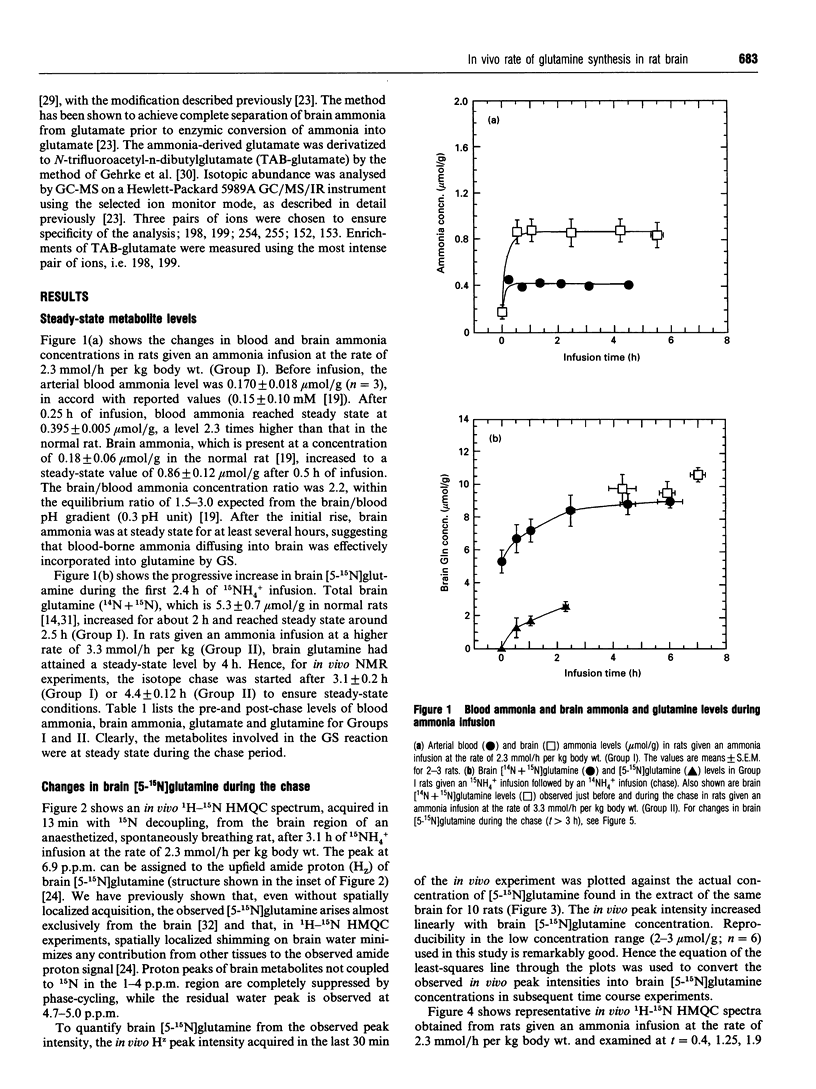
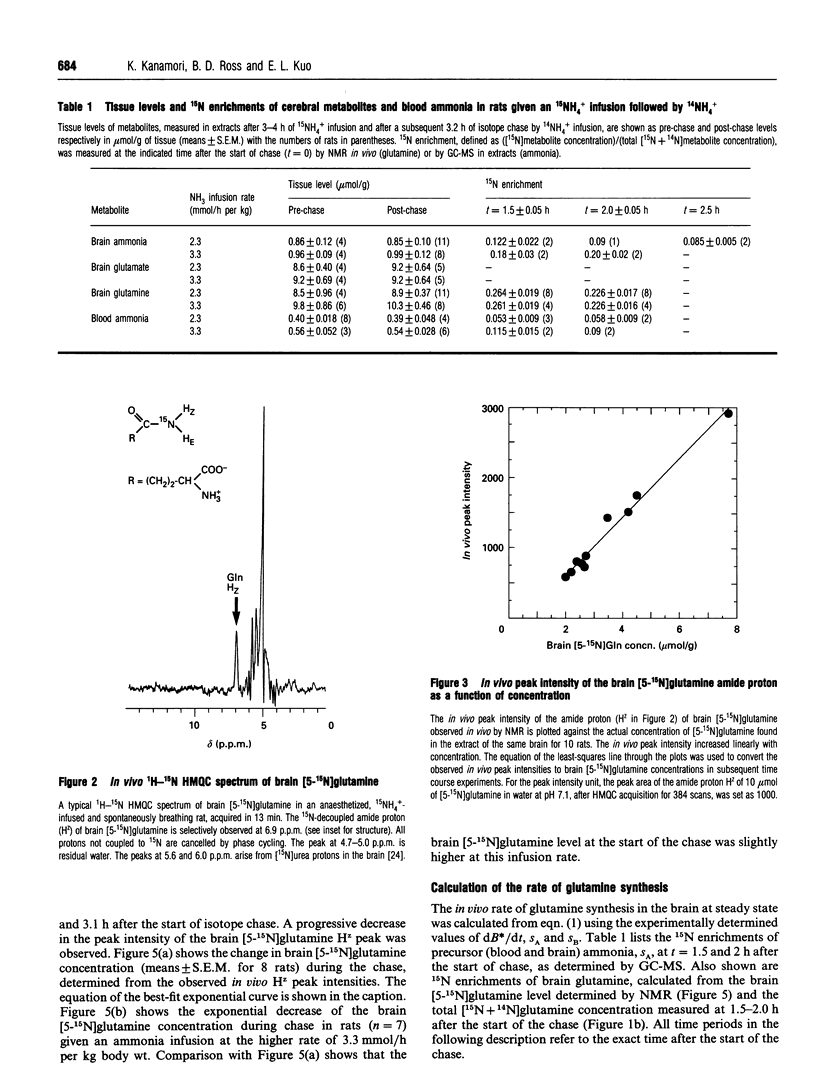
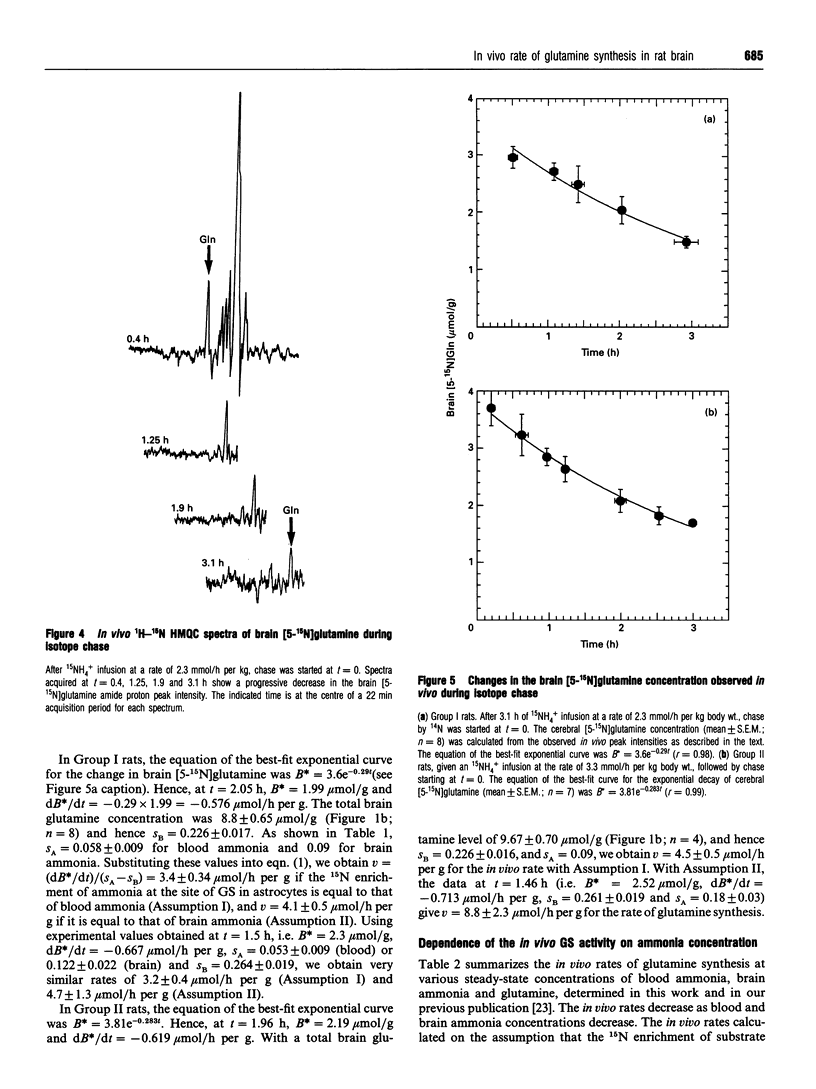
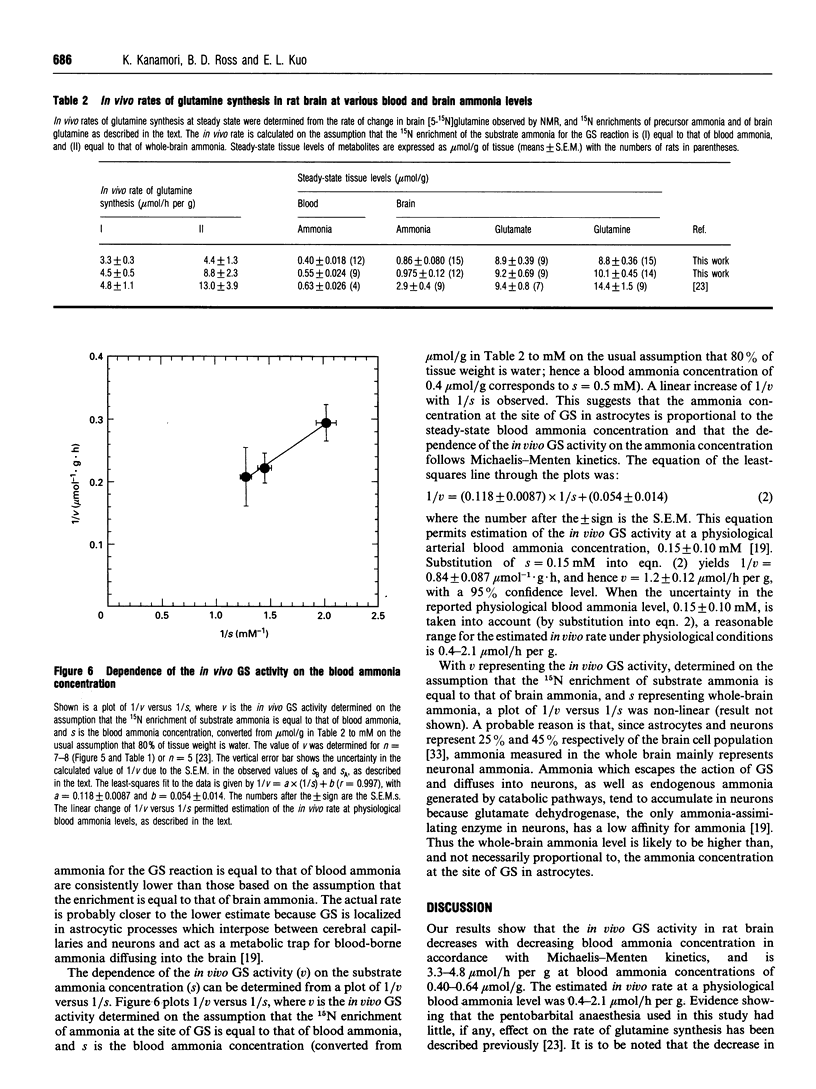
Abstract
The dependence of the in vivo rate of glutamine synthesis on the substrate ammonia concentration was studied in rat brain by 1H-15N heteronuclear multiple-quantum coherence-transfer NMR in combination with biochemical techniques. In vivo rates were measured at various steady-state blood and brain ammonia concentrations within the ranges 0.4-0.55 mumol/g and 0.86-0.98 mumol/g respectively, after low-rate intravenous 15NH4+ infusion (isotope chase). The rate of glutamine synthesis at steady state was determined from the change in brain [5-15N]glutamine levels during isotope chase, observed selectively through the amide proton by NMR, and 15N enrichments of brain glutamine and of blood and brain ammonia measured byN gas chromatography-MS. The in vivo rate (v) was 3.3-4.5 mumol/h per g of brain at blood ammonia concentrations (s) of 0.40-0.55 mumol/g. A linear increase of 1/v with 1/s permitted estimation of the in vivo glutamine synthetase (GS) activity at a physiological blood ammonia concentration to be 0.4-2.1 mumol/h per g. The observed ammonia-dependence strongly suggests that, under physiological conditions, in vivo GS activity is kinetically limited by sub-optimal in situ concentrations of ammonia as well as glutamate and ATP. Comparison of the observed in vivo GS activity with the reported in vivo rates of glutaminase and of gamma-aminobutyrate (GABA) synthesis suggests that, under mildly hyperammonaemic conditions, glutamine is synthesized at a sufficiently high rate to serve as a precursor of GABA, but glutaminase-catalysed hydrolysis of glutamine is too slow to be the sole provider of glutamate used for GABA synthesis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERL S., TAKAGAKI G., CLARKE D. D., WAELSCH H. Metabolic compartments in vivo. Ammonia and glutamic acid metabolism in brain and liver. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2562–2569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachelard H., Badar-Goffer R. NMR spectroscopy in neurochemistry. J Neurochem. 1993 Aug;61(2):412–429. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb02141.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basile A. S., Jones E. A., Skolnick P. The pathogenesis and treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: evidence for the involvement of benzodiazepine receptor ligands. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Mar;43(1):27–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battaglioli G., Martin D. L. GABA synthesis in brain slices is dependent on glutamine produced in astrocytes. Neurochem Res. 1991 Feb;16(2):151–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00965703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourget P. A., Tremblay G. C. Pyrimidine biosynthesis in rat brain. J Neurochem. 