Abstract
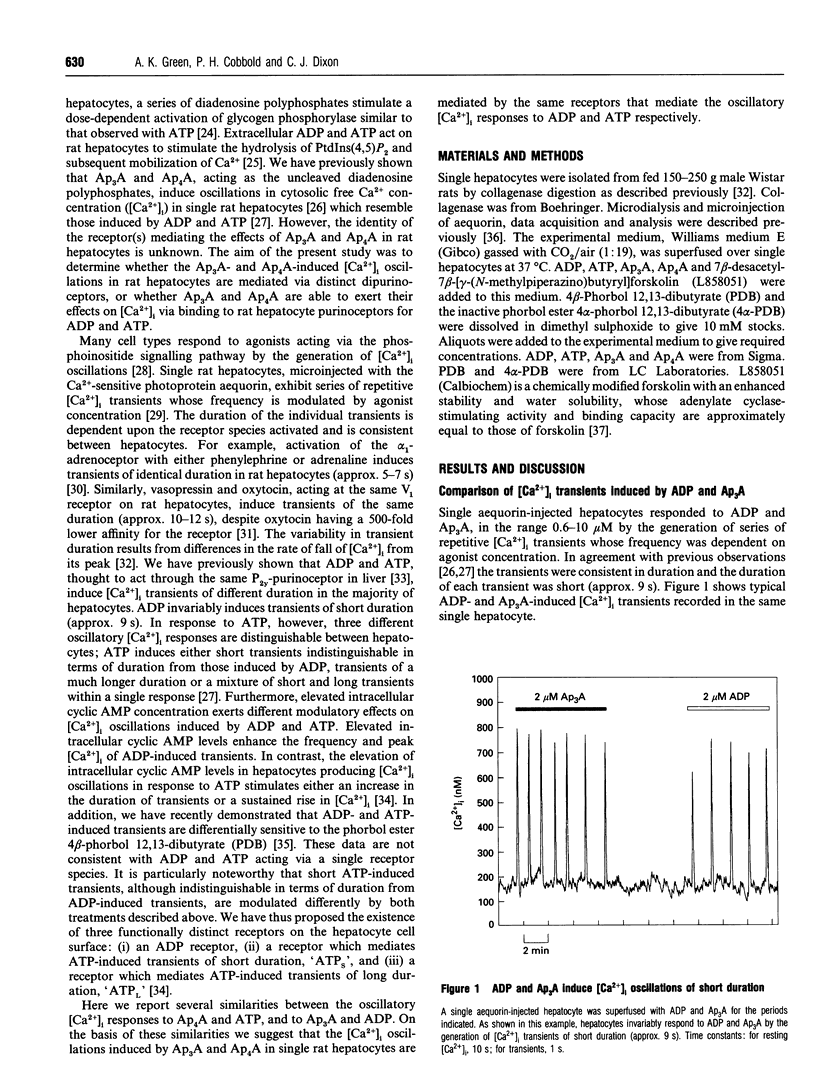
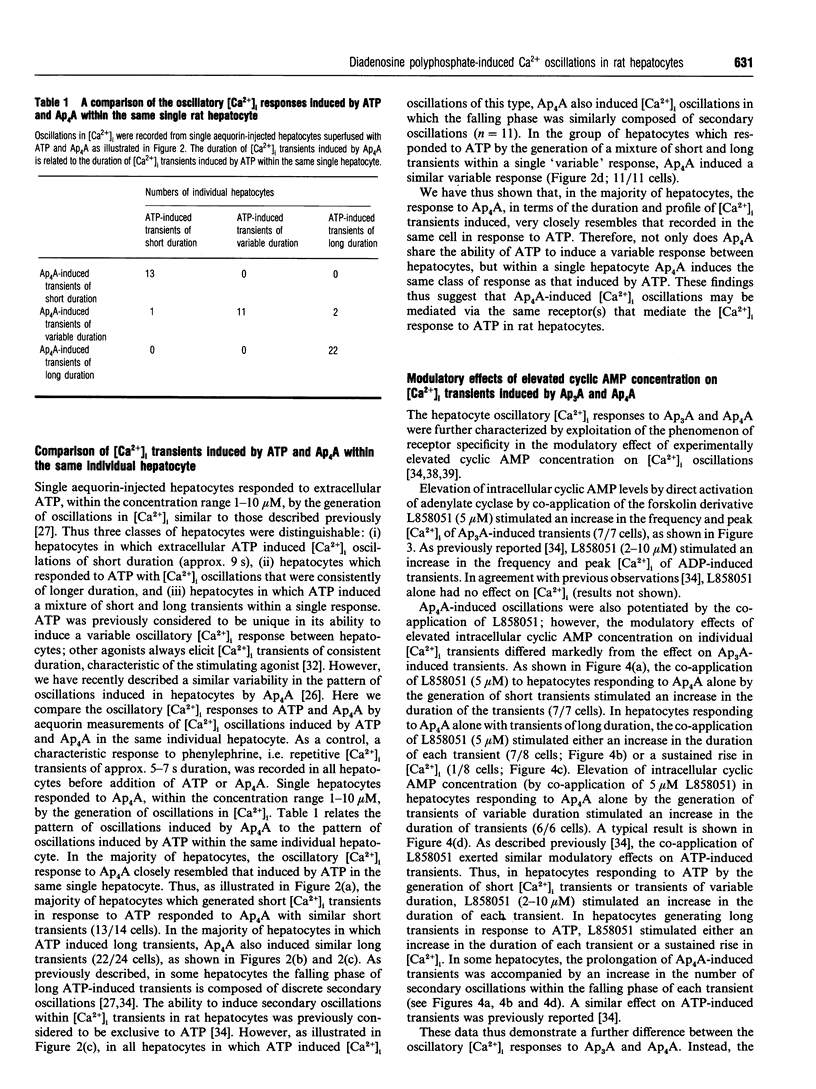
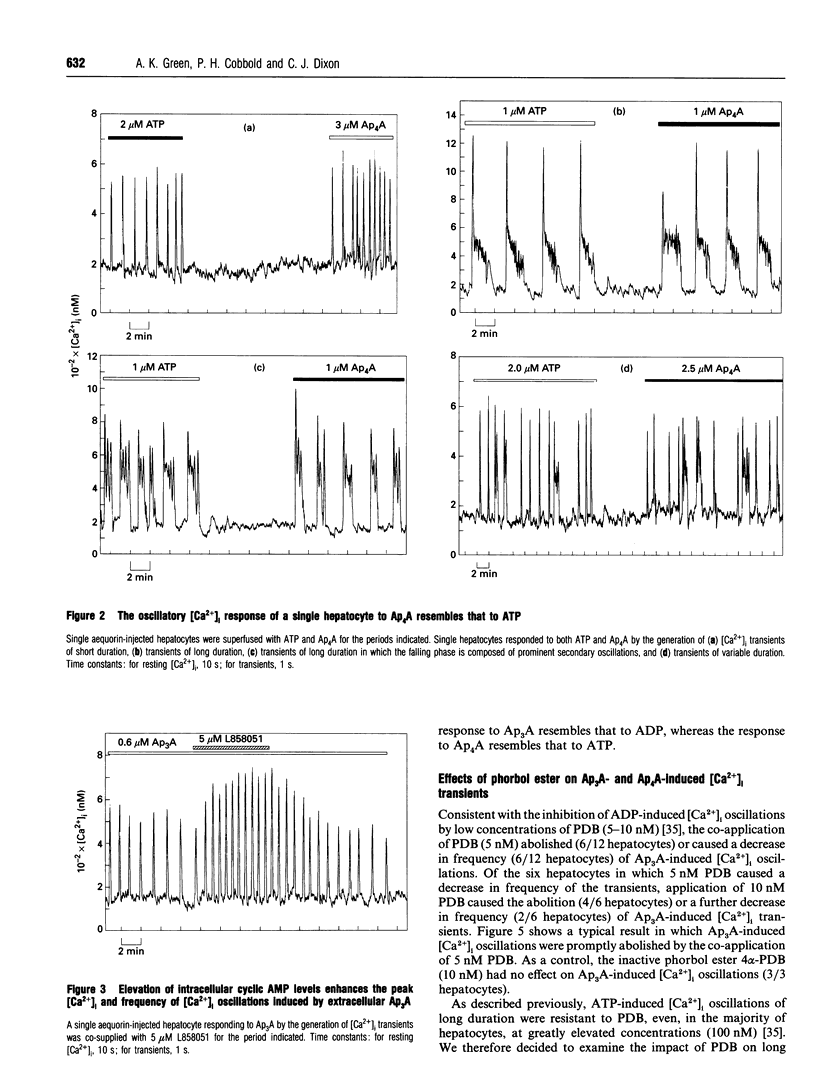
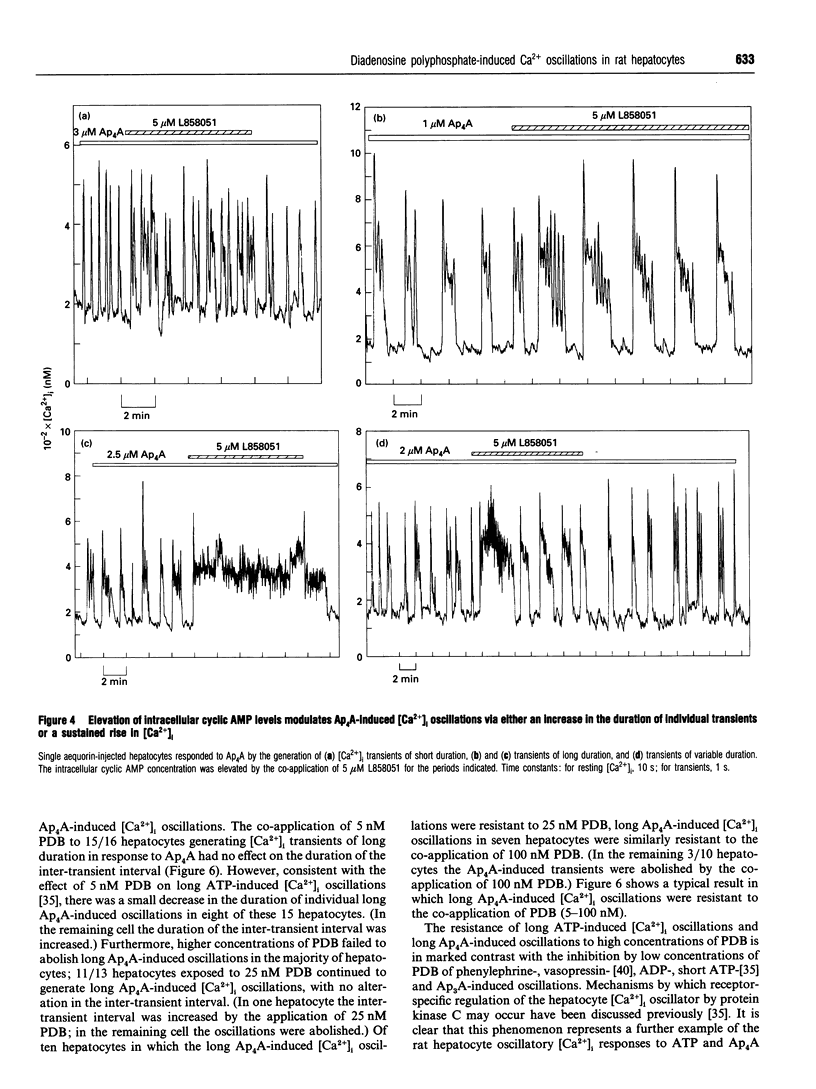
Diadenosine 5',5"'-P1,P3-triphosphate (Ap3A) and diadenosine 5',5"'-P1,P4-tetraphosphate (Ap4A) induce distinctive patterns of [Ca2+]i oscillations in single rat hepatocytes. We show here that [Ca2+]i oscillations induced by Ap3A and ADP are indistinguishable and that [Ca2+]i oscillations induced by Ap4A closely resemble those induced by ATP. These similarities embrace the following: (1) ADP and Ap3A invariably induce [Ca2+]i transients of short duration (approx. 9 s). Ap4A, like ATP, can induce, depending upon the individual cell, either transients of short duration (approx. 9 s), transients of much longer duration or a mixture of short and long transients within a single response. We show here that the pattern of oscillations induced by Ap4A is similar to that induced by ATP in the same hepatocyte. (2) Elevated intracellular cyclic AMP concentration modulates Ap3A-induced transients, like ADP-induced transients, through an increase in both the peak [Ca2+]i and the frequency of the transients. In contrast, Ap4A-induced transients, like ATP-induced transients, develop an increased duration or a sustained rise in [Ca2+]i, with no rise in peak [Ca2+]i. (3) Ap3A-induced transients, like ADP-induced transients, are abolished by low concentrations of the phorbol ester 4 beta-phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate (PDB; 5-10 nM), whereas long Ap4A-induced transients, like long ATP-induced transients, are refractory to high concentrations of PDB (100 nM). We propose that the [Ca2+]i oscillations induced in rat hepatocytes by Ap3A are mediated by the same purinoceptor that mediates the effects of ADP, whereas the oscillations induced by Ap4A are mediated by the same purinoceptor(s) that mediate the effects of ATP.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J. Calcium oscillations. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9583–9586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Kennedy C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen Pharmacol. 1985;16(5):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(85)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busse R., Ogilvie A., Pohl U. Vasomotor activity of diadenosine triphosphate and diadenosine tetraphosphate in isolated arteries. Am J Physiol. 