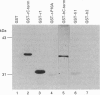
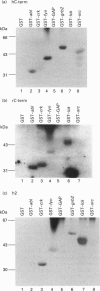
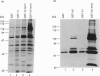
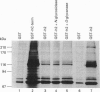
Abstract
The amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) is an important component of the Na(+)-reabsorption pathway in many epithelia. The identification of three subunits of ENaC (alpha, beta and gamma), as well as results from a number of functional and biochemical studies, suggests that functional Na+ channels are composed of a complex of proteins. To learn about possible interactions of the channel with other proteins, we studied the alpha-subunit of rat and human ENaC. We found that the proline-rich C-terminal domains of both rat and human alpha-ENaC, expressed as glutathione S-transferase fusion proteins, bound to SH3 domains in vitro. A 116 kDa protein from a human lung adenocarcinoma cell line (H441) was specifically bound by the human alpha-ENaC C-terminal fusion protein and by a shorter 18-amino acid proline-rich peptide derived from the larger fusion protein. The 116 kDa protein was not glycosylated and was not phosphorylated on tyrosine or by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA). A 134 kDa protein which was also bound by the human alpha-ENaC C-terminal fusion protein was a substrate for phosphorylation by PKA. These data suggest that the proline-rich C-terminal tail of alpha-ENaC may interact with other proteins that control its function, regulation or localization.
Full text
PDF


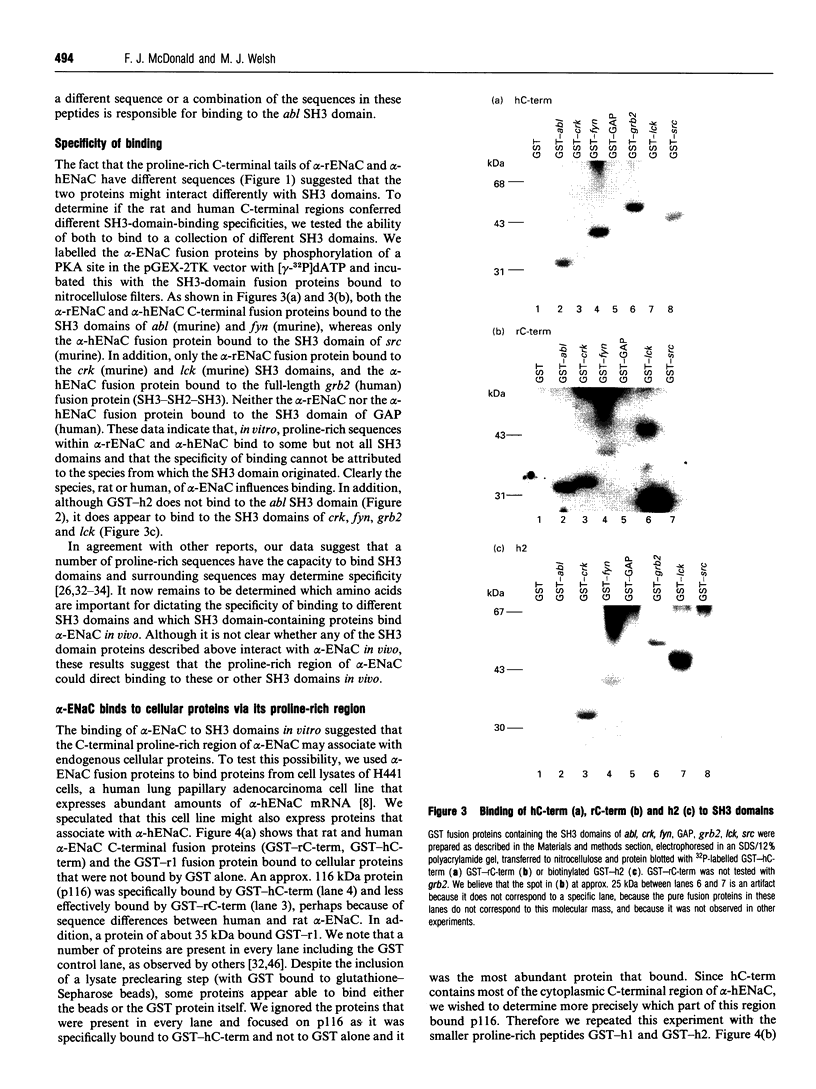
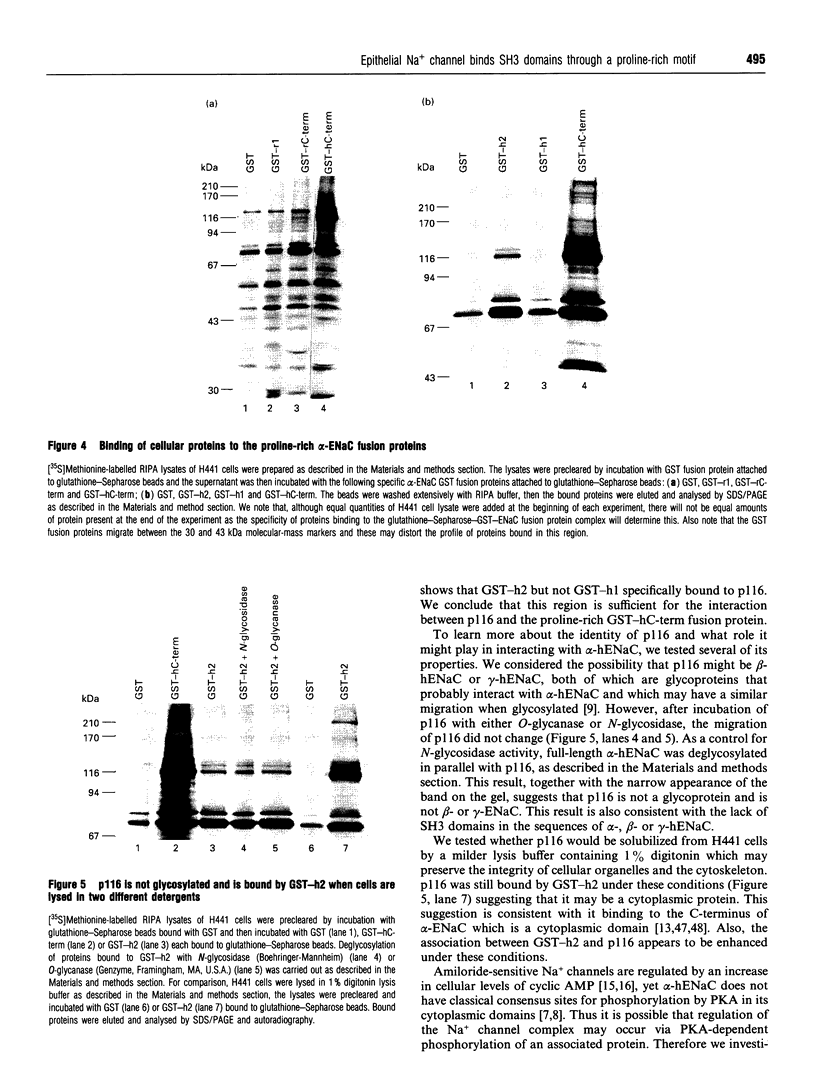
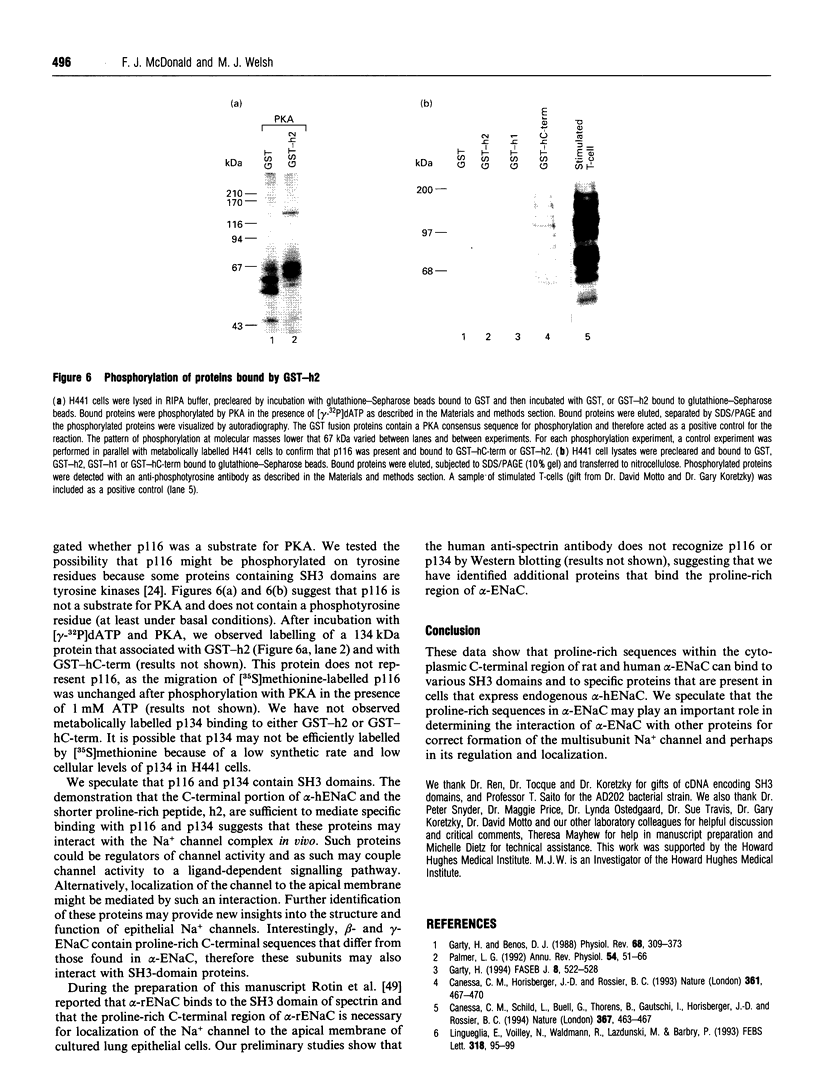

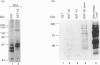
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama Y., Ito K. SecY protein, a membrane-embedded secretion factor of E. coli, is cleaved by the ompT protease in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 16;167(2):711–715. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92083-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Sagi D., Rotin D., Batzer A., Mandiyan V., Schlessinger J. SH3 domains direct cellular localization of signaling molecules. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90296-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Neriah Y., Bernards A., Paskind M., Daley G. Q., Baltimore D. Alternative 5' exons in c-abl mRNA. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):577–586. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benos D. J., Saccomani G., Sariban-Sohraby S. The epithelial sodium channel. Subunit number and location of the amiloride binding site. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10613–10618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher R. C., Stutts M. J., Knowles M. R., Cantley L., Gatzy J. T. Na+ transport in cystic fibrosis respiratory epithelia. Abnormal basal rate and response to adenylate cyclase activation. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1245–1252. doi: 10.1172/JCI112708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa C. M., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Epithelial sodium channel related to proteins involved in neurodegeneration. Nature. 1993 Feb 4;361(6411):467–470. doi: 10.1038/361467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa C. M., Schild L., Buell G., Thorens B., Gautschi I., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channel is made of three homologous subunits. Nature. 1994 Feb 3;367(6462):463–467. doi: 10.1038/367463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantiello H. F., Patenaude C. R., Codina J., Birnbaumer L., Ausiello D. A. G alpha i-3 regulates epithelial Na+ channels by activation of phospholipase A2 and lipoxygenase pathways. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21624–21628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicchetti P., Mayer B. J., Thiel G., Baltimore D. Identification of a protein that binds to the SH3 region of Abl and is similar to Bcr and GAP-rho. Science. 1992 Aug 7;257(5071):803–806. doi: 10.1126/science.1379745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll M. Molecular genetics of cell death in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. J Neurobiol. 1992 Nov;23(9):1327–1351. doi: 10.1002/neu.480230919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan S. E., Giddings B. W., Brooks M. W., Buday L., Sizeland A. M., Weinberg R. A. Association of Sos Ras exchange protein with Grb2 is implicated in tyrosine kinase signal transduction and transformation. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):45–51. doi: 10.1038/363045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finan P., Shimizu Y., Gout I., Hsuan J., Truong O., Butcher C., Bennett P., Waterfield M. D., Kellie S. An SH3 domain and proline-rich sequence mediate an interaction between two components of the phagocyte NADPH oxidase complex. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):13752–13755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garty H., Benos D. J. Characteristics and regulatory mechanisms of the amiloride-blockable Na+ channel. Physiol Rev. 1988 Apr;68(2):309–373. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1988.68.2.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garty H. Molecular properties of epithelial, amiloride-blockable Na+ channels. FASEB J. 1994 May;8(8):522–528. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.8.8181670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gout I., Dhand R., Hiles I. D., Fry M. J., Panayotou G., Das P., Truong O., Totty N. F., Hsuan J., Booker G. W. The GTPase dynamin binds to and is activated by a subset of SH3 domains. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):25–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Dixon J. E. Eukaryotic proteins expressed in Escherichia coli: an improved thrombin cleavage and purification procedure of fusion proteins with glutathione S-transferase. Anal Biochem. 