Abstract
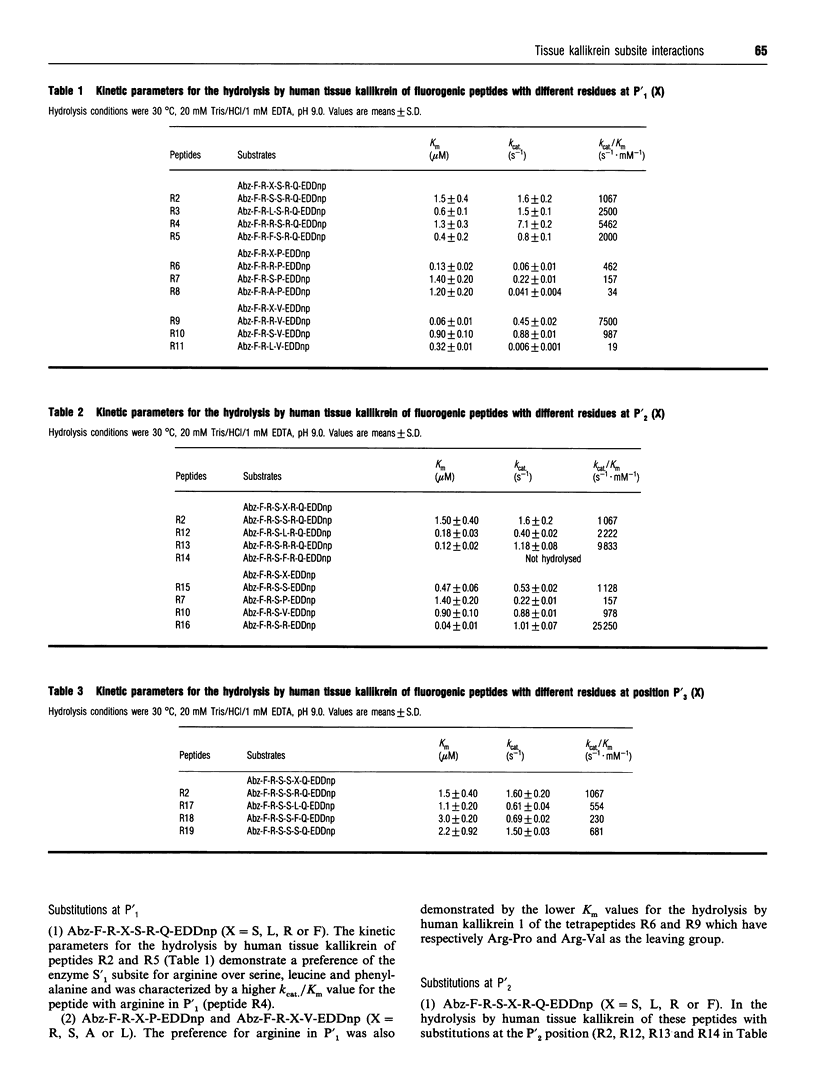
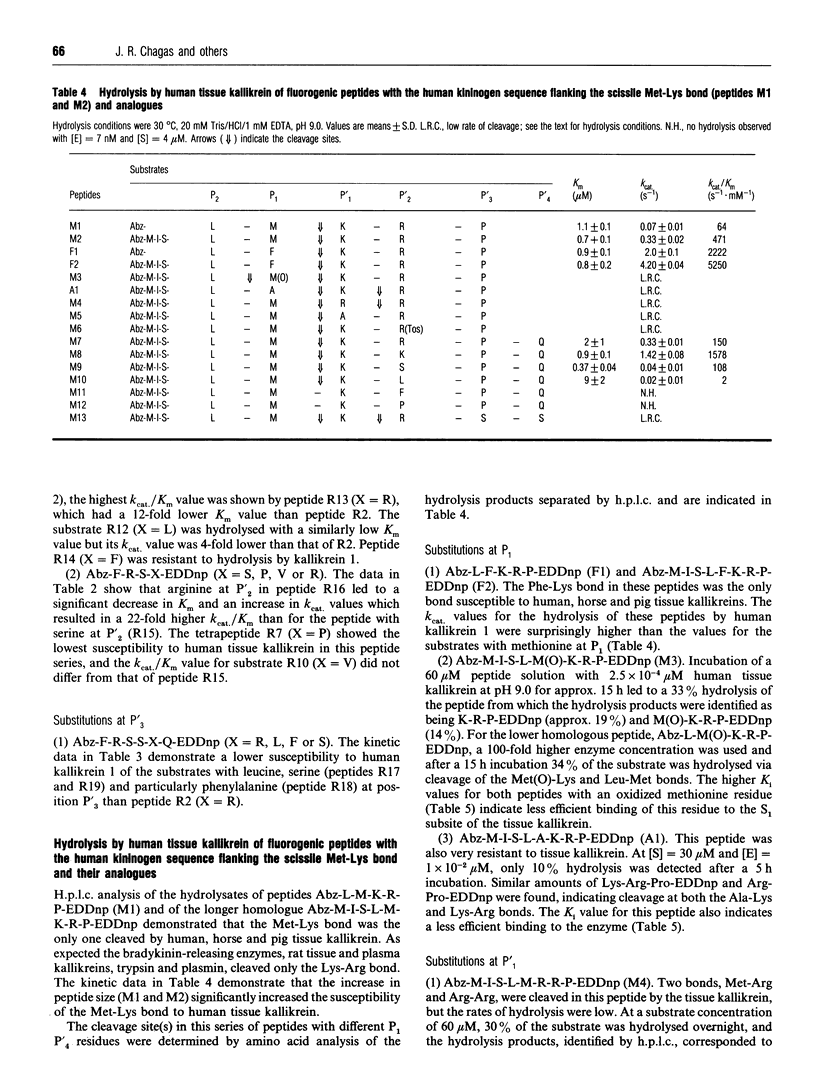
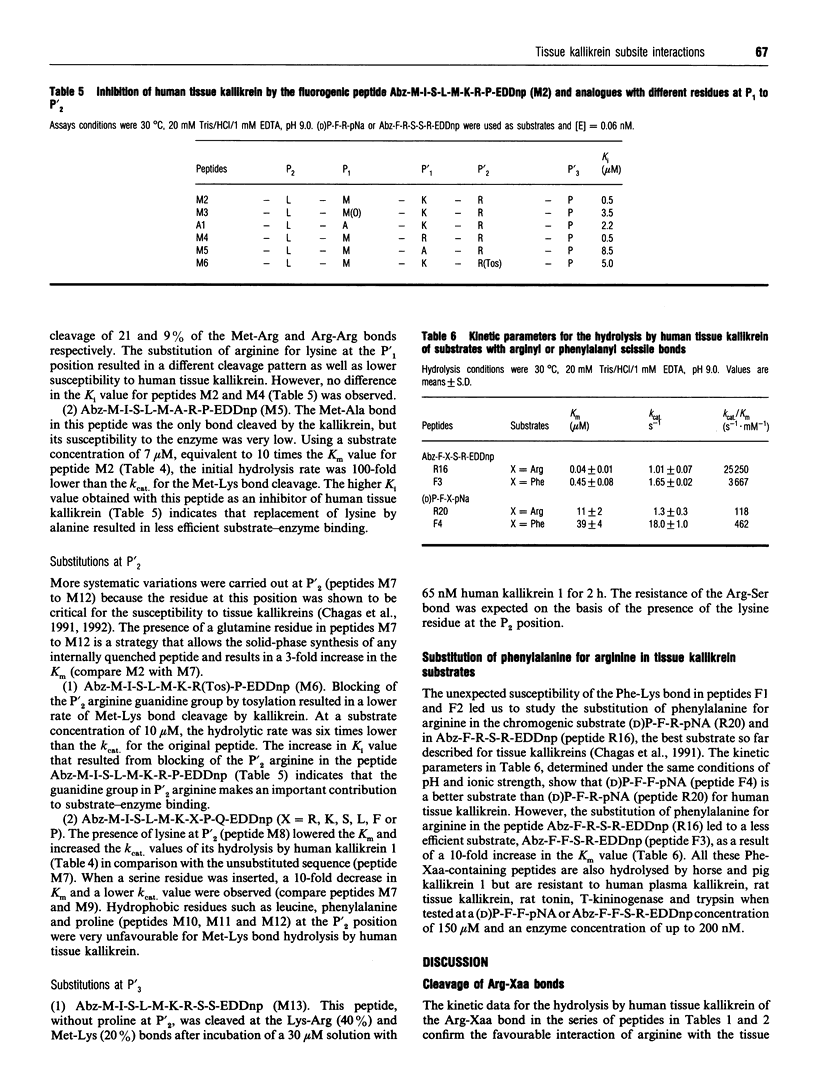
Kinetic data for the hydrolysis by human tissue kallikrein of fluorogenic peptides with o-aminobenzoyl-Phe-Arg (Abz-FR) as the acyl group and different leaving groups demonstrate that interactions with the S'1, S'2 and S'3 subsites are important for cleavage efficiency. In addition, studies on the hydrolysis of fluorogenic peptides with the human kininogen sequence spanning the scissile Met-Lys bond [Abz-M-I-S-L-M-K-R-P-N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)ethylenediamine] and analogues with different residues at positions P'1, P'2 and P'3 showed that (a) the presence of a proline residue at P'3 and the interactions with the tissue kallikrein-binding sites S2 to S'2 are determinants of Met-Lys bond cleavage and (b) residues P3, P4 and/or P5 arc important for cleavage efficiency. The substitution of phenylalanine for methionine or arginine in substrates with scissile Met-Lys or Arg-Xaa bonds demonstrated that lysyl-bradykinin-releasing tissue kallikreins also have a primary specificity for phenylalanine. The replacement of arginine by phenylalanine in (D)P-F-R-p-nitroanilide (pNA) produced an efficient and specific chromogenic substrate, (D)P-F-F-pNA, for the lysyl-bradykinin-releasing tissue kallikreins as it is resistant to plasma kallikrein and other arginine hydrolases.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alhenc-Gelas F., Marchetti J., Allegrini J., Corvol P., Menard J. Measurement of urinary kallikrein activity. Species differences in kinin production. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 5;677(3-4):477–488. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90262-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araujo-Viel M. S., Juliano L., Prado E. S. The cleavage of the Met-Lys bond in a bradykinin derivative by glandular kallikreins. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1981 Mar;362(3):337–345. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1981.362.1.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araújo-Viel M. S., Juliano M. A., Oliveira L., Prado E. S. Horse urinary kallikrein, II. Effect of subsite interactions on its catalytic activity. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1988 May;369(5):397–401. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1988.369.1.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhoola K. D., Figueroa C. D., Worthy K. Bioregulation of kinins: kallikreins, kininogens, and kininases. Pharmacol Rev. 1992 Mar;44(1):1–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Chen Z., Bartels K., Kutzbach C., Schmidt-Kastner G., Bartunik H. Refined 2 A X-ray crystal structure of porcine pancreatic kallikrein A, a specific trypsin-like serine proteinase. Crystallization, structure determination, crystallographic refinement, structure and its comparison with bovine trypsin. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 25;164(2):237–282. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90077-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chagas J. R., Hirata I. Y., Juliano M. A., Xiong W., Wang C., Chao J., Juliano L., Prado E. S. Substrate specificities of tissue kallikrein and T-kininogenase: their possible role in kininogen processing. Biochemistry. 1992 Jun 2;31(21):4969–4974. doi: 10.1021/bi00136a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chagas J. R., Juliano L., Prado E. S. Intramolecularly quenched fluorogenic tetrapeptide substrates for tissue and plasma kallikreins. Anal Biochem. 1991 Feb 1;192(2):419–425. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90558-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chai K. X., Chen L. M., Chao J., Chao L. Kallistatin: a novel human serine proteinase inhibitor. Molecular cloning, tissue distribution, and expression in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):24498–24505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao J., Margolius H. S. Isozymes of rat urinary kallikrein. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Jul 1;28(13):2071–2079. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90226-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z., Bode W. Refined 2.5 A X-ray crystal structure of the complex formed by porcine kallikrein A and the bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. Crystallization, Patterson search, structure determination, refinement, structure and comparison with its components and with the bovine trypsin-pancreatic trypsin inhibitor complex. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 25;164(2):283–311. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):170–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0550170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derkx F. H., Tan-Tjiong H. L., Man in't Veld A. J., Schalekamp M. P., Schalekamp M. A. Activation of inactive plasma renin by tissue kallikreins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Nov;49(5):765–769. doi: 10.1210/jcem-49-5-765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler F. