Abstract
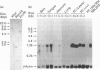
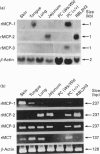
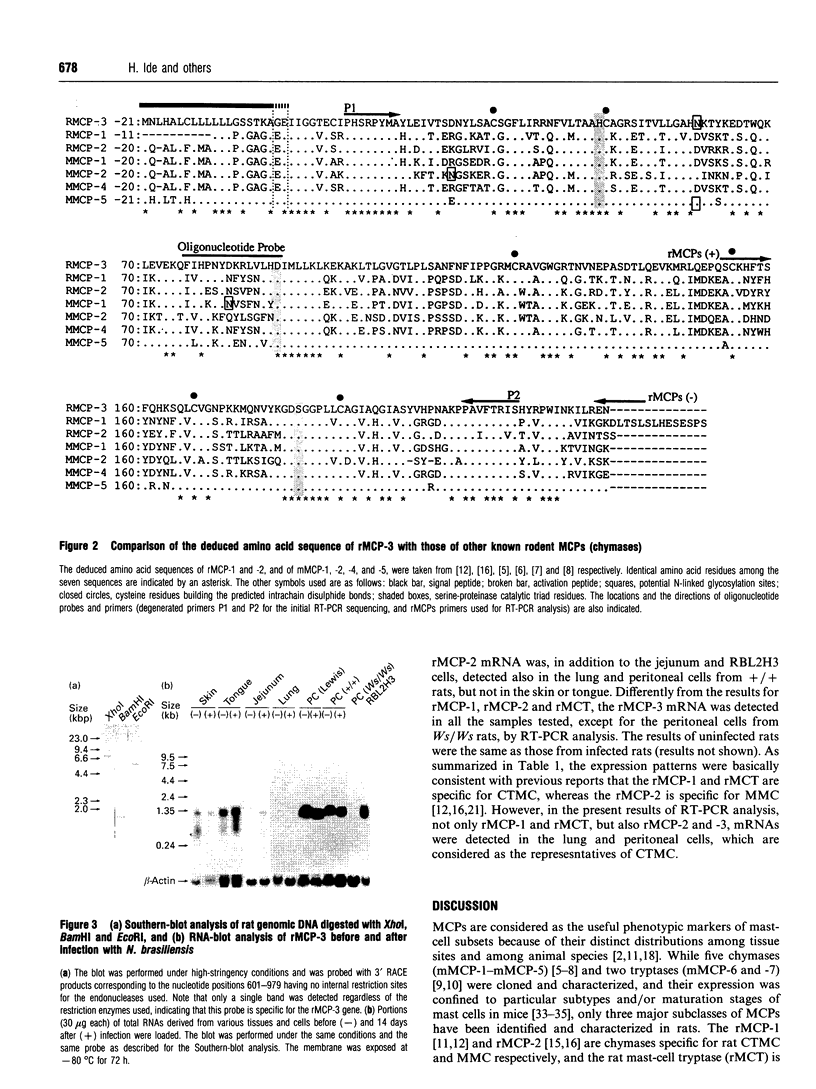
A cDNA encoding a novel rat mast-cell proteinase (MCP) named rMCP-3 was successfully cloned and sequenced from the peritoneal cells of Lewis rats infected with the intestinal nematode Nippostrongylus brasiliensis by using the combination of reverse transcription-PCR and rapid-amplification-of-cDNA-ends ('RACE') methods. The cDNA was 979 bp long and included a 741 bp open reading frame. When the deduced amino acid sequence was compared with those of other known mast-cell proteinases, rMCP-3 was considered to be translated as a preproenzyme with a 19-amino-acid signal peptide, a two-amino-acid activation peptide and a 226-amino-acid mature enzyme. The amino acid identity in the mature enzyme was 52.9% and 55.1% with rMCP-1 and rMCP-2 respectively. The rMCP-3 mRNA was not detected in the peritoneal cells of mast-cell-deficient Ws/Ws rats, though it was strongly detected in those of littermate +/+ and Lewis rats, indicating the mast-cell origin of rMCP-3 In addition to being present in peritoneal mast cells, the rMCP-3 mRNA was strongly detected in the skin, tongue, and RBL2H3 rat basophilic leukaemia cells and weakly in the jejunum of N. brasiliensis-infected rats by RNA blot analysis using a rMCP-3 gene-specific probe. By reverse transcription-PCR, the rMCP-3 mRNA was also detected in the lung. While the expression of rMCP-1 and rMCP-2 are clearly restricted in connective-tissue mast cells and mucosal mast cells respectively, rMCP-3 was widely expressed in both types of mast cells with a predominance in connective-tissue mast cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arizono N., Koreto O., Nakao S., Iwai Y., Kushima R., Takeoka O. Phenotypic changes in mast cells proliferating in the rat lung following infection with Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1987;54(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF02899191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins F. M. Intestinal mucosal mast cells. Ann Allergy. 1987 Nov;59(5 Pt 2):44–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benfey P. N., Yin F. H., Leder P. Cloning of the mast cell protease, RMCP II. Evidence for cell-specific expression and a multi-gene family. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5377–5384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caughey G. H., Zerweck E. H., Vanderslice P. Structure, chromosomal assignment, and deduced amino acid sequence of a human gene for mast cell chymase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):12956–12963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A. Rapid amplification of complementary DNA ends for generation of full-length complementary DNAs: thermal RACE. Methods Enzymol. 1993;218:340–356. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(93)18026-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J. New insights into "the riddle of the mast cells": microenvironmental regulation of mast cell development and phenotypic heterogeneity. Lab Invest. 1990 Jan;62(1):5–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson S., Mackeller A., Newlands G. F., Miller H. R. Phenotypic expression of mast cell granule proteinases. Distribution of mast cell proteinases I and II in the rat digestive system. Immunology. 1987 Dec;62(4):621–627. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurish M. F., Ghildyal N., McNeil H. P., Austen K. F., Gillis S., Stevens R. L. Differential expression of secretory granule proteases in mouse mast cells exposed to interleukin 3 and c-kit ligand. J Exp Med. 1992 Apr 1;175(4):1003–1012. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.4.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang R. Y., Blom T., Hellman L. Cloning and structural analysis of MMCP-1, MMCP-4 and MMCP-5, three mouse mast cell-specific serine proteases. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Jul;21(7):1611–1621. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huntley J. F., Mackellar A., Miller H. R. Altered expression of mast cell proteases in the rat. Quantitative and immunohistochemical analysis of the distribution of rat mast cell proteases I and II during helminth infection. APMIS. 1993 Dec;101(12):953–962. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1993.tb00207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ide H., Itoh H., Nawa Y. Sequencing of cDNAs encoding alpha 1-microglobulin/bikunin of Mongolian gerbil and Syrian golden hamster in comparison with man and other species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Dec 14;1209(2):286–292. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(94)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ide H., Itoh H., Tomita M., Murakumo Y., Kobayashi T., Maruyama H., Osada Y., Nawa Y. cDNA sequencing and expression of rat mast cell tryptase. J Biochem. 1995 Jul;118(1):210–215. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a124880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Ide H., Ishikawa N., Nawa Y. Mast cell protease inhibitor, trypstatin, is a fragment of inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor light chain. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3818–3822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Ide H., Kataoka H., Tomita M., Yoshihara H., Nawa Y. cDNA sequencing of mouse alpha 1-microglobulin/inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor light chain and its expression in acute inflammation. J Biochem. 1994 Oct;116(4):767–772. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a124594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kido H., Fukusen N., Katunuma N. Chymotrypsin- and trypsin-type serine proteases in rat mast cells: properties and functions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Jun;239(2):436–443. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90709-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kido H., Izumi K., Otsuka H., Fukusen N., Kato Y., Katunuma N. A chymotrypsin-type serine protease in rat basophilic leukemia cells: evidence for its immunologic identity with atypical mast cell protease. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):1061–1065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagunoff D., Rickard A., Marquardt C. Rat mast cell tryptase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Nov 15;291(1):52–58. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90104-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Trong H., Parmelee D. C., Walsh K. A., Neurath H., Woodbury R. G. Amino acid sequence of rat mast cell protease I (chymase). Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 3;26(22):6988–6994. doi: 10.1021/bi00396a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil H. P., Austen K. F., Somerville L. L., Gurish M. F., Stevens R. L. Molecular cloning of the mouse mast cell protease-5 gene. A novel secretory granule protease expressed early in the differentiation of serosal mast cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20316–20322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil H. P., Frenkel D. P., Austen K. F., Friend D. S., Stevens R. L. Translation and granule localization of mouse mast cell protease-5. Immunodetection with specific antipeptide Ig. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 1;149(7):2466–2472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil H. P., Reynolds D. S., Schiller V., Ghildyal N., Gurley D. S., Austen K. F., Stevens R. L. Isolation, characterization, and transcription of the gene encoding mouse mast cell protease 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11174–11178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. R., Woodbury R. G., Huntley J. F., Newlands G. Systemic release of mucosal mast-cell protease in primed rats challenged with Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. Immunology. 1983 Jul;49(3):471–479. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakumo Y., Ide H., Itoh H., Tomita M., Kobayashi T., Maruyama H., Horii Y., Nawa Y. Cloning of the cDNA encoding mast cell tryptase of Mongolian gerbil, Meriones unguiculatus, and its preferential expression in the intestinal mucosa. Biochem J. 1995 Aug 1;309(Pt 3):921–926. doi: 10.1042/bj3090921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadel J. A. Biologic effects of mast cell enzymes. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Feb;145(2 Pt 2):S37–S41. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/145.2_Pt_2.S37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niwa Y., Kasugai T., Ohno K., Morimoto M., Yamazaki M., Dohmae K., Nishimune Y., Kondo K., Kitamura Y. Anemia and mast cell depletion in mutant rats that are homozygous at "white spotting (Ws)" locus. Blood. 1991 Oct 15;78(8):1936–1941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pejler G., Maccarana M. Interaction of heparin with rat mast cell protease 1. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 20;269(20):14451–14456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pejler G., Söderström K., Karlström A. Inactivation of thrombin by a complex between rat mast-cell protease 1 and heparin proteoglycan. Biochem J. 1994 Apr 15;299(Pt 2):507–513. doi: 10.1042/bj2990507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds D. S., Gurley D. S., Austen K. F., Serafin W. E. Cloning of the cDNA and gene of mouse mast cell protease-6. Transcription by progenitor mast cells and mast cells of the connective tissue subclass. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3847–3853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds D. S., Stevens R. L., Lane W. S., Carr M. H., Austen K. F., Serafin W. E. Different mouse mast cell populations express various combinations of at least six distinct mast cell serine proteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3230–3234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouleau A., Garbarg M., Schwartz J. C., Ruat M. Molecular cloning of rat mast cell protease 1 and development of specific probes for its gene transcript. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Mar 15;199(2):593–602. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seldin D. C., Adelman S., Austen K. F., Stevens R. L., Hein A., Caulfield J. P., Woodbury R. G. Homology of the rat basophilic leukemia cell and the rat mucosal mast cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3871–3875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafin W. E., Reynolds D. S., Rogelj S., Lane W. S., Conder G. A., Johnson S. S., Austen K. F., Stevens R. L. Identification and molecular cloning of a novel mouse mucosal mast cell serine protease. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):423–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafin W. E., Sullivan T. P., Conder G. A., Ebrahimi A., Marcham P., Johnson S. S., Austen K. F., Reynolds D. S. Cloning of the cDNA and gene for mouse mast cell protease 4. Demonstration of its late transcription in mast cell subclasses and analysis of its homology to subclass-specific neutral proteases of the mouse and rat. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1934–1941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. L., Friend D. S., McNeil H. P., Schiller V., Ghildyal N., Austen K. F. Strain-specific and tissue-specific expression of mouse mast cell secretory granule proteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):128–132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji A., Akamatsu T., Nagamune H., Matsuda Y. Identification of targeting proteinase for rat alpha 1-macroglobulin in vivo. Mast-cell tryptase is a major component of the alpha 1-macroglobulin-proteinase complex endocytosed into rat liver lysosomes. Biochem J. 1994 Feb 15;298(Pt 1):79–85. doi: 10.1042/bj2980079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimura T., Hirota S., Nomura S., Niwa Y., Yamazaki M., Tono T., Morii E., Kim H. M., Kondo K., Nishimune Y. Characterization of Ws mutant allele of rats: a 12-base deletion in tyrosine kinase domain of c-kit gene. Blood. 1991 Oct 15;78(8):1942–1946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury R. G., Katunuma N., Kobayashi K., Titani K., Neurath H., Anderson W. F., Matthews B. W. Covalent structure of a group-specific protease from rat small intestine. Appendix: crystallographic data for a group specific protease from rat intestine. Biochemistry. 1978 Mar 7;17(5):811–819. doi: 10.1021/bi00598a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]