1991 Feb 1;192(2):262–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90534-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskovits J. S., Shpetner H. S., Burgess C. C., Vallee R. B. Microtubules and Src homology 3 domains stimulate the dynamin GTPase via its C-terminal domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11468–11472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong K., Driscoll M. A transmembrane domain of the putative channel subunit MEC-4 influences mechanotransduction and neurodegeneration in C. elegans. Nature. 1994 Feb 3;367(6462):470–473. doi: 10.1038/367470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M., Chalfie M. Gene interactions affecting mechanosensory transduction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1994 Feb 3;367(6462):467–470. doi: 10.1038/367467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismailov I. I., McDuffie J. H., Benos D. J. Protein kinase A phosphorylation and G protein regulation of purified renal Na+ channels in planar bilayer membranes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10235–10241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li N., Batzer A., Daly R., Yajnik V., Skolnik E., Chardin P., Bar-Sagi D., Margolis B., Schlessinger J. Guanine-nucleotide-releasing factor hSos1 binds to Grb2 and links receptor tyrosine kinases to Ras signalling. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):85–88. doi: 10.1038/363085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingueglia E., Voilley N., Waldmann R., Lazdunski M., Barbry P. Expression cloning of an epithelial amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel. A new channel type with homologies to Caenorhabditis elegans degenerins. FEBS Lett. 1993 Feb 22;318(1):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81336-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Baltimore D. Signalling through SH2 and SH3 domains. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;3(1):8–13. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald F. J., Price M. P., Snyder P. M., Welsh M. J. Cloning and expression of the beta- and gamma-subunits of the human epithelial sodium channel. Am J Physiol. 1995 May;268(5 Pt 1):C1157–C1163. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.268.5.C1157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald F. J., Snyder P. M., McCray P. B., Jr, Welsh M. J. Cloning, expression, and tissue distribution of a human amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jun;266(6 Pt 1):L728–L734. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1994.266.6.L728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki H., Miura K., Matuoka K., Nakata T., Hirokawa N., Orita S., Kaibuchi K., Takai Y., Takenawa T. Association of Ash/Grb-2 with dynamin through the Src homology 3 domain. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 25;269(8):5489–5492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motto D. G., Ross S. E., Jackman J. K., Sun Q., Olson A. L., Findell P. R., Koretzky G. A. In vivo association of Grb2 with pp116, a substrate of the T cell antigen receptor-activated protein tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 26;269(34):21608–21613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musacchio A., Gibson T., Lehto V. P., Saraste M. SH3--an abundant protein domain in search of a function. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 27;307(1):55–61. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80901-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano H., Yamazaki T., Ikeda M., Masai H., Miyatake S., Saito T. Purification of glutathione S-transferase fusion proteins as a non-degraded form by using a protease-negative E. coli strain, AD202. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Feb 11;22(3):543–544. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.3.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh Y., Smith P. R., Bradford A. L., Keeton D., Benos D. J. Regulation by phosphorylation of purified epithelial Na+ channels in planar lipid bilayers. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jul;265(1 Pt 1):C85–C91. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.1.C85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara A., Matsunaga H., Eaton D. C. G protein activation inhibits amiloride-blockable highly selective sodium channels in A6 cells. Am J Physiol. 1993 Feb;264(2 Pt 1):C352–C360. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.2.C352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L. G. Epithelial Na channels: function and diversity. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:51–66. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.000411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prat A. G., Ausiello D. A., Cantiello H. F. Vasopressin and protein kinase A activate G protein-sensitive epithelial Na+ channels. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jul;265(1 Pt 1):C218–C223. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.1.C218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prat A. G., Bertorello A. M., Ausiello D. A., Cantiello H. F. Activation of epithelial Na+ channels by protein kinase A requires actin filaments. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jul;265(1 Pt 1):C224–C233. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.1.C224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren R., Mayer B. J., Cicchetti P., Baltimore D. Identification of a ten-amino acid proline-rich SH3 binding site. Science. 1993 Feb 19;259(5098):1157–1161. doi: 10.1126/science.8438166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren R., Ye Z. S., Baltimore D. Abl protein-tyrosine kinase selects the Crk adapter as a substrate using SH3-binding sites. Genes Dev. 1994 Apr 1;8(7):783–795. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.7.