Abstract
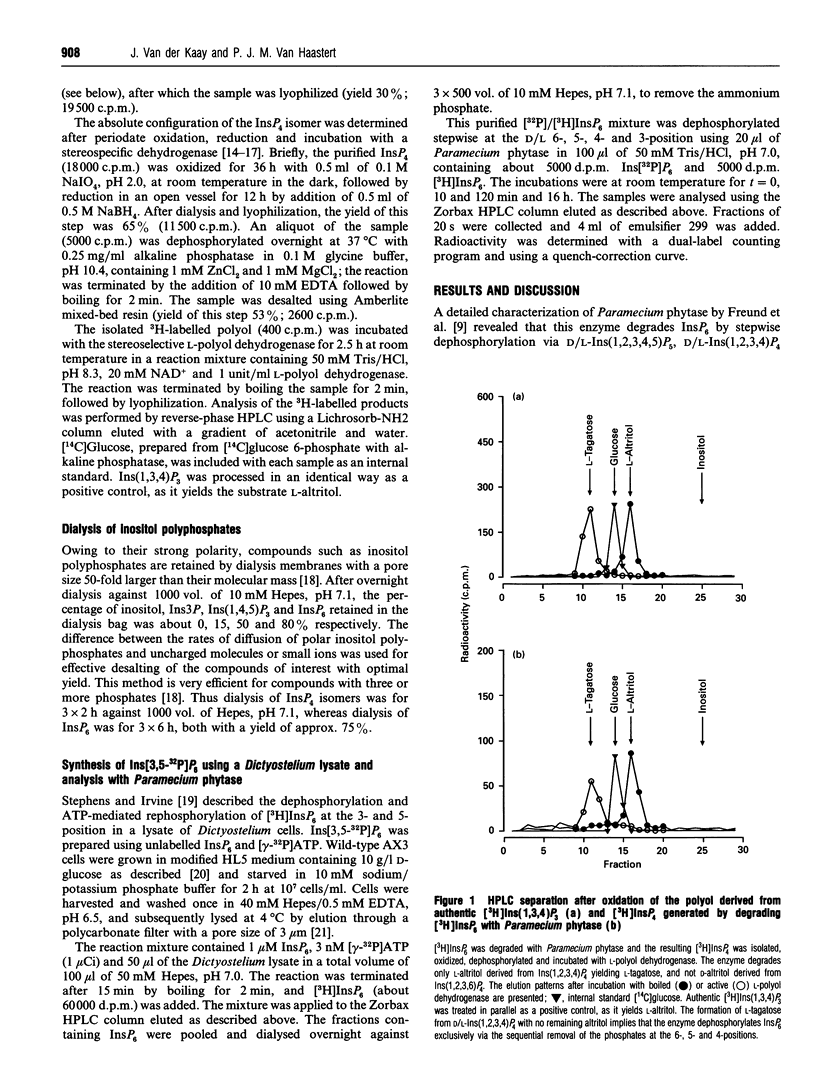
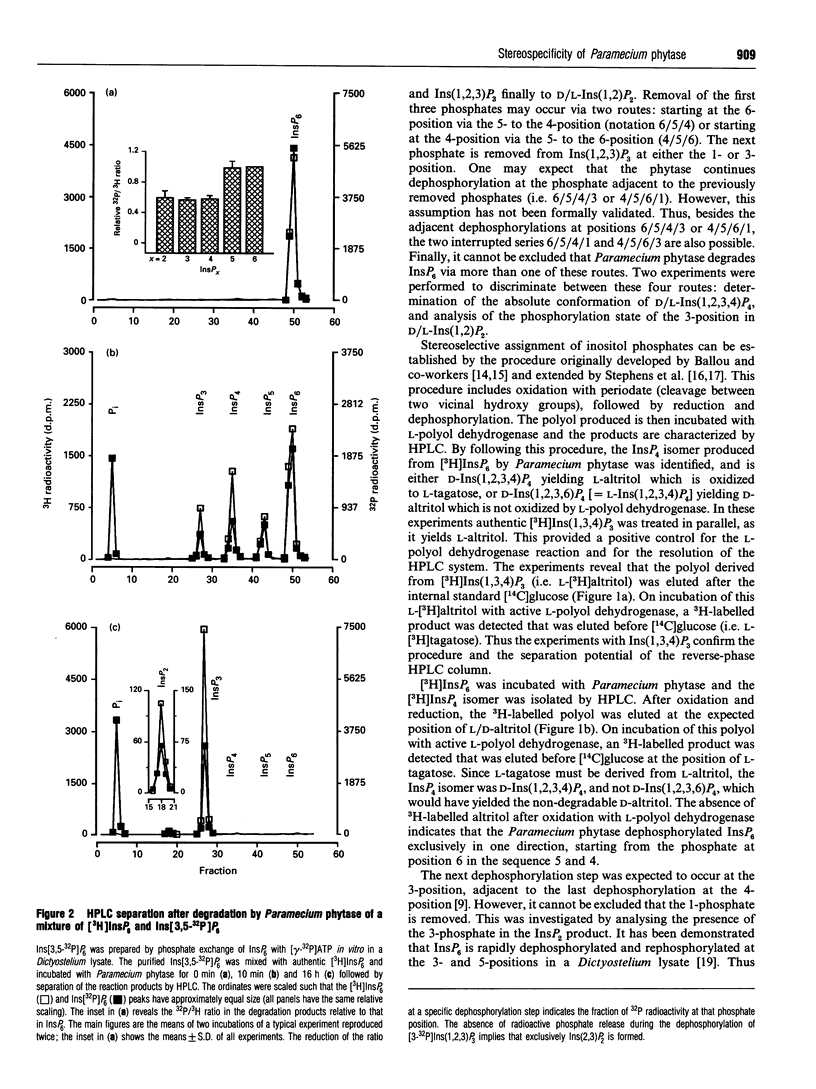
InsP6 is an abundant compound in many micro-organisms, plants and animal cells. Its function and route of synthesis are still largely unknown. Degradation of InsP6 is mediated by phytase, which in most organisms dephosphorylates InsP6 in a relatively non-specific way. In the micro-organism Paramecium, however, the enzyme has been shown to dephosphorylate InsP6 to InsP2 in a specific order, but its stereospecificity has not been established, i.e. the phosphates are removed in the sequence 6/5/4/3 or 6/5/4/1 or 4/5/6/1 or 4/5/6/3 [Freund, Mayr, Tietz and Schultz (1992) Eur. J. Biochem. 207, 359-367]. We have isolated the InsP4 intermediate and identified its absolute configuration as D-Ins(1,2,3,4)P4. Furthermore, degradation of [3,5-32P]InsP6 yielded a 32P-labelled InsP2 isomer, D-Ins(2,3)P2. These data demonstrate that Paramecium phytase removes the phosphates of InsP6 in the sequence 6/5/4/1. Knowing the stereochemical course of the enzyme, it can be used to elucidate the route of InsP6 synthesis, as it allows us to determine the specific radioactivity at individual positions of the molecular after pulse-labelling cells with [32P]P1 in vivo or [gamma-32P]ATP in vitro.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Drayer A. L., Van der Kaay J., Mayr G. W., Van Haastert P. J. Role of phospholipase C in Dictyostelium: formation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and normal development in cells lacking phospholipase C activity. EMBO J. 1994 Apr 1;13(7):1601–1609. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06423.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund W. D., Mayr G. W., Tietz C., Schultz J. E. Metabolism of inositol phosphates in the protozoan Paramecium. Characterization of a novel inositol-hexakisphosphate-dephosphorylating enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jul 1;207(1):359–367. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17058.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRADO C., BALLOU C. E. Myo-inositol phosphates obtained by alkaline hydrolysis of beef brain phosphoinositide. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jan;236:54–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greiner R., Konietzny U., Jany K. D. Purification and characterization of two phytases from Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 May 15;303(1):107–113. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guse A. H., Emmrich F. T-cell receptor-mediated metabolism of inositol polyphosphates in Jurkat T-lymphocytes. Identification of a D-myo-inositol 1,2,3,4,6-pentakisphosphate-2-phosphomonoesterase activity, a D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate-1/3-phosphatase activity and a D/L-myo-inositol 