Abstract
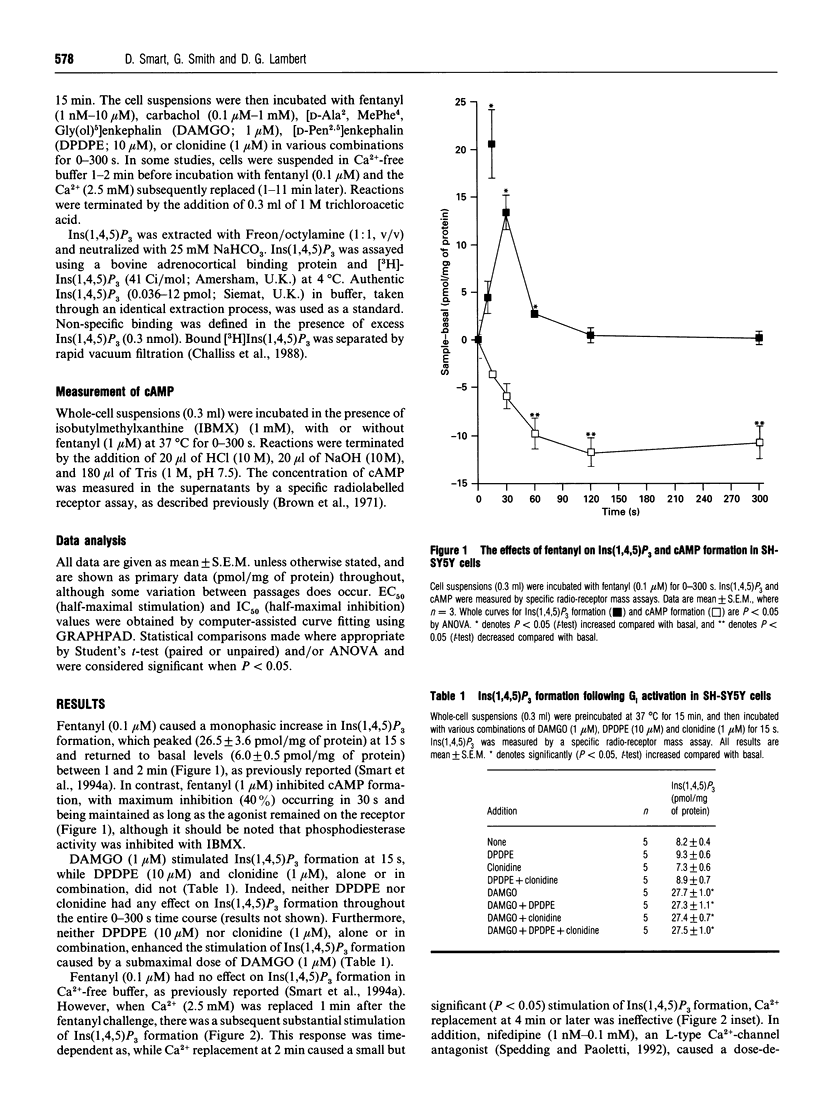
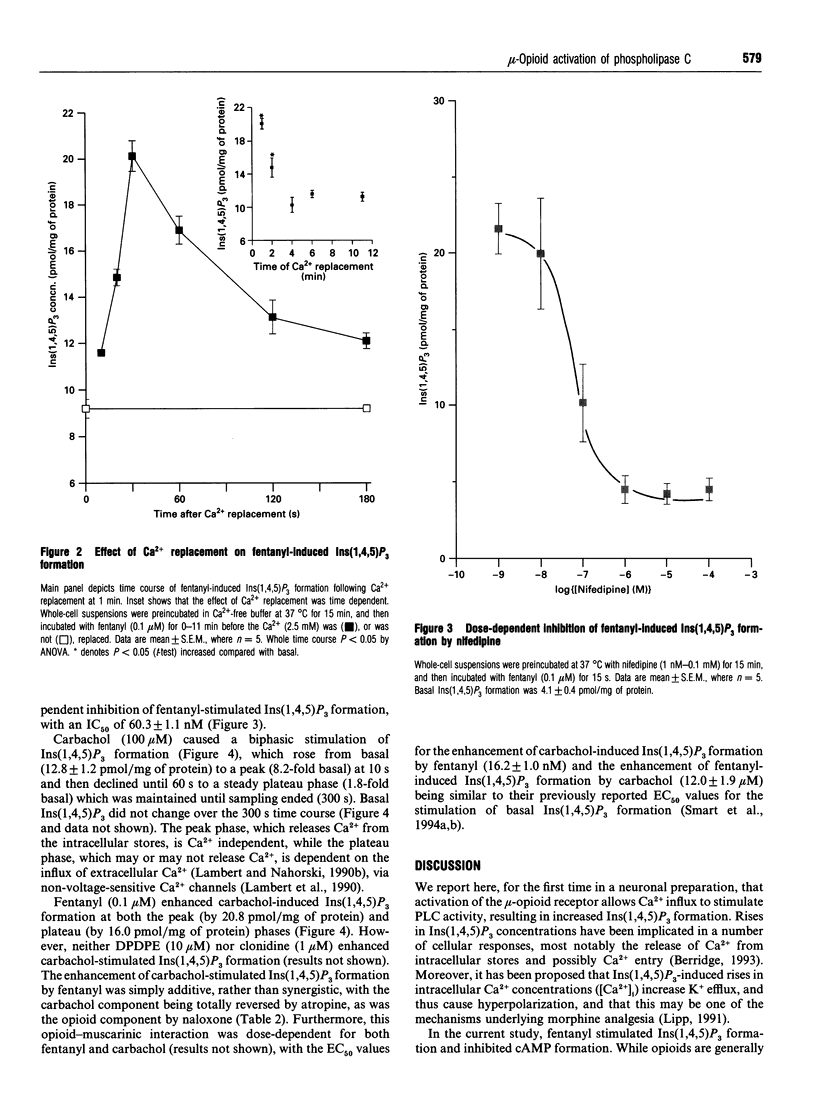
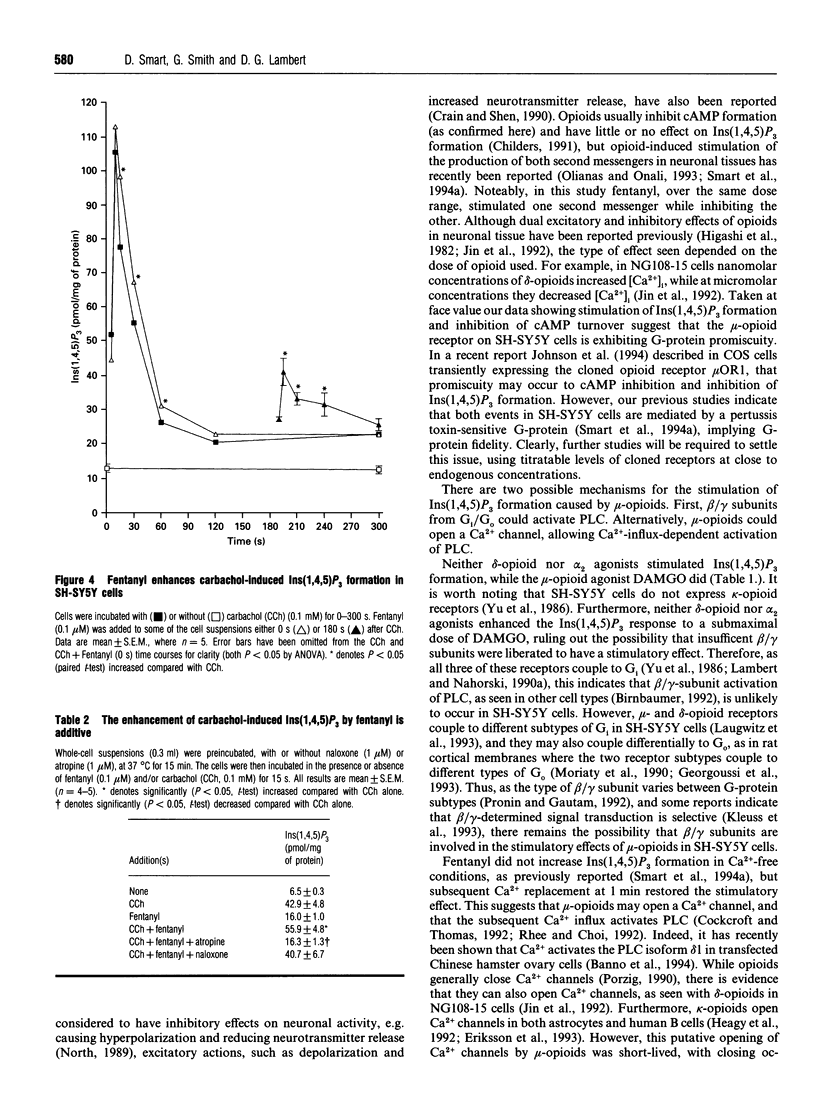
We have recently reported that, in SH-SY5Y cells, mu-opioid receptor occupancy activates phospholipase C via a pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein. In the present study we have further characterized the mechanisms involved in this process. Fentanyl (0.1 microM) caused a monophasic increase in inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate mass formation, with a peak (20.5 +/- 3.6 pmol/mg of protein) at 15 s. Incubation in Ca(2+)-free buffer abolished this response, while Ca2+ replacement 1 min later restored the stimulation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate formation (20.1 +/- 0.6 pmol/mg of protein). In addition, nifedipine (1 nM-0.1 mM), an L-type Ca(2+)-channel antagonist, caused a dose-dependent inhibition of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate formation, with an IC50 of 60.3 +/- 1.1 nM. Elevation of endogenous beta/gamma subunits by selective activation of delta-opioid and alpha 2 adrenoceptors failed to stimulate phospholipase C. Fentanyl also caused a dose-dependent (EC50 of 16.2 +/- 1.0 nM), additive enhancement of carbachol-induced inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate formation. In summary, we have demonstrated that in SH-SY5Y cells activation of the mu-opioid receptor allows Ca2+ influx to activate phospholipase C. However, the possible role of this mechanism in the process of analgesia remains to be elucidated.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atcheson R., Rowbotham D. J., Lambert D. G. Fentanyl inhibits the release of [3H]noradrenaline from SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Br J Anaesth. 1994 Jan;72(1):98–103. doi: 10.1093/bja/72.1.98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banno Y., Okano Y., Nozawa Y. Thrombin-mediated phosphoinositide hydrolysis in Chinese hamster ovary cells overexpressing phospholipase C-delta 1. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 3;269(22):15846–15852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L. Receptor-to-effector signaling through G proteins: roles for beta gamma dimers as well as alpha subunits. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1069–1072. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. L., Albano J. D., Ekins R. P., Sgherzi A. M. A simple and sensitive saturation assay method for the measurement of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(3):561–562. doi: 10.1042/bj1210561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn S. J., Marley P. D., Livett B. G. Effects of opioid compounds on basal and muscarinic induced accumulation of inositol phosphates in cultured bovine chromaffin cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Feb 1;37(3):395–399. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90205-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camps M., Carozzi A., Schnabel P., Scheer A., Parker P. J., Gierschik P. Isozyme-selective stimulation of phospholipase C-beta 2 by G protein beta gamma-subunits. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):684–686. doi: 10.1038/360684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carozzi A., Camps M., Gierschik P., Parker P. J. Activation of phosphatidylinositol lipid-specific phospholipase C-beta 3 by G-protein beta gamma subunits. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jan 11;315(3):340–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81190-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challiss R. A., Batty I. H., Nahorski S. R. Mass measurements of inositol(1,4,5)trisphosphate in rat cerebral cortex slices using a radioreceptor assay: effects of neurotransmitters and depolarization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 15;157(2):684–691. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80304-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childers S. R. Opioid receptor-coupled second messenger systems. Life Sci. 1991;48(21):1991–2003. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90154-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Thomas G. M. Inositol-lipid-specific phospholipase C isoenzymes and their differential regulation by receptors. Biochem J. 1992 Nov 15;288(Pt 1):1–14. doi: 10.1042/bj2880001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras E., Tamayo L., Amigo M. Calcium channel antagonists increase morphine-induced analgesia and antagonize morphine tolerance. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Apr 13;148(3):463–466. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crain S. M., Shen K. F. Opioids can evoke direct receptor-mediated excitatory effects on sensory neurons. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Feb;11(2):77–81. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90322-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson P. S., Nilsson M., Wågberg M., Hansson E., Rönnbäck L. Kappa-opioid receptors on astrocytes stimulate L-type Ca2+ channels. Neuroscience. 1993 May;54(2):401–407. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90261-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgoussi Z., Carr C., Milligan G. Direct measurements of in situ interactions of rat brain opioid receptors with the guanine nucleotide-binding protein Go. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;44(1):62–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heagy W., Shipp M. A., Finberg R. W. Opioid receptor agonists and Ca2+ modulation in human B cell lines. J Immunol. 1992 Dec 15;149(12):4074–4081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi H., Shinnick-Gallagher P., Gallagher J. P. Morphine enhances and depresses Ca2+-dependent responses in visceral primary afferent neurons. Brain Res. 1982 Nov 11;251(1):186–191. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91291-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hustveit O., Setekleiv J. Fentanyl and pethidine are antagonists on muscarinic receptors in guinea-pig ileum. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1993 Aug;37(6):541–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1993.tb03761.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglese J., Freedman N. J., Koch W. J., Lefkowitz R. J. Structure and mechanism of the G protein-coupled receptor kinases. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):23735–23738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin W., Lee N. M., Loh H. H., Thayer S. A. Dual excitatory and inhibitory effects of opioids on intracellular calcium in neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid NG108-15 cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;42(6):1083–1089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. S., Wang J. B., Wang W. F., Uhl G. R. Expressed mu opiate receptor couples to adenylate cyclase and phosphatidyl inositol turnover. Neuroreport. 