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renard S., Lingueglia E., Voilley N., Lazdunski M., Barbry P. Biochemical analysis of the membrane topology of the amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 29;269(17):12981–12986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotin D., Bar-Sagi D., O'Brodovich H., Merilainen J., Lehto V. P., Canessa C. M., Rossier B. C., Downey G. P. An SH3 binding region in the epithelial Na+ channel (alpha rENaC) mediates its localization at the apical membrane. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 3;13(19):4440–4450. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06766.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozakis-Adcock M., Fernley R., Wade J., Pawson T., Bowtell D. The SH2 and SH3 domains of mammalian Grb2 couple the EGF receptor to the Ras activator mSos1. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):83–85. doi: 10.1038/363083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkadi B., Bauzon D., Huckle W. R., Earp H. S., Berry A., Suchindran H., Price E. M., Olson J. C., Boucher R. C., Scarborough G. A. Biochemical characterization of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in normal and cystic fibrosis epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):2087–2095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seedorf K., Kostka G., Lammers R., Bashkin P., Daly R., Burgess W. H., van der Bliek A. M., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Dynamin binds to SH3 domains of phospholipase C gamma and GRB-2. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 10;269(23):16009–16014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small G. M., Imanaka T., Lazarow P. B. Immunoblotting of hydrophobic integral membrane proteins. Anal Biochem. 1988 Mar;169(2):405–409. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90304-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder P. M., McDonald F. J., Stokes J. B., Welsh M. J. Membrane topology of the amiloride-sensitive epithelial sodium channel. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 30;269(39):24379–24383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voilley N., Lingueglia E., Champigny G., Mattéi M. G., Waldmann R., Lazdunski M., Barbry P. The lung amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel: biophysical properties, pharmacology, ontogenesis, and molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):247–251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. S., Garbay C., Duchesne M., Cornille F., Jullian N., Fromage N., Tocque B., Roques B. P. Solution structure of GAP SH3 domain by 1H NMR and spatial arrangement of essential Ras signaling-involved sequence. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1270–1279. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06379.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu H., Chen J. K., Feng S., Dalgarno D. C., Brauer A. W., Schreiber S. L. Structural basis for the binding of proline-rich peptides to SH3 domains. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):933–945. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90367-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]