Abstract
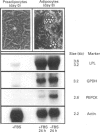
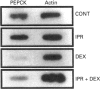
The enzyme phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) plays a key role in gluconeogenesis in liver and in glyceroneogenesis in adipose tissue. These processes, and PEPCK, are regulated by a number of hormones, some of which have different effects on the enzyme in liver and adipose tissue. To explore this phenomenon, PEPCK gene expression was studied in 3T3-F442A adipocytes maintained in a serum-free medium. The beta-adrenergic agonist isoprenaline (isoproterenol) and a cyclic AMP analogue (8-CPT-cAMP) increased PEPCK mRNA. A maximal 3-fold induction occurred in 2 h. Dexamethasone decreased PEPCK mRNA by 80% in 4 h. Dexamethasone also counteracted the inductive effects of isoprenaline and 8-CPT-cAMP. Run-on transcription experiments showed that the isoprenaline and dexamethasone actions were, at least in part, exerted at the level of PEPCK gene transcription. These effects were further analysed by using transient and stable transfection of adipocytes with a plasmid containing bp -2100 to 69 of the PEPCK gene promoter fused to the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) gene. In such cells isoprenaline stimulated CAT expression, an effect that was prevented if the cells were also exposed to dexamethasone.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ailhaud G., Grimaldi P., Négrel R. Cellular and molecular aspects of adipose tissue development. Annu Rev Nutr. 1992;12:207–233. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.12.070192.001231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antras-Ferry J., Franckhauser S., Robin D., Robin P., Granner D. K., Forest C. Expression of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene in 3T3-F442A adipose cells: effects of retinoic acid and differentiation. Biochem J. 1994 Sep 15;302(Pt 3):943–948. doi: 10.1042/bj3020943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antras J., Lasnier F., Pairault J. Adipsin gene expression in 3T3-F442A adipocytes is posttranscriptionally down-regulated by retinoic acid. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1157–1161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale E. G., Chrapkiewicz N. B., Scoble H. A., Metz R. J., Quick D. P., Noble R. L., Donelson J. E., Biemann K., Granner D. K. Rat hepatic cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP). Structures of the protein, messenger RNA, and gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10748–10760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale E. G., Clouthier D. E., Hammer R. E. Cell-specific expression of cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in transgenic mice. FASEB J. 1992 Dec;6(15):3330–3337. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.15.1281456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale E. G., Tishler E. J. Expression and regulation of cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Dec 15;189(2):925–930. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92292-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benvenisty N., Nechushtan H., Cohen H., Reshef L. Separate cis-regulatory elements confer expression of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) gene in different cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1118–1122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christ B., Nath A. The glucagon-insulin antagonism in the regulation of cytosolic protein binding to the 3' end of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase mRNA in cultured rat hepatocytes. Possible involvement in the stabilization of the mRNA. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Aug 1;215(3):541–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18063.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. R., Docherty K. Negative regulation of transcription in eukaryotes. Biochem J. 1993 Dec 15;296(Pt 3):521–541. doi: 10.1042/bj2960521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani C., Doglio A., Grimaldi P., Ailhaud G. Expression of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene and its insulin regulation during differentiation of preadipose cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jul 16;138(1):468–475. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90304-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. I., Miner J. N., Yoshinaga S. K., Yamamoto K. R. Transcription factor interactions: selectors of positive or negative regulation from a single DNA element. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1266–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.2119054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberger C. L., Nechushtan H., Cohen H., Shani M., Reshef L. Differential regulation of the rat phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene expression in several tissues of transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1396–1403. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forest C. D., O'Brien R. M., Lucas P. C., Magnuson M. A., Granner D. K. Regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene expression by insulin. Use of the stable transfection approach to locate an insulin responsive sequence. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1302–1310. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-9-1302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fève B., Emorine L. J., Lasnier F., Blin N., Baude B., Nahmias C., Strosberg A. D., Pairault J. Atypical beta-adrenergic receptor in 3T3-F442A adipocytes. Pharmacological and molecular relationship with the human beta 3-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20329–20336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giralt M., Park E. A., Gurney A. L., Liu J. S., Hakimi P., Hanson R. W. Identification of a thyroid hormone response element in the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) gene. Evidence for synergistic interaction between thyroid hormone and cAMP cis-regulatory elements. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21991–21996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granner D. K., Andreone T. L. Insulin modulation of gene expression. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1985;1(1-2):139–170. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610010108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainque B., Moustaid N., Quignard-Boulange A., Ardouin B., Lavau M. Glucocorticoid binding during the differentiation of 3T3-F442A fibroblasts into adipocytes. A possible regulatory effect of insulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Dec 10;931(3):347–353. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90226-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hod Y., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP stabilizes the mRNA for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) against degradation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7747–7752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai E., Miner J. N., Mitchell J. A., Yamamoto K. R., Granner D. K. Glucocorticoid receptor-cAMP response element-binding protein interaction and the response of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene to glucocorticoids. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5353–5356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai E., Stromstedt P. E., Quinn P. G., Carlstedt-Duke J., Gustafsson J. A., Granner D. K. Characterization of a complex glucocorticoid response unit in the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4712–4719. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ireland R. C., Kotarski M. A., Johnston L. A., Stadler U., Birkenmeier E., Kozak L. P. Primary structure of the mouse glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11779–11785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchgessner T. G., Svenson K. L., Lusis A. J., Schotz M. C. The sequence of cDNA encoding lipoprotein lipase. A member of a lipase gene family. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8463–8466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepar G. J., Jump D. B. Hormonal regulation of the S14 gene in 3T3-F442A cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Aug;3(8):1207–1214. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-8-1207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J. S., Park E. A., Gurney A. L., Roesler W. J., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP induction of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) gene transcription is mediated by multiple promoter elements. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):19095–19102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas P. C., Granner D. K. Hormone response domains in gene transcription. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1131–1173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyuhas O., Reshef L., Gunn J. M., Hanson R. W., Ballard F. J. Regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) in adipose tissue in vivo by glucocorticoids and insulin. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 15;158(1):1–7. doi: 10.1042/bj1580001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner J. N., Yamamoto K. R. Regulatory crosstalk at composite response elements. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90168-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nechushtan H., Benvenisty N., Brandeis R., Reshef L. Glucocorticoids control phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene expression in a tissue specific manner. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6405–6417. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordeen S. K., Green P. P., 3rd, Fowlkes D. M. A rapid, sensitive, and inexpensive assay for chloramphenicol acetyltransferase. DNA. 1987 Apr;6(2):173–178. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. M., Bonovich M. T., Forest C. D., Granner D. K. Signal transduction convergence: phorbol esters and insulin inhibit phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene transcription through the same 10-base-pair sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6580–6584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. M., Lucas P. C., Forest C. D., Magnuson M. A., Granner D. K. Identification of a sequence in the PEPCK gene that mediates a negative effect of insulin on transcription. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):533–537. doi: 10.1126/science.2166335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen D. D., Koch S. R., Granner D. K. 3' noncoding region of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase mRNA contains a glucocorticoid-responsive mRNA-stabilizing element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7800–7804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postic C., Leturque A., Rencurel F., Printz R. L., Forest C., Granner D. K., Girard J. The effects of hyperinsulinemia and hyperglycemia on GLUT4 and hexokinase II mRNA and protein in rat skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Diabetes. 1993 Jun;42(6):922–929. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.6.922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reshef L., Hanson R. W., Ballard F. J. A possible physiological role for glyceroneogenesis in rat adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 25;245(22):5979–5984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short M. K., Clouthier D. E., Schaefer I. M., Hammer R. E., Magnuson M. A., Beale E. G. Tissue-specific, developmental, hormonal, and dietary regulation of rat phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase-human growth hormone fusion genes in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1007–1020. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]