Abstract
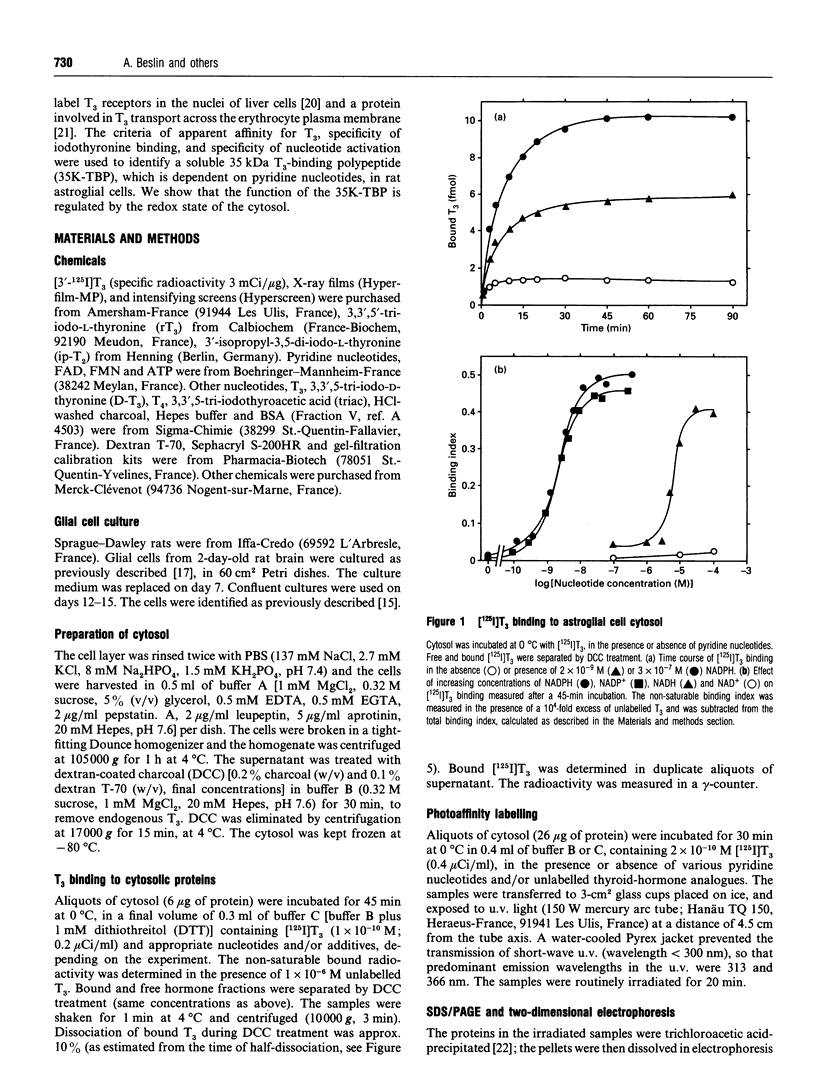
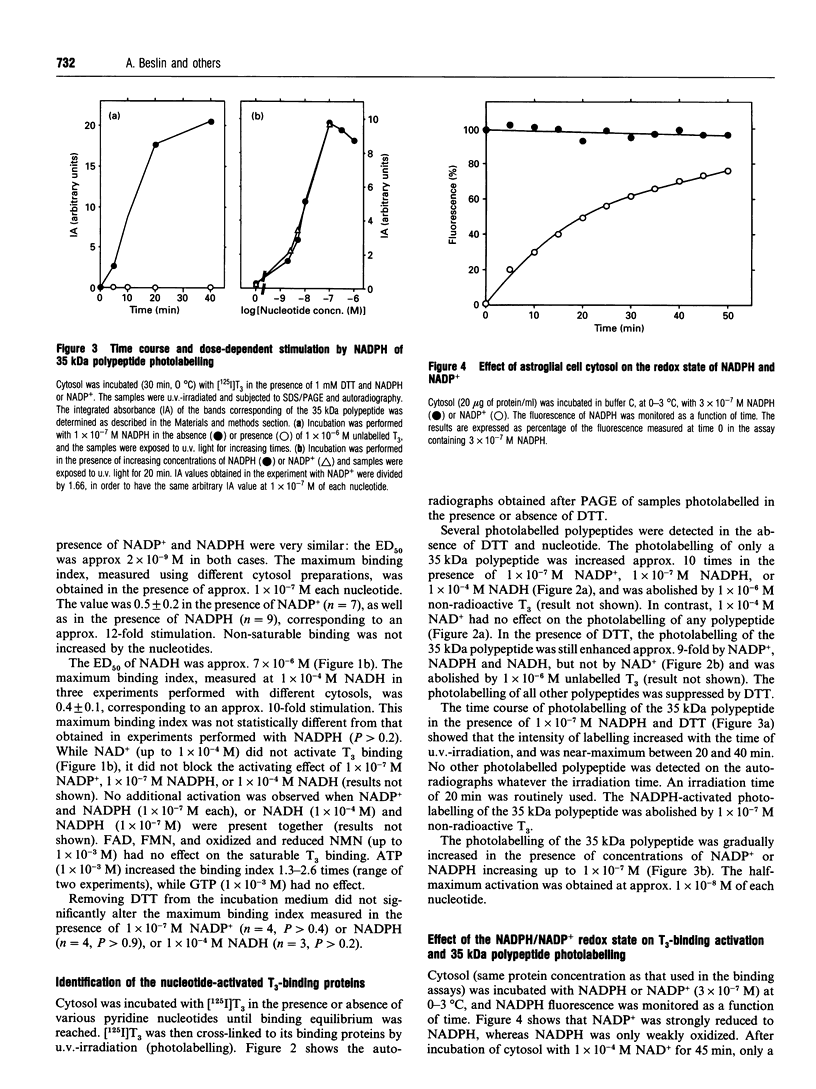
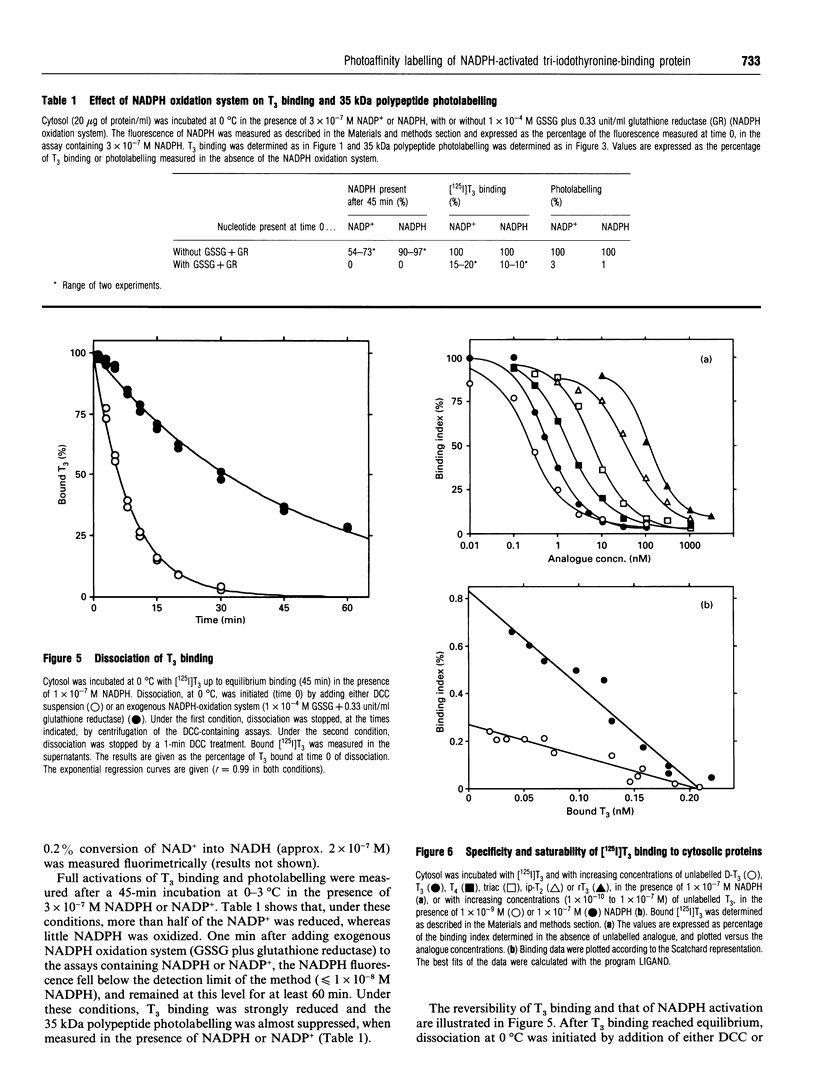
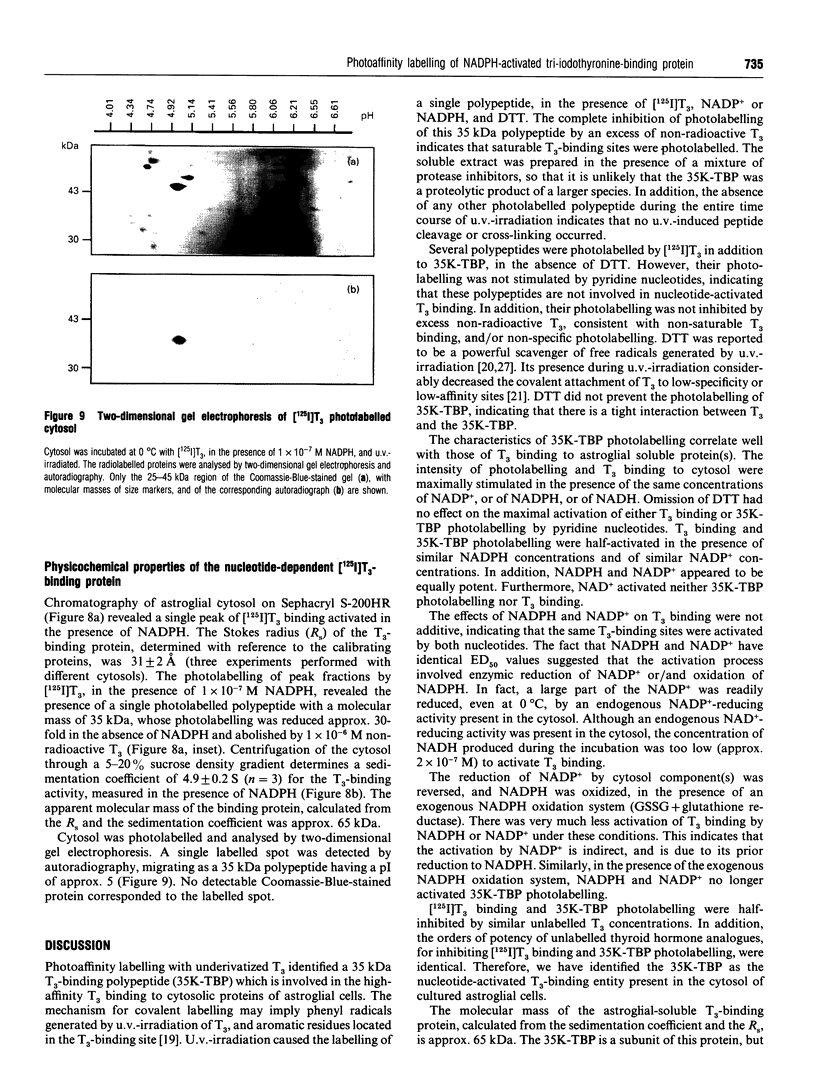
High-affinity 3,3',5-tri-iodo-L-thyronine (T3) binding (Kd approximately 0.3 nM) to the cytosol of cultured rat astroglial cells was strongly activated in the presence of pyridine nucleotides. A 35 kDa pyridine nucleotide-dependent T3-binding polypeptide (35K-TBP) was photoaffinity labelled using underivatized [125I]T3 in the presence of pyridine nucleotides and the free-radical scavenger dithiothreitol. Maximum activations of T3 binding and 35K-TBP photolabelling were obtained at approx. 1 x 10(-7) M NADP+ or NADPH, or 1 x 10(-4) M NADH. NAD+ and other nucleotides were without effect. NADPH is the form which activates T3 binding and 35K-TBP photolabelling, since cytosol contains NADP(+)-reducing activity, and the activation of both processes in the presence of NADPH and NADP+ was prevented by an exogenous NADPH oxidation system. NADPH behaved as an allosteric activator of T3 binding. The NADPH oxidation system promoted the release of bound T3 in the absence of any change in the total concentration of the hormone. The 35K-TBP photolabelling and [125I]T3 binding were similarly inhibited by non-radioactive T3 (half-maximum effect at 0.5-1.0 nM T3). The concentrations of iodothyronine analogues that inhibited both processes were correlated (3,3',5-tri-iodo-D-thyronine > or = T3 > L-thyroxine > tri-iodothyroacetic acid > 3,3'5'-tri-iodo-L-thyronine). Molecular sieving and density-gradient centrifugation of cytosol identified a 65 kDa T3-binding entity, which included the 35K-TBP. These results indicate that 35K-TBP is the cytosolic entity involved in the pyridine nucleotide-dependent T3 binding, and suggest that the sequestration and release of intracellular thyroid hormones are regulated by the redox state of astroglial cell compartment(s).
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashizawa K., Cheng S. Y. Regulation of thyroid hormone receptor-mediated transcription by a cytosol protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9277–9281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomhoff R., Green M. H., Berg T., Norum K. R. Transport and storage of vitamin A. Science. 1990 Oct 19;250(4979):399–404. doi: 10.1126/science.2218545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blondeau J. P., Beslin A., Chantoux F., Francon J. Triiodothyronine is a high-affinity inhibitor of amino acid transport system L1 in cultured astrocytes. J Neurochem. 1993 Apr;60(4):1407–1413. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bründl A., Buff K. Partial purification and characterization of a rat liver polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) binding protein. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Feb 24;45(4):885–891. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90173-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtin F., Chantoux F., Francon J. Thyroid hormone metabolism by glial cells in primary culture. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1986 Dec;48(2-3):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(86)90039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dozin B., Cahnmann H. J., Nikodem V. M. Identification of thyroid hormone receptors in rat liver nuclei by photoaffinity labeling with L-thyroxine and triiodo-L-thyronine. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 10;24(19):5197–5202. doi: 10.1021/bi00340a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francon J., Chantoux F., Blondeau J. P. Carrier-mediated transport of thyroid hormones into rat glial cells in primary culture. J Neurochem. 1989 Nov;53(5):1456–1463. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb08538.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francon J., Osty J., Chantoux F., Lennon A. M. Cellular location of cytosolic triiodothyronine binding protein in primary cultures of fetal rat brain. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1985 Mar;39(3):197–207. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(85)90063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashizume K., Miyamoto T., Ichikawa K., Yamauchi K., Sakurai A., Ohtsuka H., Kobayashi M., Nishii Y., Yamada T. Evidence for the presence of two active forms of cytosolic 3,5,3'-triiodo-L-thyronine (T3)-binding protein (CTBP) in rat kidney. Specialized functions of two CTBPs in intracellular T3 translocation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4864–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Fukuda T., Parkison C., McPhie P., Cheng S. Y. Cytosolic thyroid hormone-binding protein is a monomer of pyruvate kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7861–7865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Hashizume K., Suzuki S., Ichikawa K., Takeda T. A novel NADPH-dependent cytosolic 3,5,3'-triiodo-L-thyronine-binding protein (CTBP; 5.1S) in rat liver: a comparison with 4.7S NADPH-dependent CTBP. Endocrinology. 1991 Oct;129(4):1701–1708. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-4-1701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. C., Oeda T., Driscoll W. J., Fales H. M., Strott C. A. Purification and identification of the heat-stable factor required for pregnenolone-binding protein activity. Evidence that the factor is adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):10982–10987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. J., Strott C. A. Adrenocortical pregnenolone-binding protein: identification and antibody development. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jan 15;150(1):456–462. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90542-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon A. M. Purification and characterization of rat brain cytosolic 3,5,3'-triiodo-L-thyronine-binding protein. Evidence for binding activity dependent on NADPH, NADP and thioredoxin. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Nov 15;210(1):79–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macaulay J. O., Warne G. L., Smith A. I., Krozowski Z. S. The methyltrienolone binding protein of human placenta requires nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide cofactor(s) for steroid binding. Endocrinology. 1990 May;126(5):2506–2513. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-5-2506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Schwartz H. L. Stereospecific transport of triiodothyronine from plasma to cytosol and from cytosol to nucleus in rat liver, kidney, brain, and heart. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):147–154. doi: 10.1172/JCI111667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price E. M., Ratnam M., Rodeman K. M., Freisheim J. H. Characterization of the methotrexate transport pathway in murine L1210 leukemia cells: involvement of a membrane receptor and a cytosolic protein. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 4;27(20):7853–7858. doi: 10.1021/bi00420a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson M., Osty J., Blondeau J. P. Identification by photoaffinity labeling of a membrane thyroid hormone-binding protein associated with the triiodothyronine transport system in rat erythrocytes. Endocrinology. 1993 Jun;132(6):2470–2476. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.6.8504750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Arai H., Miyata A., Tokita S., Yamamoto K., Tanabe T., Inoue K. Primary structure of alpha-tocopherol transfer protein from rat liver. Homology with cellular retinaldehyde-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):17705–17710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. M., Cunningham E., Fensome A., Ball A., Totty N. F., Truong O., Hsuan J. J., Cockcroft S. An essential role for phosphatidylinositol transfer protein in phospholipase C-mediated inositol lipid signaling. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):919–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90471-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veech R. L., Eggleston L. V., Krebs H. A. The redox state of free nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate in the cytoplasm of rat liver. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(4):609–619. doi: 10.1042/bj1150609a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Jarvis S. M., Robins M. J., Paterson A. R. Photoaffinity labeling of the human erythrocyte nucleoside transporter by N6-(p-Azidobenzyl)adenosine and nitrobenzylthioinosine. Evidence that the transporter is a band 4.5 polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2202–2208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yusta B., Besnard F., Ortiz-Caro J., Pascual A., Aranda A., Sarliève L. Evidence for the presence of nuclear 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine receptors in secondary cultures of pure rat oligodendrocytes. Endocrinology. 1988 May;122(5):2278–2284. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-5-2278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Walt B., Nikodem V. M., Cahnmann H. J. Use of un-derivatized thyroid hormones for photoaffinity labeling of binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3508–3512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





