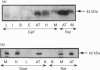
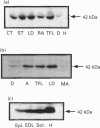
Abstract
It is well accepted that skeletal muscle is a major glucose-utilizing tissue and that insulin is able to stimulate in vivo glucose utilization in ruminants as in monogastrics. In order to determine precisely how glucose uptake is controlled in various ruminant muscles, particularly by insulin, this study was designed to investigate in vitro glucose transport and insulin-regulatable glucose-transporter protein (GLUT4) in muscle from calf and goat. Our data demonstrate that glucose transport is the rate-limiting step for glucose uptake in bovine fibre strips, as in rat muscle. Insulin increases the rate of in vitro glucose transport in bovine muscle, but to a lower extent than in rat muscle. A GLUT4-like protein was detected by immunoblot assay in all insulin-responsive tissues from calf and goat (heart, skeletal muscle, adipose tissue) but not in liver, brain, erythrocytes and intestine. Unlike the rat, bovine and goat GLUT4 content is higher in glycolytic and oxido-glycolytic muscles than in oxidative muscles. In conclusion, using both a functional test (insulin stimulation of glucose transport) and an immunological approach, this study demonstrates that ruminant muscles express GLUT4 protein. Our data also suggest that, in ruminants, glucose is the main energy-yielding substrate for glycolytic but not for oxidative muscles, and that insulin responsiveness may be lower in oxidative than in other skeletal muscles.
Full text
PDF

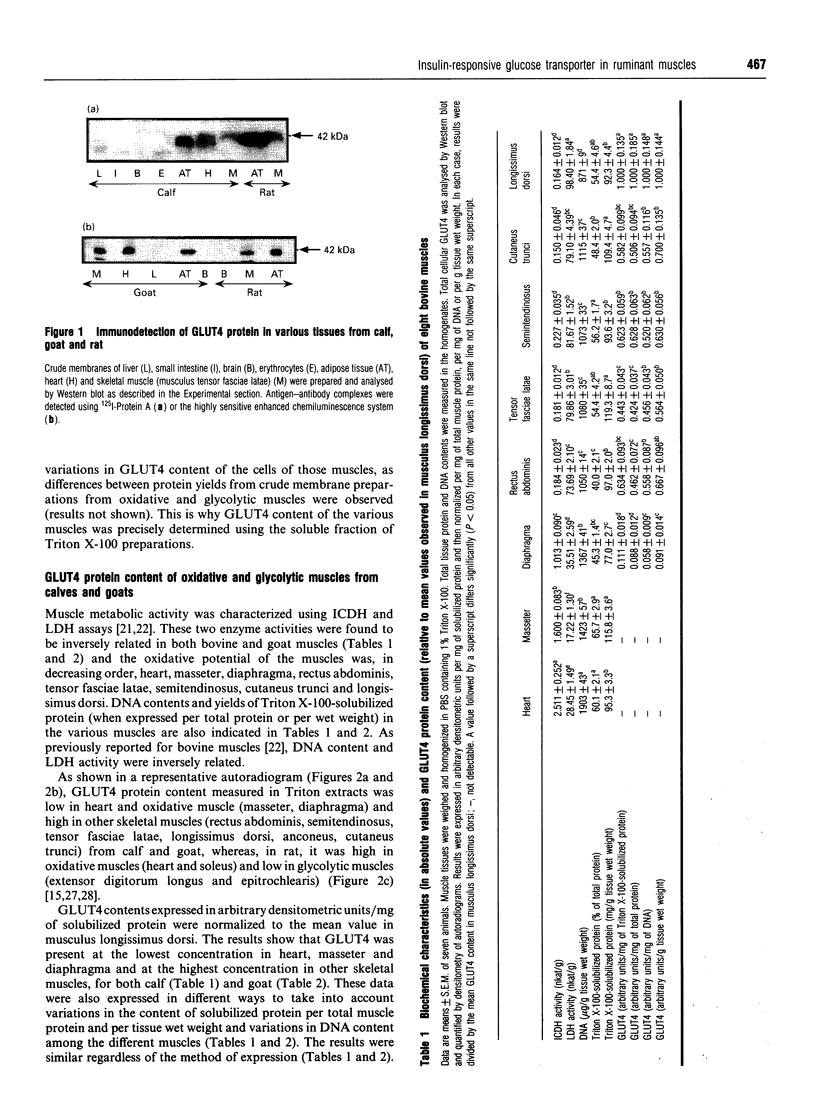
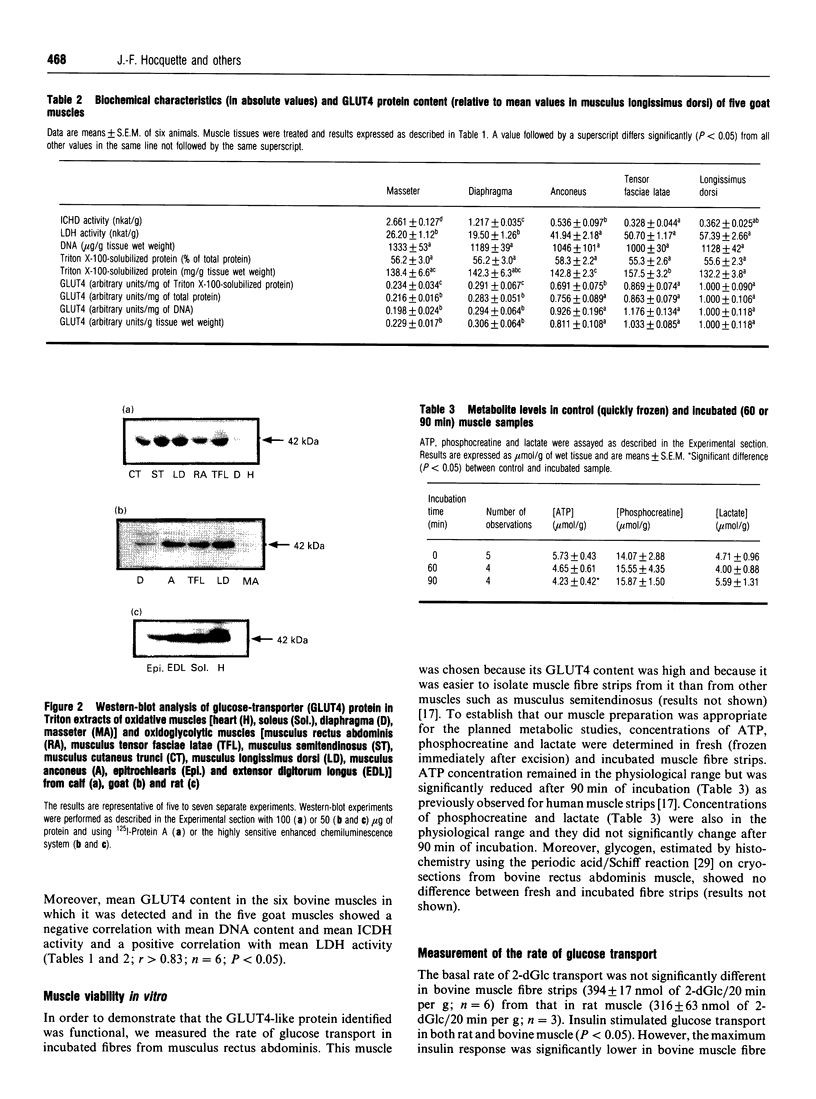


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balage M., Sornet C., Grizard J. Insulin receptor binding and kinase activity in liver and skeletal muscles of lactating goats. Am J Physiol. 1992 May;262(5 Pt 1):E561–E568. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1992.262.5.E561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin S. A. Mammalian passive glucose transporters: members of an ubiquitous family of active and passive transport proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jun 8;1154(1):17–49. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(93)90015-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briand M., Talmant A., Briand Y., Monin G., Durand R. Metabolic types of muscle in the sheep: II. Lactate dehydrogenase activity and LDH isoenzyme distribution. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1981;46(4):359–365. doi: 10.1007/BF00422123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dardevet D., Sornet C., Attaix D., Baracos V. E., Grizard J. Insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin resistance in skeletal muscles of adult and old rats. Endocrinology. 1994 Mar;134(3):1475–1484. doi: 10.1210/endo.134.3.8119189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debras E., Grizard J., Aina E., Tesseraud S., Champredon C., Arnal M. Insulin sensitivity and responsiveness during lactation and dry period in goats. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 1):E295–E302. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.256.2.E295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohm G. L., Tapscott E. B., Pories W. J., Dabbs D. J., Flickinger E. G., Meelheim D., Fushiki T., Atkinson S. M., Elton C. W., Caro J. F. An in vitro human muscle preparation suitable for metabolic studies. Decreased insulin stimulation of glucose transport in muscle from morbidly obese and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):486–494. doi: 10.1172/JCI113622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferré P., Leturque A., Burnol A. F., Penicaud L., Girard J. A method to quantify glucose utilization in vivo in skeletal muscle and white adipose tissue of the anaesthetized rat. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):103–110. doi: 10.1042/bj2280103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grizard J. Insulin binding to skeletal muscle membranes in growing ruminating sheep fed different diets. Reprod Nutr Dev. 1983;23(2 B):389–401. doi: 10.1051/rnd:19830309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen E. J., Bourey R. E., Rodnick K. J., Koranyi L., Permutt M. A., Holloszy J. O. Glucose transporter protein content and glucose transport capacity in rat skeletal muscles. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 1):E593–E598. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.259.4.E593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostettler-Allen R. L., Tappy L., Blum J. W. Insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, and glucosuria in intensively milk-fed calves. J Anim Sci. 1994 Jan;72(1):160–173. doi: 10.2527/1994.721160x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issad T., Coupé C., Pastor-Anglada M., Ferré P., Girard J. Development of insulin-sensitivity at weaning in the rat. Role of the nutritional transition. Biochem J. 1988 May 1;251(3):685–690. doi: 10.1042/bj2510685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issad T., Pénicaud L., Ferré P., Kandé J., Baudon M. A., Girard J. Effects of fasting on tissue glucose utilization in conscious resting rats. Major glucose-sparing effect in working muscles. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 15;246(1):241–244. doi: 10.1042/bj2460241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Strube M., Mueckler M. Molecular cloning and characterization of an insulin-regulatable glucose transporter. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):83–87. doi: 10.1038/338083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern M., Tapscott E. B., Snider R. D., Dohm G. L. Differences in glucose transport rates between perfused and in vitro incubated muscles. Horm Metab Res. 1990 Jul;22(7):366–368. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1004923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koranyi L. I., Bourey R. E., Vuorinen-Markkola H., Koivisto V. A., Mueckler M., Permutt M. A., Yki-Järvinen H. Level of skeletal muscle glucose transporter protein correlates with insulin-stimulated whole body glucose disposal in man. Diabetologia. 1991 Oct;34(10):763–765. doi: 10.1007/BF00401526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillioja S., Young A. A., Culter C. L., Ivy J. L., Abbott W. G., Zawadzki J. K., Yki-Järvinen H., Christin L., Secomb T. W., Bogardus C. Skeletal muscle capillary density and fiber type are possible determinants of in vivo insulin resistance in man. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):415–424. doi: 10.1172/JCI113088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. L., Asano T., Shibasaki Y., Tsukuda K., Katagiri H., Ishihara H., Takaku F., Oka Y. Altered expression of glucose transporter isoforms with aging in rats--selective decrease in GluT4 in the fat tissue and skeletal muscle. Diabetologia. 1991 Jul;34(7):477–482. doi: 10.1007/BF00403283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marette A., Richardson J. M., Ramlal T., Balon T. W., Vranic M., Pessin J. E., Klip A. Abundance, localization, and insulin-induced translocation of glucose transporters in red and white muscle. Am J Physiol. 1992 Aug;263(2 Pt 1):C443–C452. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.2.C443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. S., Dennis S. C., DeBuysere M. S., Padma A. The regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase in the isolated perfused rat heart. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7369–7375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pethick D. W., Lindsay D. B. Acetate metabolism in lactating sheep. Br J Nutr. 1982 Sep;48(2):319–328. doi: 10.1079/bjn19820116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prior R. L., Huntington G. B., Reynolds P. J. Role of insulin and glucose on metabolite uptake by the hind half of beef steers. J Anim Sci. 1984 Jun;58(6):1446–1453. doi: 10.2527/jas1984.5861446x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren J. M., Marshall B. A., Gulve E. A., Gao J., Johnson D. W., Holloszy J. O., Mueckler M. Evidence from transgenic mice that glucose transport is rate-limiting for glycogen deposition and glycolysis in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16113–16115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Mandarino L. J., Gerich J. E. Dose-response characteristics for effects of insulin on production and utilization of glucose in man. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jun;240(6):E630–E639. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.6.E630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano H., Nakai M., Kondo T., Terashima Y. Insulin responsiveness to glucose and tissue responsiveness to insulin in lactating, pregnant, and nonpregnant, nonlactating beef cows. J Anim Sci. 1991 Mar;69(3):1122–1127. doi: 10.2527/1991.6931122x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki S. Mechanism of insulin resistance in the post receptor events in sheep: 3-O-methylglucose transport in ovine adipocytes. Horm Metab Res. 1990 Sep;22(9):457–461. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1004947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. B., Ekeren P. A., Sanders J. O. Fatty acid-binding protein activities in bovine muscle, liver and adipose tissue. J Nutr. 1985 Nov;115(11):1535–1539. doi: 10.1093/jn/115.11.1535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trayhurn P., Thomas M. E., Keith J. S. Postnatal development of uncoupling protein, uncoupling protein mRNA, and GLUT4 in adipose tissues of goats. Am J Physiol. 1993 Sep;265(3 Pt 2):R676–R682. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1993.265.3.R676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMSON J. R. GLYCOLYTIC CONTROL MECHANISMS. I. INHIBITION OF GLYCOLYSIS BY ACETATE AND PYRUVATE IN THE ISOLATED, PERFUSED RAT HEART. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2308–2321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao F. Q., Glimm D. R., Kennelly J. J. Distribution of mammalian facilitative glucose transporter messenger RNA in bovine tissues. Int J Biochem. 1993 Dec;25(12):1897–1903. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(88)90322-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziel F. H., Venkatesan N., Davidson M. B. Glucose transport is rate limiting for skeletal muscle glucose metabolism in normal and STZ-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1988 Jul;37(7):885–890. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.7.885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Walt J. G., Linington M. J. A review of energy metabolism in producing ruminants. Part 1: Metabolism of energy substrates. J S Afr Vet Assoc. 1989 Dec;60(4):223–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]