Abstract
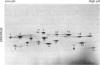
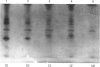
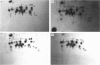
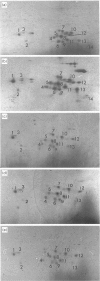
The proteasome or multicatalytic endopeptidase from eukaryotic cells consists of at least 14 subunits that fall into two families, alpha and beta. Subunit-specific monoclonal antibodies against ten different subunits of human proteasomes have been produced, together with an antibody that reacts with a motif (prosbox 1), common to alpha-type subunits. Four of the subunit-specific antibodies were able to precipitate proteasomes. The subunit composition of HeLa-cell proteasomes precipitated with these four different antibodies were identical, as judged from two-dimensional electrophoresis. One of the four antibodies was used to obtain proteasomes from cell lines (HeLa, Daudi, IMR90 and BSC-1) and human tissues (placenta, kidney, and liver). Electrophoretic analysis of these proteasomes, combined with peptide mapping of some subunits, suggests that they all contain 14 types of subunits as their major constituents. However, one subunit was present in two isoelectric isoforms in all cells examined. Two other subunits occurred in two or three isoelectric isoforms in placenta, liver and kidney, but not in the cell cultures. Extracts of human cells (HeLa, IMR90, Daudi and erythrocytes) were analysed by non-denaturing electrophoresis and immunoblotting. All of the 11 subunits detected by antibodies were present in a pair of ATP-stabilized protein complexes, presumed to be the 26 S proteinase, and in a doublet of complexes which migrated more slowly than purified proteasomes. Besides being present in proteasomes, one subunit was also found to occur in the free state in cell extracts.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn J. Y., Hong S. O., Kwak K. B., Kang S. S., Tanaka K., Ichihara A., Ha D. B., Chung C. H. Developmental regulation of proteolytic activities and subunit pattern of 20 S proteasome in chick embryonic muscle. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15746–15749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aki M., Shimbara N., Takashina M., Akiyama K., Kagawa S., Tamura T., Tanahashi N., Yoshimura T., Tanaka K., Ichihara A. Interferon-gamma induces different subunit organizations and functional diversity of proteasomes. J Biochem. 1994 Feb;115(2):257–269. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a124327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama K., Kagawa S., Tamura T., Shimbara N., Takashina M., Kristensen P., Hendil K. B., Tanaka K., Ichihara A. Replacement of proteasome subunits X and Y by LMP7 and LMP2 induced by interferon-gamma for acquirement of the functional diversity responsible for antigen processing. FEBS Lett. 1994 Apr 18;343(1):85–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80612-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo A. P., Mehlen P. Hela cells proteasome interacts with leucine-rich polypeptides and contains a phosphorylated subunit. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Aug 16;194(3):1387–1393. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belich M. P., Glynne R. J., Senger G., Sheer D., Trowsdale J. Proteasome components with reciprocal expression to that of the MHC-encoded LMP proteins. Curr Biol. 1994 Sep 1;4(9):769–776. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00174-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bey F., Silva Pereira I., Coux O., Viegas-Péquignot E., Recillas Targa F., Nothwang H. G., Dutrillaux B., Scherrer K. The prosomal RNA-binding protein p27K is a member of the alpha-type human prosomal gene family. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Feb;237(1-2):193–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00282801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. G., Driscoll J., Monaco J. J. MHC-linked low-molecular mass polypeptide subunits define distinct subsets of proteasomes. Implications for divergent function among distinct proteasome subsets. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 1;151(3):1193–1204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu-Ping M., Slaughter C. A., DeMartino G. N. Purification and characterization of a protein inhibitor of the 20S proteasome (macropain). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Mar 12;1119(3):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(92)90218-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu-Ping M., Vu J. H., Proske R. J., Slaughter C. A., DeMartino G. N. Identification, purification, and characterization of a high molecular weight, ATP-dependent activator (PA700) of the 20 S proteasome. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3539–3547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
