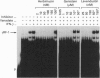
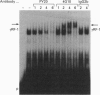
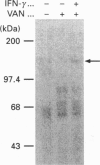
Abstract
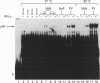
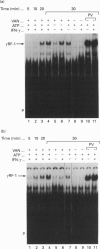
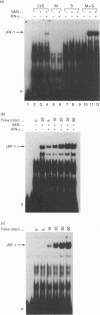
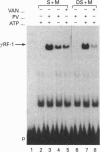
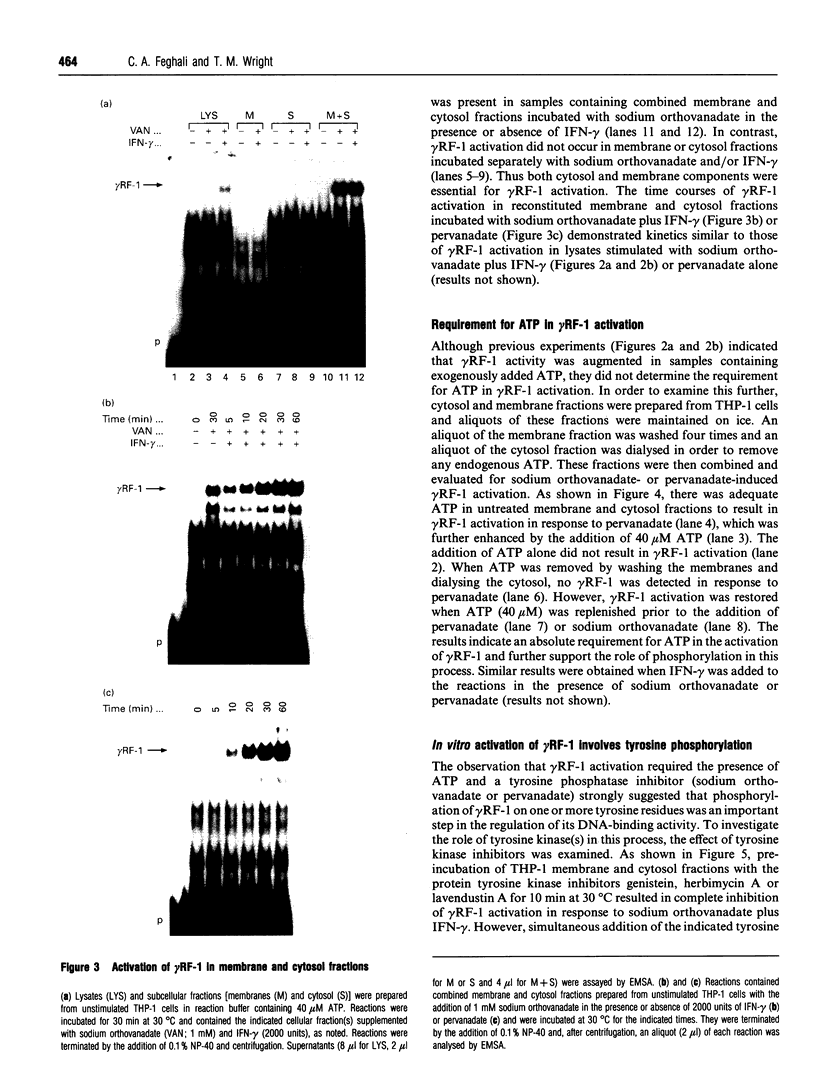
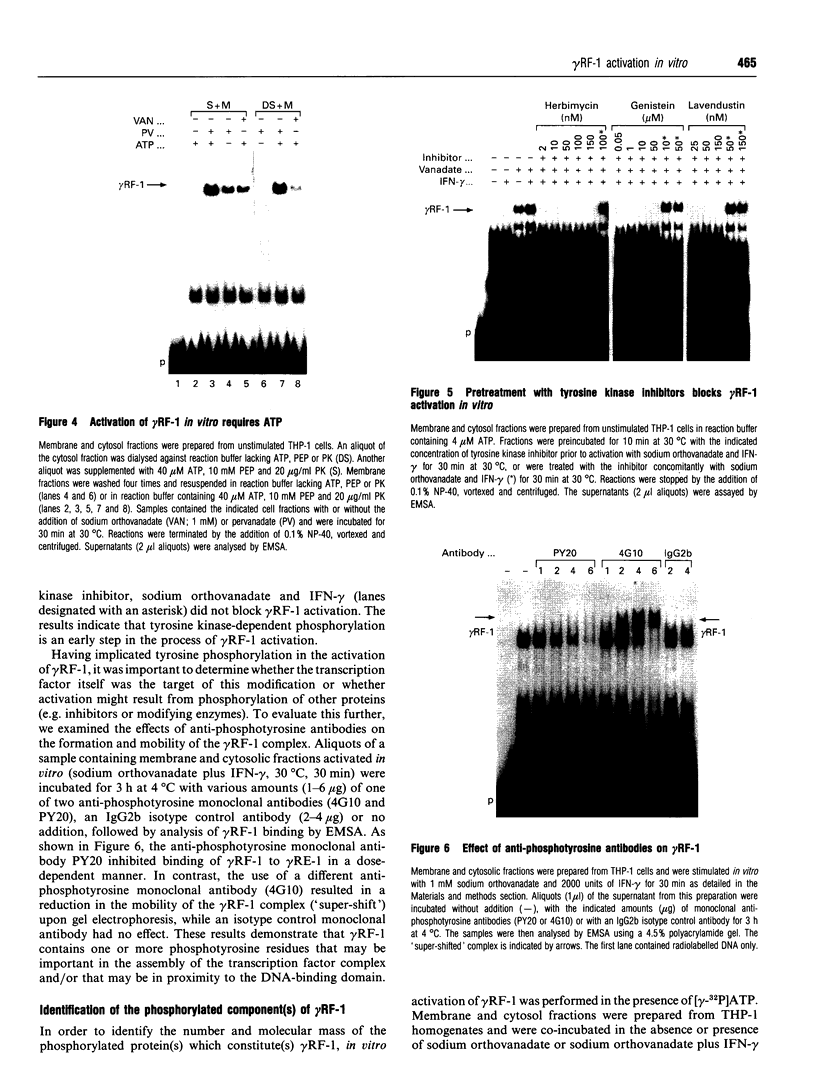
gamma RF-1 is a recently identified transcription factor induced by interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) which binds to a unique palindromic enhancer, gamma RE-1, in the promoter of the mig gene. This paper describes the ligand-dependent and ligand-independent activation of gamma RF-1 in a cell-free system. gamma RF-1 activity was induced by IFN-gamma in a time-dependent manner from 5 to 60 min in lysates prepared from the human monocytic leukaemia line THP-1 and the human epidermoid carcinoma line A431. The activation of gamma RF-1 in vitro required both ATP and an inhibitor of tyrosine phosphatases (sodium orthovanadate or pervanadate). In the presence of limiting concentrations (micromolar) of ATP, activation was also dependent upon stimulation with IFN-gamma, whereas at millimolar concentrations of ATP, gamma RF-1 was activated by either sodium orthovanadate or pervanadate in the absence of ligand. Based on cell fractionation studies, both membrane and cytosol components were essential for activation of gamma RF-1 in vitro. Consistent with a role for one or more tyrosine kinases in the activation of gamma RF-1, its DNA binding activity was blocked by monoclonal anti-phosphotyrosine antibodies and by the tyrosine kinase inhibitors genistein, lavendustin A and herbimycin A. A comparison with recently described pathways of IFN-mediated transcription factor regulation indicates that the in vitro activation of gamma RF-1 is unique, requiring both membrane and cytosol fractions and inhibition of endogenous tyrosine phosphatase activity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argetsinger L. S., Campbell G. S., Yang X., Witthuhn B. A., Silvennoinen O., Ihle J. N., Carter-Su C. Identification of JAK2 as a growth hormone receptor-associated tyrosine kinase. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90415-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr, Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1415–1421. doi: 10.1126/science.8197455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Larner A. C. Activation of transcription factors by interferon-alpha in a cell-free system. Science. 1992 Aug 7;257(5071):813–815. doi: 10.1126/science.1496402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Romero G., Zhang Z. Y., Dixon J. E., Larner A. C. In vitro activation of the transcription factor ISGF3 by interferon alpha involves a membrane-associated tyrosine phosphatase and tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6593–6599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lew D. J., Mirkovitch J., Darnell J. E., Jr Cytoplasmic activation of GAF, an IFN-gamma-regulated DNA-binding factor. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):927–932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driggers P. H., Ennist D. L., Gleason S. L., Mak W. H., Marks M. S., Levi B. Z., Flanagan J. R., Appella E., Ozato K. An interferon gamma-regulated protein that binds the interferon-inducible enhancer element of major histocompatibility complex class I genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3743–3747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. M. A macrophage mRNA selectively induced by gamma-interferon encodes a member of the platelet factor 4 family of cytokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5238–5242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar M. A., Schreiber R. D. The molecular cell biology of interferon-gamma and its receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:571–611. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.003035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman G. M., Petricoin E. F., 3rd, David M., Larner A. C., Finbloom D. S. Cytokines that associate with the signal transducer gp130 activate the interferon-induced transcription factor p91 by tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10747–10752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Kessler D. S., Veals S. A., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr ISGF3, the transcriptional activator induced by interferon alpha, consists of multiple interacting polypeptide chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8555–8559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halloran P. F. Interferon-gamma, prototype of the proinflammatory cytokines--importance in activation, suppression, and maintenance of the immune response. Transplant Proc. 1993 Apr;25(2 Suppl 1):10–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., David M., Finbloom D. S., Larner A. C. In vitro activation of the transcription factor gamma interferon activation factor by gamma interferon: evidence for a tyrosine phosphatase/kinase signaling cascade. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1634–1640. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., David M., Larner A. C., Finbloom D. S. In vitro activation of a transcription factor by gamma interferon requires a membrane-associated tyrosine kinase and is mimicked by vanadate. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3984–3989. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Yamamoto K., Thierfelder W. E., Kreider B., Silvennoinen O. Signaling by the cytokine receptor superfamily: JAKs and STATs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 May;19(5):222–227. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler D. S., Veals S. A., Fu X. Y., Levy D. E. Interferon-alpha regulates nuclear translocation and DNA-binding affinity of ISGF3, a multimeric transcriptional activator. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1753–1765. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. J., Decker T., Strehlow I., Darnell J. E. Overlapping elements in the guanylate-binding protein gene promoter mediate transcriptional induction by alpha and gamma interferons. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):182–191. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Briscoe J., Laxton C., Guschin D., Ziemiecki A., Silvennoinen O., Harpur A. G., Barbieri G., Witthuhn B. A., Schindler C. The protein tyrosine kinase JAK1 complements defects in interferon-alpha/beta and -gamma signal transduction. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):129–135. doi: 10.1038/366129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse R. N., Feinman R., Ravetch J. V. Characterization of the promoter of the human gene encoding the high-affinity IgG receptor: transcriptional induction by gamma-interferon is mediated through common DNA response elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11305–11309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini S., Schindler C. Early events in signalling by interferons. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Sep;18(9):338–342. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pumiglia K. M., Lau L. F., Huang C. K., Burroughs S., Feinstein M. B. Activation of signal transduction in platelets by the tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor pervanadate (vanadyl hydroperoxide). Biochem J. 1992 Sep 1;286(Pt 2):441–449. doi: 10.1042/bj2860441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Ziemiecki A., Wilks A. F., Harpur A. G., Sadowski H. B., Gilman M. Z., Darnell J. E. Polypeptide signalling to the nucleus through tyrosine phosphorylation of Jak and Stat proteins. Nature. 1993 Dec 9;366(6455):580–583. doi: 10.1038/366580a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvennoinen O., Ihle J. N., Schlessinger J., Levy D. E. Interferon-induced nuclear signalling by Jak protein tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1993 Dec 9;366(6455):583–585. doi: 10.1038/366583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvennoinen O., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Cleveland J. L., Yi T., Ihle J. N. Structure of the murine Jak2 protein-tyrosine kinase and its role in interleukin 3 signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8429–8433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims S. H., Cha Y., Romine M. F., Gao P. Q., Gottlieb K., Deisseroth A. B. A novel interferon-inducible domain: structural and functional analysis of the human interferon regulatory factor 1 gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):690–702. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Boulton T. G., Farruggella T., Ip N. Y., Davis S., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Silvennoinen O., Barbieri G., Pellegrini S. Association and activation of Jak-Tyk kinases by CNTF-LIF-OSM-IL-6 beta receptor components. Science. 1994 Jan 7;263(5143):92–95. doi: 10.1126/science.8272873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Yancopoulos G. D. The alphas, betas, and kinases of cytokine receptor complexes. Cell. 1993 Aug 27;74(4):587–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90506-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swarup G., Cohen S., Garbers D. L. Inhibition of membrane phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatase activity by vanadate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):1104–1109. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90635-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watling D., Guschin D., Müller M., Silvennoinen O., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Rogers N. C., Schindler C., Stark G. R., Ihle J. N. Complementation by the protein tyrosine kinase JAK2 of a mutant cell line defective in the interferon-gamma signal transduction pathway. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):166–170. doi: 10.1038/366166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. C., Finbloom D. S. Interferon gamma rapidly induces in human monocytes a DNA-binding factor that recognizes the gamma response region within the promoter of the gene for the high-affinity Fc gamma receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11964–11968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Silvennoinen O., Yi T., Tang B., Miura O., Ihle J. N. JAK2 associates with the erythropoietin receptor and is tyrosine phosphorylated and activated following stimulation with erythropoietin. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):227–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90414-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P., Severns C. W., Guyer N. B., Wright T. M. A unique palindromic element mediates gamma interferon induction of mig gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):914–922. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright T. M., Farber J. M. 5' regulatory region of a novel cytokine gene mediates selective activation by interferon gamma. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):417–422. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]