1994 Jan 12;5(4):507–509. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199401120-00035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleuss C., Scherübl H., Hescheler J., Schultz G., Wittig B. Selectivity in signal transduction determined by gamma subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins. Science. 1993 Feb 5;259(5096):832–834. doi: 10.1126/science.8094261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert D. G., Atcheson R., Hirst R. A., Rowbotham D. J. Effects of morphine and its metabolites on opiate receptor binding, cAMP formation and [3H]noradrenaline release from SH-SY5Y cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Oct 5;46(7):1145–1150. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90462-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert D. G., Nahorski S. R. Muscarinic-receptor-mediated changes in intracellular Ca2+ and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate mass in a human neuroblastoma cell line, SH-SY5Y. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):555–562. doi: 10.1042/bj2650555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert D. G., Nahorski S. R. Pertussis toxin inhibits alpha 2-adrenoceptor-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase without affecting muscarinic regulation of [Ca2+]i or inositol phosphate generation in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 15;40(10):2291–2295. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90725-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert D. G., Whitham E. M., Baird J. G., Nahorski S. R. Different mechanisms of Ca2+ entry induced by depolarization and muscarinic receptor stimulation in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1990 Aug;8(3):263–266. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(90)90026-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laugwitz K. L., Offermanns S., Spicher K., Schultz G. mu and delta opioid receptors differentially couple to G protein subtypes in membranes of human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Neuron. 1993 Feb;10(2):233–242. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90314-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp J. Possible mechanisms of morphine analgesia. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1991 Apr;14(2):131–147. doi: 10.1097/00002826-199104000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J. Molecular mechanisms of membrane receptor desensitization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Nov 7;1179(2):171–188. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(93)90139-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriarty T. M., Padrell E., Carty D. J., Omri G., Landau E. M., Iyengar R. Go protein as signal transducer in the pertussis toxin-sensitive phosphatidylinositol pathway. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):79–82. doi: 10.1038/343079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton A. J., Hammond C., Mason W. T., Henderson G. Characterisation of the L- and N-type calcium channels in differentiated SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells: calcium imaging and single channel recording. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1992 Mar;13(1-2):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(92)90044-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A. Twelfth Gaddum memorial lecture. Drug receptors and the inhibition of nerve cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;98(1):13–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb16855.