Abstract
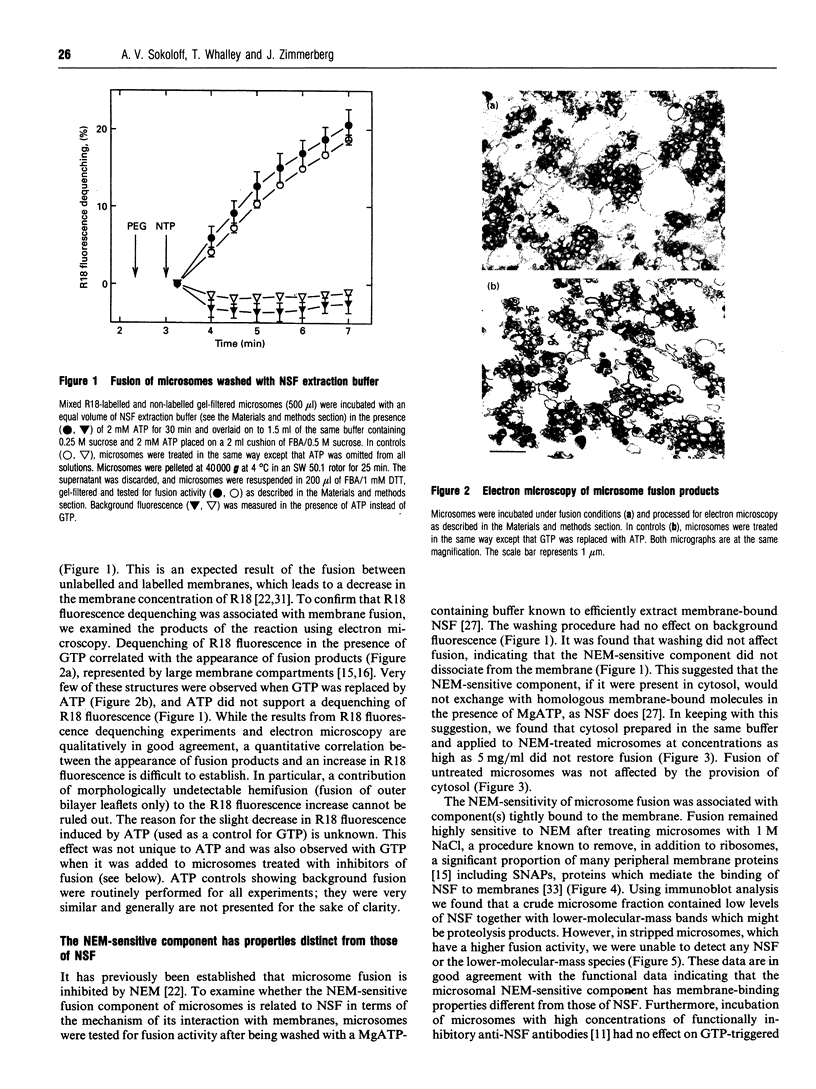
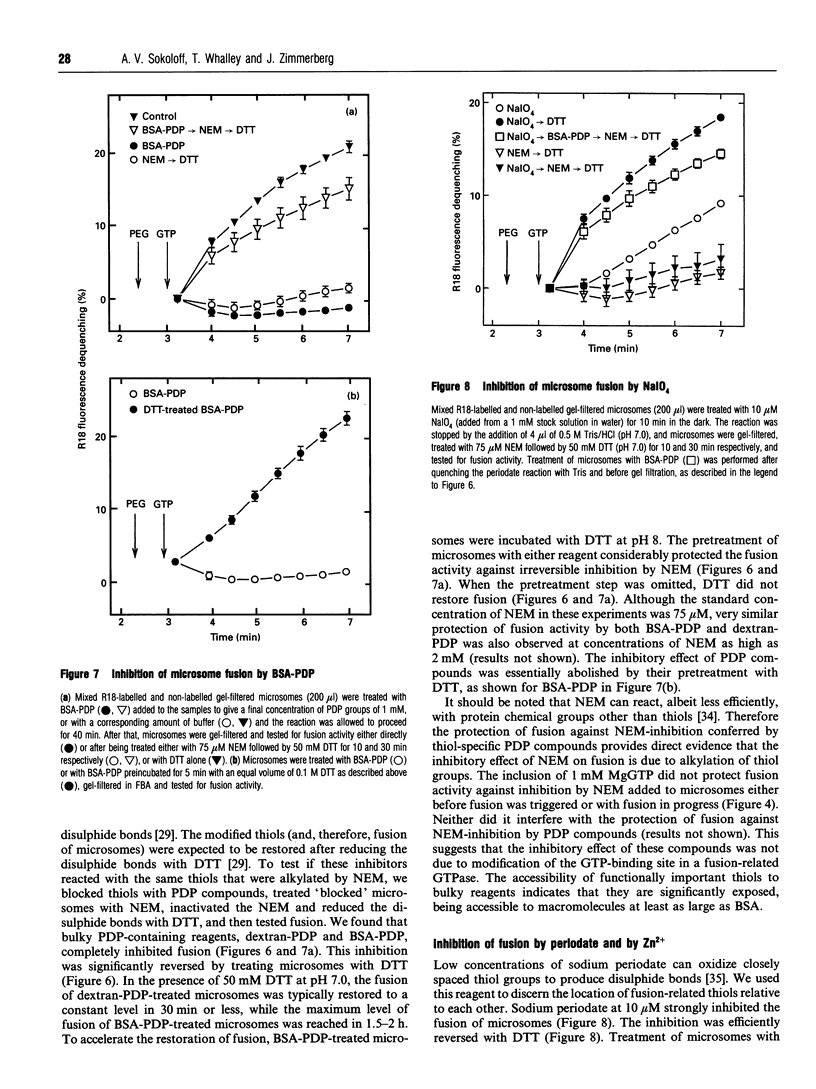
The GTP-dependent fusion activity of endoplasmic reticulum membranes is thought to be required for the structural maintenance and post-mitotic regeneration of the endoplasmic reticulum. This fusion is sensitive to the thiol-alkylating agent N-ethylmaleimide. In many intracellular fusion events N-ethylmaleimide-sensitivity is associated with a homotrimeric ATPase called N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein or NSF. The addition of cytosol containing NSF is known to restore fusion activity to N-ethylmaleimide-treated membranes. We found that the inhibition of fusion of rat liver endoplasmic reticulum membranes (microsomes) by N-ethylmaleimide was not reversed by the addition of untreated cytosol. Fusion was also unaffected by treatment with a buffer known to remove NSF from membranes. Accordingly, no membrane-associated NSF was detected by immunoblot analysis. These data suggest that microsome fusion requires an N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive component distinct from NSF. This component was tightly associated with the membranes, so we used a number of chemical probes to characterize it in situ. Its thiol groups did not appear to be part of a GTP-binding site. They showed relatively low reactivity with sodium periodate, which induces the formation of disulphide bonds between proximate thiol groups. The thiols were not protected against N-ethylmaleimide by Zn2+, a potent inhibitor of fusion which is known to efficiently co-ordinate thiol groups. To characterize the topology of the fusion-related thiol groups we used bulky thiol-specific reagents prepared by conjugating BSA or 10 kDa aminodextran to the bifunctional reagent N-succinimidyl 3-(2-pyridyldithio)propionate. The inhibition of fusion by these reagents indicated that these thiols are highly exposed on the membranes. This exposure might be important for the function of these groups during GTP-triggered fusion.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E., Dunphy W. G., Braell W. A., Rothman J. E. Reconstitution of the transport of protein between successive compartments of the Golgi measured by the coupled incorporation of N-acetylglucosamine. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):405–416. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckers C. J., Block M. R., Glick B. S., Rothman J. E., Balch W. E. Vesicular transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi stack requires the NEM-sensitive fusion protein. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):397–398. doi: 10.1038/339397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block M. R., Glick B. S., Wilcox C. A., Wieland F. T., Rothman J. E. Purification of an N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive protein catalyzing vesicular transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7852–7856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J., Drevin H., Axén R. Protein thiolation and reversible protein-protein conjugation. N-Succinimidyl 3-(2-pyridyldithio)propionate, a new heterobifunctional reagent. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 1;173(3):723–737. doi: 10.1042/bj1730723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernomordik L. V., Vogel S. S., Sokoloff A., Onaran H. O., Leikina E. A., Zimmerberg J. Lysolipids reversibly inhibit Ca(2+)-, GTP- and pH-dependent fusion of biological membranes. FEBS Lett. 1993 Feb 22;318(1):71–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81330-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clary D. O., Griff I. C., Rothman J. E. SNAPs, a family of NSF attachment proteins involved in intracellular membrane fusion in animals and yeast. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):709–721. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90482-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comerford J. G., Dawson A. P. The effect of limited proteolysis on GTP-dependent Ca2+ efflux and GTP-dependent fusion in rat liver microsomal vesicles. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 15;258(3):823–829. doi: 10.1042/bj2580823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabora S. L., Sheetz M. P. The microtubule-dependent formation of a tubulovesicular network with characteristics of the ER from cultured cell extracts. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson A. P., Hills G., Comerford J. G. The mechanism of action of GTP on Ca2+ efflux from rat liver microsomal vesicles. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):87–92. doi: 10.1042/bj2440087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson A. P., Irvine R. F. Inositol (1,4,5)trisphosphate-promoted Ca2+ release from microsomal fractions of rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):858–864. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80186-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Mayorga L. S., Weidman P. J., Rothman J. E., Stahl P. D. Vesicle fusion following receptor-mediated endocytosis requires a protein active in Golgi transport. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):398–400. doi: 10.1038/339398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goda Y., Pfeffer S. R. Identification of a novel, N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive cytosolic factor required for vesicular transport from endosomes to the trans-Golgi network in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(5):823–831. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.5.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampe W., Zimmermann P., Schulz I. GTP-induced fusion of isolated pancreatic microsomal vesicles is increased by acidification of the vesicle lumen. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 1;271(1-2):62–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80372-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller K. B., Poser B., Haest C. W., Deuticke B. Oxidative stress of human erythrocytes by iodate and periodate. Reversible formation of aqueous membrane pores due to SH-group oxidation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Oct 17;777(1):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90502-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra D., de Boer T., Klappe K., Wilschut J. Fluorescence method for measuring the kinetics of fusion between biological membranes. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5675–5681. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison K. A., Matić G., Meshinchi S., Bresnick E. H., Pratt W. B. Redox manipulation of DNA binding activity and BuGR epitope reactivity of the glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10505–10509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latterich M., Schekman R. The karyogamy gene KAR2 and novel proteins are required for ER-membrane fusion. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):87–98. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90575-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra V., Orci L., Glick B. S., Block M. R., Rothman J. E. Role of an N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive transport component in promoting fusion of transport vesicles with cisternae of the Golgi stack. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):221–227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90554-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monsigny M., Petit C., Roche A. C. Colorimetric determination of neutral sugars by a resorcinol sulfuric acid micromethod. Anal Biochem. 1988 Dec;175(2):525–530. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90578-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER K. R., MACHADO R. D. Studies on the endoplasmic reticulum. IV. Its form and distribution during mitosis in cells of onion root tip. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Feb;7:167–180. doi: 10.1083/jcb.7.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paiement J., Beaufay H., Godelaine D. Coalescence of microsomal vesicles from rat liver: a phenomenon occurring in parallel with enhancement of the glycosylation activity during incubation of stripped rough microsomes with GTP. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jul;86(1):29–37. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paiement J. Physiological concentrations of GTP stimulate fusion of the endoplasmic reticulum and the nuclear envelope. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Apr;151(2):354–366. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90386-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paiement J., Rindress D., Smith C. E., Poliquin L., Bergeron J. J. Properties of a GTP sensitive microdomain in rough microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Mar 26;898(1):6–22. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podbilewicz B., Mellman I. ATP and cytosol requirements for transferrin recycling in intact and disrupted MDCK cells. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3477–3487. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07556.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rippa M., Bellini T., Signorini M., Dallocchio F. Evidence for multiple pairs of vicinal thiols in some proteins. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):451–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez L., Stirling C. J., Woodman P. G. Multiple N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive components are required for endosomal vesicle fusion. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Jul;5(7):773–783. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.7.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross P. D., Minton A. P. The effect of non-aggregating proteins upon the gelation of sickle cell hemoglobin: model calculations and data analysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jun 27;88(4):1308–1314. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91123-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Orci L. Molecular dissection of the secretory pathway. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):409–415. doi: 10.1038/355409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suprynowicz F. A., Prusmack C., Whalley T. Ca2+ triggers premature inactivation of the cdc2 protein kinase in permeabilized sea urchin embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):6176–6180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.6176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söllner T., Bennett M. K., Whiteheart S. W., Scheller R. H., Rothman J. E. A protein assembly-disassembly pathway in vitro that may correspond to sequential steps of synaptic vesicle docking, activation, and fusion. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):409–418. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90376-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagaya M., Wilson D. W., Brunner M., Arango N., Rothman J. E. Domain structure of an N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein involved in vesicular transport. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2662–2666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub L. M., Ostrom J. A., Kornfeld S. Biochemical dissection of AP-1 recruitment onto Golgi membranes. J Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;123(3):561–573. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Hotani H. Formation of membrane networks in vitro by kinesin-driven microtubule movement. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2233–2241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee B. L., Falchuk K. H. The biochemical basis of zinc physiology. Physiol Rev. 1993 Jan;73(1):79–118. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1993.73.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wattenberg B. W., Raub T. J., Hiebsch R. R., Weidman P. J. The activity of Golgi transport vesicles depends on the presence of the N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor (NSF) and a soluble NSF attachment protein (alpha SNAP) during vesicle formation. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(6):1321–1332. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.6.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidman P. J., Melançon P., Block M. R., Rothman J. E. Binding of an N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein to Golgi membranes requires both a soluble protein(s) and an integral membrane receptor. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1589–1596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel D., Flügge U. I. A method for the quantitative recovery of protein in dilute solution in the presence of detergents and lipids. Anal Biochem. 1984 Apr;138(1):141–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90782-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalley T., Sokoloff A. The N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive protein thiol groups necessary for sea-urchin egg cortical-granule exocytosis are highly exposed to the medium and are required for triggering by Ca2+. Biochem J. 1994 Sep 1;302(Pt 2):391–396. doi: 10.1042/bj3020391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteheart S. W., Rossnagel K., Buhrow S. A., Brunner M., Jaenicke R., Rothman J. E. N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein: a trimeric ATPase whose hydrolysis of ATP is required for membrane fusion. J Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;126(4):945–954. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.4.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. W., Whiteheart S. W., Wiedmann M., Brunner M., Rothman J. E. A multisubunit particle implicated in membrane fusion. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(3):531–538. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.3.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. W., Yarbrough L. R. N-(1-pyrene)maleimide: a fluorescent cross-linking reagent. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 29;15(13):2863–2868. doi: 10.1021/bi00658a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




