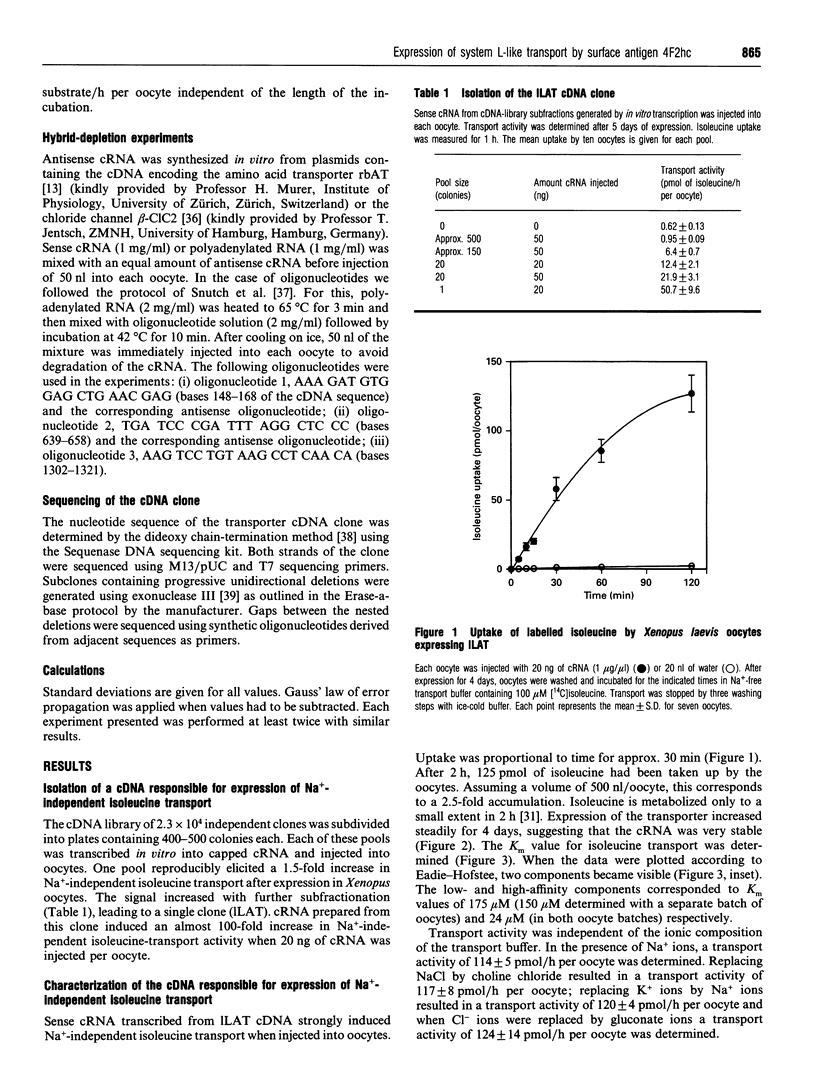
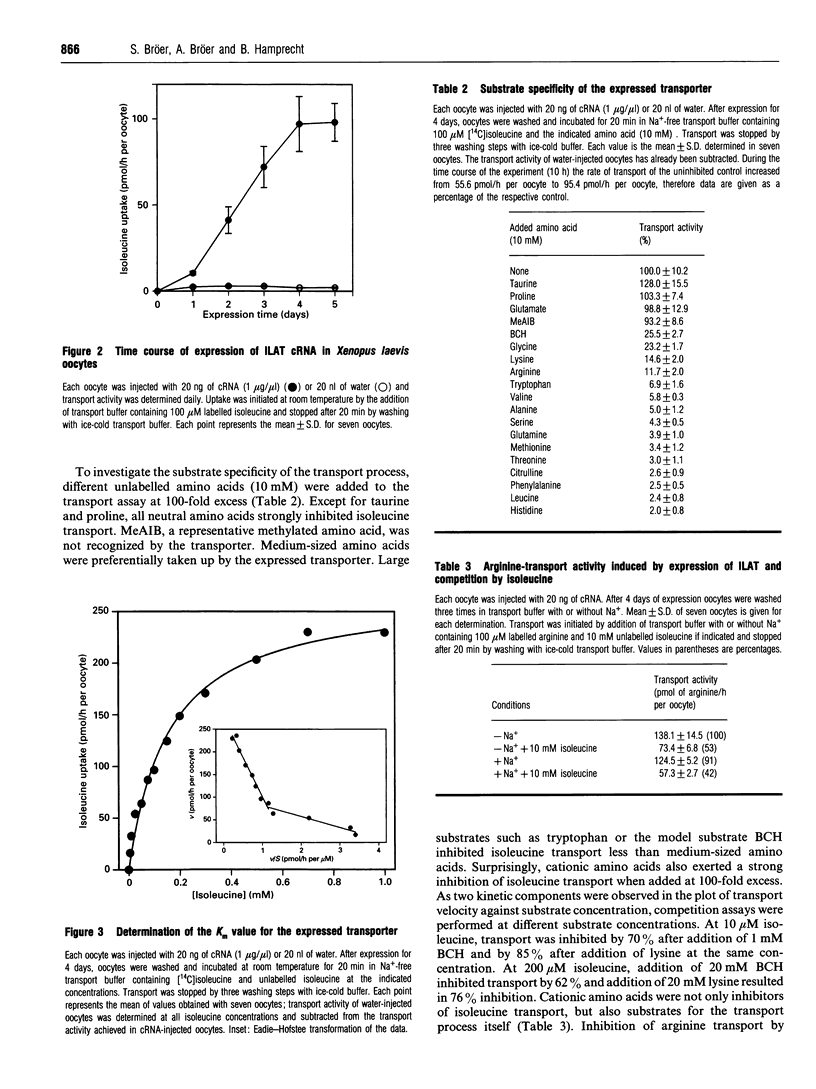
Abstract
Mammalian cells possess a variety of amino acid-transport systems with overlapping substrate specificity. System L is one of the major amino acid-transport systems in all non-epithelial cells. Its molecular structure is not known. To clone the neutral amino acid-transporter system L, we followed an expression cloning strategy using Xenopus laevis oocytes. A cDNA library derived from C6-BU-1 rat glioma cells was used as a source, because high expression of system L activity could be demonstrated with polyadenylated RNA isolated from these cells, when injected into Xenopus laevis oocytes [Bröer, Bröer and Hamprecht (1994) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1192, 95-100]. A single clone (ILAT) was identified, the sense cRNA of which, on injection into Xenopus laevis oocytes, stimulated sodium-independent isoleucine transport by about 100-fold. Further characterization revealed that transport of cationic amino acids was also stimulated. Sequencing of the cDNA showed that the identified clone is the heavy chain of the rat 4F2 surface antigen, a marker of tumour cells and activated lymphocytes. Uptake of neutral and cationic amino acids was not stimulated by the presence of Na+ ions. Antisense cRNA transcribed from this clone or antisense oligonucleotides, when co-injected with polyadenylated RNA from C6-BU-1 rat glioma cells, completely suppressed system L-like isoleucine-transport activity. We conclude that ILAT is necessary for expression of system L-like amino acid-transport activity by polyadenylated RNA from C6-BU-1 rat glioma cells.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. D., Kerlavage A. R., Fields C., Venter J. C. 3,400 new expressed sequence tags identify diversity of transcripts in human brain. Nat Genet. 1993 Jul;4(3):256–267. doi: 10.1038/ng0793-256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amano T., Hamprecht B., Kemper W. High activity of choline acetyltransferase induced in neuroblastoma x glia hybrid cells. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Apr;85(2):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90142-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertran J., Magagnin S., Werner A., Markovich D., Biber J., Testar X., Zorzano A., Kühn L. C., Palacin M., Murer H. Stimulation of system y(+)-like amino acid transport by the heavy chain of human 4F2 surface antigen in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5606–5610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertran J., Werner A., Moore M. L., Stange G., Markovich D., Biber J., Testar X., Zorzano A., Palacin M., Murer H. Expression cloning of a cDNA from rabbit kidney cortex that induces a single transport system for cystine and dibasic and neutral amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5601–5605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookes N. Effect of intracellular glutamine on the uptake of large neutral amino acids in astrocytes: concentrative Na(+)-independent transport exhibits metastability. J Neurochem. 1992 Jul;59(1):227–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb08895.