1972 Jul;19(7):1617–1624. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb06207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth R. F., Girard G., Giguère J. F. Regional differences in the capacity for ammonia removal by brain following portocaval anastomosis. J Neurochem. 1988 Aug;51(2):486–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth R. F. Portal-systemic encephalopathy: a disorder of neuron-astrocytic metabolic trafficking. Dev Neurosci. 1993;15(3-5):313–319. doi: 10.1159/000111350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammer W. Glutamine synthetase in the central nervous system is not confined to astrocytes. J Neuroimmunol. 1990 Feb;26(2):173–178. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(90)90088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casu M., Gale K. Intracerebral injection of gamma vinyl GABA: method for measuring rates of GABA synthesis in specific brain regions in vivo. Life Sci. 1981 Aug 17;29(7):681–688. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman A. G., Evans M. C. Cortical GABA turnover during bicuculline seizures in rats. J Neurochem. 1983 Sep;41(3):886–889. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb04823.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. J., McDonald J. M., Gelbard A. S., Gledhill R. F., Duffy T. E. The metabolic fate of 13N-labeled ammonia in rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):4982–4992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. J., Mora S. N., Cruz N. F., Gelbard A. S. Cerebral ammonia metabolism in hyperammonemic rats. J Neurochem. 1985 Jun;44(6):1716–1723. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07159.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. J., Plum F. Biochemistry and physiology of brain ammonia. Physiol Rev. 1987 Apr;67(2):440–519. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.2.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejong C. H., Deutz N. E., Soeters P. B. Cerebral cortex ammonia and glutamine metabolism in two rat models of chronic liver insufficiency-induced hyperammonemia: influence of pair-feeding. J Neurochem. 1993 Mar;60(3):1047–1057. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejong C. H., Kampman M. T., Deutz N. E., Soeters P. B. Cerebral cortex ammonia and glutamine metabolism during liver insufficiency-induced hyperammonemia in the rat. J Neurochem. 1992 Sep;59(3):1071–1079. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb08349.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F., Lerner A., Albrycht D. Regulatory properties of rat liver glutamine synthetase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 26;48(6):1419–1425. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90871-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F., Louie M., Lerner A. Glutamine synthetase from rat liver. Purification, properties, and preparation of specific antisera. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):6111–6118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erecińska M., Silver I. A. Metabolism and role of glutamate in mammalian brain. Prog Neurobiol. 1990;35(4):245–296. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(90)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrow N. A., Kanamori K., Ross B. D., Parivar F. A 15N-n.m.r. study of cerebral, hepatic and renal nitrogen metabolism in hyperammonaemic rats. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 1;270(2):473–481. doi: 10.1042/bj2700473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberger A. C., Chiang G. H., Nylén E. S., Scheff S. W., Cotman C. W. Glutamate as a CNS transmitter. I. Evaluation of glucose and glutamine as precursors for the synthesis of preferentially released glutamate. Brain Res. 1979 Jun 8;168(3):513–530. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90306-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanamori K., Parivar F., Ross B. D. A 15N NMR study of in vivo cerebral glutamine synthesis in hyperammonemic rats. NMR Biomed. 1993 Jan-Feb;6(1):21–26. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1940060104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanamori K., Ross B. D. 15N n.m.r. measurement of the in vivo rate of glutamine synthesis and utilization at steady state in the brain of the hyperammonaemic rat. Biochem J. 1993 Jul 15;293(Pt 2):461–468. doi: 10.1042/bj2930461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanamori K., Ross B. D. In vivo activity of glutaminase in the brain of hyperammonaemic rats measured by 15N nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochem J. 1995 Jan 1;305(Pt 1):329–336. doi: 10.1042/bj3050329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanamori K., Ross B. D., Tropp J. Selective, in vivo observation of [5-15N]glutamine amide protons in rat brain by 1H-15N heteronuclear multiple-quantum-coherence transfer NMR. J Magn Reson B. 1995 May;107(2):107–115. doi: 10.1006/jmrb.1995.1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood A. H., McDonald J. M., Reiman R. E., Gelbard A. S., Laughlin J. S., Duffy T. E., Plum F. The dynamics of ammonia metabolism in man. Effects of liver disease and hyperammonemia. J Clin Invest. 1979 Mar;63(3):449–460. doi: 10.1172/JCI109322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löscher W., Hönack D., Gramer M. Use of inhibitors of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transaminase for the estimation of GABA turnover in various brain regions of rats: a reevaluation of aminooxyacetic acid. J Neurochem. 1989 Dec;53(6):1737–1750. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb09239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mans A. M., DeJoseph M. R., Hawkins R. A. Metabolic abnormalities and grade of encephalopathy in acute hepatic failure. J Neurochem. 1994 Nov;63(5):1829–1838. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.63051829.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason G. F., Gruetter R., Rothman D. L., Behar K. L., Shulman R. G., Novotny E. J. Simultaneous determination of the rates of the TCA cycle, glucose utilization, alpha-ketoglutarate/glutamate exchange, and glutamine synthesis in human brain by NMR. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1995 Jan;15(1):12–25. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1995.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mill J. F., Mearow K. M., Purohit H. J., Haleem-Smith H., King R., Freese E. Cloning and functional characterization of the rat glutamine synthetase gene. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Feb;9(3):197–207. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90003-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norenberg M. D., Martinez-Hernandez A. Fine structural localization of glutamine synthetase in astrocytes of rat brain. Brain Res. 1979 Feb 2;161(2):303–310. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottersen O. P., Zhang N., Walberg F. Metabolic compartmentation of glutamate and glutamine: morphological evidence obtained by quantitative immunocytochemistry in rat cerebellum. Neuroscience. 1992;46(3):519–534. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90141-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen R. E., Odden E., Fonnum F. Importance of glutamine for gamma-aminobutyric acid synthesis in rat neostriatum in vivo. J Neurochem. 1988 Oct;51(4):1294–1299. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb03099.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimvall K., Martin D. L. The level of GAD67 protein is highly sensitive to small increases in intraneuronal gamma-aminobutyric acid levels. J Neurochem. 1994 Apr;62(4):1375–1381. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.62041375.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos J. N., Hempstead K. W., Kopp L. E., Miech R. P. Nucleotide metabolism in rat brain. J Neurochem. 1968 May;15(5):367–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb11623.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szerb J. C. Storage and release of endogenous and labelled GABA formed from [3H]glutamine and [14C]glucose in hippocampal slices: effect of depolarization. Brain Res. 1984 Feb 20;293(2):293–303. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Leu F. Y., Meister A. Rat liver glutamine synthetase. Preparation, properties, and mechanism of inhibition by carbamyl phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 10;247(17):5312–5321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanki C. M., Sugden D., Thomas A. J., Bradford H. F. In vivo release from cerebral cortex of [14C]glutamate synthesized from [U-14C]glutamine. J Neurochem. 