Abstract
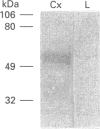
In this work, the molecular forms of the rat neurotensin receptor (NTR) expressed in transfected Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells, in infected Sf9 insect cells and in rat cerebral cortex were immunologically detected by means of an anti-peptide antibody raised against a fragment of the third intracellular loop of the receptor. Immunoblot experiments against a fusion protein indicated that the anti-peptide antibody recognized, under denaturing conditions, the corresponding amino acid sequence within the NTR. In immunoblot analysis of membranes from NTR-transfected CHO cells, high levels of immunoreactivity were observed between 60 and 72 kDa, while only a faint labelling was observed at 47 kDa, the molecular mass deduced for the rat NTR cDNA. The bands of high molecular mass were no longer observed after deglycosylation of membrane proteins by peptide N-glycosidase F, indicating that they represented glycosylated forms of the receptor. Extracts of membranes derived from baculovirus-infected Sf9 insect-cells expressing the NTR provided a quite different immunoblot pattern, since the major band detected in that case was at 47 kDa, the molecular size of the non-glycosylated receptor. Taken together, these data show that, while most of the NTR protein was glycosylated in CHO cells, it was unglycosylated in Sf9 insect-cells. In addition, molecular sizes of the receptor proteins observed in these two cell lines differed from those obtained for the NTR endogenously expressed in the rat cerebral cortex of 7 day-old rats, where bands at 56 and 54 kDa were detected. Binding experiments carried out on membrane preparations obtained from baculovirus-infected Sf9 cells demonstrated that the immunogenic sequence was still accessible to the antibody when the receptor was embedded in the cell membrane. Immunohistochemical studies carried out on both transfected CHO cells and infected Sf9 cells confirmed this interpretation and further indicated that the antibody could be applied in the visualization of the receptor.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Saffar A., Rosell S. Effects of neurotensin and neurotensin analogues on the migrating myoelectrical complexes in the small intestine of rats. Acta Physiol Scand. 1981 Jun;112(2):203–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1981.tb06805.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behbehani M. M. Physiological mechanisms of the analgesic effect of neurotensin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992;668:253–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb27354.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissette G., Nemeroff C. B., Loosen P. T., Prange A. J., Jr, Lipton M. A. Hypothermia and intolerance to cold induced by intracisternal administration of the hypothalamic peptide neurotensin. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):607–609. doi: 10.1038/262607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boundy V. A., Luedtke R. R., Artymyshyn R. P., Filtz T. M., Molinoff P. B. Development of polyclonal anti-D2 dopamine receptor antibodies using sequence-specific peptides. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 May;43(5):666–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boundy V. A., Luedtke R. R., Gallitano A. L., Smith J. E., Filtz T. M., Kallen R. G., Molinoff P. B. Expression and characterization of the rat D3 dopamine receptor: pharmacologic properties and development of antibodies. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Feb;264(2):1002–1011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boundy V. A., Luedtke R. R., Molinoff P. B. Development of polyclonal anti-D2 dopamine receptor antibodies to fusion proteins: inhibition of D2 receptor-G protein interaction. J Neurochem. 1993 Jun;60(6):2181–2191. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03504.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Leeman S. E. Characterization of radioimmunoassayable neurotensin in the rat. Its differential distribution in the central nervous system, small intestine, and stomach. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 25;251(22):7045–7052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Leeman S. E. The isolation of a new hypotensive peptide, neurotensin, from bovine hypothalami. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6854–6861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabry J., Gaudriault G., Vincent J. P., Mazella J. Implication of various forms of neurotensin receptors in the mechanism of internalization of neurotensin in cerebral neurons. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):17138–17144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garver D. L., Bissette G., Yao J. K., Nemeroff C. B. Relation of CSF neurotensin concentrations to symptoms and drug response of psychotic patients. Am J Psychiatry. 1991 Apr;148(4):484–488. doi: 10.1176/ajp.148.4.484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George S. T., Arbabian M. A., Ruoho A. E., Kiely J., Malbon C. C. High-efficiency expression of mammalian beta-adrenergic receptors in baculovirus-infected insect cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Sep 29;163(3):1265–1269. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91114-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabgi P., Checler F., Mazella J., Vincent J. P. Pharmacology and biochemistry of neurotensin receptors. Rev Clin Basic Pharm. 1985 Jul-Dec;5(3-4):397–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levey A. I., Kitt C. A., Simonds W. F., Price D. L., Brann M. R. Identification and localization of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor proteins in brain with subtype-specific antibodies. J Neurosci. 1991 Oct;11(10):3218–3226. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-10-03218.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazella J., Chabry J., Zsurger N., Vincent J. P. Purification of the neurotensin receptor from mouse brain by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5559–5563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazella J., Kitabgi P., Vincent J. P. Molecular properties of neurotensin receptors in rat brain. Identification of subunits by covalent labeling. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):508–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann S. M., Vijayan E. Control of anterior pituitary hormone secretion by neurotensin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992;668:287–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb27357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McVittie L. D., Ariano M. A., Sibley D. R. Characterization of anti-peptide antibodies for the localization of D2 dopamine receptors in rat striatum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1441–1445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills A., Demoliou-Mason C. D., Barnard E. A. Purification of the neurotensin receptor from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):13–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto-Lee Y., Shiosaka S., Tohyama M. Purification and characterization of neurotensin receptor from rat brain with special reference to comparison between newborn and adult age rats. Peptides. 1991 Sep-Oct;12(5):1001–1006. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(91)90050-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouillac B., Caron M., Bonin H., Dennis M., Bouvier M. Agonist-modulated palmitoylation of beta 2-adrenergic receptor in Sf9 cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21733–21737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muraki K., Nishi Y., Arai M., Kubo N., Ueda K., Shikata H., Nakata Y., Segawa T., Yanaihara N., Yajima H. Neurotensin receptors on the rat liver plasma membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jun 30;145(3):1071–1079. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91546-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirion R., Rowe W. B., Lapchak P. A., Araujo D. M., Beaudet A. Distribution of neurotensin receptors in mammalian brain. What it is telling us about its interactions with other neurotransmitter systems. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992;668:109–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb27343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rioux F., Kérouac R., Quirion R., St-Pierre S. Mechanisms of the cardiovascular effects of neurotensin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;400:56–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb31560.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostène W., Brouard A., Dana C., Masuo Y., Agid F., Vial M., Lhiaubet A. M., Pelaprat D. Interaction between neurotensin and dopamine in the brain. Morphofunctional and clinical evidence. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992;668:217–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb27352.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoul J. L., Mazella J., Amar S., Kitabgi P., Vincent J. P. Preparation of neurotensin selectively iodinated on the tyrosine 3 residue. Biological activity and binding properties on mammalian neurotensin receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):812–819. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schotte A., Leysen J. E., Laduron P. M. Evidence for a displaceable non-specific [3H]neurotensin binding site in rat brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Aug;333(4):400–405. doi: 10.1007/BF00500016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigemoto R., Nakaya Y., Nomura S., Ogawa-Meguro R., Ohishi H., Kaneko T., Nakanishi S., Mizuno N. Immunocytochemical localization of rat substance P receptor in the striatum. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Apr 30;153(2):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90311-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Masu M., Nakanishi S. Structure and functional expression of the cloned rat neurotensin receptor. Neuron. 1990 Jun;4(6):847–854. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vialard J., Lalumière M., Vernet T., Briedis D., Alkhatib G., Henning D., Levin D., Richardson C. Synthesis of the membrane fusion and hemagglutinin proteins of measles virus, using a novel baculovirus vector containing the beta-galactosidase gene. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):37–50. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.37-50.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vita N., Laurent P., Lefort S., Chalon P., Dumont X., Kaghad M., Gully D., Le Fur G., Ferrara P., Caput D. Cloning and expression of a complementary DNA encoding a high affinity human neurotensin receptor. FEBS Lett. 1993 Feb 8;317(1-2):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81509-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall S. J., Yasuda R. P., Li M., Wolfe B. B. Development of an antiserum against m3 muscarinic receptors: distribution of m3 receptors in rat tissues and clonal cell lines. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;40(5):783–789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Lipfert L., Malbon C. C., Bahouth S. Site-directed anti-peptide antibodies define the topography of the beta-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14424–14431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Silverstein S., Lee L. S., Pellicer A., Cheng Y. c., Axel R. Transfer of purified herpes virus thymidine kinase gene to cultured mouse cells. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]