Abstract
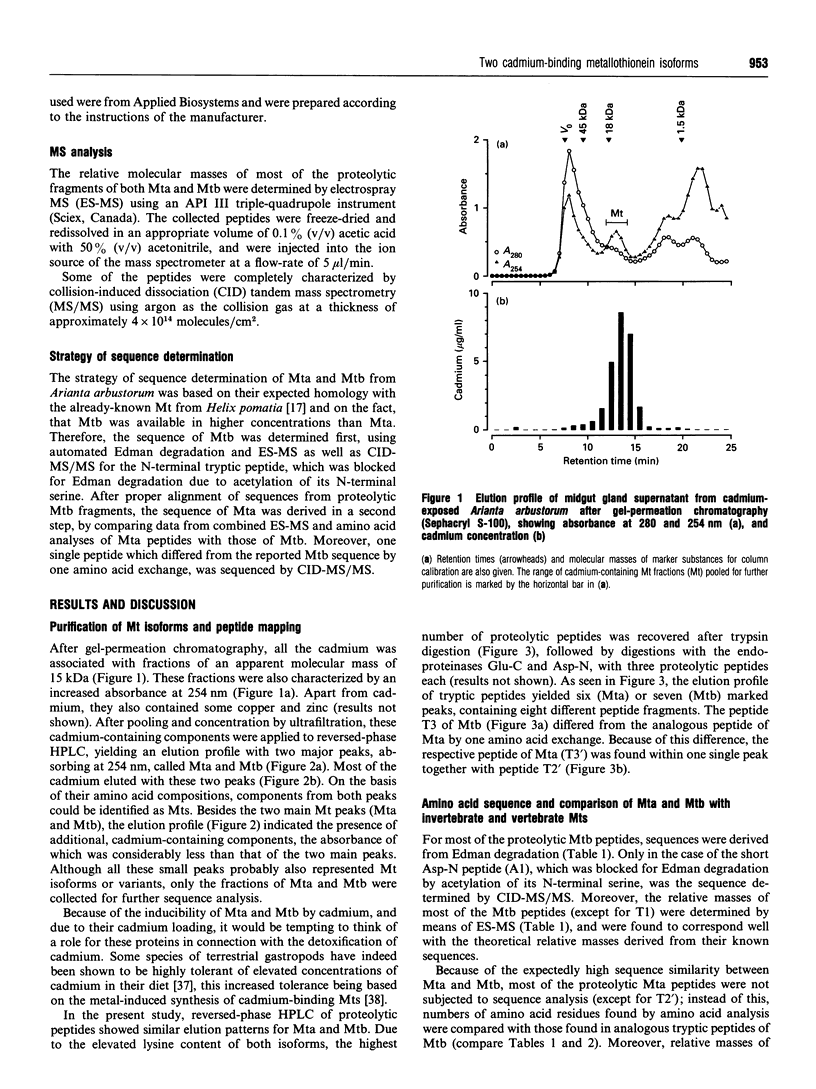
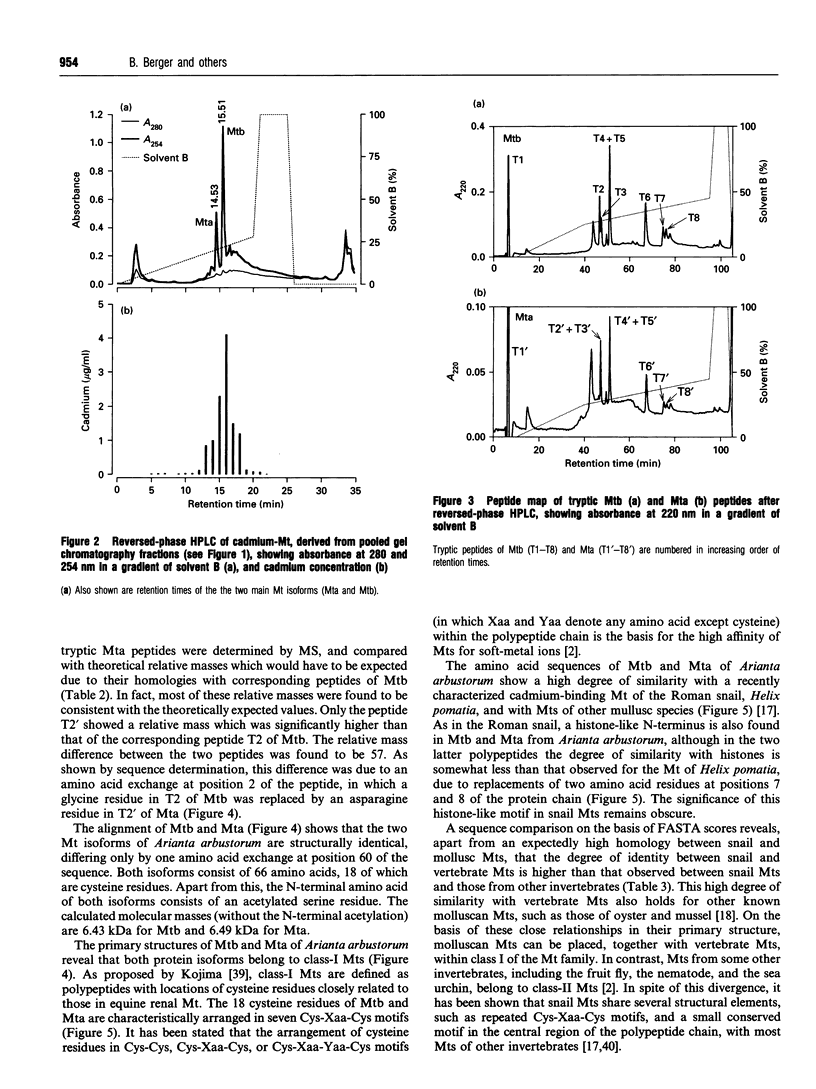
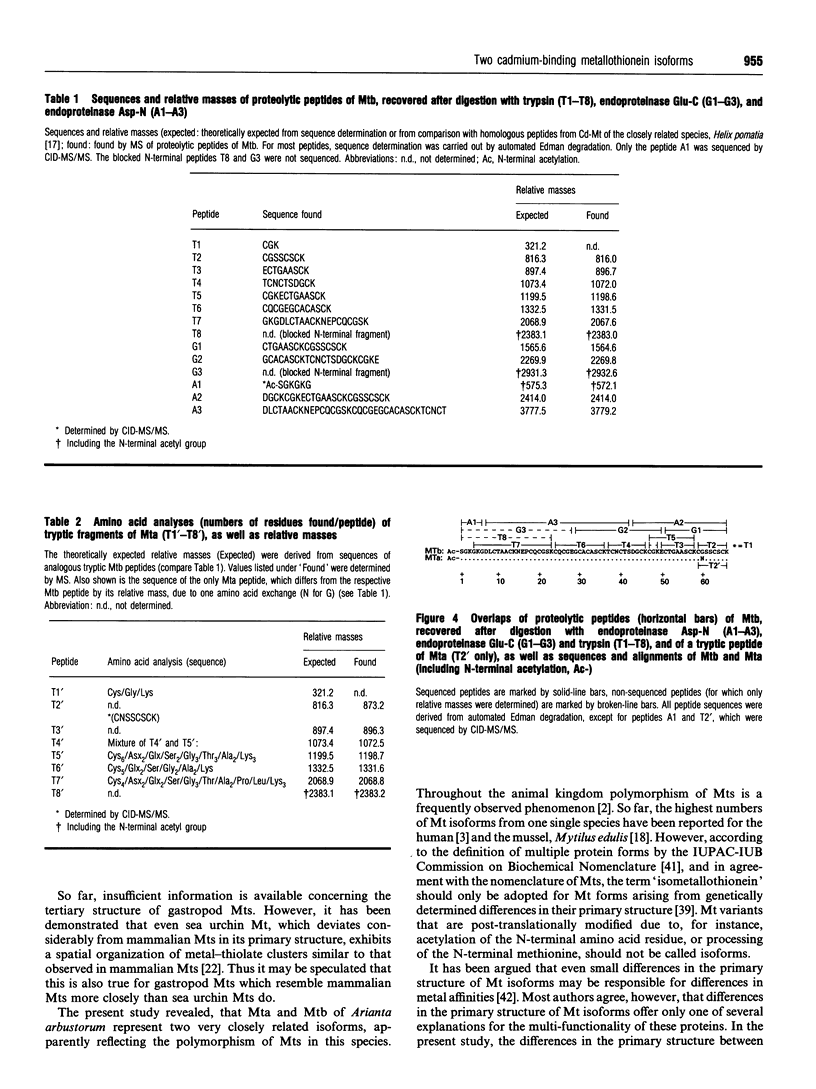
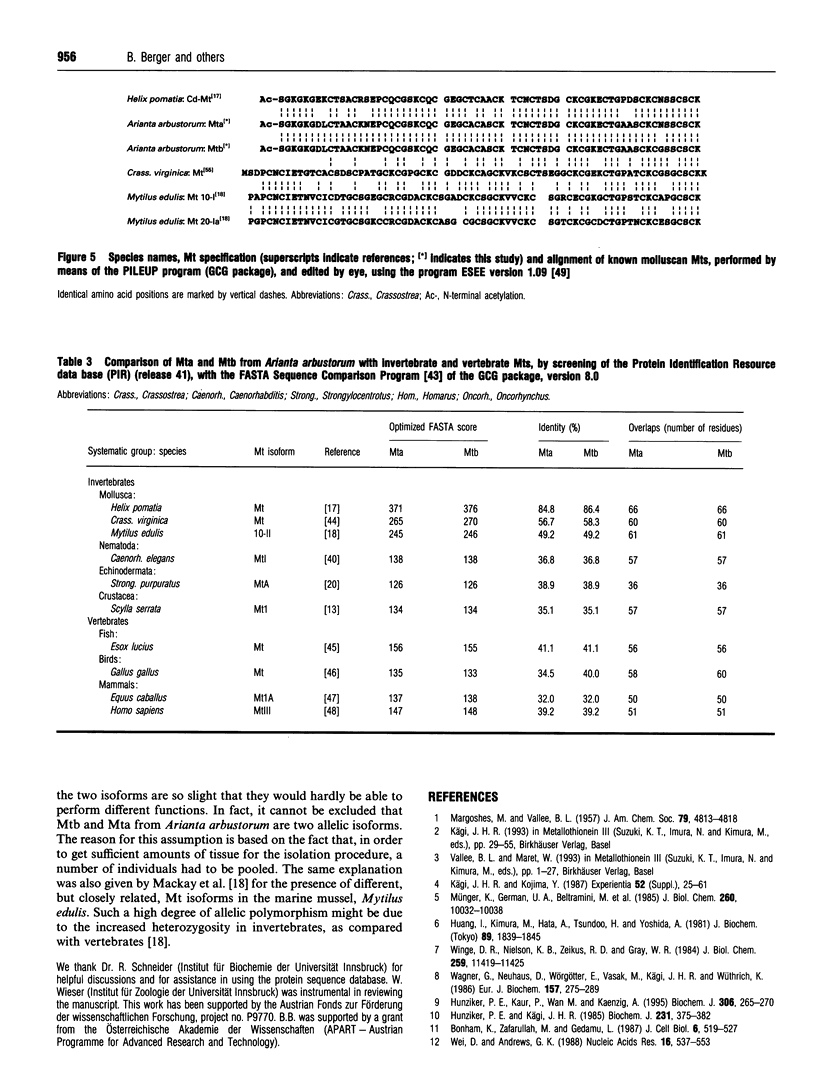
1. Two cadmium-binding metallothionein (Mt) isoforms, called Mta and Mtb, were isolated from terrestrial snails (Arianta arbustorum), using various chromatographic techniques, such as gel-permeation chromatography and reversed-phase HPLC. The purified proteins were S-methylated and cleaved by means of different enzymes (trypsin, endoproteinase Glu-C, and endoproteinase Asp-N). Amino acid sequences were determined by automated Edman degradation and collision-induced dissociation (CID) tandem MS. According to their primary structures, both isoforms should be attributed to class-I Mts. 2. The two forms are structurally identical, differing only by one amino acid exchange in position 60 of the peptide chain. Both isoproteins consist of 66 amino acids, 18 of which are cysteine residues. Most of the cysteine residues are arranged in seven Cys-Xaa-Cys motifs. Mta and Mtb possess an N-terminal acetylated-serine residue and contain a short N-terminal motif which shows a high degree of similarity with the N-termini of histones H4 and H2A. 3. A comparison of Mta and Mtb with other invertebrate Mts shows a very high degree of sequence similarity with a cadmium-binding Mt from Helix pomatia, a species that is closely related to Arianta arbustorum. Moreover, Mta and Mtb, as expected, also exhibit structural similarities with Mts from other molluscan species, such as mussels and oysters. It is suggested that Mta and Mtb represent two allelic isoforms, reflecting the genetic polymorphism of Mt in Arianta arbustorum.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abel J., de Ruiter N. Inhibition of hydroxyl-radical-generated DNA degradation by metallothionein. Toxicol Lett. 1989 May;47(2):191–196. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(89)90075-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonham K., Zafarullah M., Gedamu L. The rainbow trout metallothioneins: molecular cloning and characterization of two distinct cDNA sequences. DNA. 1987 Dec;6(6):519–528. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremner I. Nutritional and physiologic significance of metallothionein. Methods Enzymol. 1991;205:25–35. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)05080-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabot E. L., Beckenbach A. T. Simultaneous editing of multiple nucleic acid and protein sequences with ESEE. Comput Appl Biosci. 1989 Jul;5(3):233–234. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/5.3.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallinger R., Berger B., Hunziker P. E., Birchler N., Hauer C. R., Kägi J. H. Purification and primary structure of snail metallothionein. Similarity of the N-terminal sequence with histones H4 and H2A. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Sep 15;216(3):739–746. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18193.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernando L. P., Andrews G. K. Cloning and expression of an avian metallothionein-encoding gene. Gene. 1989 Sep 1;81(1):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90349-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H. Metallothionein. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:913–951. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H., Thiele D. J., Lemontt J. E. Function and autoregulation of yeast copperthionein. Science. 1985 May 10;228(4700):685–690. doi: 10.1126/science.3887570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang I. Y., Kimura M., Hata A., Tsunoo H., Yoshida A. Complete amino acid sequence of mouse liver metallothionein-II. J Biochem. 1981 Jun;89(6):1839–1845. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunziker P. E. Cysteine modification of metallothionein. Methods Enzymol. 1991;205:399–400. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)05121-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunziker P. E., Kaur P., Wan M., Känzig A. Primary structures of seven metallothioneins from rabbit tissue. Biochem J. 1995 Feb 15;306(Pt 1):265–270. doi: 10.1042/bj3060265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunziker P. E., Kägi J. H. Isolation and characterization of six human hepatic isometallothioneins. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 15;231(2):375–382. doi: 10.1042/bj2310375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Onozawa T., Okumura K., Osada S., Nishihara T., Kondo M. Characterization of metallothionein cDNAs induced by cadmium in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Biochem J. 1990 May 15;268(1):237–240. doi: 10.1042/bj2680237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kille P., Kay J., Sweeney G. E. Analysis of regulatory elements flanking metallothionein genes in Cd-tolerant fish (pike and stone loach). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Oct 19;1216(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90037-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima Y. Definitions and nomenclature of metallothioneins. Methods Enzymol. 1991;205:8–10. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)05078-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kägi J. H., Kojima Y. Chemistry and biochemistry of metallothionein. Experientia Suppl. 1987;52:25–61. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-6784-9_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kägi J. H. Overview of metallothionein. Methods Enzymol. 1991;205:613–626. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)05145-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lastowski-Perry D., Otto E., Maroni G. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a Drosophila metallothionein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1527–1530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerch K., Ammer D., Olafson R. W. Crab metallothionein. Primary structures of metallothioneins 1 and 2. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2420–2426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay E. A., Overnell J., Dunbar B., Davidson I., Hunziker P. E., Kägi J. H., Fothergill J. E. Complete amino acid sequences of five dimeric and four monomeric forms of metallothionein from the edible mussel Mytilus edulis. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Nov 15;218(1):183–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18364.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroni G., Wise J., Young J. E., Otto E. Metallothionein gene duplications and metal tolerance in natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1987 Dec;117(4):739–744. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.4.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemer M., Wilkinson D. G., Travaglini E. C., Sternberg E. J., Butt T. R. Sea urchin metallothionein sequence: key to an evolutionary diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4992–4994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otvos J. D., Olafson R. W., Armitage I. M. Structure of an invertebrate metallothionein from Scylla serrata. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2427–2431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Findley S. D., Whitmore T. E., Durnam D. M. MT-III, a brain-specific member of the metallothionein gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6333–6337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K. L., Pedersen S. N., Højrup P., Andersen J. S., Roepstorff P., Knudsen J., Depledge M. H. Purification and characterization of a cadmium-induced metallothionein from the shore crab Carcinus maenas (L.). Biochem J. 1994 Feb 1;297(Pt 3):609–614. doi: 10.1042/bj2970609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccinni E., Staudenmann W., Albergoni V., De Gabrieli R., James P. Purification and primary structure of metallothioneins induced by cadmium in the protists Tetrahymena pigmentosa and Tetrahymena pyriformis. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Dec 15;226(3):853–859. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.t01-1-00853.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards M. P. Recent developments in trace element metabolism and function: role of metallothionein in copper and zinc metabolism. J Nutr. 1989 Jul;119(7):1062–1070. doi: 10.1093/jn/119.7.1062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. H., McRee D. E., Williamson M., Collett S. A., Xuong N. H., Furey W. F., Wang B. C., Stout C. D. Refined crystal structure of Cd, Zn metallothionein at 2.0 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 20;221(4):1269–1293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roesijadi G., Kielland S., Klerks P. Purification and properties of novel molluscan metallothioneins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Sep;273(2):403–413. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90499-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger M. E., Chen T. T., Murphy C. M., Vestling M. M., Fenselau C., Roesijadi G. Primary structure of molluscan metallothioneins deduced from PCR-amplified cDNA and mass spectrometry of purified proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Aug 6;1074(3):371–377. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(91)90087-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner G., Neuhaus D., Wörgötter E., Vasák M., Kägi J. H., Wüthrich K. Sequence-specific 1H-NMR assignments in rabbit-liver metallothionein-2. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jun 2;157(2):275–289. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09666.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei D. Y., Andrews G. K. Molecular cloning of chicken metallothionein. Deduction of the complete amino acid sequence and analysis of expression using cloned cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):537–553. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winge D. R., Miklossy K. A. Domain nature of metallothionein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3471–3476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winge D. R., Nielson K. B., Zeikus R. D., Gray W. R. Structural characterization of the isoforms of neonatal and adult rat liver metallothionein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11419–11425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich K. Determination of the three-dimensional structure of metallothioneins by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in solution. Methods Enzymol. 1991;205:502–520. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)05135-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng J., Heuchel R., Schaffner W., Kägi J. H. Thionein (apometallothionein) can modulate DNA binding and transcription activation by zinc finger containing factor Sp1. FEBS Lett. 1991 Feb 25;279(2):310–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80175-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


