(2):227–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar G. B., Black P. N. Bacterial long-chain fatty acid transport. Identification of amino acid residues within the outer membrane protein FadL required for activity. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15469–15476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar G. B., Black P. N. Linker mutagenesis of a bacterial fatty acid transport protein. Identification of domains with functional importance. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1348–1353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangroo D., Gerber G. E. Photoaffinity labeling of fatty acid-binding proteins involved in long chain fatty acid transport in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17095–17101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles E. W. Modification of histidyl residues in proteins by diethylpyrocarbonate. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:431–442. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn W. D., Colburn R. W., Black P. N. Transport of long-chain fatty acids in Escherichia coli. Evidence for role of fadL gene product as long-chain fatty acid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):167–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silber K. R., Keiler K. C., Sauer R. T. Tsp: a tail-specific protease that selectively degrades proteins with nonpolar C termini. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):295–299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Egan P. A., Chute H. T., Nunn W. D. Regulation of fatty acid degradation in Escherichia coli: isolation and characterization of strains bearing insertion and temperature-sensitive mutations in gene fadR. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):621–632. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.621-632.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




