Abstract
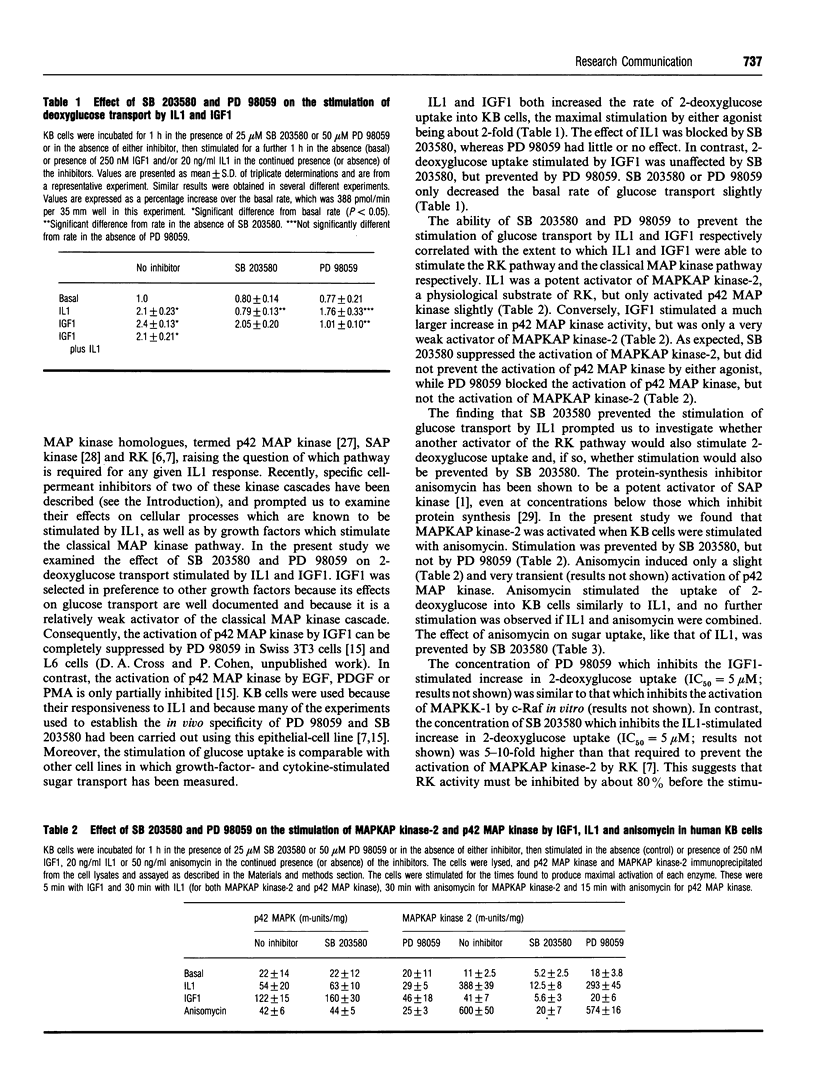
The uptake of 2-deoxyglucose into KB cells was stimulated about 2-fold by interleukin-1 (IL1), anisomycin or insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF1). Stimulation by IL1 and anisomycin was prevented by SB 203580, a specific inhibitor of the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase homologue termed 're-activating kinase' [RK; also known as p38, p40 and CSBP (cytokine synthesis anti-inflammatory-drug-binding protein)], but was unaffected by PD 98059, a specific inhibitor of the activation of the classical MAP kinase pathway. In contrast, the stimulation of 2-deoxyglucose uptake by IGF1 was blocked by PD 98059 and unaffected by SB 203580. Consistent with these observations, IL1 and anisomycin were potent activators of MAP kinase-activated protein (MAPKAP) kinase-2, a physiological substrate of RK, whereas IGF1 was only a very weak activator of MAPKAP kinase-2. Conversely, IGF1 was a stronger activator of p42 MAP kinase than IL1 or anisomycin. These results imply that the activation of distinct MAP kinase pathways is required for the stimulation of glucose transport by IL1/anisomycin and IGF1 in KB cells, and suggest that the combined use of SB 203580 and PD 98059 is a powerful new approach to explore the roles of different MAP kinase cascades in cell regulation.
