Abstract
Protein S is a plasma factor essential for prevention of thrombosis, partly due to its activity as a cofactor for the plasma anticoagulant protease-activated protein C. To expand knowledge about structure-function relationships in homologous protein S molecules, studies of protein S from different species have been performed. Protein S anti-coagulant activity in human, monkey, bovine, and porcine plasma has been inactivated by purified human C4b binding protein (C4BP) with dose-dependence, suggesting that each protein S can bind human C4BP and that only the free form of each is anti-coagulantly active. Purified porcine protein S has a 10-fold higher Kd for human C4BP than has human protein S. Protein S residues 420-434 provide an essential binding site for the negative regulator C4BP. cDNA sequences show that protein S residues 420-434 are highly conserved in all four species with the notable exception of Lys-429-Ile in porcine protein S. Differences between porcine and human protein S, e.g. Lys-429-Ile, Lys-43-Ala, Ser-197-Leu, Ser 199-Phe, Glu-463-Gly, Lys-571-Glu, Asn-602-Ile, Gln-607-Pro, may contribute to the decreased affinity of porcine protein S for human C4BP. Moreover, the species specificity of cofactor activities of various species of protein S is determined for human versus bovine-activated protein C, and these results, combined with sequence comparisons, agree with previous evidence that the thrombin-sensitive region and the first epidermal growth factor domain of protein S, i.e. residues 47-116, are responsible for recognition of activated protein C.
Full text
PDF

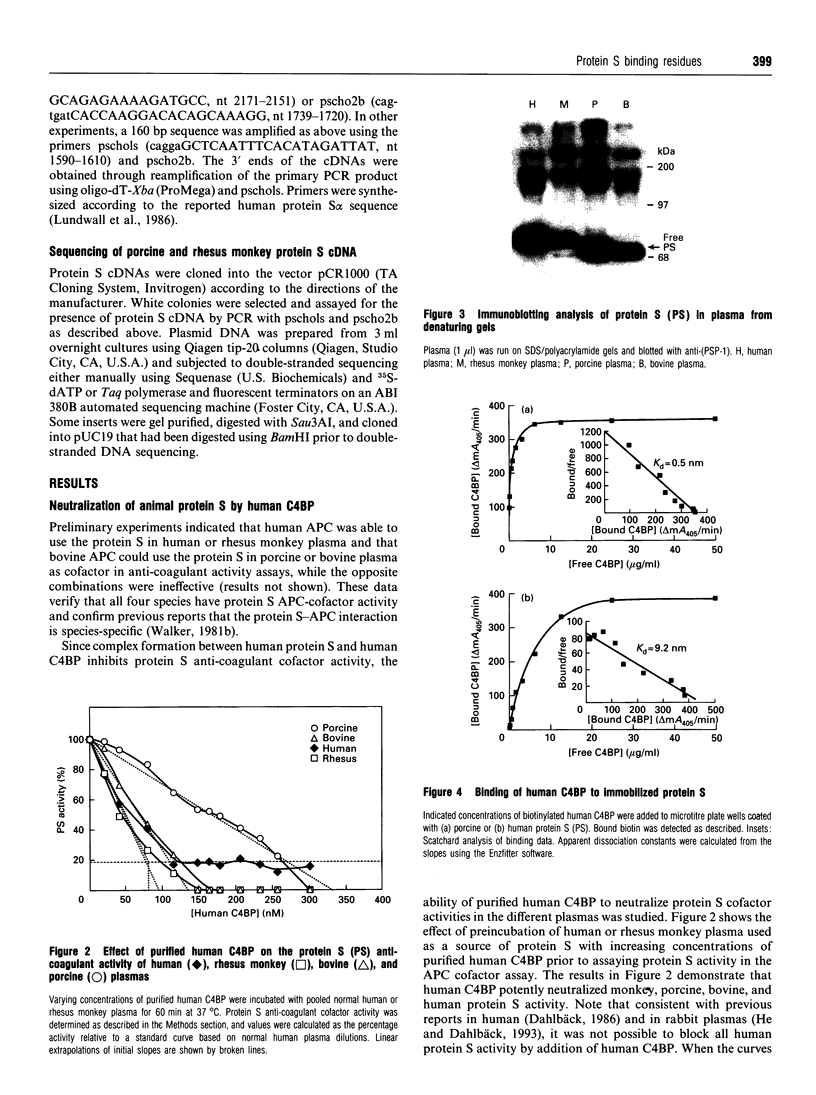

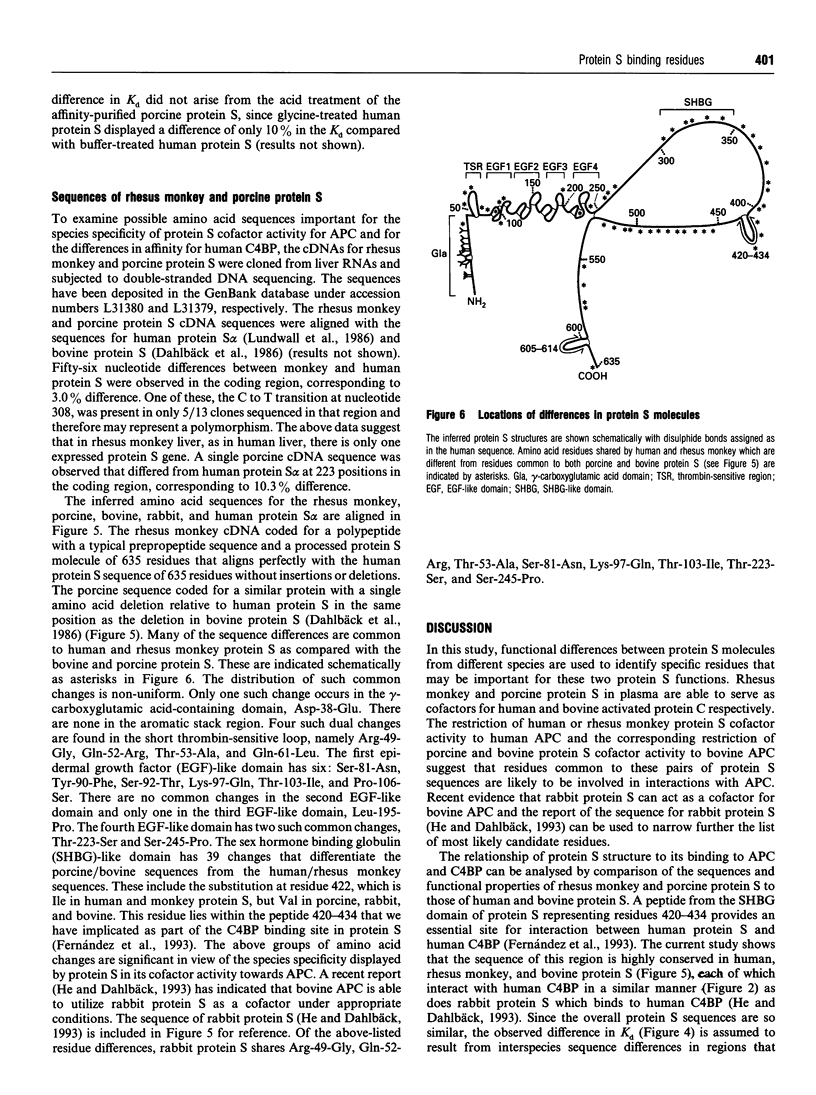


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertina R. M. Hereditary protein S deficiency. Haemostasis. 1985;15(4):241–246. doi: 10.1159/000215155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang G. T., Ploos van Amstel H. K., Hessing M., Reitsma P. H., Bertina R. M., Bouma B. N. Expression and characterization of recombinant human protein S in heterologous cells--studies of the interaction of amino acid residues leu-608 to glu-612 with human C4b-binding protein. Thromb Haemost. 1992 May 4;67(5):526–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comp P. C., Doray D., Patton D., Esmon C. T. An abnormal plasma distribution of protein S occurs in functional protein S deficiency. Blood. 1986 Feb;67(2):504–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Hildebrand B., Malm J. Characterization of functionally important domains in human vitamin K-dependent protein S using monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8127–8135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B. Inhibition of protein Ca cofactor function of human and bovine protein S by C4b-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12022–12027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Lundwall A., Stenflo J. Primary structure of bovine vitamin K-dependent protein S. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4199–4203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B. Purification of human vitamin K-dependent protein S and its limited proteolysis by thrombin. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 1;209(3):837–846. doi: 10.1042/bj2090837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Stenflo J. High molecular weight complex in human plasma between vitamin K-dependent protein S and complement component C4b-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2512–2516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiScipio R. G., Davie E. W. Characterization of protein S, a gamma-carboxyglutamic acid containing protein from bovine and human plasma. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 6;18(5):899–904. doi: 10.1021/bi00572a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edenbrandt C. M., Lundwall A., Wydro R., Stenflo J. Molecular analysis of the gene for vitamin K dependent protein S and its pseudogene. Cloning and partial gene organization. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 28;29(34):7861–7868. doi: 10.1021/bi00486a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fair D. S., Marlar R. A., Levin E. G. Human endothelial cells synthesize protein S. Blood. 1986 Apr;67(4):1168–1171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández J. A., Griffin J. H. A protein S binding site on C4b-binding protein involves beta chain residues 31-45. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 28;269(4):2535–2540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández J. A., Heeb M. J., Griffin J. H. Identification of residues 413-433 of plasma protein S as essential for binding to C4b-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16788–16794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladson C. L., Scharrer I., Hach V., Beck K. H., Griffin J. H. The frequency of type I heterozygous protein S and protein C deficiency in 141 unrelated young patients with venous thrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Feb 25;59(1):18–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladson C. L., Schleef R. R., Binder B. R., Loskutoff D. J., Griffin J. H. A comparison between activated protein C and des-1-41-light chain-activated protein C in reactions with type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):173–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. H., Gruber A., Fernández J. A. Reevaluation of total, free, and bound protein S and C4b-binding protein levels in plasma anticoagulated with citrate or hirudin. Blood. 1992 Jun 15;79(12):3203–3211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber A., Griffin J. H., Harker L. A., Hanson S. R. Inhibition of platelet-dependent thrombus formation by human activated protein C in a primate model. Blood. 1989 Feb 15;73(3):639–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X., Dahlbäck B. Molecular cloning, expression and functional characterization of rabbit anticoagulant vitamin-K-dependent protein S. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Nov 1;217(3):857–865. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heeb M. J., Mesters R. M., Tans G., Rosing J., Griffin J. H. Binding of protein S to factor Va associated with inhibition of prothrombinase that is independent of activated protein C. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2872–2877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundwall A., Dackowski W., Cohen E., Shaffer M., Mahr A., Dahlbäck B., Stenflo J., Wydro R. Isolation and sequence of the cDNA for human protein S, a regulator of blood coagulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6716–6720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lämmle B., Berrettini M., Griffin J. H. Enhanced specificity of immunoblotting using radiolabeled antigen overlay: studies of blood coagulation factor XII and prekallikrein in plasma. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jul;156(1):118–125. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90162-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manfioletti G., Brancolini C., Avanzi G., Schneider C. The protein encoded by a growth arrest-specific gene (gas6) is a new member of the vitamin K-dependent proteins related to protein S, a negative coregulator in the blood coagulation cascade. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4976–4985. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. M., Long G. L. Binding of protein S to C4b-binding protein. Mutagenesis of protein S. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8140–8145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploos van Amstel H. K., Reitsma P. H., van der Logt C. P., Bertina R. M. Intron-exon organization of the active human protein S gene PS alpha and its pseudogene PS beta: duplication and silencing during primate evolution. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 28;29(34):7853–7861. doi: 10.1021/bi00486a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidel D. K., Tatro A. V., Phelps L. G., Tomczak J. A., Long G. L. Organization of the human protein S genes. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 28;29(34):7845–7852. doi: 10.1021/bi00486a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwalbe R., Dahlbäck B., Hillarp A., Nelsestuen G. Assembly of protein S and C4b-binding protein on membranes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16074–16081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz H. P., Heeb M. J., Wencel-Drake J. D., Griffin J. H. Identification and quantitation of protein S in human platelets. Blood. 1985 Dec;66(6):1452–1455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J. Structure-function relationships of epidermal growth factor modules in vitamin K-dependent clotting factors. Blood. 1991 Oct 1;78(7):1637–1651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thommen D., Buhrfeind E., Felix R., Sulzer I., Furlan M., Lämmle B. Hämostaseparameter bei 55 Patienten mit venösen und/oder arteriellen Thromboembolien. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1989 Apr 22;119(16):493–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J. Characterization of a synthetic peptide that inhibits the interaction between protein S and C4b-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17645–17648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J. Protein S and the regulation of activated protein C. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1984 Apr;10(2):131–138. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1004415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J. Regulation of activated protein C by protein S. The role of phospholipid in factor Va inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11128–11131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J. Regulation of bovine activated protein C by protein S: the role of the cofactor protein in species specificity. Thromb Res. 1981 May 1;22(3):321–327. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(81)90125-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]