1988 May;254(5 Pt 2):H828–H832. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.254.5.H828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busshardt E., Gerok W., Häussinger D. Regulation of hepatic parenchymal and non-parenchymal cell function by the diadenine nucleotides Ap3A and Ap4A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 9;1010(2):151–159. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90155-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro E., Pintor J., Miras-Portugal M. T. Ca(2+)-stores mobilization by diadenosine tetraphosphate, Ap4A, through a putative P2Y purinoceptor in adrenal chromaffin cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Aug;106(4):833–837. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14421.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro E., Torres M., Miras-Portugal M. T., Gonzalez M. P. Effect of diadenosine polyphosphates on catecholamine secretion from isolated chromaffin cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jun;100(2):360–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charest R., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Characterization of responses of isolated rat hepatocytes to ATP and ADP. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15789–15794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craik K. M., McLennan A. G., Fisher M. J. Adenine dinucleotide-mediated activation of glycogen phosphorylase in isolated liver cells. Cell Signal. 1993 Jan;5(1):89–96. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(93)90011-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon C. J., Cobbold P. H., Green A. K. Oscillations in cytosolic free Ca2+ induced by ADP and ATP in single rat hepatocytes display differential sensitivity to application of phorbol ester. Biochem J. 1995 Jul 1;309(Pt 1):145–149. doi: 10.1042/bj3090145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon C. J., Woods N. M., Cuthbertson K. S., Cobbold P. H. Evidence for two Ca2(+)-mobilizing purinoceptors on rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):499–502. doi: 10.1042/bj2690499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flodgaard H., Klenow H. Abundant amounts of diadenosine 5',5"'-P1,P4-tetraphosphate are present and releasable, but metabolically inactive, in human platelets. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 15;208(3):737–742. doi: 10.1042/bj2080737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. K., Cobbold P. H., Dixon C. J. Elevated intracellular cyclic AMP exerts different modulatory effects on cytosolic free Ca2+ oscillations induced by ADP and ATP in single rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1994 Sep 15;302(Pt 3):949–955. doi: 10.1042/bj3020949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. K., Dixon C. J., McLennan A. G., Cobbold P. H., Fisher M. J. Adenine dinucleotide-mediated cytosolic free Ca2+ oscillations in single hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1993 May 10;322(2):197–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81567-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison M. J., Brossmer R. Inhibition of platelet aggregation and the platelet release reaction by alpha, omega diadenosine polyphosphates. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jun 1;54(1):57–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilderman R. H., Martin M., Zimmerman J. K., Pivorun E. B. Identification of a unique membrane receptor for adenosine 5',5"'-P1,P4-tetraphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):6915–6918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle C. H., Chapple C., Burnstock G. Isolated human bladder: evidence for an adenine dinucleotide acting on P2X-purinoceptors and for purinergic transmission. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec 12;174(1):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90881-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppens S., De Wulf H. Characterization of the liver P2-purinoceptor involved in the activation of glycogen phosphorylase. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):367–371. doi: 10.1042/bj2400367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishtal O. A., Marchenko S. M., Obukhov A. G., Volkova T. M. Receptors for ATP in rat sensory neurones: the structure-function relationship for ligands. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;95(4):1057–1062. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11739.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurenza A., Khandelwal Y., De Souza N. J., Rupp R. H., Metzger H., Seamon K. B. Stimulation of adenylate cyclase by water-soluble analogues of forskolin. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Jul;32(1):133–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazewska D., Guranowski A. P alpha-chiral phosphorothioate analogues of bis(5'-adenosyl)tetraphosphate (Ap4A); their enzymatic synthesis and degradation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6083–6088. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüthje J., Baringer J., Ogilvie A. Effects of diadenosine triphosphate (Ap3A) and diadenosine tetraphosphate (Ap4A) on platelet aggregation in unfractionated human blood. Blut. 1985 Dec;51(6):405–413. doi: 10.1007/BF00320727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüthje J., Ogilvie A. Catabolism of Ap4A and Ap3A in whole blood. The dinucleotides are long-lived signal molecules in the blood ending up as intracellular ATP in the erythrocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Apr 5;173(1):241–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüthje J., Ogilvie A. Diadenosine triphosphate (Ap3A) mediates human platelet aggregation by liberation of ADP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 14;118(3):704–709. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91451-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüthje J., Ogilvie A. The presence of diadenosine 5',5'''-P1,P3-triphosphate (Ap3A) in human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 30;115(1):253–260. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90997-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintor J., Díaz-Rey M. A., Miras-Portugal M. T. Ap4A and ADP-beta-S binding to P2 purinoceptors present on rat brain synaptic terminals. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Apr;108(4):1094–1099. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13510.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintor J., Rotllán P., Torres M., Miras-Portugal M. T. Characterization and quantification of diadenosine hexaphosphate in chromaffin cells: granular storage and secretagogue-induced release. Anal Biochem. 1992 Feb 1;200(2):296–300. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90469-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintor J., Torres M., Castro E., Miras-Portugal M. T. Characterization of diadenosine tetraphosphate (Ap4A) binding sites in cultured chromaffin cells: evidence for a P2y site. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;103(4):1980–1984. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez del Castillo A., Torres M., Delicado E. G., Miras-Portugal M. T. Subcellular distribution studies of diadenosine polyphosphates--Ap4A and Ap5A--in bovine adrenal medulla: presence in chromaffin granules. J Neurochem. 