Abstract
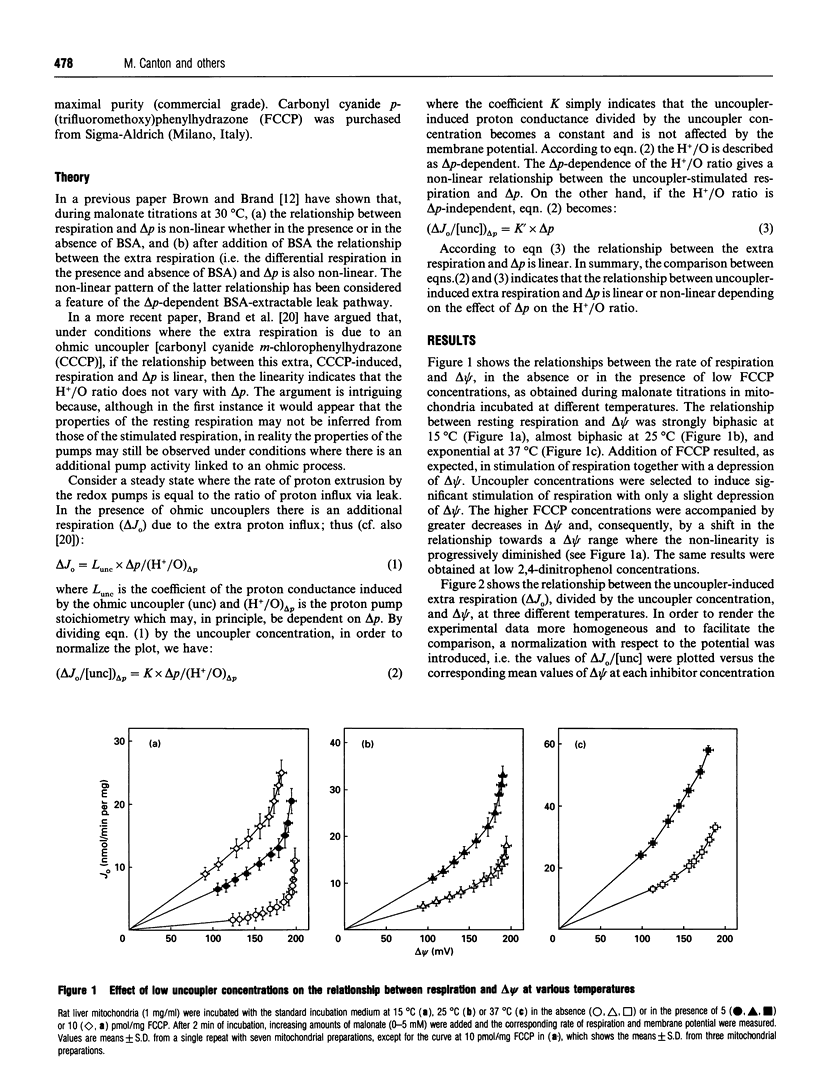
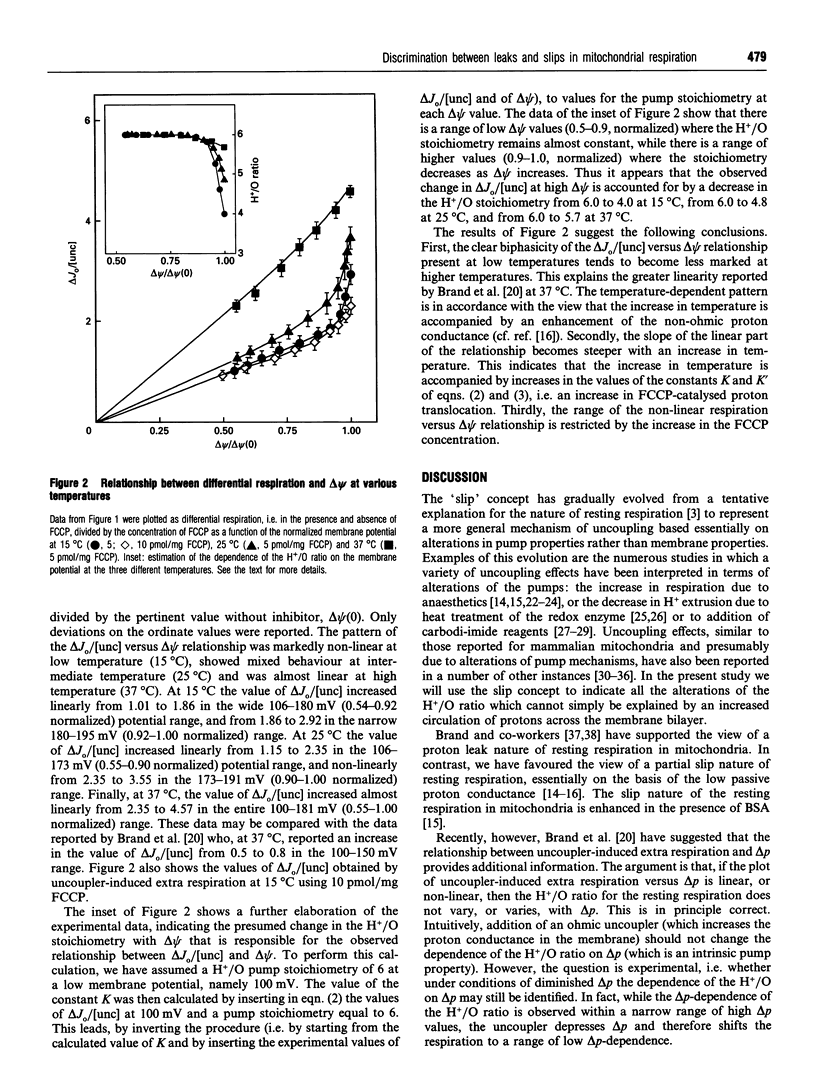
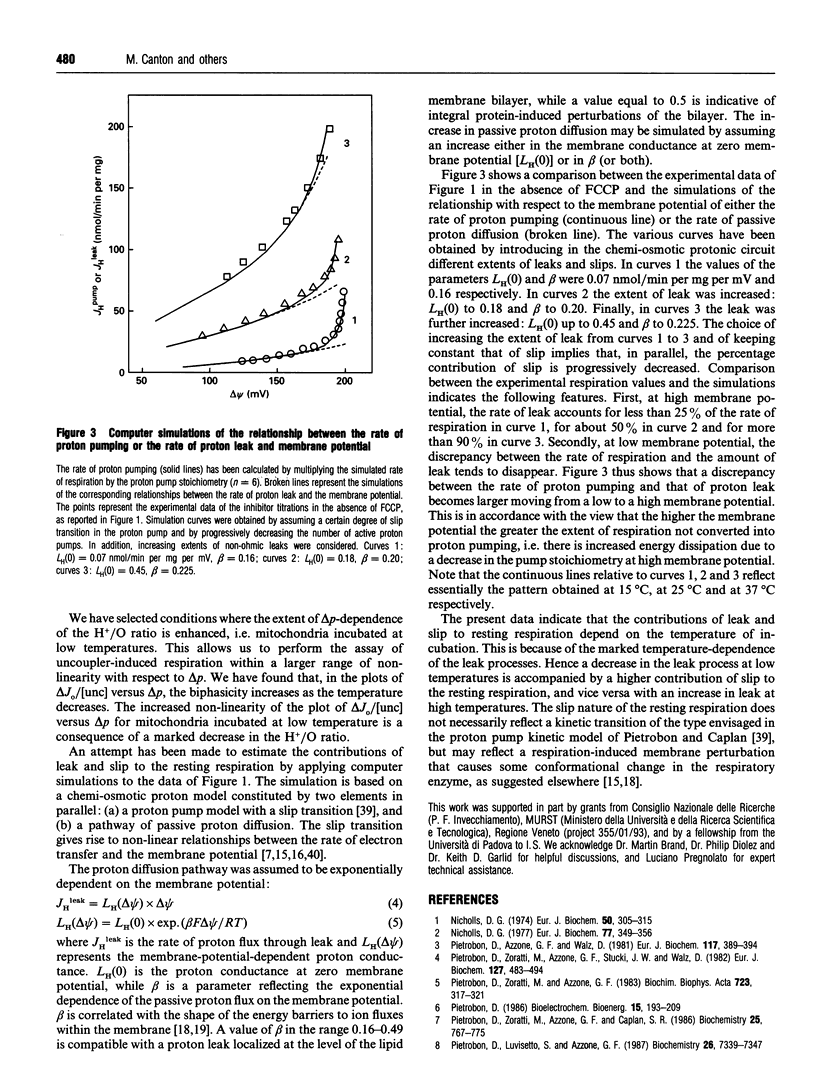
A new criterion is utilized for the interpretation of flow-force relationships in rat liver mitochondria. The criterion is based on the view that the nature of the relationship between the H+/O ratio and the membrane potential can be inferred from the relationship between ohmic-uncoupler-induced extra respiration and the membrane potential. Thus a linear relationship between extra respiration and membrane potential indicates unequivocally the independence of the H+/O ratio from the membrane potential and the leak nature of the resting respiration [Brand, Chien, and Diolez (1994) Biochem. J. 297, 27-29]. On the other hand, a non-linear relationship indicates that the H+/O ratio is dependent on the membrane potential. The experimental assessment of this relationship in the presence of an additional ohmic leak, however, is rendered difficult by both the uncoupler-induced depression of membrane potential and the limited range of dependence of the H+/O ratio on the membrane potential. We have selected conditions, i.e. incubation of mitochondria at low temperatures, where the extent of non-linearity is markedly increased. It appears that the nature of the resting respiration of mitochondria in vitro is markedly dependent on the temperature: at low temperatures the percentage of resting respiration due to membrane leak decreases and that due to intrinsic uncoupling of the proton pumps increases.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berman M. C. Energy coupling and uncoupling of active calcium transport by sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 11;694(1):95–121. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand M. D., Chien L. F., Diolez P. Experimental discrimination between proton leak and redox slip during mitochondrial electron transport. Biochem J. 1994 Jan 1;297(Pt 1):27–29. doi: 10.1042/bj2970027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand M. D., Steverding D., Kadenbach B., Stevenson P. M., Hafner R. P. The mechanism of the increase in mitochondrial proton permeability induced by thyroid hormones. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jun 15;206(3):775–781. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16984.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. C., Brand M. D. Changes in permeability to protons and other cations at high proton motive force in rat liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 15;234(1):75–81. doi: 10.1042/bj2340075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. C., Brand M. D. On the nature of the mitochondrial proton leak. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Aug 2;1059(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(05)80187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey R. P., Thelen M., Azzi A. Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide binds specifically and covalently to cytochrome c oxidase while inhibiting its H+-translocating activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3994–4000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlid K. D., Beavis A. D., Ratkje S. K. On the nature of ion leaks in energy-transducing membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Sep 28;976(2-3):109–120. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(89)80219-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafner R. P., Nobes C. D., McGown A. D., Brand M. D. Altered relationship between protonmotive force and respiration rate in non-phosphorylating liver mitochondria isolated from rats of different thyroid hormone status. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Dec 15;178(2):511–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14477.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inesi G., de Meis L. Regulation of steady state filling in sarcoplasmic reticulum. Roles of back-inhibition, leakage, and slippage of the calcium pump. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5929–5936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kell D. B., John P., Ferguson S. J. On the current-voltage relationships of energy-transducing membranes: phosphorylating membrane vesicles from Paracoccus denitrificans [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1978;6(6):1292–1295. doi: 10.1042/bst0061292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamoorthy G., Hinkle P. C. Non-ohmic proton conductance of mitochondria and liposomes. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 10;23(8):1640–1645. doi: 10.1021/bi00303a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li P. M., Morgan J. E., Nilsson T., Ma M., Chan S. I. Heat treatment of cytochrome c oxidase perturbs the CuA site and affects proton pumping behavior. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 20;27(19):7538–7546. doi: 10.1021/bi00419a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luvisetto S., Conti E., Buso M., Azzone G. F. Flux ratios and pump stoichiometries at sites II and III in liver mitochondria. Effect of slips and leaks. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1034–1042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luvisetto S., Pietrobon D., Azzone G. F. Uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation. 1. Protonophoric effects account only partially for uncoupling. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 17;26(23):7332–7338. doi: 10.1021/bi00397a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luvisetto S., Schmehl I., Intravaia E., Conti E., Azzone G. F. Mechanism of loss of thermodynamic control in mitochondria due to hyperthyroidism and temperature. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15348–15355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G. The effective proton conductance of the inner membrane of mitochondria from brown adipose tissue. Dependency on proton electrochemical potential gradient. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jul 15;77(2):349–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G. The influence of respiration and ATP hydrolysis on the proton-electrochemical gradient across the inner membrane of rat-liver mitochondria as determined by ion distribution. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Dec 16;50(1):305–315. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea P. S., Petrone G., Casey R. P., Azzi A. The current-voltage relationships of liposomes and mitochondria. Biochem J. 1984 May 1;219(3):719–726. doi: 10.1042/bj2190719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouhabi R., Rigoulet M., Lavie J. L., Guérin B. Respiration in non-phosphorylating yeast mitochondria. Roles of non-ohmic proton conductance and intrinsic uncoupling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Nov 7;1060(3):293–298. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(05)80319-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietrobon D., Azzone G. F., Walz D. Effect of funiculosin and antimycin A on the redox-driven H+-pumps in mitochondria: on the nature of "leaks'. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jul;117(2):389–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06350.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietrobon D., Caplan S. R. Flow-force relationships for a six-state proton pump model: intrinsic uncoupling, kinetic equivalence of input and output forces, and domain of approximate linearity. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 8;24(21):5764–5776. doi: 10.1021/bi00342a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietrobon D., Luvisetto S., Azzone G. F. Uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation. 2. Alternative mechanisms: intrinsic uncoupling or decoupling? Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 17;26(23):7339–7347. doi: 10.1021/bi00397a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietrobon D., Zoratti M., Azzone G. F., Caplan S. R. Intrinsic uncoupling of mitochondrial proton pumps. 2. Modeling studies. Biochemistry. 1986 Feb 25;25(4):767–775. doi: 10.1021/bi00352a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietrobon D., Zoratti M., Azzone G. F., Stucki J. W., Walz D. Non-equilibrium thermodynamic assessment of redox-driven H+ pumps in mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Oct;127(3):483–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06897.