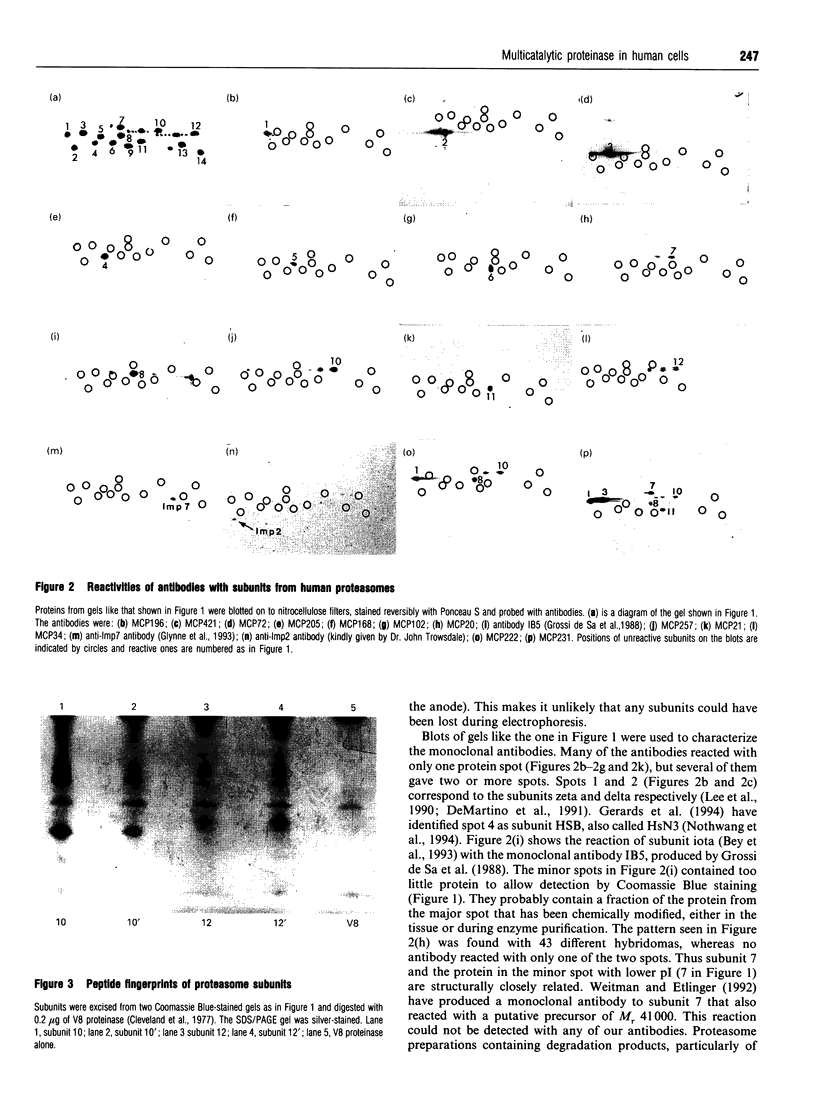
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMartino G. N., Orth K., McCullough M. L., Lee L. W., Munn T. Z., Moomaw C. R., Dawson P. A., Slaughter C. A. The primary structures of four subunits of the human, high-molecular-weight proteinase, macropain (proteasome), are distinct but homologous. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Aug 9;1079(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(91)90020-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll J., Frydman J., Goldberg A. L. An ATP-stabilized inhibitor of the proteasome is a component of the 1500-kDa ubiquitin conjugate-degrading complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4986–4990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubiel W., Pratt G., Ferrell K., Rechsteiner M. Purification of an 11 S regulator of the multicatalytic protease. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22369–22377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkenburg P. E., Kloetzel P. M. Identification and characterization of three different subpopulations of the Drosophila multicatalytic proteinase (proteasome). J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6660–6666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frentzel S., Kuhn-Hartmann I., Gernold M., Gött P., Seelig A., Kloetzel P. M. The major-histocompatibility-complex-encoded beta-type proteasome subunits LMP2 and LMP7. Evidence that LMP2 and LMP7 are synthesized as proproteins and that cellular levels of both mRNA and LMP-containing 20S proteasomes are differentially regulated. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Aug 15;216(1):119–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18123.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Früh K., Yang Y., Arnold D., Chambers J., Wu L., Waters J. B., Spies T., Peterson P. A. Alternative exon usage and processing of the major histocompatibility complex-encoded proteasome subunits. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22131–22140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerards W. L., Hop F. W., Hendriks I. L., Bloemendal H. Cloning and expression of a human pro(tea)some beta-subunit cDNA: a homologue of the yeast PRE4-subunit essential for peptidylglutamyl-peptide hydrolase activity. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jun 13;346(2-3):151–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00454-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynne R., Kerr L. A., Mockridge I., Beck S., Kelly A., Trowsdale J. The major histocompatibility complex-encoded proteasome component LMP7: alternative first exons and post-translational processing. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Apr;23(4):860–866. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Antibody production by hybridomas. J Immunol Methods. 1980;39(4):285–308. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
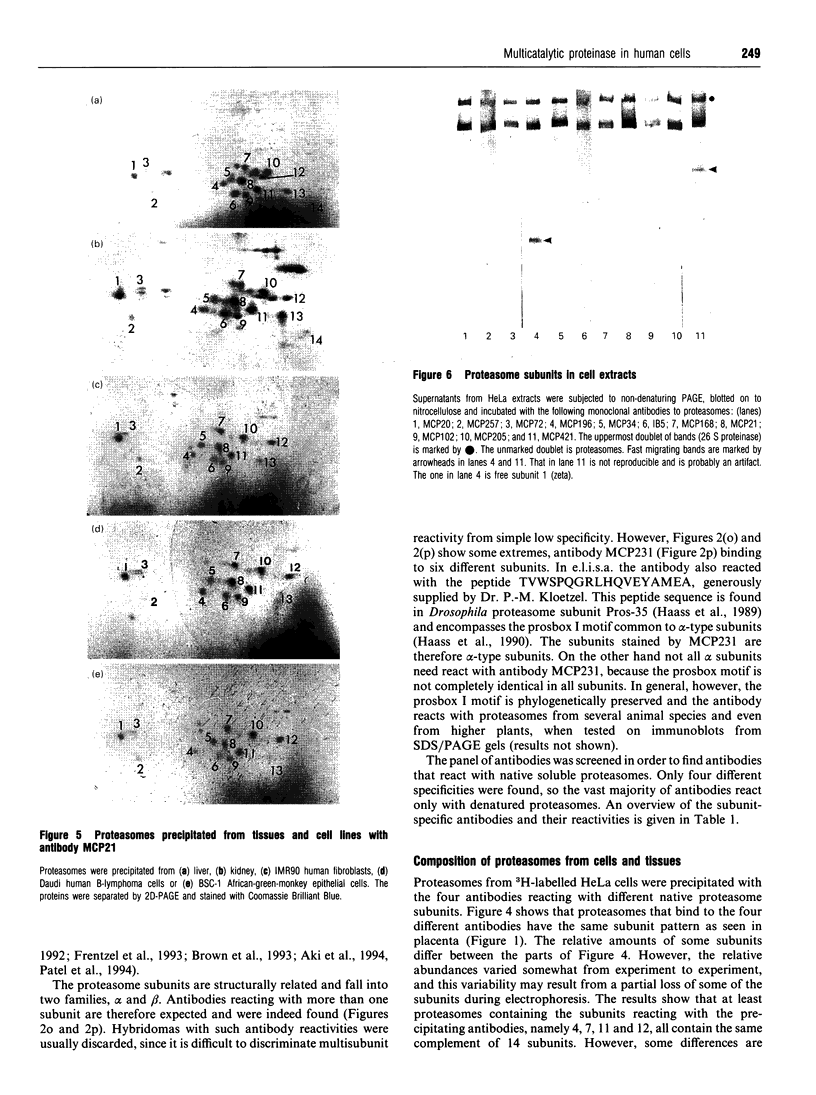