1,2,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate-1/3-kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24498–24502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Connolly T. M., Bansal V. S., Inhorn R. C., Ross T. S., Lips D. L. Inositol phosphates: synthesis and degradation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3051–3054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. B., Foray M. F., Klein G., Satre M. Identification of inositol hexaphosphate in 31P-NMR spectra of Dictyostelium discoideum amoebae. Relevance to intracellular pH determination. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Oct 22;931(1):16–25. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayr G. W. A novel metal-dye detection system permits picomolar-range h.p.l.c. analysis of inositol polyphosphates from non-radioactively labelled cell or tissue specimens. Biochem J. 1988 Sep 1;254(2):585–591. doi: 10.1042/bj2540585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy N. R., Sathe S. K., Salunkhe D. K. Phytates in legumes and cereals. Adv Food Res. 1982;28:1–92. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2628(08)60110-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Irvine R. F. Stepwise phosphorylation of myo-inositol leading to myo-inositol hexakisphosphate in Dictyostelium. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):580–583. doi: 10.1038/346580a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L., Hawkins P. T., Carter N., Chahwala S. B., Morris A. J., Whetton A. D., Downes P. C. L-myo-inositol 1,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate is present in both mammalian and avian cells. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 1;249(1):271–282. doi: 10.1042/bj2490271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMLINSON R. V., BALLOU C. E. Complete characterization of the myo-inositol polyphosphates from beef brain phosphoinositide. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jul;236:1902–1906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallejo M., Jackson T., Lightman S., Hanley M. R. Occurrence and extracellular actions of inositol pentakis- and hexakisphosphate in mammalian brain. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):656–658. doi: 10.1038/330656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Kaay J., Van Haastert P. J. Desalting inositolpolyphosphates by dialysis. Anal Biochem. 1995 Feb 10;225(1):183–185. doi: 10.1006/abio.1995.1135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Kaay J., Wesseling J., Van Haastert P. J. Nucleus-associated phosphorylation of Ins(1,4,5)P3 to InsP6 in Dictyostelium. Biochem J. 1995 Dec 15;312(Pt 3):911–917. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts D. J., Ashworth J. M. Growth of myxameobae of the cellular slime mould Dictyostelium discoideum in axenic culture. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(2):171–174. doi: 10.1042/bj1190171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


