Abstract
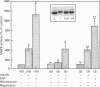
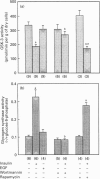
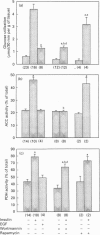
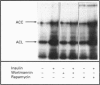
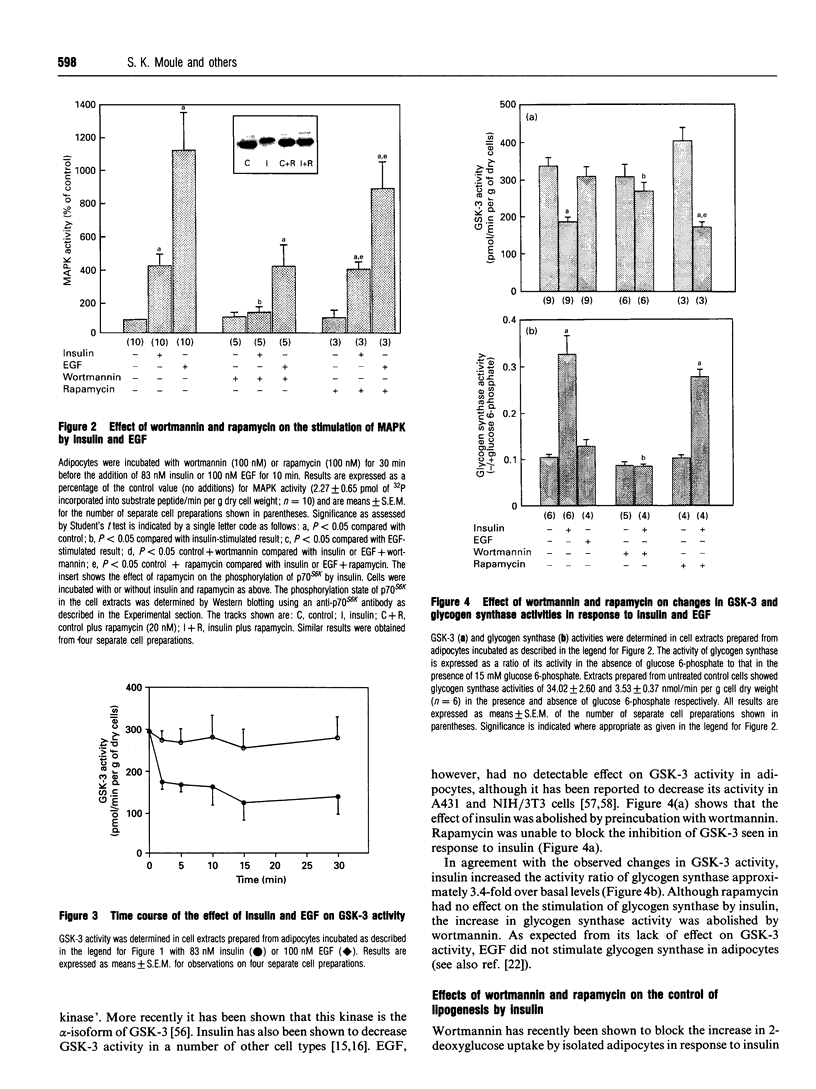
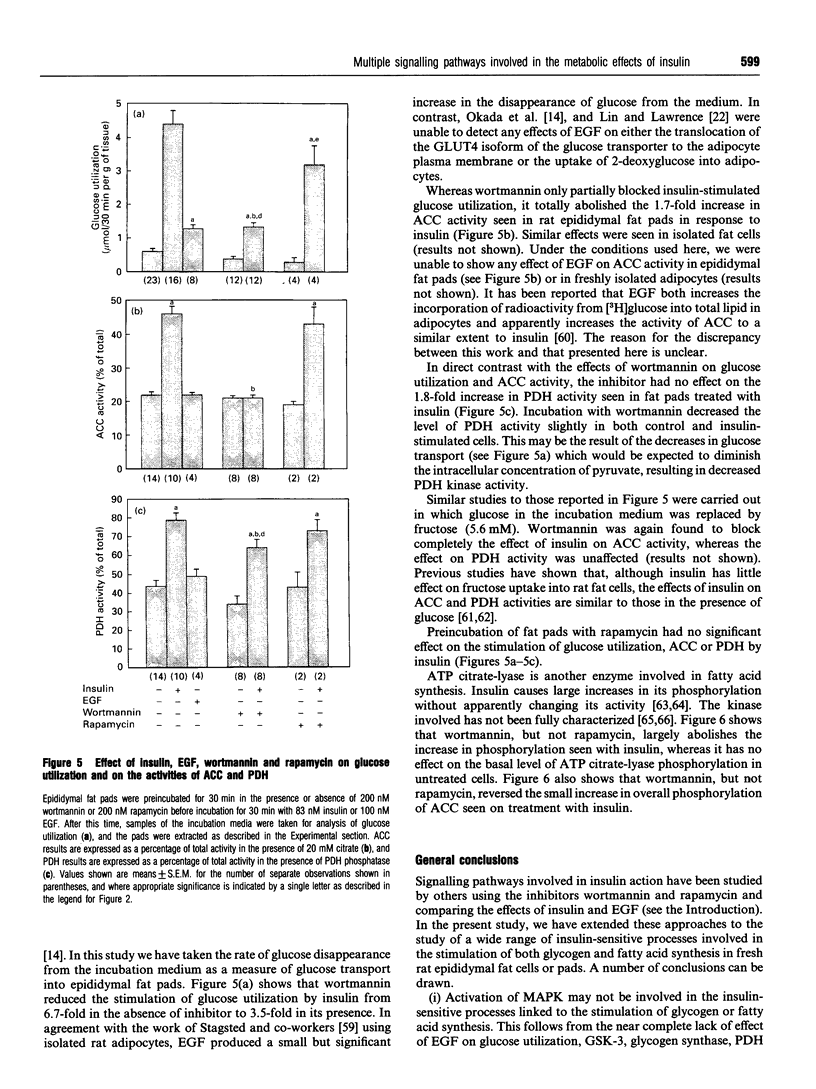
We have investigated the signalling pathways involved in the stimulation of glycogen and fatty acid synthesis by insulin in rat fat cells using wortmannin, an inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and rapamycin, which blocks activation of p70 ribosomal S6 protein kinase (p70S6K). Insulin produced a decrease in the activity of glycogen synthase kinase-3 which is likely to be important in the observed stimulation of glycogen synthase. Both of these actions were found to be sensitive to inhibition by wortmannin. Activation of three processes is involved in the stimulation of fatty acid synthesis from glucose by insulin, namely glucose uptake, acetyl-CoA carboxylase and pyruvate dehydrogenase. Whereas wortmannin largely abolished the effects of insulin on glucose utilization and acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity, it was without effect on the stimulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase. Although epidermal growth factor stimulated mitogen-activated protein kinase to a greater extent than insulin, it was unable to mimic the effect of insulin on glycogen synthase, glycogen synthase kinase-3, glucose utilization, acetyl-CoA carboxylase or pyruvate dehydrogenase. Rapamycin also failed to have any appreciable effect on stimulation of these parameters by insulin, although it did block the effect of insulin on p70S6K. We conclude that the activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is required for the effects of insulin on glycogen synthesis, glucose uptake and acetyl-Co-AN carboxylase, but is not involved in signalling to pyruvate dehydrogenase. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase or p70S6K, however, does not appear to be sufficient to bring about the stimulation of fatty acid or glycogen synthesis. Altogether is seems likely that at least four distinct signalling pathways are involved in the effects of insulin on rat fat cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Backer J. M., Myers M. G., Jr, Shoelson S. E., Chin D. J., Sun X. J., Miralpeix M., Hu P., Margolis B., Skolnik E. Y., Schlessinger J. Phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase is activated by association with IRS-1 during insulin stimulation. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3469–3479. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borthwick A. C., Edgell N. J., Denton R. M. Protein-serine kinase from rat epididymal adipose tissue which phosphorylates and activates acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Possible role in insulin action. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 15;270(3):795–801. doi: 10.1042/bj2700795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheatham B., Vlahos C. J., Cheatham L., Wang L., Blenis J., Kahn C. R. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation is required for insulin stimulation of pp70 S6 kinase, DNA synthesis, and glucose transporter translocation. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4902–4911. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Grammer T. C., Lemon K. P., Kazlauskas A., Blenis J. PDGF- and insulin-dependent pp70S6k activation mediated by phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase. Nature. 1994 Jul 7;370(6484):71–75. doi: 10.1038/370071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Kuo C. J., Crabtree G. R., Blenis J. Rapamycin-FKBP specifically blocks growth-dependent activation of and signaling by the 70 kd S6 protein kinases. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1227–1236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90643-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. Dissection of the protein phosphorylation cascades involved in insulin and growth factor action. Biochem Soc Trans. 1993 Aug;21(3):555–567. doi: 10.1042/bst0210555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coore H. G., Denton R. M., Martin B. R., Randle P. J. Regulation of adipose tissue pyruvate dehydrogenase by insulin and other hormones. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(1):115–127. doi: 10.1042/bj1250115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross D. A., Alessi D. R., Vandenheede J. R., McDowell H. E., Hundal H. S., Cohen P. The inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin or insulin-like growth factor 1 in the rat skeletal muscle cell line L6 is blocked by wortmannin, but not by rapamycin: evidence that wortmannin blocks activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in L6 cells between Ras and Raf. Biochem J. 1994 Oct 1;303(Pt 1):21–26. doi: 10.1042/bj3030021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent P., Lavoinne A., Nakielny S., Caudwell F. B., Watt P., Cohen P. The molecular mechanism by which insulin stimulates glycogen synthesis in mammalian skeletal muscle. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):302–308. doi: 10.1038/348302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Halperin M. L. The control of fatty acid and triglyceride synthesis in rat epididymal adipose tissue. Roles of coenzyme A derivatives, citrate and L-glycerol 3-phosphate. Biochem J. 1968 Nov;110(1):27–38. doi: 10.1042/bj1100027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Midgley P. J., Rutter G. A., Thomas A. P., McCormack J. G. Studies into the mechanism whereby insulin activates pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in adipose tissue. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;573:285–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb15005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Tavaré J. M. Does mitogen-activated-protein kinase have a role in insulin action? The cases for and against. Eur J Biochem. 1995 Feb 1;227(3):597–611. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.tb20179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhand R., Hiles I., Panayotou G., Roche S., Fry M. J., Gout I., Totty N. F., Truong O., Vicendo P., Yonezawa K. PI 3-kinase is a dual specificity enzyme: autoregulation by an intrinsic protein-serine kinase activity. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 1;13(3):522–533. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06290.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diggle T. A., Bloomberg G. B., Denton R. M. Further characterization of the acid-soluble phosphoprotein (SDS/PAGE apparent molecular mass of 22 kDa) in rat fat-cells by peptide sequencing and immuno-analysis: effects of insulin and isoprenaline. Biochem J. 1995 Feb 15;306(Pt 1):135–139. doi: 10.1042/bj3060135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diggle T. A., Schmitz-Peiffer C., Borthwick A. C., Welsh G. I., Denton R. M. Evidence that insulin activates casein kinase 2 in rat epididymal fat-cells and that this may result in the increased phosphorylation of an acid-soluble 22 kDa protein. Biochem J. 1991 Oct 15;279(Pt 2):545–551. doi: 10.1042/bj2790545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldar-Finkelman H., Seger R., Vandenheede J. R., Krebs E. G. Inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by epidermal growth factor is mediated by mitogen-activated protein kinase/p90 ribosomal protein S6 kinase signaling pathway in NIH/3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 20;270(3):987–990. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.3.987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fingar D. C., Birnbaum M. J. Characterization of the mitogen-activated protein kinase/90-kilodalton ribosomal protein S6 kinase signaling pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and its role in insulin-stimulated glucose transport. Endocrinology. 1994 Feb;134(2):728–735. doi: 10.1210/endo.134.2.8299568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fingar D. C., Hausdorff S. F., Blenis J., Birnbaum M. J. Dissociation of pp70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase from insulin-stimulated glucose transport in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):3005–3008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund G. G., Wittig J. G., Mooney R. A. The PI3-kinase serine kinase phosphorylates its p85 subunit and IRS-1 in PI3-kinase/IRS-1 complexes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Jan 5;206(1):272–278. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., Holman G. D. The glucose transporter family: structure, function and tissue-specific expression. Biochem J. 1993 Oct 15;295(Pt 2):329–341. doi: 10.1042/bj2950329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove J. R., Banerjee P., Balasubramanyam A., Coffer P. J., Price D. J., Avruch J., Woodgett J. R. Cloning and expression of two human p70 S6 kinase polypeptides differing only at their amino termini. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5541–5550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halestrap A. P., Denton R. M. Hormonal regulation of adipose-tissue acetyl-Coenzyme A carboxylase by changes in the polymeric state of the enzyme. The role of long-chain fatty acyl-Coenzyme A thioesters and citrate. Biochem J. 1974 Aug;142(2):365–377. doi: 10.1042/bj1420365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haystead T. A., Hardie D. G. Both insulin and epidermal growth factor stimulate lipogenesis and acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity in isolated adipocytes. Importance of homogenization procedure in avoiding artefacts in acetyl-CoA carboxylase assay. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 1;234(2):279–284. doi: 10.1042/bj2340279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard M. J., Cohen P. On target with a new mechanism for the regulation of protein phosphorylation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 May;18(5):172–177. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90109-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard M. J., Cohen P. Regulation of protein phosphatase-1G from rabbit skeletal muscle. 2. Catalytic subunit translocation is a mechanism for reversible inhibition of activity toward glycogen-bound substrates. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 22;186(3):711–716. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15264.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes K., Ramakrishna S., Benjamin W. B., Woodgett J. R. Identification of multifunctional ATP-citrate lyase kinase as the alpha-isoform of glycogen synthase kinase-3. Biochem J. 1992 Nov 15;288(Pt 1):309–314. doi: 10.1042/bj2880309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. A., Denton R. M. Incorporation of 32Pi into pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate in mitochondria from control and insulin-treated adipose tissue. Nature. 1976 Dec 2;264(5585):471–473. doi: 10.1038/264471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam K., Carpenter C. L., Ruderman N. B., Friel J. C., Kelly K. L. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase serine kinase phosphorylates IRS-1. Stimulation by insulin and inhibition by Wortmannin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 12;269(32):20648–20652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavoinne A., Erikson E., Maller J. L., Price D. J., Avruch J., Cohen P. Purification and characterisation of the insulin-stimulated protein kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle; close similarity to S6 kinase II. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Aug 1;199(3):723–728. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. C., Jr Signal transduction and protein phosphorylation in the regulation of cellular metabolism by insulin. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:177–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.001141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. A., Lawrence J. C., Jr Activation of ribosomal protein S6 kinases does not increase glycogen synthesis or glucose transport in rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 19;269(33):21255–21261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. R., Denton R. M. The intracellular localization of enzymes in white-adipose-tissue fat-cells and permeability properties of fat-cell mitochondria. Transfer of acetyl units and reducing power between mitochondria and cytoplasm. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(5):861–877. doi: 10.1042/bj1170861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley P. J., Rutter G. A., Thomas A. P., Denton R. M. Effects of Ca2+ and Mg2+ on the activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate phosphatase within toluene-permeabilized mitochondria. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 15;241(2):371–377. doi: 10.1042/bj2410371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. G., Jr, Backer J. M., Sun X. J., Shoelson S., Hu P., Schlessinger J., Yoakim M., Schaffhausen B., White M. F. IRS-1 activates phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase by associating with src homology 2 domains of p85. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10350–10354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. G., Jr, Sun X. J., White M. F. The IRS-1 signaling system. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Jul;19(7):289–293. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S., Kakita S., Takahashi I., Kawahara K., Tsukuda E., Sano T., Yamada K., Yoshida M., Kase H., Matsuda Y. Wortmannin, a microbial product inhibitor of myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2157–2163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northwood I. C., Gonzalez F. A., Wartmann M., Raden D. L., Davis R. J. Isolation and characterization of two growth factor-stimulated protein kinases that phosphorylate the epidermal growth factor receptor at threonine 669. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15266–15276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada T., Kawano Y., Sakakibara T., Hazeki O., Ui M. Essential role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in insulin-induced glucose transport and antilipolysis in rat adipocytes. Studies with a selective inhibitor wortmannin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3568–3573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Caudwell F. B., Cohen P. Glycogen synthase from rabbit skeletal muscle; effect of insulin on the state of phosphorylation of the seven phosphoserine residues in vivo. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jan 17;130(1):227–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce M. W., Palmer J. L., Keutmann H. T., Avruch J. ATP-citrate lyase. Structure of a tryptic peptide containing the phosphorylation site directed by glucagon and the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8867–8870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce M. W., Palmer J. L., Keutmann H. T., Hall T. A., Avruch J. The insulin-directed phosphorylation site on ATP-citrate lyase is identical with the site phosphorylated by the cAMP-dependent protein kinase in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10681–10686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. J., Grove J. R., Calvo V., Avruch J., Bierer B. E. Rapamycin-induced inhibition of the 70-kilodalton S6 protein kinase. Science. 