Abstract
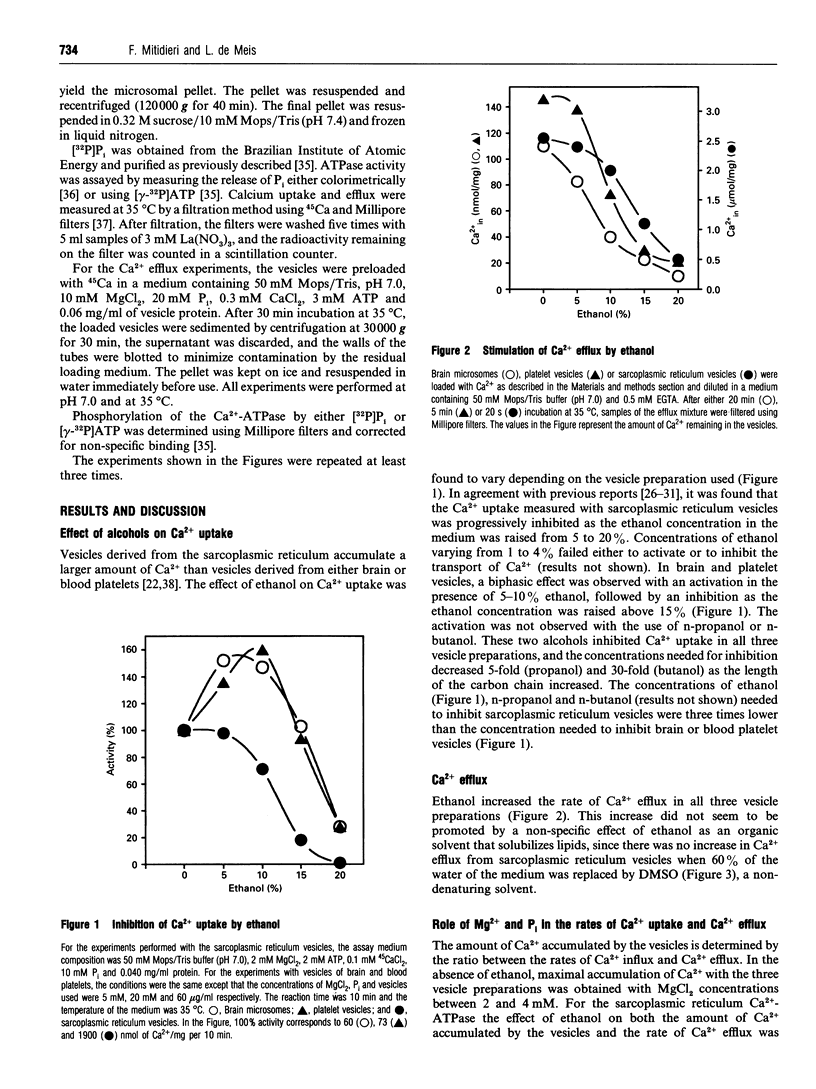
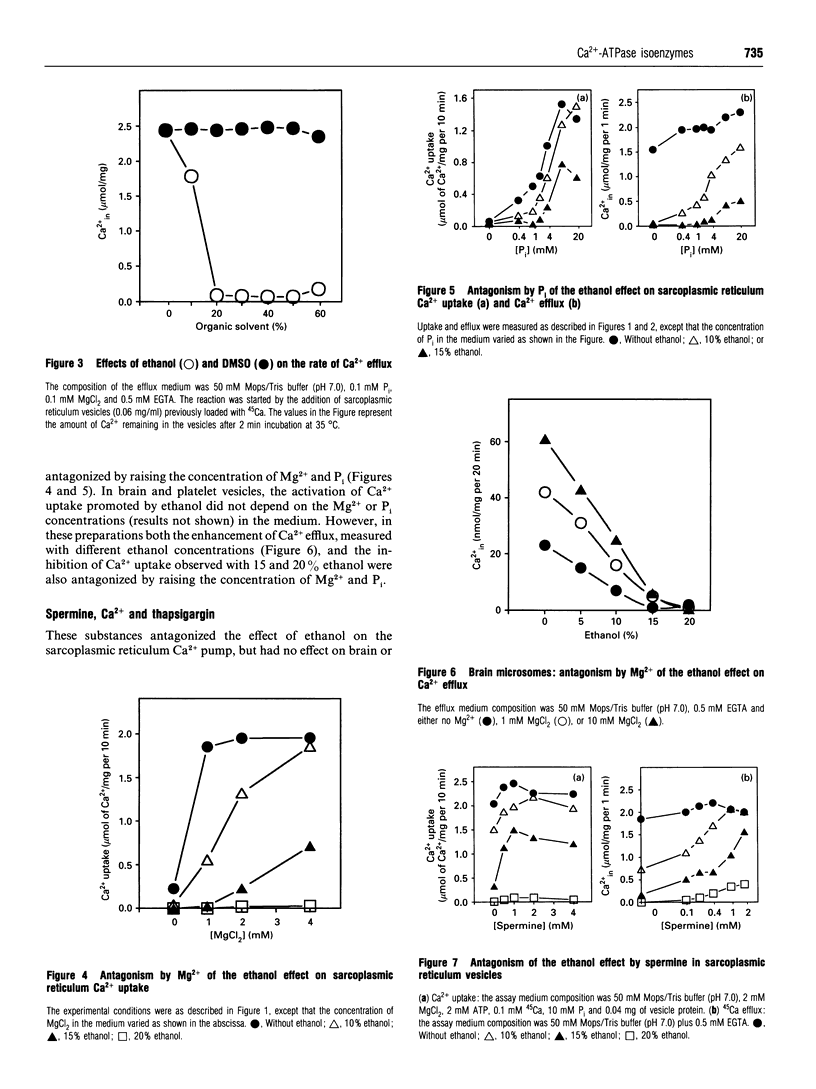
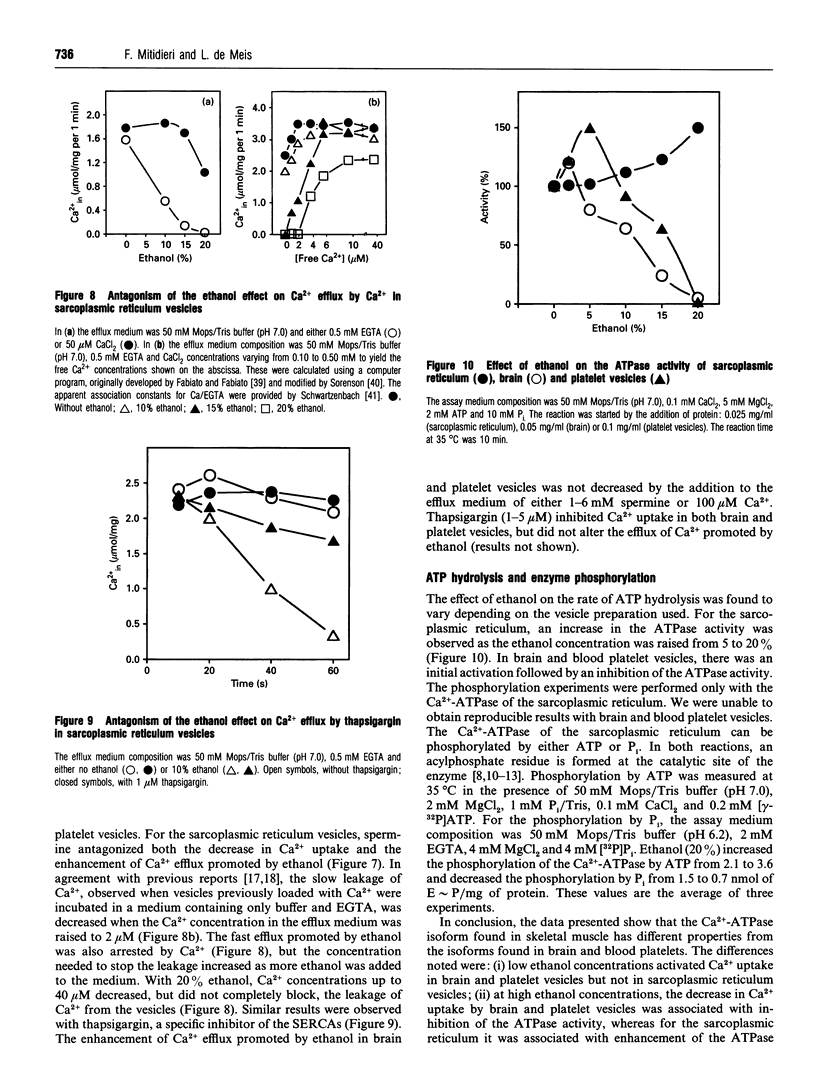
The effects of ethanol on different sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-transport ATPases (SERCAs) were studied. In sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles, ethanol concentrations varying from 5 to 20% promoted a progressive inhibition of Ca2+ uptake, enhancement of Ca2+ efflux, activation of the ATPase activity, increase of the enzyme phosphorylation by ATP and inhibition of enzyme phosphorylation by P1. The effects of ethanol on Ca2+ uptake and Ca2+ efflux were antagonized by Mg2+, P(i) and spermine. The increased efflux promoted by ethanol was antagonized by Ca2+ and thapsigargin. In brain and platelet vesicles a biphasic effect of ethanol was observed, so that activation occurred at low concentrations (5-10%) and inhibition at higher concentrations. The activation was not observed with the use of n-propanol and n-butanol. Different from the situation in sarcoplasmic reticulum, the decrease of the Ca2+ uptake in brain and platelet vesicles was associated with an inhibition of the ATPase activity. Mg2+ and P(i) antagonized the enhancement of Ca2+ efflux and the inhibition of Ca2+ uptake promoted by ethanol. However, thapsigargin and Ca2+ did not arrest the Ca2+ efflux promoted by ethanol in brain and platelet preparations. These results suggest that, in sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles, ethanol uncouples the pump, promoting its activity as a Ca2+ channel. The SERCA isoform found in skeletal muscle has different properties from the isoforms found in brain and blood platelets.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bobe R., Bredoux R., Wuytack F., Quarck R., Kovàcs T., Papp B., Corvazier E., Magnier C., Enouf J. The rat platelet 97-kDa Ca2+ATPase isoform is the sarcoendoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ATPase 3 protein. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1417–1424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandl C. J., deLeon S., Martin D. R., MacLennan D. H. Adult forms of the Ca2+ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Expression in developing skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3768–3774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burk S. E., Lytton J., MacLennan D. H., Shull G. E. cDNA cloning, functional expression, and mRNA tissue distribution of a third organellar Ca2+ pump. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18561–18568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso C. M., De Meis L. Modulation by fatty acids of Ca2+ fluxes in sarcoplasmic-reticulum vesicles. Biochem J. 1993 Nov 15;296(Pt 1):49–52. doi: 10.1042/bj2960049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho M. G., de Souza D. G., de Meis L. On a possible mechanism of energy conservation in sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 25;251(12):3629–3636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiesi M., Inesi G. The use of quench reagents for resolution of single transport cycles in sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10370–10377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Meis L., Tuena de Gómez Puyou M., Gómez Puyou A. Inhibition of mitochondrial F1 ATPase and sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase by hydrophobic molecules. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):343–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13796.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eletr S., Inesi G. Phospholipid orientation in sarcoplasmic membranes: spin-label ESR and proton MNR studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 1;282(1):174–179. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90321-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enouf J., Bredoux R., Papp B., Djaffar I., Lompré A. M., Kieffer N., Gayet O., Clemetson K., Wuytack F., Rosa J. P. Human platelets express the SERCA2-b isoform of Ca(2+)-transport ATPase. Biochem J. 1992 Aug 15;286(Pt 1):135–140. doi: 10.1042/bj2860135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J Physiol (Paris) 1979;75(5):463–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman S. A., Verkman A. S., Dix J. A., Solomon A. K. n-Alkanols and halothane inhibit red cell anion transport and increase band 3 conformational change rate. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 27;24(18):4859–4866. doi: 10.1021/bi00339a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galina A., de Meis L. Ca2+ translocation and catalytic activity of the sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. Modulation by ATP, Ca2+, and Pi. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):17978–17982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes U., Møller J. V. The Ca2+ permeability of sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. II. Ca2+ efflux in the energized state of the calcium pump. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Oct 12;734(2):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara K., Kasai M. The mechanism of increase in the ATPase activity of sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles treated with n-alcohols. J Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(4):1005–1017. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasselbach W., Oetliker H. Energetics and electrogenicity of the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:325–339. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.001545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inesi G. Mechanism of calcium transport. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:573–601. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.003041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo M., Kasai M. The effects of n-alcohols on sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 6;311(3):391–399. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90319-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Peuch C. J., Le Peuch D. A., Katz S., Demaille J. G., Hincke M. T., Bredoux R., Enouf J., Levy-Toledano S., Caen J. Regulation of calcium accumulation and efflux from platelet vesicles. Possible role for cyclic-AMP-dependent phosphorylation and calmodulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jun 23;731(3):456–464. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes C. M., Louro S. R. The effects of n-alkanols on the lipid/protein interface of Ca(2+)-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 9;1070(2):467–473. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90088-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lytton J., Zarain-Herzberg A., Periasamy M., MacLennan D. H. Molecular cloning of the mammalian smooth muscle sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):7059–7065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H., Brandl C. J., Korczak B., Green N. M. Amino-acid sequence of a Ca2+ + Mg2+-dependent ATPase from rabbit muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum, deduced from its complementary DNA sequence. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):696–700. doi: 10.1038/316696a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McWhirter J. M., Gould G. W., East J. M., Lee A. G. A kinetic model for Ca2+ efflux mediated by the Ca2+ + Mg2+-activated ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 1;245(3):713–721. doi: 10.1042/bj2450713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melgunov V. I., Jindal S., Belikova M. P. Short-chain alkanols and the functional efficiency of the Ca pump in the sarcoplasmic reticulum of rabbit skeletal muscles. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 25;227(2):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80888-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi S. T., Flick J. L., Rubin E. Ethanol increases calcium permeability of heavy sarcoplasmic reticulum of skeletal muscle. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Sep;233(2):588–594. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90483-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petretski J. H., Wolosker H., de Meis L. Activation of Ca2+ uptake and inhibition of reversal of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ pump by aromatic compounds. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20339–20343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorenson M. M., Reuben J. P., Eastwood A. B., Orentlicher M., Katz G. M. Functional heterogeneity of the sarcoplasmic reticulum within sarcomeres of skinned muscle fibers. J Membr Biol. 1980 Mar 31;53(1):1–17. doi: 10.1007/BF01871168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C. Twenty questions concerning the reaction cycle of the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984;17(2):123–151. doi: 10.3109/10409238409113603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolosker H., Pacheco A. G., de Meis L. Local anesthetics induce fast Ca2+ efflux through a nonenergized state of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5785–5789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuytack F., Papp B., Verboomen H., Raeymaekers L., Dode L., Bobe R., Enouf J., Bokkala S., Authi K. S., Casteels R. A sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase 3-type Ca2+ pump is expressed in platelets, in lymphoid cells, and in mast cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1410–1416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meis L. Approaches to studying the mechanisms of ATP synthesis in sarcoplasmic reticulum. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:190–206. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57075-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meis L. Fast efflux of Ca2+ mediated by the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2(+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5736–5742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meis L., Inesi G. Functional evidence of a transmembrane channel within the Ca2+ transport ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. FEBS Lett. 1992 Mar 24;299(1):33–35. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80093-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meis L., Suzano V. A., Inesi G. Functional interactions of catalytic site and transmembrane channel in the sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18848–18851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meis L., Suzano V. A. Uncoupling of muscle and blood platelets Ca2+ transport ATPases by heparin. Regulation by K+. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 20;269(20):14525–14529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meis L., Vianna A. L. Energy interconversion by the Ca2+-dependent ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:275–292. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