- Grossi de Sa M. F., Martins de Sa C., Harper F., Coux O., Akhayat O., Pal J. K., Florentin Y., Scherrer K. Cytolocalization of prosomes as a function of differentiation. J Cell Sci. 1988 Feb;89(Pt 2):151–165. doi: 10.1242/jcs.89.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grziwa A., Baumeister W., Dahlmann B., Kopp F. Localization of subunits in proteasomes from Thermoplasma acidophilum by immunoelectron microscopy. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 23;290(1-2):186–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81256-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haass C., Kloetzel P. M. The Drosophila proteasome undergoes changes in its subunit pattern during development. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Jan;180(1):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90228-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haass C., Pesold-Hurt B., Kloetzel P. M. The Drosophila PROS-29 gene is a new member of the PROS-gene family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):4018–4018. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.4018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haass C., Pesold-Hurt B., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Kloetzel P. M. The PROS-35 gene encodes the 35 kd protein subunit of Drosophila melanogaster proteasome. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2373–2379. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08366.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendil K. B., Uerkvitz W. The human multicatalytic proteinase: affinity purification using a monoclonal antibody. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1991 Feb-Mar;22(2):159–165. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(91)90028-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system for protein degradation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:761–807. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman L., Pratt G., Rechsteiner M. Multiple forms of the 20 S multicatalytic and the 26 S ubiquitin/ATP-dependent proteases from rabbit reticulocyte lysate. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22362–22368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltoft M. B., Koch C., Uerkvitz W., Hendil K. B. Monoclonal antibodies to the human multicatalytic proteinase (proteasome). Hybridoma. 1992 Aug;11(4):507–517. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1992.11.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloetzel P. M., Frentzel S., Gernold M., Haass C., Klein U., Pesold-Hurt B., Seelig A. The proteasome of Drosophila and features of the evolutionarily conserved PROS-gene family. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1991;50(4-6):451–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopp F., Dahlmann B., Hendil K. B. Evidence indicating that the human proteasome is a complex dimer. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jan 5;229(1):14–19. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. C., Gu M. Z., Etlinger J. D. Isolation and characterization of a novel endogenous inhibitor of the proteasome. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 8;30(40):9709–9715. doi: 10.1021/bi00104a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludemann R., Lerea K. M., Etlinger J. D. Copurification of casein kinase II with 20 S proteasomes and phosphorylation of a 30-kDa proteasome subunit. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):17413–17417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma C. P., Slaughter C. A., DeMartino G. N. Identification, purification, and characterization of a protein activator (PA28) of the 20 S proteasome (macropain). J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10515–10523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalek M. T., Grant E. P., Gramm C., Goldberg A. L., Rock K. L. A role for the ubiquitin-dependent proteolytic pathway in MHC class I-restricted antigen presentation. Nature. 1993 Jun 10;363(6429):552–554. doi: 10.1038/363552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco J. J. A molecular model of MHC class-I-restricted antigen processing. Immunol Today. 1992 May;13(5):173–179. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90122-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami K., Etlinger J. D. Endogenous inhibitor of nonlysosomal high molecular weight protease and calcium-dependent protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7588–7592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel S. D., Monaco J. J., McDevitt H. O. Delineation of the subunit composition of human proteasomes using antisera against the major histocompatibility complex-encoded LMP2 and LMP7 subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):296–300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira M. E., Wilk S. Phosphorylation of the multicatalytic proteinase complex from bovine pituitaries by a copurifying cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Nov 15;283(1):68–74. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90613-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pühler G., Weinkauf S., Bachmann L., Müller S., Engel A., Hegerl R., Baumeister W. Subunit stoichiometry and three-dimensional arrangement in proteasomes from Thermoplasma acidophilum. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1607–1616. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05206.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechsteiner M., Hoffman L., Dubiel W. The multicatalytic and 26 S proteases. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6065–6068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivett A. J. Proteasomes: multicatalytic proteinase complexes. Biochem J. 1993 Apr 1;291(Pt 1):1–10. doi: 10.1042/bj2910001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivett A. J., Sweeney S. T. Properties of subunits of the multicatalytic proteinase complex revealed by the use of subunit-specific antibodies. Biochem J. 1991 Aug 15;278(Pt 1):171–177. doi: 10.1042/bj2780171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada H., Muto K., Fujimuro M., Akaishi T., Sawada M. T., Yokosawa H., Goldberg A. L. Different ratios in 20 S proteasomes and regulatory subunit complexes in two isoforms of the 26 S proteasome purified from rabbit skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1993 Dec 6;335(2):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80731-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva Pereira I., Bey F., Coux O., Scherrer K. Two mRNAs exist for the Hs PROS-30 gene encoding a component of human prosomes. Gene. 1992 Oct 21;120(2):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90098-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater G. G. Stable pattern formation and determination of molecular size by pore-limit electrophoresis. Anal Chem. 1969 Jul;41(8):1039–1041. doi: 10.1021/ac60277a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spies T., Bresnahan M., Bahram S., Arnold D., Blanck G., Mellins E., Pious D., DeMars R. A gene in the human major histocompatibility complex class II region controlling the class I antigen presentation pathway. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):744–747. doi: 10.1038/348744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strack P. R., Wajnberg E. F., Waxman L., Fagan J. M. Comparison of the multicatalytic proteinases isolated from the nucleus and cytoplasm of chicken red blood cells. Int J Biochem. 1992 Jun;24(6):887–895. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(92)90093-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T., Lee D. H., Osaka F., Fujiwara T., Shin S., Chung C. H., Tanaka K., Ichihara A. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of cDNAs for five major subunits of human proteasomes (multi-catalytic proteinase complexes). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 2;1089(1):95–102. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90090-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugai S., Tamura T., Tanahashi N., Takai S., Komi N., Chung C. H., Tanaka K., Ichihara A. Purification and characterization of the 26S proteasome complex catalyzing ATP-dependent breakdown of ubiquitin-ligated proteins from rat liver. J Biochem. 1993 Jun;113(6):754–768. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a124116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitman D., Etlinger J. D. A monoclonal antibody that distinguishes latent and active forms of the proteasome (multicatalytic proteinase complex). J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6977–6982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y., Waters J. B., Früh K., Peterson P. A. Proteasomes are regulated by interferon gamma: implications for antigen processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4928–4932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]