1983 Sep;41(3):611–617. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb04785.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waniewski R. A. Physiological levels of ammonia regulate glutamine synthesis from extracellular glutamate in astrocyte cultures. J Neurochem. 1992 Jan;58(1):167–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09292.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward H. K., Thanki C. M., Bradford H. F. Glutamine and glucose as precursors of transmitter amino acids: ex vivo studies. J Neurochem. 1983 Mar;40(3):855–860. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb08058.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedler F. C., Denman R. B., Roby W. G. Glutamine synthetase from ovine brain is a manganese(II) enzyme. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 7;21(25):6389–6396. doi: 10.1021/bi00268a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedler F. C., Ley B. W. Kinetic, ESR, and trapping evidence for in vivo binding of Mn(II) to glutamine synthetase in brain cells. Neurochem Res. 1994 Feb;19(2):139–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00966808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto H., Konno H., Yamamoto T., Ito K., Mizugaki M., Iwasaki Y. Glutamine synthetase of the human brain: purification and characterization. J Neurochem. 1987 Aug;49(2):603–609. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb02906.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu A. C., Schousboe A., Hertz L. Influence of pathological concentrations of ammonia on metabolic fate of 14C-labeled glutamate in astrocytes in primary cultures. J Neurochem. 1984 Feb;42(2):594–597. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb02721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu A. C., Schousboe A., Hertz L. Metabolic fate of 14C-labeled glutamate in astrocytes in primary cultures. J Neurochem. 1982 Oct;39(4):954–960. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb11482.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yudkoff M., Nissim I., Hummeler K., Medow M., Pleasure D. Utilization of [15N]glutamate by cultured astrocytes. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 15;234(1):185–192. doi: 10.1042/bj2340185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Zande L., Labruyère W. T., Arnberg A. C., Wilson R. H., van den Bogaert A. J., Das A. T., van Oorschot D. A., Frijters C., Charles R., Moorman A. F. Isolation and characterization of the rat glutamine synthetase-encoding gene. Gene. 1990 Mar 15;87(2):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90306-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