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochaska L. J., Bisson R., Capaldi R. A., Steffens G. C., Buse G. Inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase function by dicyclohexylcarbodiimide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 14;637(2):360–373. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(81)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H. Decoupling of oxidative phosphorylation and photophosphorylation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jul 17;1018(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(90)90103-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H., Hashimoto K. Fatty acid uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation in rat liver mitochondria. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 8;25(7):1747–1755. doi: 10.1021/bi00355a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sone N., Nicholls P. Effect of heat treatment on oxidase activity and proton-pumping capability of proteoliposome-incorporated beef heart cytochrome aa3. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6550–6554. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steverding D., Kadenbach B. Influence of N-ethoxycarbonyl-2-ethoxy-1,2-dihydroquinoline modification on proton translocation and membrane potential of reconstituted cytochrome-c oxidase support "proton slippage". J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8097–8101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steverding D., Köhnke D., Ludwig B., Kadenbach B. Proton slippage in cytochrome c oxidase of Paracoccus denitrificans. Membrane-potential measurements with the two-subunit and three-subunit enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Mar 15;212(3):827–831. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17724.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrigglesworth J. M., Cooper C. E., Sharpe M. A., Nicholls P. The proteoliposomal steady state. Effect of size, capacitance and membrane permeability on cytochrome-oxidase-induced ion gradients. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 15;270(1):109–118. doi: 10.1042/bj2700109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoratti M., Favaron M., Pietrobon D., Azzone G. F. Intrinsic uncoupling of mitochondrial proton pumps. 1. Non-ohmic conductance cannot account for the nonlinear dependence of static head respiration on delta microH. Biochemistry. 1986 Feb 25;25(4):760–767. doi: 10.1021/bi00352a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dam K., Shinohara Y., Unami A., Yoshida K., Terada H. Slipping pumps or proton leaks in oxidative phosphorylation. The local anesthetic bupivacaine causes slip in cytochrome c oxidase of mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1990 Dec 17;277(1-2):131–133. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80826-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


