Abstract
The synthesis of C2 and factor B, the key components of complement system, is performed by various kinds of cells and is also up-regulated by interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma). By using human fibroblasts, human glioblastoma cell line A172 and monocytes, we investigated the signal-transduction mechanism for IFN-gamma-induced synthesis of C2 and factor B. The C2 and factor B synthesis induced by IFN-gamma in all three cell types was inhibited by a protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor, 1-(5-isoquinolinyl-sulphonyl)-2-methylpiperazine (H-7). The depletion of PKC in these cell types after treatment with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) resulted in inhibition of IFN-gamma-induced C2 production. In addition, IFN-gamma treatment elicited a decrease in cytoplasmic PKC in A172 cells, indicating that PKC is activated by IFN-gamma. These results suggest that PKC is crucial for IFN-gamma-induced C2 and factor B synthesis. Northern-blot analysis showed that the effects at H-7 were at least partly mediated by modulation of C2 and factor B mRNA abundance in A172 cells. Since treatment of fibroblasts and A172 cells with IFN-gamma had no effect on intracellular Ca2+ concentration, and since neither EGTA nor nifedipine inhibited C2 or factor B synthesis induced by IFN-gamma, we concluded that intracellular Ca2+ mobilization was not involved in the effect of IFN-gamma. In addition, genistein, herbimycin A and N-(6-aminohexyl)-5-chloro-1-naphthalene-sulphonamide (W-7) had no inhibitory effect on IFN-gamma-mediated action in any of the three cell types, which suggests that IFN-gamma acts independently of tyrosine kinases and calmodulin-dependent protein kinases.
Full text
PDF


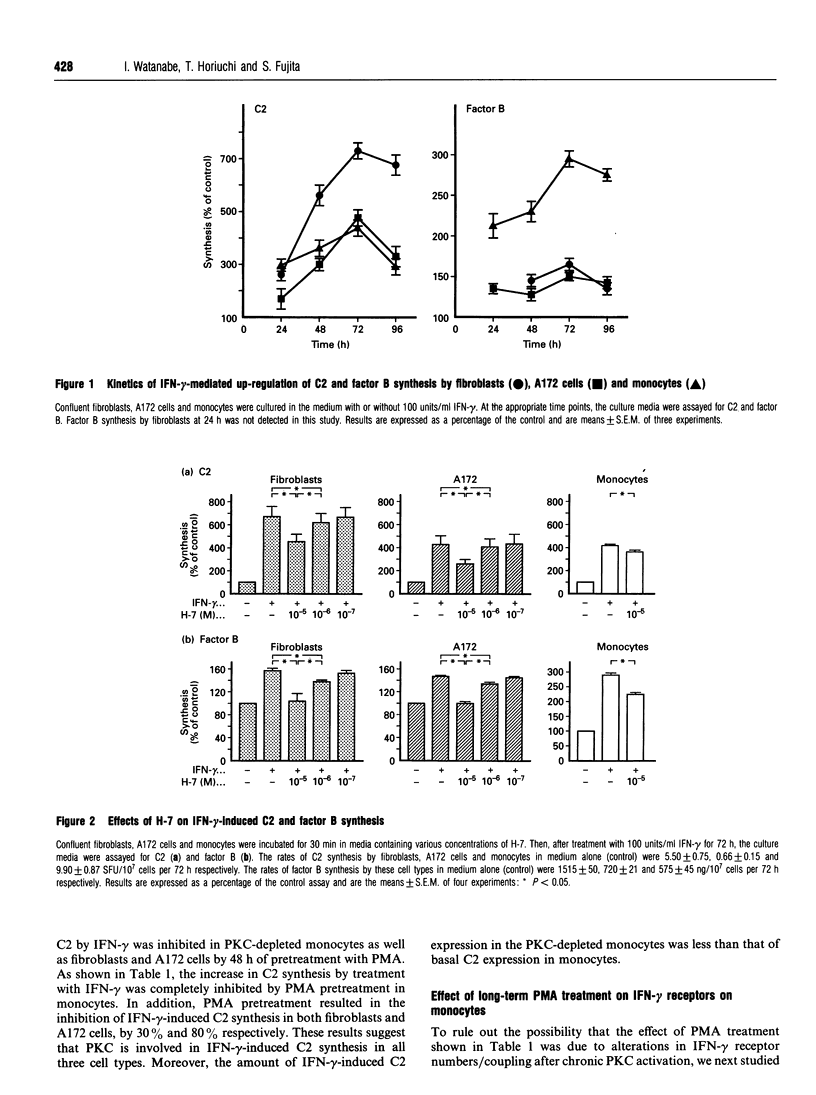
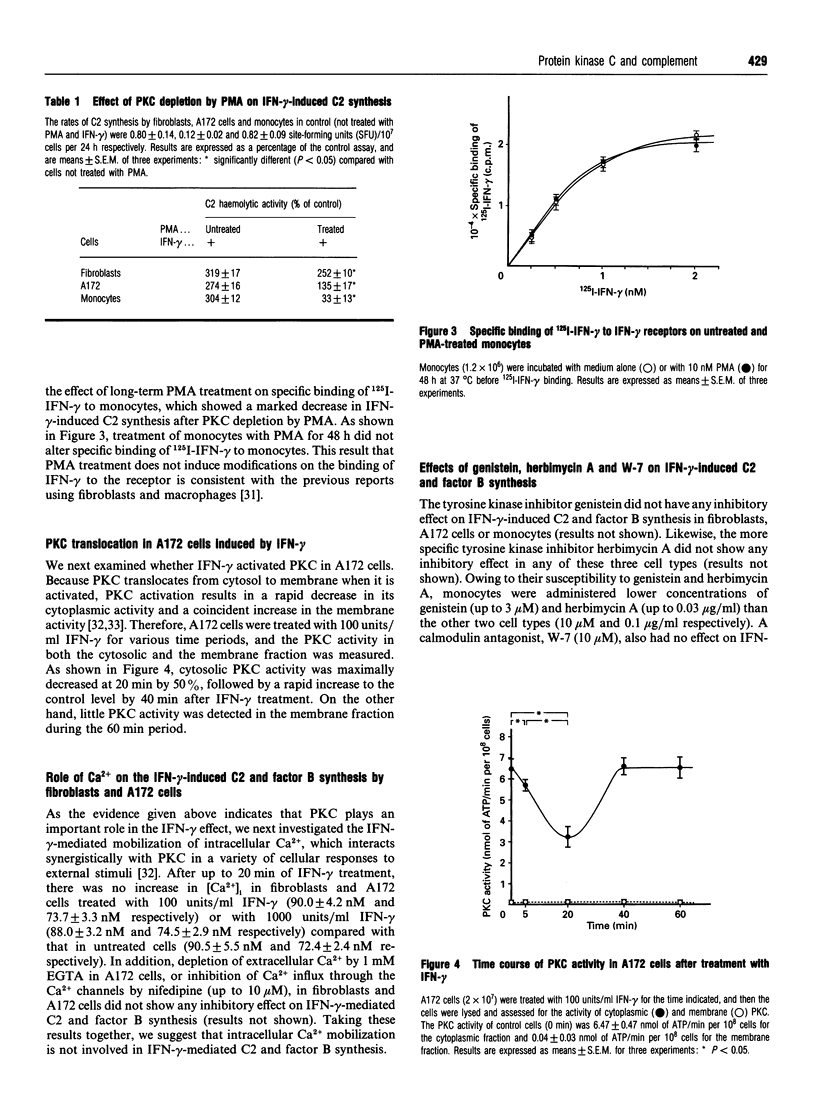
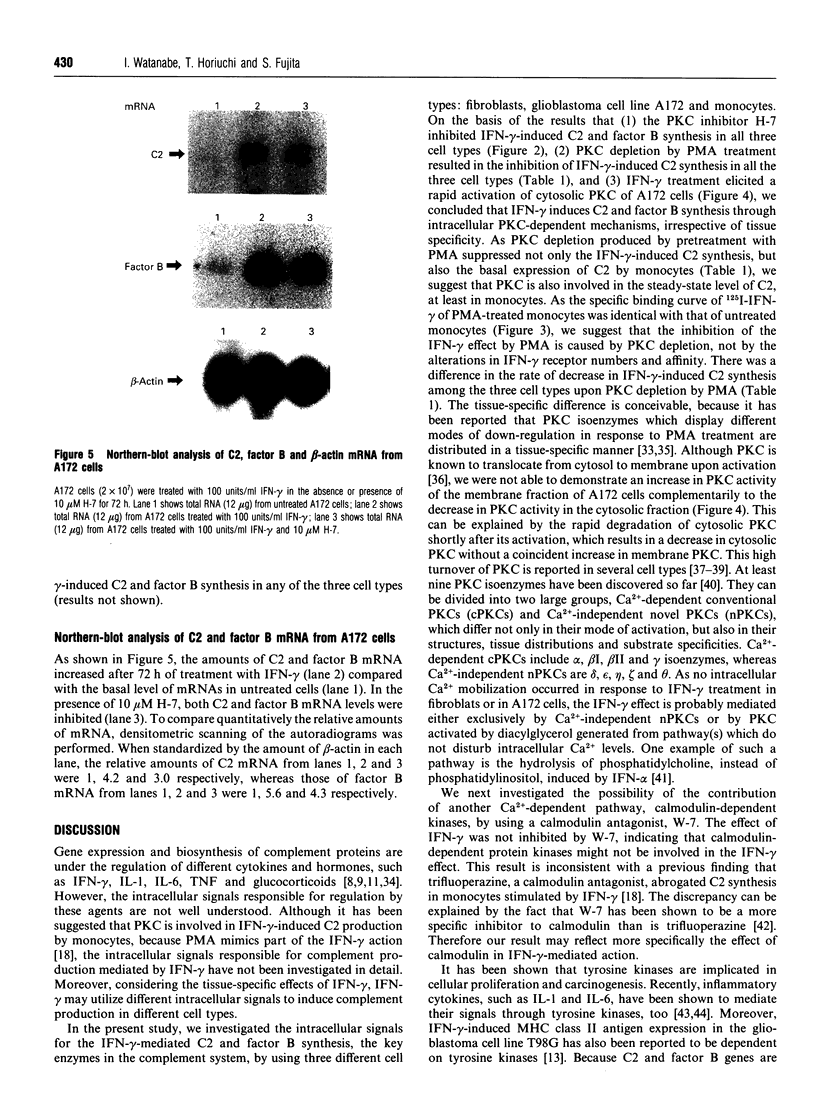

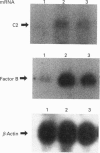
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnum S. R., Ishii Y., Agrawal A., Volanakis J. E. Production and interferon-gamma-mediated regulation of complement component C2 and factors B and D by the astroglioma cell line U105-MG. Biochem J. 1992 Oct 15;287(Pt 2):595–601. doi: 10.1042/bj2870595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Campbell R. D., Bentley D. R., Porter R. R. A molecular map of the human major histocompatibility complex class III region linking complement genes C4, C2 and factor B. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):237–241. doi: 10.1038/307237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celada A., Maki R. A. IFN-gamma induces the expression of the genes for MHC class II I-A beta and tumor necrosis factor through a protein kinase C-independent pathway. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):114–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celada A. The interferon gamma receptor. Lymphokine Res. 1988 Spring;7(1):61–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chida K., Kato N., Kuroki T. Down regulation of phorbol diester receptors by proteolytic degradation of protein kinase C in a cultured cell line of fetal rat skin keratinocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13013–13018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colten H. R. Biosynthesis of complement. Adv Immunol. 