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Tomura H., Kondo Y. Enkephalin activates the phospholipase C/Ca2+ system through cross-talk between opioid receptors and P2-purinergic or bradykinin receptors in NG 108-15 cells. A permissive role for pertussis toxin-sensitive G-proteins. Biochem J. 1993 Feb 15;290(Pt 1):241–247. doi: 10.1042/bj2900241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olianas M. C., Onali P. Synergistic interaction of muscarinic and opioid receptors with GS-linked neurotransmitter receptors to stimulate adenylyl cyclase activity of rat olfactory bulb. J Neurochem. 1993 Dec;61(6):2183–2190. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb07458.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omote K., Sonoda H., Kawamata M., Iwasaki H., Namiki A. Potentiation of antinociceptive effects of morphine by calcium-channel blockers at the level of the spinal cord. Anesthesiology. 1993 Oct;79(4):746–752. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199310000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porzig H. Pharmacological modulation of voltage-dependent calcium channels in intact cells. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1990;114:209–262. doi: 10.1007/BFb0031020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pronin A. N., Gautam N. Interaction between G-protein beta and gamma subunit types is selective. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6220–6224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Choi K. D. Regulation of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12393–12396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart D., Smith G., Lambert D. G. Halothane and isoflurane enhance basal and carbachol-stimulated inositol(1,4,5)triphosphate formation in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1994 Mar 15;47(6):939–945. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(94)90403-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart D., Smith G., Lambert D. G. mu-Opioid receptor stimulation of inositol (1,4,5)trisphosphate formation via a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein. J Neurochem. 1994 Mar;62(3):1009–1014. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.62031009.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spedding M., Paoletti R. Classification of calcium channels and the sites of action of drugs modifying channel function. Pharmacol Rev. 1992 Sep;44(3):363–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toselli M., Masetto S., Rossi P., Taglietti V. Characterization of a Voltage-dependent Calcium Current in the Human Neuroblastoma Cell Line SH-SY5Y During Differentiation. Eur J Neurosci. 1991 Jun;3(6):514–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1991.tb00838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C. H., Wu W. H., Yarmush J., Zbuzek V. K. An antinociceptive effect of the intraperitoneal injection of nifedipine in rats, measured by tail-flick test. Life Sci. 1993;53(16):PL249–PL253. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(93)90579-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Richards M. L., Sadée W. A human neuroblastoma cell line expresses mu and delta opioid receptor sites. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1065–1070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


