Abstract
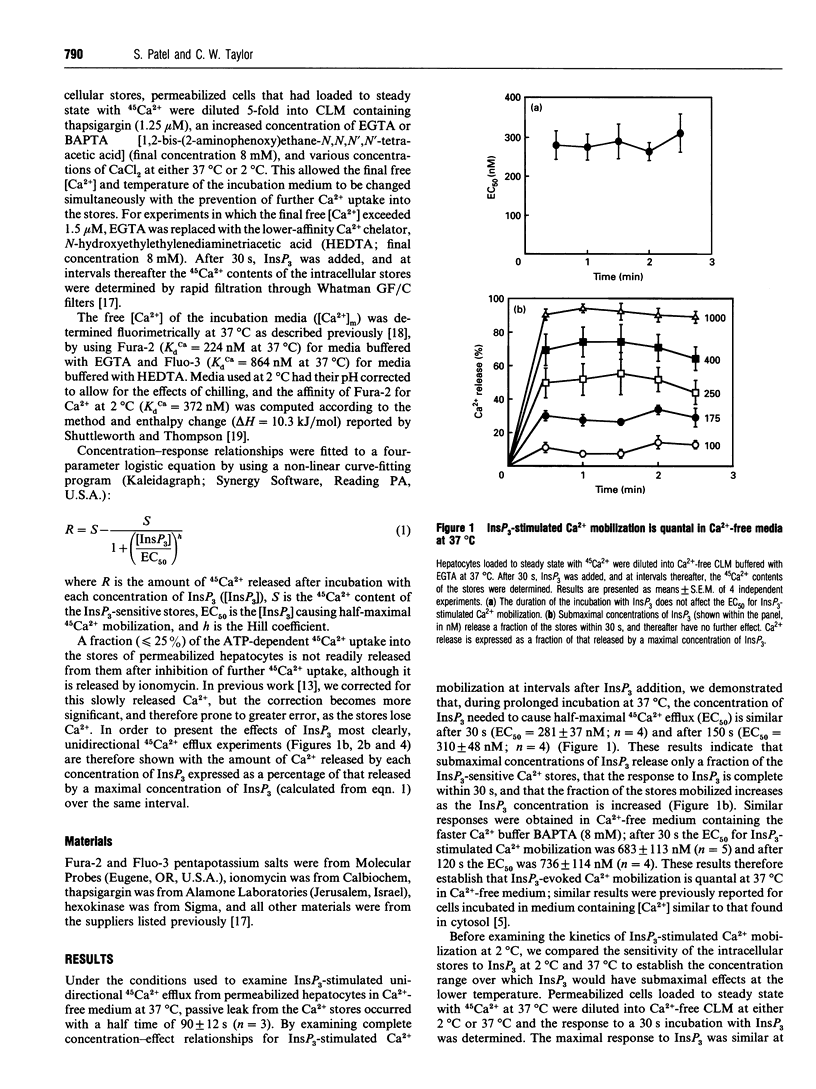
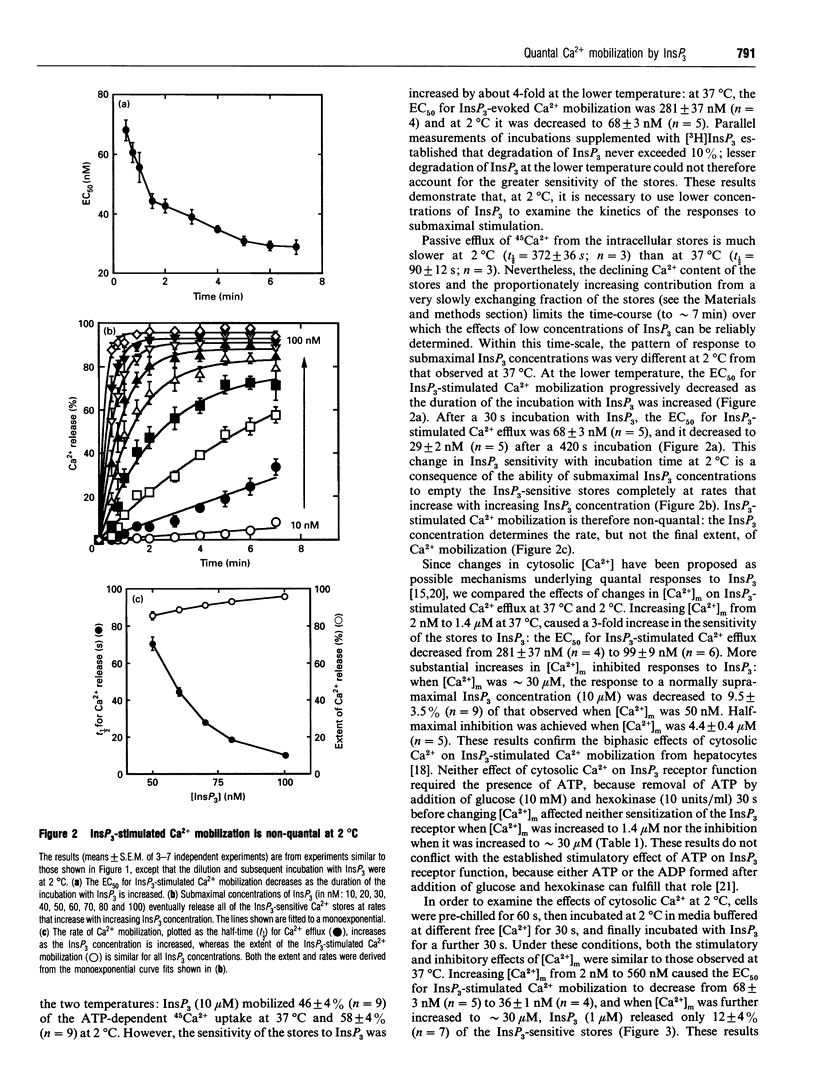
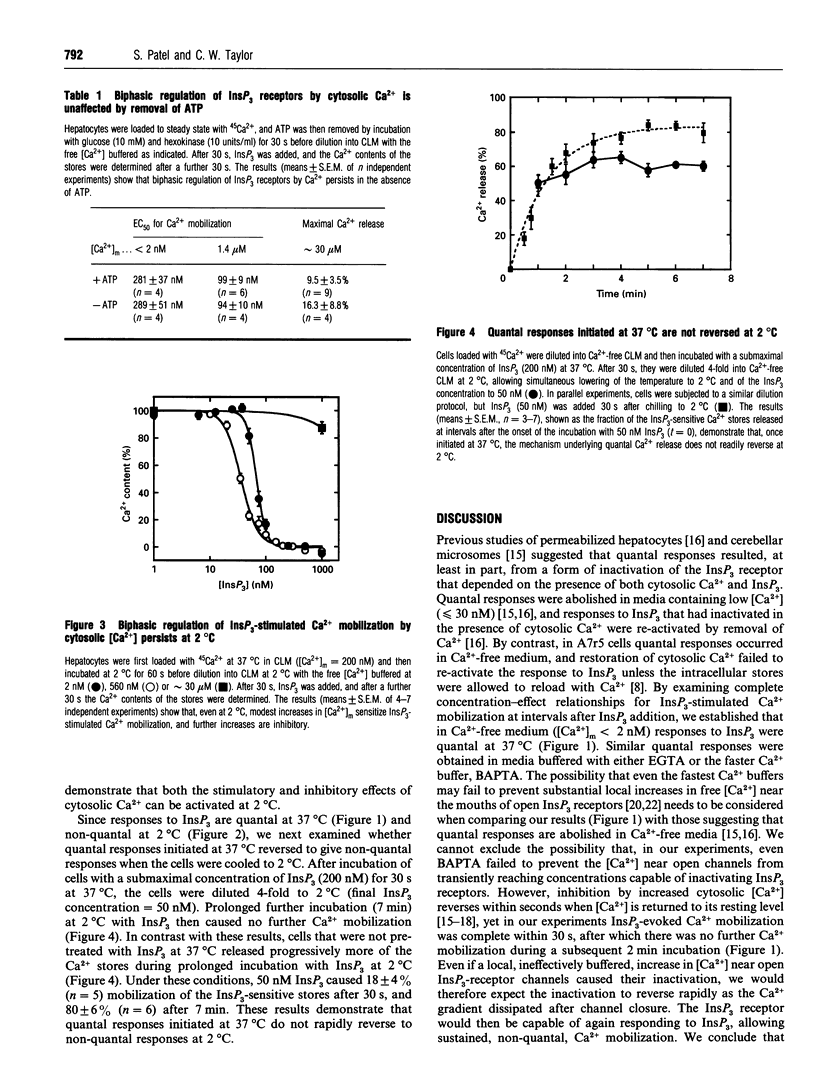
Submaximal concentrations of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) rapidly release only a fraction of the InsP3-sensitive intracellular Ca2+ stores, despite the ability of further increases in InsP3 concentration to evoke further Ca2+ release. The mechanisms underlying such quantal Ca2+ mobilization are not understood, but have been proposed to involve regulatory effects of cytosolic Ca2+ on InsP3 receptors. By examining complete concentration-effect relationships for InsP3-stimulated 45Ca2+ efflux from the intracellular stores of permeabilized hepatocytes, we demonstrate that, at 37 degrees C, responses to InsP3 are quantal in Ca(2+)-free media heavily buffered with either EGTA or BAPTA [1,2-bis-(2-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N',N'-tetra-acetic acid]. Lower concentrations of InsP3 were used to examine the kinetics of Ca2+ mobilization at 2 degrees C, because at the lower temperature the stores were more sensitive to InsP3: the concentration of InsP3 causing half-maximal Ca2+ release (EC50) after a 30 s incubation decreased from 281 +/- 37 nM at 37 degrees C to 68 +/- 3 nM at 2 degrees C. At 2 degrees C, the EC50 for InsP3-stimulated Ca2+ mobilization decreased as the duration of exposure to InsP3 was increased: the EC50 was 68 +/- 3 nM after 30 s, and 29 +/- 2 nM after 420 s. InsP3-stimulated Ca2+ mobilization is therefore non-quantal at 2 degrees C: InsP3 concentration determines the rate, but not the extent, of Ca2+ release. By initiating quantal responses to InsP3 at 37 degrees C and then simultaneously diluting and chilling cells to 2 degrees C, we demonstrated that the changes that underlie quantal responses do not rapidly reverse at 2 degrees C. At both 37 degrees C and 2 degrees C, modest increases in cytosolic Ca2+ increased the sensitivity of the stores to InsP3, whereas further increases were inhibitory; both Ca2+ effects persisted after prior removal of ATP. We conclude that the effects of Ca2+ on InsP3 receptors are unlikely either to be enzyme-mediated or to underlie the quantal pattern of Ca2+ release evoked by InsP3.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bootman M. D., Berridge M. J., Taylor C. W. All-or-nothing Ca2+ mobilization from the intracellular stores of single histamine-stimulated HeLa cells. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:163–178. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champeil P., Combettes L., Berthon B., Doucet E., Orlowski S., Claret M. Fast kinetics of calcium release induced by myo-inositol trisphosphate in permeabilized rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17665–17673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheek T. R., Berridge M. J., Moreton R. B., Stauderman K. A., Murawsky M. M., Bootman M. D. Quantal Ca2+ mobilization by ryanodine receptors is due to all-or-none release from functionally discrete intracellular stores. Biochem J. 1994 Aug 1;301(Pt 3):879–883. doi: 