Abstract
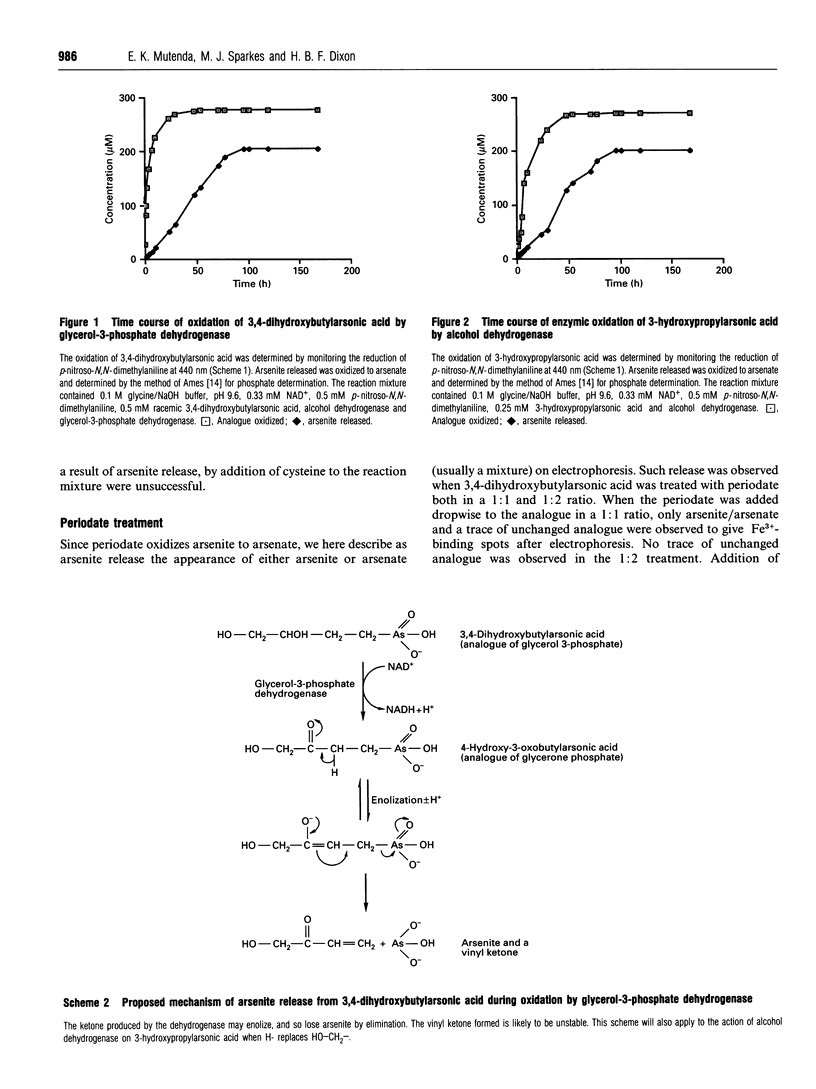
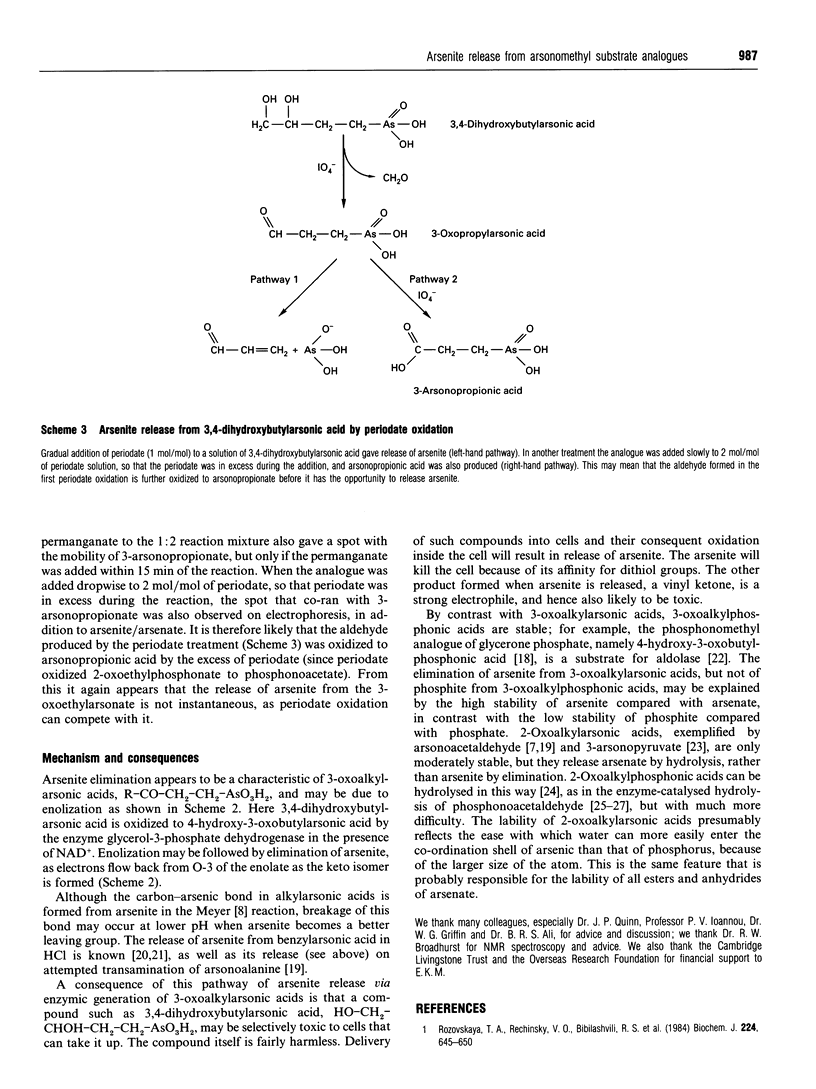
The isosteric arsenical analogue of glycerol 3-phosphate, 3,4-dihydroxybutylarsonic acid, is a good substrate for rabbit muscle glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Its oxidation is accompanied by release of arsenite. This release seems to be due to a spontaneous elimination of arsenite by 3-oxoalkylarsonic acids, as it is also observed in (1) the oxidation of 3-hydroxypropylarsonic acid by yeast alcohol dehydrogenase, (2) treatment of 3,4-dihydroxybutylarsonic acid with periodate and (3) nonenzymic transamination of the glutamate analogue 2-amino-4-arsonobutyric acid. Enzymic formation of 3-oxoalkylarsonic acids in cells can therefore be lethal, as arsenite is poisonous to most organisms because of its high affinity for dithiols such as dihydrolipoyl groups.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Harrison R. Dehydration of a phosphonate substrate analogue by glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):729–732. doi: 10.1042/bj1410729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams S. R., Sparkes M. J., Dixon H. B. The arsonomethyl analogue of 3-phosphoglycerate. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 1;213(1):211–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2130211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams S. R., Sparkes M. J., Dixon H. B. The arsonomethyl analogue of adenosine 5'-phosphate. An uncoupler of adenylate kinase. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 1;221(3):829–836. doi: 10.1042/bj2210829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali B. R., Dixon H. B. Synthesis of 3-arsonoalanine and its action on aspartate aminotransferase and aspartate ammonia-lyase. Comparison with arsenical analogues of malate and fumarate. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Jul 1;215(1):161–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18018.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chawla S., Mutenda E. K., Dixon H. B., Freeman S., Smith A. W. Synthesis of 3-arsonopyruvate and its interaction with phosphoenolpyruvate mutase. Biochem J. 1995 Jun 15;308(Pt 3):931–935. doi: 10.1042/bj3080931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng P. J., Hickey R., Engel R., Tropp B. E. Rabbit muscle L-glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Substrate activity of 3,4-dihydroxybutyl 1-phosphonate and 4-hydroxy-3-oxobutyl 1-phosphonate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 21;341(1):85–92. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon H. B., Sparkes M. J. Phosphonomethyl analogues of phosphate ester glycolytic intermediates. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):715–719. doi: 10.1042/bj1410715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn M. F., Bernhard S. A. Rapid kinetic evidence for adduct formation between the substrate analog p-nitroso-N,N-dimethylaniline and reduced nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide during enzymic reduction. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov 23;10(24):4569–4575. doi: 10.1021/bi00800a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Nauze J. M., Coggins J. R., Dixon H. B. Aldolase-like imine formation in the mechanism of action of phosphonoacetaldehyde hydrolase. Biochem J. 1977 Aug 1;165(2):409–411. doi: 10.1042/bj1650409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Nauze J. M., Rosenberg H., Shaw D. C. The enzymic cleavage of the carbon-phosphorus bond: purification and properties of phosphonatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 15;212(2):332–350. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90214-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacoste A. M., Dumora C., Ali B. R., Neuzil E., Dixon H. B. Utilization of 2-aminoethylarsonic acid in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Jun;138(6):1283–1287. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-6-1283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen D. B., Hepburn T. W., Lee S. L., Martin B. M., Mariano P. S., Dunaway-Mariano D. Investigation of the substrate binding and catalytic groups of the P-C bond cleaving enzyme, phosphonoacetaldehyde hydrolase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Jul;296(1):144–151. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90556-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozovskaya T. A., Rechinsky V. O., Bibilashvili R. S., Karpeisky MYa, Tarusova N. B., Khomutov R. M., Dixon H. B. The mechanism of pyrophosphorolysis of RNA by RNA polymerase. Endowment of RNA polymerase with artificial exonuclease activity. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 1;224(2):645–650. doi: 10.1042/bj2240645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparkes M. J., Rogers K. L., Dixon H. B. The synthesis of 3-phosphonoalanine, phosphonopyruvic acid and phosphonolactic acid. Scission of the C-P bond during diazotization of phosphonoalanine. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Dec 12;194(2):373–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15628.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stribling D. Properties of the phosphonomethyl isosteres of two phosphate ester glycolytic intermediates. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):725–728. doi: 10.1042/bj1410725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visedo-Gonzalez E., Dixon H. B. 2-Aminoethylarsonic acid as an analogue of ethanolamine phosphate. Endowment of ethanolamine-phosphate cytidylyltransferase with CTP pyrophosphatase activity. Biochem J. 1989 May 15;260(1):299–301. doi: 10.1042/bj2600299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WADE H. E., MORGAN D. M. Detection of phosphate esters on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1953 Mar 21;171(4351):529–530. doi: 10.1038/171529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