Full text
PDF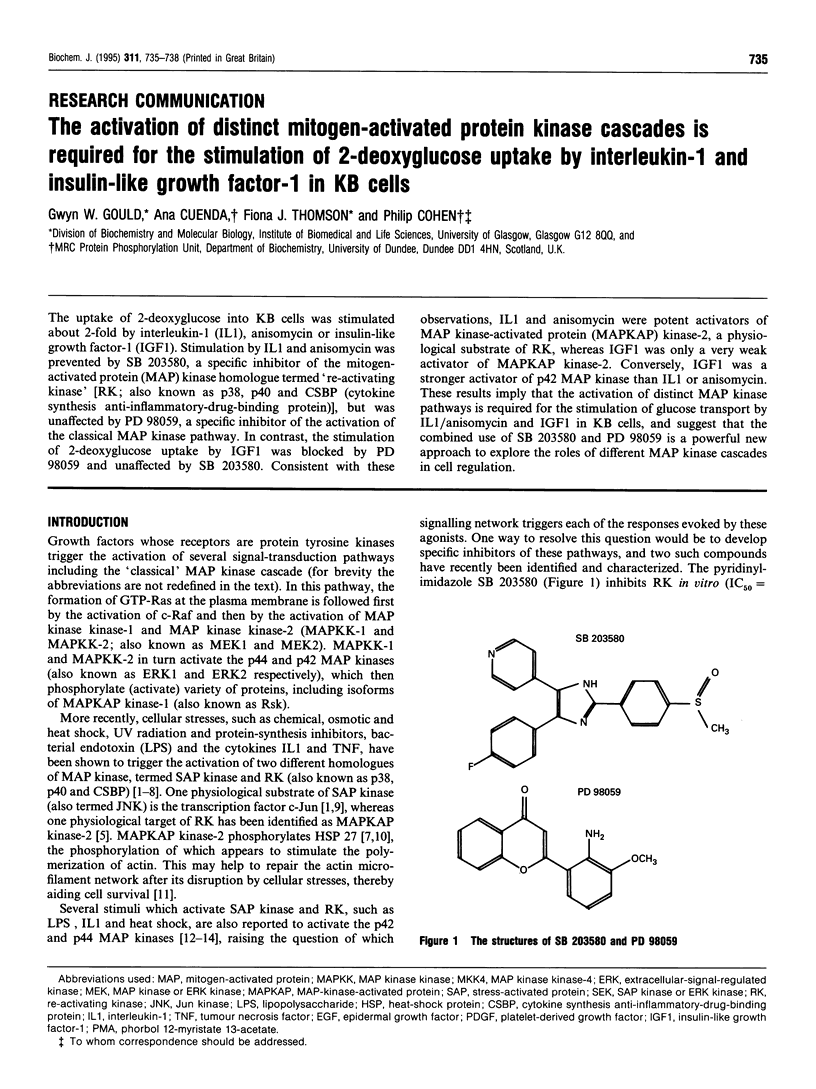


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alessi D. R., Cohen P., Ashworth A., Cowley S., Leevers S. J., Marshall C. J. Assay and expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase, MAP kinase kinase, and Raf. Methods Enzymol. 1995;255:279–290. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(95)55031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird T. A., Kyriakis J. M., Tyshler L., Gayle M., Milne A., Virca G. D. Interleukin-1 activates p54 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase/stress-activated protein kinase by a pathway that is independent of p21ras, Raf-1, and MAP kinase kinase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 16;269(50):31836–31844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch R. Inhibition of glucose transport in the human erythrocyte by cytochalasin B. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 6;12(23):4799–4801. doi: 10.1021/bi00747a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuenda A., Rouse J., Doza Y. N., Meier R., Cohen P., Gallagher T. F., Young P. R., Lee J. C. SB 203580 is a specific inhibitor of a MAP kinase homologue which is stimulated by cellular stresses and interleukin-1. FEBS Lett. 1995 May 8;364(2):229–233. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00357-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois M. F., Bensaude O. MAP kinase activation during heat shock in quiescent and exponentially growing mammalian cells. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jun 14;324(2):191–195. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81391-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dérijard B., Hibi M., Wu I. H., Barrett T., Su B., Deng T., Karin M., Davis R. J. JNK1: a protein kinase stimulated by UV light and Ha-Ras that binds and phosphorylates the c-Jun activation domain. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1025–1037. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90380-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dérijard B., Raingeaud J., Barrett T., Wu I. H., Han J., Ulevitch R. J., Davis R. J. Independent human MAP-kinase signal transduction pathways defined by MEK and MKK isoforms. Science. 1995 Feb 3;267(5198):682–685. doi: 10.1126/science.7839144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freshney N. W., Rawlinson L., Guesdon F., Jones E., Cowley S., Hsuan J., Saklatvala J. Interleukin-1 activates a novel protein kinase cascade that results in the phosphorylation of Hsp27. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):1039–1049. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90278-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galcheva-Gargova Z., Dérijard B., Wu I. H., Davis R. J. An osmosensing signal transduction pathway in mammalian cells. Science. 1994 Aug 5;265(5173):806–808. doi: 10.1126/science.8047888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs E. M., Lienhard G. E., Gould G. W. Insulin-induced translocation of glucose transporters to the plasma membrane precedes full stimulation of hexose transport. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):6681–6685. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guesdon F., Freshney N., Waller R. J., Rawlinson L., Saklatvala J. Interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor stimulate two novel protein kinases that phosphorylate the heat shock protein hsp27 and beta-casein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4236–4243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Lee J. D., Bibbs L., Ulevitch R. J. A MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian cells. Science. 1994 Aug 5;265(5173):808–811. doi: 10.1126/science.7914033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kracht M., Truong O., Totty N. F., Shiroo M., Saklatvala J. Interleukin 1 alpha activates two forms of p54 alpha mitogen-activated protein kinase in rabbit liver. J Exp Med. 1994 Dec 1;180(6):2017–2025. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.6.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., Banerjee P., Nikolakaki E., Dai T., Rubie E. A., Ahmad M. F., Avruch J., Woodgett J. R. The stress-activated protein kinase subfamily of c-Jun kinases. Nature. 1994 May 12;369(6476):156–160. doi: 10.1038/369156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavoie J. N., Lambert H., Hickey E., Weber L. A., Landry J. Modulation of cellular thermoresistance and actin filament stability accompanies phosphorylation-induced changes in the oligomeric structure of heat shock protein 27. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jan;15(1):505–516. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.1.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar D. F., Wiese R. J., Brady M. J., Mastick C. C., Waters S. B., Yamauchi K., Pessin J. E., Cuatrecasas P., Saltiel A. R. Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase inhibition does not block the stimulation of glucose utilization by insulin. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 1;270(35):20801–20807. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.35.20801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Laydon J. T., McDonnell P. C., Gallagher T. F., Kumar S., Green D., McNulty D., Blumenthal M. J., Heys J. R., Landvatter S. W. A protein kinase involved in the regulation of inflammatory cytokine biosynthesis. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):739–746. doi: 10.1038/372739a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan L. C., Edwards D. R. Signalling and superinduction. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):747–748. doi: 10.1038/349747c0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda S., Kawasaki H., Moriguchi T., Gotoh Y., Nishida E. Activation of protein kinase cascades by osmotic shock. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 26;270(21):12781–12786. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.21.12781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrall N. W., Plevin R. J., Stokoe D., Cohen P., Nebreda A. R., Gould G. W. Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP kinase), MAP kinase kinase and c-Mos stimulate glucose transport in Xenopus oocytes. Biochem J. 1993 Oct 15;295(Pt 2):351–355. doi: 10.1042/bj2950351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minden A., Lin A., McMahon M., Lange-Carter C., Dérijard B., Davis R. J., Johnson G. L., Karin M. Differential activation of ERK and JNK mitogen-activated protein kinases by Raf-1 and MEKK. Science. 1994 Dec 9;266(5191):1719–1723. doi: 10.1126/science.7992057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raingeaud J., Gupta S., Rogers J. S., Dickens M., Han J., Ulevitch R. J., Davis R. J. Pro-inflammatory cytokines and environmental stress cause p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation by dual phosphorylation on tyrosine and threonine. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 31;270(13):7420–7426. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.13.7420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse J., Cohen P., Trigon S., Morange M., Alonso-Llamazares A., Zamanillo D., Hunt T., Nebreda A. R. A novel kinase cascade triggered by stress and heat shock that stimulates MAPKAP kinase-2 and phosphorylation of the small heat shock proteins. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):1027–1037. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90277-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saklatvala J., Rawlinson L. M., Marshall C. J., Kracht M. Interleukin 1 and tumour necrosis factor activate the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase kinase in cultured cells. FEBS Lett. 1993 Nov 15;334(2):189–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81709-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokoe D., Caudwell B., Cohen P. T., Cohen P. The substrate specificity and structure of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase-activated protein kinase-2. Biochem J. 1993 Dec 15;296(Pt 3):843–849. doi: 10.1042/bj2960843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokoe D., Engel K., Campbell D. G., Cohen P., Gaestel M. Identification of MAPKAP kinase 2 as a major enzyme responsible for the phosphorylation of the small mammalian heat shock proteins. FEBS Lett. 1992 Nov 30;313(3):307–313. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81216-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez I., Hughes R. T., Mayer B. J., Yee K., Woodgett J. R., Avruch J., Kyriakis J. M., Zon L. I. Role of SAPK/ERK kinase-1 in the stress-activated pathway regulating transcription factor c-Jun. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):794–798. doi: 10.1038/372794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein S. L., Sanghera J. S., Lemke K., DeFranco A. L., Pelech S. L. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide induces tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14955–14962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan M., Dai T., Deak J. C., Kyriakis J. M., Zon L. I., Woodgett J. R., Templeton D. J. Activation of stress-activated protein kinase by MEKK1 phosphorylation of its activator SEK1. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):798–800. doi: 10.1038/372798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