10.1042/bj3010879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheek T. R., Moreton R. B., Berridge M. J., Stauderman K. A., Murawsky M. M., Bootman M. D. Quantal Ca2+ release from caffeine-sensitive stores in adrenal chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 25;268(36):27076–27083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combettes L., Hannaert-Merah Z., Coquil J. F., Rousseau C., Claret M., Swillens S., Champeil P. Rapid filtration studies of the effect of cytosolic Ca2+ on inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced 45Ca2+ release from cerebellar microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 1;269(26):17561–17571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danoff S. K., Supattapone S., Snyder S. H. Characterization of a membrane protein from brain mediating the inhibition of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor binding by calcium. Biochem J. 1988 Sep 15;254(3):701–705. doi: 10.1042/bj2540701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard M., Erne P. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced calcium release in permeabilized platelets is coupled to hydrolysis of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate to inositol 1,4-bisphosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Aug 31;195(1):19–24. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Calcium-induced release of calcium from the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):C1–14. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.1.C1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris C. D., Cameron A. M., Huganir R. L., Snyder S. H. Quantal calcium release by purified reconstituted inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors. Nature. 1992 Mar 26;356(6367):350–352. doi: 10.1038/356350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch E. A., Turner T. J., Goldin S. M. Calcium as a coagonist of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced calcium release. Science. 1991 Apr 19;252(5004):443–446. doi: 10.1126/science.2017683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galione A., McDougall A., Busa W. B., Willmott N., Gillot I., Whitaker M. Redundant mechanisms of calcium-induced calcium release underlying calcium waves during fertilization of sea urchin eggs. Science. 1993 Jul 16;261(5119):348–352. doi: 10.1126/science.8392748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajnóczky G., Thomas A. P. The inositol trisphosphate calcium channel is inactivated by inositol trisphosphate. Nature. 1994 Aug 11;370(6489):474–477. doi: 10.1038/370474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose K., Iino M. Heterogeneity of channel density in inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive Ca2+ stores. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):791–794. doi: 10.1038/372791a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M. Biphasic Ca2+ dependence of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca release in smooth muscle cells of the guinea pig taenia caeci. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Jun;95(6):1103–1122. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.6.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. 'Quantal' Ca2+ release and the control of Ca2+ entry by inositol phosphates--a possible mechanism. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 9;263(1):5–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80692-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindman L. A., Meyer T. Use of intracellular Ca2+ stores from rat basophilic leukemia cells to study the molecular mechanism leading to quantal Ca2+ release by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Biochemistry. 1993 Feb 9;32(5):1270–1277. doi: 10.1021/bi00056a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall I. C., Taylor C. W. Biphasic effects of cytosolic Ca2+ on Ins(1,4,5)P3-stimulated Ca2+ mobilization in hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13214–13220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall I. C., Taylor C. W. Two calcium-binding sites mediate the interconversion of liver inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors between three conformational states. Biochem J. 1994 Jul 15;301(Pt 2):591–598. doi: 10.1042/bj3010591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Stryer L. Transient calcium release induced by successive increments of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3841–3845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Wensel T., Stryer L. Kinetics of calcium channel opening by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 9;29(1):32–37. doi: 10.1021/bi00453a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Missiaen L., De Smedt H., Droogmans G., Casteels R. Ca2+ release induced by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate is a steady-state phenomenon controlled by luminal Ca2+ in permeabilized cells. Nature. 1992 Jun 18;357(6379):599–602. doi: 10.1038/357599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muallem S., Pandol S. J., Beeker T. G. Hormone-evoked calcium release from intracellular stores is a quantal process. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):205–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn D. L., Taylor C. W. Liver inositol, 1,4,5-trisphosphate-binding sites are the Ca2(+)-mobilizing receptors. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 15;270(1):227–232. doi: 10.1042/bj2700227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn D. L., Taylor C. W. Luminal Ca2+ increases the sensitivity of Ca2+ stores to inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Jan;41(1):115–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldershaw K. A., Nunn D. L., Taylor C. W. Quantal Ca2+ mobilization stimulated by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in permeabilized hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1991 Sep 15;278(Pt 3):705–708. doi: 10.1042/bj2780705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parys J. B., Missiaen L., De Smedt H., Casteels R. Loading dependence of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ release in the clonal cell line A7r5. Implications for the mechanism of quantal Ca2+ release. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):25206–25212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro-do-Valle R. M., Poitras M., Boulay G., Guillemette G. The important discrepancy between the apparent affinity observed in Ca2+ mobilization studies and the Kd measured in binding studies is a consequence of the quantal process by which inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate releases Ca2+ from bovine adrenal cortex microsomes. Cell Calcium. 1994 Jan;15(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(94)90106-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuttleworth T. J. Ca2+ release from inositol trisphosphate-sensitive stores is not modulated by intraluminal [Ca2+]. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3573–3576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuttleworth T. J., Thompson J. L. Effect of temperature on receptor-activated changes in [Ca2+]i and their determination using fluorescent probes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1410–1414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. D. Buffering of calcium in the vicinity of a channel pore. Cell Calcium. 1992 Mar;13(3):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(92)90046-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swillens S., Combettes L., Champeil P. Transient inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ release: a model based on regulatory Ca(2+)-binding sites along the permeation pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):10074–10078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.10074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. W. Kinetics of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-stimulated Ca2+ mobilization. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1992;26:109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. W., Marshall I. C. Calcium and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors: a complex relationship. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):403–407. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. W., Potter B. V. The size of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive Ca2+ stores depends on inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate concentration. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 15;266(1):189–194. doi: 10.1042/bj2660189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. W., Richardson A. Structure and function of inositol trisphosphate receptors. Pharmacol Ther. 1991;51(1):97–137. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(91)90043-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang B. X., Zhao H., Muallem S. Ca(2+)-dependent kinase and phosphatase control inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-mediated Ca2+ release. Modification by agonist stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):10997–11001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