1988 Dec;51(6):1696–1703. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01147.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Bueno A., Cobbold P. H. Agonist-specificity in the role of Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ release in hepatocyte Ca2+ oscillations. Biochem J. 1993 Apr 1;291(Pt 1):169–172. doi: 10.1042/bj2910169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Bueno A., Marrero I., Cobbold P. H. Different modulatory effects of elevated cyclic AMP on cytosolic Ca2+ spikes induced by phenylephrine or vasopressin in single rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1993 Apr 1;291(Pt 1):163–168. doi: 10.1042/bj2910163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlüter H., Offers E., Brüggemann G., van der Giet M., Tepel M., Nordhoff E., Karas M., Spieker C., Witzel H., Zidek W. Diadenosine phosphates and the physiological control of blood pressure. Nature. 1994 Jan 13;367(6459):186–188. doi: 10.1038/367186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöfl C., Sanchez-Bueno A., Brabant G., Cobbold P. H., Cuthbertson K. S. Frequency and amplitude enhancement of calcium transients by cyclic AMP in hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 1;273(Pt 3):799–802. doi: 10.1042/bj2730799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R. P., Delicado E. G., Castro E., Miras-Portugal M. T. Effect of P2Y agonists on adenosine transport in cultured chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1993 Feb;60(2):613–619. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W., Paton D. M. Possible subtypes of ATP receptor producing contraction of rat vas deferens, revealed by cross-desensitisation. Gen Pharmacol. 1989;20(1):61–64. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(89)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods N. M., Cuthbertson K. S., Cobbold P. H. Phorbol-ester-induced alterations of free calcium ion transients in single rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 15;246(3):619–623. doi: 10.1042/bj2460619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods N. M., Cuthbertson K. S., Cobbold P. H. Repetitive transient rises in cytoplasmic free calcium in hormone-stimulated hepatocytes. Nature. 1986 Feb 13;319(6054):600–602. doi: 10.1038/319600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