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookes N. Neutral amino acid transport in astrocytes: characterization of Na+-dependent and Na+-independent components of alpha-aminoisobutyric acid uptake. J Neurochem. 1988 Dec;51(6):1913–1918. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bröer S., Bröer A., Hamprecht B. Expression of Na+-independent isoleucine transport activity from rat brain in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Jun 1;1192(1):95–100. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(94)90147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H. N., Albritton L. M., Kakuda D. K., MacLeod C. L. Gene-product designations for amino acid transporters. J Exp Biol. 1994 Nov;196:51–57. doi: 10.1242/jeb.196.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H. N., Handlogten M. E., Lam I., Tager H. S., Zand R. A bicyclic amino acid to improve discriminations among transport systems. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 25;244(6):1510–1520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H. N. On the strategy of kinetic discrimination of amino acid transport systems. J Membr Biol. 1985;84(2):97–103. doi: 10.1007/BF01872207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H. N. Role of amino acid transport and countertransport in nutrition and metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jan;70(1):43–77. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devés R., Chavez P., Boyd C. A. Identification of a new transport system (y+L) in human erythrocytes that recognizes lysine and leucine with high affinity. J Physiol. 1992 Aug;454:491–501. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eleno N., Devés R., Boyd C. A. Membrane potential dependence of the kinetics of cationic amino acid transport systems in human placenta. J Physiol. 1994 Sep 1;479(Pt 2):291–300. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Hemler M. E., Mann D. L., Eisenbarth G. S., Shelhamer J., Mostowski H. S., Thomas C. A., Strominger J. L., Fauci A. S. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody (4F2) that binds to human monocytes and to a subset of activated lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1409–1414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E., Strominger J. L. Characterization of antigen recognized by the monoclonal antibody (4F2): different molecular forms on human T and B lymphoblastoid cell lines. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):623–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakuda D. K., MacLeod C. L. Na(+)-independent transport (uniport) of amino acids and glucose in mammalian cells. J Exp Biol. 1994 Nov;196:93–108. doi: 10.1242/jeb.196.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai Y., Smith C. P., Hediger M. A. The elusive transporters with a high affinity for glutamate. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Sep;16(9):365–370. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90094-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong C. T., Yet S. F., Lever J. E. Cloning and expression of a mammalian Na+/amino acid cotransporter with sequence similarity to Na+/glucose cotransporters. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1509–1512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod C. L., Finley K. D., Kakuda D. K. y(+)-type cationic amino acid transport: expression and regulation of the mCAT genes. J Exp Biol. 1994 Nov;196:109–121. doi: 10.1242/jeb.196.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie B., Panayotova-Heiermann M., Loo D. D., Lever J. E., Wright E. M. SAAT1 is a low affinity Na+/glucose cotransporter and not an amino acid transporter. A reinterpretation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 9;269(36):22488–22491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao M., Kubo K., Hara A., Hirohashi N., Futagami E., Shichijo S., Sagawa K., Itoh K. A monoclonal antibody (H227) recognizing a new epitope of 4F2 molecular complex associated with T cell activation. Cell Immunol. 1993 Nov;152(1):226–233. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1993.1282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OXENDER D. L., CHRISTENSEN H. N. DISTINCT MEDIATING SYSTEMS FOR THE TRANSPORT OF NEUTRAL AMINO ACIDS BY THE EHRLICH CELL. J Biol Chem. 1963 Nov;238:3686–3699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacín M. A new family of proteins (rBAT and 4F2hc) involved in cationic and zwitterionic amino acid transport: a tale of two proteins in search of a transport function. J Exp Biol. 1994 Nov;196:123–137. doi: 10.1242/jeb.196.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardridge W. M., Oldendorf W. H. Transport of metabolic substrates through the blood-brain barrier. J Neurochem. 1977 Jan;28(1):5–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb07702.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmacek M. S., Karpinski B. A., Gottesdiener K. M., Thompson C. B., Leiden J. M. Structure, expression and regulation of the murine 4F2 heavy chain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1915–1931. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quackenbush E., Clabby M., Gottesdiener K. M., Barbosa J., Jones N. H., Strominger J. L., Speck S., Leiden J. M. Molecular cloning of complementary DNAs encoding the heavy chain of the human 4F2 cell-surface antigen: a type II membrane glycoprotein involved in normal and neoplastic cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6526–6530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafqat S., Velaz-Faircloth M., Guadaño-Ferraz A., Fremeau R. T., Jr Molecular characterization of neurotransmitter transporters. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Dec;7(12):1517–1529. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.12.7908408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotwell M. A., Jayme D. W., Kilberg M. S., Oxender D. L. Neutral amino acid transport systems in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5422–5427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snutch T. P., Leonard J. P., Gilbert M. M., Lester H. A., Davidson N. Rat brain expresses a heterogeneous family of calcium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3391–3395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su T. Z., Logsdon C. D., Oxender D. L. Chinese hamster ovary mRNA-dependent, Na(+)-independent L-leucine transport in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5281–5287. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Yan N., Udenfriend S. Expression cloning of a Na(+)-independent neutral amino acid transporter from rat kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):1–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira S., Di Grandi S., Kühn L. C. Primary structure of the human 4F2 antigen heavy chain predicts a transmembrane protein with a cytoplasmic NH2 terminus. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9574–9580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiemann A., Gründer S., Pusch M., Jentsch T. J. A chloride channel widely expressed in epithelial and non-epithelial cells. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):57–60. doi: 10.1038/356057a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Winkle L. J. Amino acid transport in developing animal oocytes and early conceptuses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 24;947(1):173–208. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Winkle L. J., Campione A. L., Gorman J. M. Na+-independent transport of basic and zwitterionic amino acids in mouse blastocysts by a shared system and by processes which distinguish between these substrates. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3150–3163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Winkle L. J., Kakuda D. K., MacLeod C. L. Multiple components of transport are associated with murine cationic amino acid transporter (mCAT) expression in Xenopus oocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 Feb 15;1233(2):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(94)00303-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach L., Handlogten M. E., Christensen H. N., Kilberg M. S. Evidence for two Na+-independent neutral amino acid transport systems in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Time-dependent changes in activity. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12006–12011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. G., Hediger M. A. Cloning of a rat kidney cDNA that stimulates dibasic and neutral amino acid transport and has sequence similarity to glucosidases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5596–5600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. G., Lee W. S., Kanai Y., Leiden J. M., Hediger M. A. The 4F2 antigen heavy chain induces uptake of neutral and dibasic amino acids in Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15285–15288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodlock T. J., Young D. A., Boal T. R., Lichtman M. A., Segel G. B. Phorbol ester-induced membrane proteins in chronic leukemic B-lymphocytes. Candidate proteins for the L-system amino acid transporter. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):16020–16027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao S. Y., Muzyka W. R., Elliott J. F., Cheeseman C. I., Young J. D. Poly(A)+ RNA from the mucosa of rat jejunum induces novel Na(+)-dependent and Na(+)-independent leucine transport activities in in oocytes of Xenopus laevis. Mol Membr Biol. 1994 Apr-Jun;11(2):109–118. doi: 10.3109/09687689409162228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


