Abstract
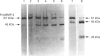
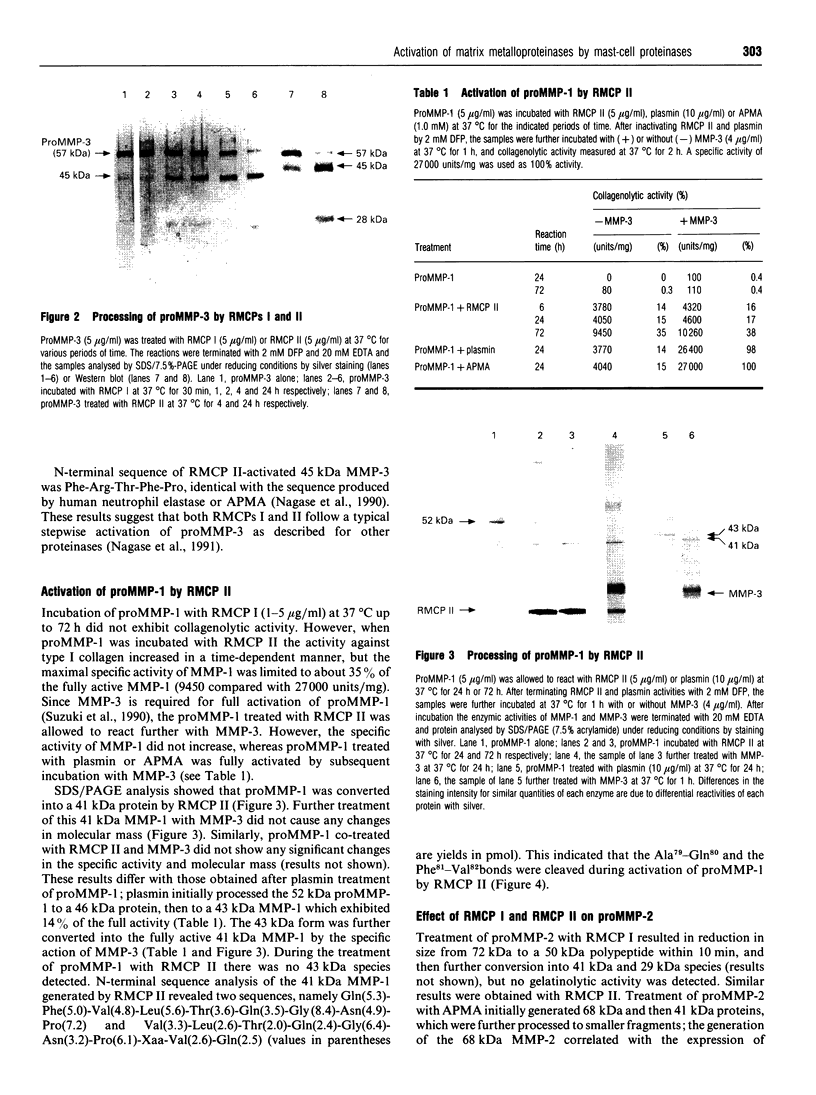
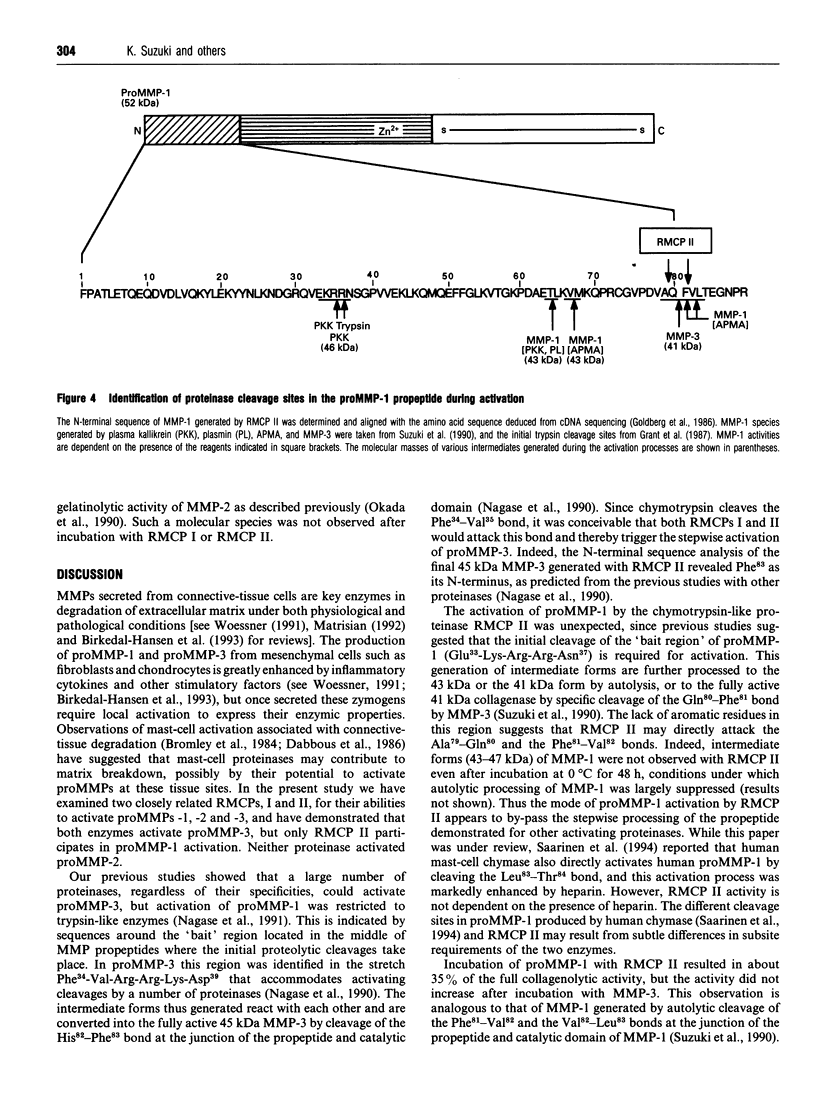
Histological studies have previously demonstrated an association between mast-cell activation/degranulation and areas of connective-tissue lysis in vivo; in addition, mast-cell extracts have been shown to activate latent forms of collagenase and stromelysin. In the present study we have examined the potential roles of rat mast-cell proteinase (RMCP) I and RMCP II as activators of the precursors of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-1 (interstitial collagenase), MMP-2 (gelatinase A) and MMP-3 (stromelysin 1). Both RMCPs I and II activated proMMP-3 by converting the 57 kDa precursor into a 45 kDa polypeptide. The N-terminal amino acid of 45 kDa MMP-3 activated by RMCP II was identified as Phe83. By contrast, only RMCP II activated the 52 kDa proMMP-1 by converting it into a 41 kDa protein and generating the new N-termini, namely Gln80 and Val82. The collagenolytic activity which resulted from this cleavage was only 35% of the full activity, but this could not be augmented by subsequent treatment with MMP-3, the latter being a crucial enzyme for the generation of the fully active MMP-1 with Phe81 at the N-terminus, in conjunction with other serine proteinases. Thus RMCP II activates proMMP-1 via a mechanism different from that reported for the stepwise processing by combinations of other trypsin-like enzymes and MMP-3. ProMMP-2 (pro-gelatinase A) was not activated by either RMCP I or RMCP II, despite processing to smaller products.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birkedal-Hansen H., Cobb C. M., Taylor R. E., Fullmer H. M. Activation of fibroblast procollagenase by mast cell proteases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 7;438(1):273–286. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90243-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkedal-Hansen H., Moore W. G., Bodden M. K., Windsor L. J., Birkedal-Hansen B., DeCarlo A., Engler J. A. Matrix metalloproteinases: a review. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1993;4(2):197–250. doi: 10.1177/10454411930040020401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Reinemer P., Huber R., Kleine T., Schnierer S., Tschesche H. The X-ray crystal structure of the catalytic domain of human neutrophil collagenase inhibited by a substrate analogue reveals the essentials for catalysis and specificity. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1263–1269. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06378.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromley M., Fisher W. D., Woolley D. E. Mast cells at sites of cartilage erosion in the rheumatoid joint. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Feb;43(1):76–79. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.1.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromley M., Woolley D. E. Histopathology of the rheumatoid lesion. Identification of cell types at sites of cartilage erosion. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Aug;27(8):857–863. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. D., Levy A. T., Margulies I. M., Liotta L. A., Stetler-Stevenson W. G. Independent expression and cellular processing of Mr 72,000 type IV collagenase and interstitial collagenase in human tumorigenic cell lines. Cancer Res. 1990 Oct 1;50(19):6184–6191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawston T. E., Barrett A. J. A rapid and reproducible assay for collagenase using [1-14C]acetylated collagen. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 1;99(2):340–345. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabbous M. K., Haney L., Nicolson G. L., Eckley D., Woolley D. E. Mast cell modulation of tumour cell proliferation in rat mammary adenocarcinoma 13762NF. Br J Cancer. 1991 Jun;63(6):873–878. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabbous M. K., Walker R., Haney L., Carter L. M., Nicolson G. L., Woolley D. E. Mast cells and matrix degradation at sites of tumour invasion in rat mammary adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 1986 Sep;54(3):459–465. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1986.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J., Gordon J. R., Wershil B. K. Cytokine production by mast cells and basophils. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Dec;3(6):865–872. doi: 10.1016/s0952-7915(05)80005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson S., Mackeller A., Newlands G. F., Miller H. R. Phenotypic expression of mast cell granule proteinases. Distribution of mast cell proteinases I and II in the rat digestive system. Immunology. 1987 Dec;62(4):621–627. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson S., Miller H. R. Mast cell subsets in the rat distinguished immunohistochemically by their content of serine proteinases. Immunology. 1986 May;58(1):101–104. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg G. I., Wilhelm S. M., Kronberger A., Bauer E. A., Grant G. A., Eisen A. Z. Human fibroblast collagenase. Complete primary structure and homology to an oncogene transformation-induced rat protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6600–6605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. R., Burd P. R., Galli S. J. Mast cells as a source of multifunctional cytokines. Immunol Today. 1990 Dec;11(12):458–464. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90176-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant G. A., Eisen A. Z., Marmer B. L., Roswit W. T., Goldberg G. I. The activation of human skin fibroblast procollagenase. Sequence identification of the major conversion products. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5886–5889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber B. L., Marchese M. J., Suzuki K., Schwartz L. B., Okada Y., Nagase H., Ramamurthy N. S. Synovial procollagenase activation by human mast cell tryptase dependence upon matrix metalloproteinase 3 activation. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1657–1662. doi: 10.1172/JCI114344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HE C. S., Wilhelm S. M., Pentland A. P., Marmer B. L., Grant G. A., Eisen A. Z., Goldberg G. I. Tissue cooperation in a proteolytic cascade activating human interstitial collagenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2632–2636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartveit F., Thoresen S., Tangen M., Maartmann-Moe H. Mast cell changes and tumour dissemination in human breast carcinoma. Invasion Metastasis. 1984;4(3):146–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes C., Murphy G., Hardingham T. E. Metalloproteinase digestion of cartilage proteoglycan. Pattern of cleavage by stromelysin and susceptibility to collagenase. Biochem J. 1991 Nov 1;279(Pt 3):733–739. doi: 10.1042/bj2790733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irani A. A., Schechter N. M., Craig S. S., DeBlois G., Schwartz L. B. Two types of human mast cells that have distinct neutral protease compositions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4464–4468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito A., Nagase H. Evidence that human rheumatoid synovial matrix metalloproteinase 3 is an endogenous activator of procollagenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Nov 15;267(1):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katunuma N., Kominami E., Kobayashi K., Banno Y., Suzuki K. Studies on new intracellular proteases in various organs of rat. 1. Purification and comparison of their properties. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Mar 3;52(1):37–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keski-Oja J., Lohi J., Tuuttila A., Tryggvason K., Vartio T. Proteolytic processing of the 72,000-Da type IV collagenase by urokinase plasminogen activator. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Oct;202(2):471–476. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90101-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Trong H., Parmelee D. C., Walsh K. A., Neurath H., Woodbury R. G. Amino acid sequence of rat mast cell protease I (chymase). Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 3;26(22):6988–6994. doi: 10.1021/bi00396a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M. The matrix-degrading metalloproteinases. Bioessays. 1992 Jul;14(7):455–463. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Cockett M. I., Stephens P. E., Smith B. J., Docherty A. J. Stromelysin is an activator of procollagenase. A study with natural and recombinant enzymes. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 15;248(1):265–268. doi: 10.1042/bj2480265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Cockett M. I., Ward R. V., Docherty A. J. Matrix metalloproteinase degradation of elastin, type IV collagen and proteoglycan. A quantitative comparison of the activities of 95 kDa and 72 kDa gelatinases, stromelysins-1 and -2 and punctuated metalloproteinase (PUMP). Biochem J. 1991 Jul 1;277(Pt 1):277–279. doi: 10.1042/bj2770277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., McAlpine C. G., Poll C. T., Reynolds J. J. Purification and characterization of a bone metalloproteinase that degrades gelatin and types IV and V collagen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 20;831(1):49–58. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(85)90148-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagase H., Enghild J. J., Suzuki K., Salvesen G. Stepwise activation mechanisms of the precursor of matrix metalloproteinase 3 (stromelysin) by proteinases and (4-aminophenyl)mercuric acetate. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 19;29(24):5783–5789. doi: 10.1021/bi00476a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagase H., Ogata Y., Suzuki K., Enghild J. J., Salvesen G. Substrate specificities and activation mechanisms of matrix metalloproteinases. Biochem Soc Trans. 1991 Aug;19(3):715–718. doi: 10.1042/bst0190715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newlands G. F., Gibson S., Knox D. P., Grencis R., Wakelin D., Miller H. R. Characterization and mast cell origin of a chymotrypsin-like proteinase isolated from intestines of mice infected with Trichinella spiralis. Immunology. 1987 Dec;62(4):629–634. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Harris E. D., Jr, Nagase H. The precursor of a metalloendopeptidase from human rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Purification and mechanisms of activation by endopeptidases and 4-aminophenylmercuric acetate. Biochem J. 1988 Sep 15;254(3):731–741. doi: 10.1042/bj2540731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Konomi H., Yada T., Kimata K., Nagase H. Degradation of type IX collagen by matrix metalloproteinase 3 (stromelysin) from human rheumatoid synovial cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Feb 27;244(2):473–476. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80586-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Morodomi T., Enghild J. J., Suzuki K., Yasui A., Nakanishi I., Salvesen G., Nagase H. Matrix metalloproteinase 2 from human rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Purification and activation of the precursor and enzymic properties. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Dec 27;194(3):721–730. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19462.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overall C. M., Sodek J. Concanavalin A produces a matrix-degradative phenotype in human fibroblasts. Induction and endogenous activation of collagenase, 72-kDa gelatinase, and Pump-1 is accompanied by the suppression of the tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21141–21151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinemer P., Grams F., Huber R., Kleine T., Schnierer S., Piper M., Tschesche H., Bode W. Structural implications for the role of the N terminus in the 'superactivation' of collagenases. A crystallographic study. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jan 31;338(2):227–233. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saarinen J., Kalkkinen N., Welgus H. G., Kovanen P. T. Activation of human interstitial procollagenase through direct cleavage of the Leu83-Thr84 bond by mast cell chymase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 8;269(27):18134–18140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid T. M., Mayne R., Jeffrey J. J., Linsenmayer T. F. Type X collagen contains two cleavage sites for a vertebrate collagenase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4184–4189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Riedel C., Caulfield J. P., Wasserman S. I., Austen K. F. Cell association of complexes of chymase, heparin proteoglycan, and protein after degranulation by rat mast cells. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2071–2078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seltzer J. L., Eisen A. Z., Bauer E. A., Morris N. P., Glanville R. W., Burgeson R. E. Cleavage of type VII collagen by interstitial collagenase and type IV collagenase (gelatinase) derived from human skin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):3822–3826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior R. M., Griffin G. L., Fliszar C. J., Shapiro S. D., Goldberg G. I., Welgus H. G. Human 92- and 72-kilodalton type IV collagenases are elastases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7870–7875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Enghild J. J., Morodomi T., Salvesen G., Nagase H. Mechanisms of activation of tissue procollagenase by matrix metalloproteinase 3 (stromelysin). Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 6;29(44):10261–10270. doi: 10.1021/bi00496a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vater C. A., Nagase H., Harris E. D., Jr Purification of an endogenous activator of procollagenase from rabbit synovial fibroblast culture medium. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9374–9382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N., Austen K. F. Heterogeneity of mast cells at multiple body sites. Fluorescent determination of avidin binding and immunofluorescent determination of chymase, tryptase, and carboxypeptidase content. Pathol Res Pract. 1993 Mar;189(2):156–162. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(11)80086-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windsor L. J., Birkedal-Hansen H., Birkedal-Hansen B., Engler J. A. An internal cysteine plays a role in the maintenance of the latency of human fibroblast collagenase. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 22;30(3):641–647. doi: 10.1021/bi00217a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woessner J. F., Jr Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in connective tissue remodeling. FASEB J. 1991 May;5(8):2145–2154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury R. G., Everitt M. T., Neurath H. Mast cell proteases. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):588–609. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury R. G., Everitt M., Sanada Y., Katunuma N., Lagunoff D., Neurath H. A major serine protease in rat skeletal muscle: evidence for its mast cell origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5311–5313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury R. G., Gruzenski G. M., Lagunoff D. Immunofluorescent localization of a serine protease in rat small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2785–2789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury R. G., Neurath H. Purification of an atypical mast cell protease and its levels in developing rats. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 3;17(20):4298–4304. doi: 10.1021/bi00613a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoffe J. R., Taylor D. J., Wooley D. E. Mast cell products stimulate collagenase and prostaglandin E production by cultures of adherent rheumatoid synovial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 18;122(1):270–276. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoffe J. R., Taylor D. J., Woolley D. E. Mast-cell products and heparin stimulate the production of mononuclear-cell factor by cultured human monocyte/macrophages. Biochem J. 1985 Aug 15;230(1):83–88. doi: 10.1042/bj2300083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]