1992 Aug 14;257(5072):973–977. doi: 10.1126/science.1380182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahn T., Ridderstråle M., Tornqvist H., Manganiello V., Fredrikson G., Belfrage P., Degerman E. Essential role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in insulin-induced activation and phosphorylation of the cGMP-inhibited cAMP phosphodiesterase in rat adipocytes. Studies using the selective inhibitor wortmannin. FEBS Lett. 1994 Aug 22;350(2-3):314–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00797-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson L. J., Razzack Z. F., Lawrence J. C., Jr, James D. E. Mitogen-activated protein kinase activation is not sufficient for stimulation of glucose transport or glycogen synthase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26422–26427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter G. A., Borthwick A. C., Denton R. M. Effects of protein phosphatase inhibitors on the regulation of insulin-sensitive enzymes within rat epididymal fat-pads and cells. Biochem J. 1991 Jun 15;276(Pt 3):649–654. doi: 10.1042/bj2760649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rylatt D. B., Aitken A., Bilham T., Condon G. D., Embi N., Cohen P. Glycogen synthase from rabbit skeletal muscle. Amino acid sequence at the sites phosphorylated by glycogen synthase kinase-3, and extension of the N-terminal sequence containing the site phosphorylated by phosphorylase kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):529–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito Y., Vandenheede J. R., Cohen P. The mechanism by which epidermal growth factor inhibits glycogen synthase kinase 3 in A431 cells. Biochem J. 1994 Oct 1;303(Pt 1):27–31. doi: 10.1042/bj3030027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sevetson B. R., Kong X., Lawrence J. C., Jr Increasing cAMP attenuates activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10305–10309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd P. R., Navé B. T., Siddle K. Insulin stimulation of glycogen synthesis and glycogen synthase activity is blocked by wortmannin and rapamycin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: evidence for the involvement of phosphoinositide 3-kinase and p70 ribosomal protein-S6 kinase. Biochem J. 1995 Jan 1;305(Pt 1):25–28. doi: 10.1042/bj3050025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagsted J., Ziebe S., Satoh S., Holman G. D., Cushman S. W., Olsson L. Insulinomimetic effect on glucose transport by epidermal growth factor when combined with a major histocompatibility complex class I-derived peptide. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1770–1774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strålfors P., Hiraga A., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. Purification and characterisation of the glycogen-bound form of protein phosphatase-1 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jun 3;149(2):295–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Ray L. B., Erikson E., Maller J. L. Insulin-stimulated MAP-2 kinase phosphorylates and activates ribosomal protein S6 kinase II. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):715–718. doi: 10.1038/334715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. J., Rothenberg P., Kahn C. R., Backer J. M., Araki E., Wilden P. A., Cahill D. A., Goldstein B. J., White M. F. Structure of the insulin receptor substrate IRS-1 defines a unique signal transduction protein. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):73–77. doi: 10.1038/352073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland C., Cohen P. The alpha-isoform of glycogen synthase kinase-3 from rabbit skeletal muscle is inactivated by p70 S6 kinase or MAP kinase-activated protein kinase-1 in vitro. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jan 24;338(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80112-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland C., Leighton I. A., Cohen P. Inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta by phosphorylation: new kinase connections in insulin and growth-factor signalling. Biochem J. 1993 Nov 15;296(Pt 1):15–19. doi: 10.1042/bj2960015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanti J. F., Grémeaux T., Van Obberghen E., Le Marchand-Brustel Y. Insulin receptor substrate 1 is phosphorylated by the serine kinase activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Biochem J. 1994 Nov 15;304(Pt 1):17–21. doi: 10.1042/bj3040017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lint J., Khandelwal R. L., Merlevede W., Vandenheede J. R. A specific immunoprecipitation assay for the protein kinase FA/glycogen synthase kinase 3. Anal Biochem. 1993 Jan;208(1):132–137. doi: 10.1006/abio.1993.1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh G. I., Foulstone E. J., Young S. W., Tavaré J. M., Proud C. G. Wortmannin inhibits the effects of insulin and serum on the activities of glycogen synthase kinase-3 and mitogen-activated protein kinase. Biochem J. 1994 Oct 1;303(Pt 1):15–20. doi: 10.1042/bj3030015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh G. I., Proud C. G. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 is rapidly inactivated in response to insulin and phosphorylates eukaryotic initiation factor eIF-2B. Biochem J. 1993 Sep 15;294(Pt 3):625–629. doi: 10.1042/bj2940625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Kahn C. R. The insulin signaling system. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiese R. J., Mastick C. C., Lazar D. F., Saltiel A. R. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase is not sufficient for the hormonal stimulation of glucose uptake, lipogenesis, or glycogen synthesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 17;270(7):3442–3446. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.7.3442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto-Honda R., Tobe K., Kaburagi Y., Ueki K., Asai S., Yachi M., Shirouzu M., Yodoi J., Akanuma Y., Yokoyama S. Upstream mechanisms of glycogen synthase activation by insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I. Glycogen synthase activation is antagonized by wortmannin or LY294002 but not by rapamycin or by inhibiting p21ras. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 10;270(6):2729–2734. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.6.2729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano H., Nakanishi S., Kimura K., Hanai N., Saitoh Y., Fukui Y., Nonomura Y., Matsuda Y. Inhibition of histamine secretion by wortmannin through the blockade of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in RBL-2H3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25846–25856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. W., Dickens M., Tavaré J. M. Differentiation of PC12 cells in response to a cAMP analogue is accompanied by sustained activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Comparison with the effects of insulin, growth factors and phorbol esters. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jan 31;338(2):212–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80367-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu K. T., Benjamin W. B., Ramakrishna S., Khalaf N., Czech M. P. An insulin-sensitive cytosolic protein kinase accounts for the regulation of ATP citrate-lyase phosphorylation. Biochem J. 1990 Jun 15;268(3):539–545. doi: 10.1042/bj2680539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]