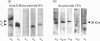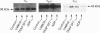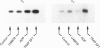Abstract
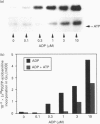
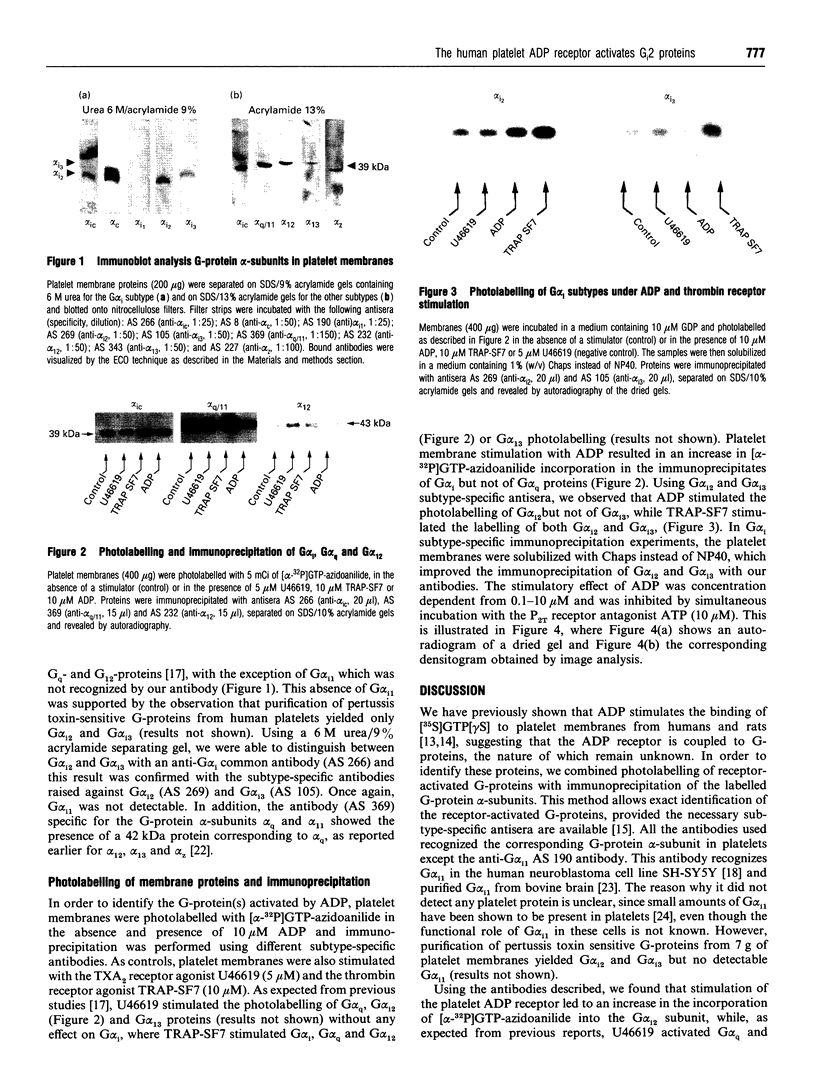
We have previously shown that platelet ADP receptors are coupled to G-proteins by measuring the binding of [35S]guanosine-5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate ([35S]GTP gamma S) to human platelet membranes stimulated with ADP. In order to identify the activated G-proteins, we used an approach which combines photolabelling of receptor-activated G-proteins with 4-azidoanilido-[alpha-32P]GTP and immunoprecipitation of the G-protein alpha-subunits with subtype-specific antibodies. Stimulation of human platelet membranes with ADP resulted in an increase in 4-azidoanilido-[alpha-32P]GTP incorporation into the immunoprecipitates of G alpha i but not of G alpha q proteins, whereas stimulation with the thromboxane analogue U46619 resulted in an increase in 4-azidoanilido-[alpha-32P]GTP incorporation into the immunoprecipitates of G alpha q but not of G alpha i proteins, and thrombin activated both G-proteins. This effect of ADP was concentration dependent and inhibited by the class P2 purinoceptor (P2T) antagonist ATP. Using specific antisera against subtypes of Gi proteins, we found that ADP stimulated labelling of the G alpha 12 immunoprecipitate, but not of the G alpha 13 precipitate. G alpha i1 was not detectable by immunoblotting of platelet membrane proteins. These data suggest that ADP inhibits cAMP formation by activation of G alpha 12 proteins and add evidence in support of the hypothesis that human platelet ADP receptors do not activate PLC through Gq activation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cattaneo M., Lecchi A., Randi A. M., McGregor J. L., Mannucci P. M. Identification of a new congenital defect of platelet function characterized by severe impairment of platelet responses to adenosine diphosphate. Blood. 1992 Dec 1;80(11):2787–2796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazenave J. P., Hemmendinger S., Beretz A., Sutter-Bay A., Launay J. L'agrégation plaquettaire: outil d'investigation clinique et d'étude pharmacologique. Méthodologie. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1983;41(3):167–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W. Aggregin: a platelet ADP receptor that mediates activation. FASEB J. 1990 Mar;4(5):1425–1435. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.5.2407587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cristalli G., Mills D. C. Identification of a receptor for ADP on blood platelets by photoaffinity labelling. Biochem J. 1993 May 1;291(Pt 3):875–881. doi: 10.1042/bj2910875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubyak G. R., el-Moatassim C. Signal transduction via P2-purinergic receptors for extracellular ATP and other nucleotides. Am J Physiol. 1993 Sep;265(3 Pt 1):C577–C606. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.3.C577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feliste R., Simon M. F., Chap H., Douste-Blazy L., Defreyn G., Maffrand J. P. Effect of PCR 4099 on ADP-induced calcium movements and phosphatidic acid production in rat platelets. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 1;37(13):2559–2564. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90246-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gachet C., Cazenave J. P. ADP induced blood platelet activation: a review. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1991;33(5):347–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gachet C., Cazenave J. P., Ohlmann P., Bouloux C., Defreyn G., Driot F., Maffrand J. P. The thienopyridine ticlopidine selectively prevents the inhibitory effects of ADP but not of adrenaline on cAMP levels raised by stimulation of the adenylate cyclase of human platelets by PGE1. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Dec 15;40(12):2683–2687. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90587-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gachet C., Cazenave J. P., Ohlmann P., Hilf G., Wieland T., Jakobs K. H. ADP receptor-induced activation of guanine-nucleotide-binding proteins in human platelet membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jul 1;207(1):259–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gachet C., Savi P., Ohlmann P., Maffrand J. P., Jakobs K. H., Cazenave J. P. ADP receptor induced activation of guanine nucleotide binding proteins in rat platelet membranes--an effect selectively blocked by the thienopyridine clopidogrel. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Jul 6;68(1):79–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger J., Walter U. Properties and regulation of human platelet cation channels. EXS. 1993;66:281–288. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7327-7_22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinsch K. D., Tychowiecka I., Gausepohl H., Frank R., Rosenthal W., Schultz G. Tissue distribution of beta 1- and beta 2-subunits of regulatory guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Sep 4;1013(1):60–67. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90128-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hourani S. M., Hall D. A. Receptors for ADP on human blood platelets. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Apr;15(4):103–108. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laugwitz K. L., Offermanns S., Spicher K., Schultz G. mu and delta opioid receptors differentially couple to G protein subtypes in membranes of human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Neuron. 1993 Feb;10(2):233–242. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90314-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laugwitz K. L., Spicher K., Schultz G., Offermanns S. Identification of receptor-activated G proteins: selective immunoprecipitation of photolabeled G-protein alpha subunits. Methods Enzymol. 1994;237:283–294. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(94)37069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maffrand J. P., Bernat A., Delebassée D., Defreyn G., Cazenave J. P., Gordon J. L. ADP plays a key role in thrombogenesis in rats. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Apr 8;59(2):225–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Mullaney I., McCallum J. F. Distribution and relative levels of expression of the phosphoinositidase-C-linked G-proteins Gq alpha and G11 alpha: absence of G11 alpha in human platelets and haemopoietically derived cell lines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Nov 7;1179(2):208–212. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(93)90143-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murgo A. J., Contrera J. G., Sistare F. D. Evidence for separate calcium-signaling P2T and P2U purinoceptors in human megakaryocytic Dami cells. Blood. 1994 Mar 1;83(5):1258–1267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murgo A. J., Sistare F. D. K562 leukemia cells express P2T (adenosine diphosphate) purinergic receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 May;261(2):580–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurden P., Savi P., Heilmann E., Bihour C., Herbert J. M., Maffrand J. P., Nurden A. An inherited bleeding disorder linked to a defective interaction between ADP and its receptor on platelets. Its influence on glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex function. J Clin Invest. 1995 Apr;95(4):1612–1622. doi: 10.1172/JCI117835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nürnberg B., Spicher K., Harhammer R., Bosserhoff A., Frank R., Hilz H., Schultz G. Purification of a novel G-protein alpha 0-subtype from mammalian brain. Biochem J. 1994 Jun 1;300(Pt 2):387–394. doi: 10.1042/bj3000387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offermanns S., Laugwitz K. L., Spicher K., Schultz G. G proteins of the G12 family are activated via thromboxane A2 and thrombin receptors in human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):504–508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offermanns S., Schultz G., Rosenthal W. Identification of receptor-activated G proteins with photoreactive GTP analog, [alpha-32P]GTP azidoanilide. Methods Enzymol. 1991;195:286–301. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)95174-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonds W. F., Goldsmith P. K., Codina J., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. M. Gi2 mediates alpha 2-adrenergic inhibition of adenylyl cyclase in platelet membranes: in situ identification with G alpha C-terminal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7809–7813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. G., Woolkalis M. J., Poncz M., Manning D. R., Gewirtz A. M., Brass L. F. Identification of the pertussis toxin-sensitive G proteins in platelets, megakaryocytes, and human erythroleukemia cells. Blood. 1990 Aug 15;76(4):721–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]