1976;22:67–118. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60548-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colten H. R. Biosynthesis of the MHC-linked complement proteins (C2, C4 and factor B) by mononuclear phagocytes. Mol Immunol. 1982 Oct;19(10):1279–1285. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90294-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dauchel H., Julen N., Lemercier C., Daveau M., Ozanne D., Fontaine M., Ripoche J. Expression of complement alternative pathway proteins by endothelial cells. Differential regulation by interleukin 1 and glucocorticoids. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Aug;20(8):1669–1675. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falus A., Rokita H., Walcz E., Brozik M., Hidvégi T., Merétey K. Hormonal regulation of complement biosynthesis in human cell lines--II. Upregulation of the biosynthesis of complement components C3, factor B and C1 inhibitor by interleukin-6 and interleukin-1 in human hepatoma cell line. Mol Immunol. 1990 Feb;27(2):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(90)90115-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heasley L. E., Johnson G. L. Regulation of protein kinase C by nerve growth factor, epidermal growth factor, and phorbol esters in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8646–8652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi T., Kim S., Matsumoto M., Watanabe I., Fujita S., Volanakis J. E. Human complement factor B: cDNA cloning, nucleotide sequencing, phenotypic conversion by site-directed mutagenesis and expression. Mol Immunol. 1993 Dec;30(17):1587–1592. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(93)90450-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi T., Macon K. J., Engler J. A., Volanakis J. E. Site-directed mutagenesis of the region around Cys-241 of complement component C2. Evidence for a C4b binding site. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 15;147(2):584–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi T., Macon K. J., Kidd V. J., Volanakis J. E. Translational regulation of complement protein C2 expression by differential utilization of the 5'-untranslated region of mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6521–6524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi T., Macon K. J., Kidd V. J., Volanakis J. E. cDNA cloning and expression of human complement component C2. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):2105–2111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hug H., Sarre T. F. Protein kinase C isoenzymes: divergence in signal transduction? Biochem J. 1993 Apr 15;291(Pt 2):329–343. doi: 10.1042/bj2910329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki T., Uehara Y., Graves L., Rachie N., Bomsztyk K. Herbimycin A blocks IL-1-induced NF-kappa B DNA-binding activity in lymphoid cell lines. FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 24;298(2-3):240–244. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80067-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaraman S., Mensi N., Webb D. R., Dorf M. E. Involvement of protein kinase C in competence induction of macrophages to generate T suppressor cells. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 15;146(12):4085–4091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kariya K., Takai Y. Distinct functions of down-regulation-sensitive and -resistant types of protein kinase C in rabbit aortic smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jul 13;219(1):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81202-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz Y., Cole F. S., Strunk R. C. Synergism between gamma interferon and lipopolysaccharide for synthesis of factor B, but not C2, in human fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):1–14. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz Y., Strunk R. C. IL-1 and tumor necrosis factor. Similarities and differences in stimulation of expression of alternative pathway of complement and IFN-beta 2/IL-6 genes in human fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):3862–3867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. B., Schepers T. M., Dean W. L., Sonnenfeld G., McLeish K. R. Role of intracellular calcium concentration and protein kinase C activation in IFN-gamma stimulation of U937 cells. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4305–4311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koide Y., Ina Y., Nezu N., Yoshida T. O. Calcium influx and the Ca2+-calmodulin complex are involved in interferon-gamma-induced expression of HLA class II molecules on HL-60 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3120–3124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft A. S., Anderson W. B. Phorbol esters increase the amount of Ca2+, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase associated with plasma membrane. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):621–623. doi: 10.1038/301621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakauer T., Oppenheim J. J. IL-1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha each up-regulate both the expression of IFN-gamma receptors and enhance IFN-gamma-induced HLA-DR expression on human monocytes and a human monocytic cell line (THP-1). J Immunol. 1993 Feb 15;150(4):1205–1211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lappin D. F., Guc D., Hill A., McShane T., Whaley K. Effect of interferon-gamma on complement gene expression in different cell types. Biochem J. 1992 Jan 15;281(Pt 2):437–442. doi: 10.1042/bj2810437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lappin D. F., Whaley K. Modulation of complement gene expression by glucocorticoids. Biochem J. 1991 Nov 15;280(Pt 1):117–123. doi: 10.1042/bj2800117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lappin D., Whaley K. The role of ion channels and protein kinase C activation in the stimulation of complement protein synthesis. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1987 Oct;24(2):57–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littman B. H., Hall R. E., Muchmore A. V. Lymphokine and phorbol (PMA) regulation of complement (C2) synthesis using U937. Cell Immunol. 1983 Feb 15;76(1):189–195. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90360-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews W. J., Jr, Goldberger G., Marino J. T., Jr, Einstein L. P., Gash D. J., Colten H. R. Complement proteins C2, C4 and factor B. Effect of glycosylation on their secretion and catabolism. Biochem J. 1982 Jun 15;204(3):839–846. doi: 10.1042/bj2040839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCubrey J. A., Steelman L. S., Sandlin G., Riddle R. S., Ways D. K. Effects of phorbol esters on an interleukin-3-dependent cell line. Blood. 1990 Jul 1;76(1):63–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muldoon L. L., Jamieson G. A., Jr, Kao A. C., Palfrey H. C., Villereal M. L. Mitogen stimulation of Na+-H+ exchange: differential involvement of protein kinase C. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 1):C219–C229. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.2.C219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima K., Wall R. Interleukin-6 signals activating junB and TIS11 gene transcription in a B-cell hybridoma. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1409–1418. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nezu N., Ryu K., Koide Y., Yoshida T. O. Regulation of HLA class II molecule expressions by IFN-gamma. The signal transduction mechanism in glioblastoma cell lines. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):3126–3135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter D. H., Goldberger G., Dinarello C. A., Mizel S. B., Colten H. R. Regulation of class III major histocompatibility complex gene products by interleukin-1. Science. 1986 May 16;232(4752):850–852. doi: 10.1126/science.3010455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer L. M., Eisenkraft B. L., Reich N. C., Improta T., Baxter G., Daniel-Issakani S., Strulovici B. Transmembrane signaling by interferon alpha involves diacylglycerol production and activation of the epsilon isoform of protein kinase C in Daudi cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):7988–7992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.7988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer L. M., Strulovici B., Saltiel A. R. Interferon-alpha selectively activates the beta isoform of protein kinase C through phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6537–6541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strunk R. C., Cole F. S., Perlmutter D. H., Colten H. R. gamma-Interferon increases expression of class III complement genes C2 and factor B in human monocytes and in murine fibroblasts transfected with human C2 and factor B genes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15280–15285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Ohmura T., Hidaka H. Hydrophobic interaction of the Ca2+-calmodulin complex with calmodulin antagonists. Naphthalenesulfonamide derivatives. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;22(2):403–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto H., Ueda A., Nagasawa K., Tada Y., Niho Y. Increased production of the third component of complement (C3) by monocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Nov;82(2):257–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05436.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S., Parker P. J., Ullrich A., Stabel S. Down-regulation of protein kinase C is due to an increased rate of degradation. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 15;244(3):775–779. doi: 10.1042/bj2440775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]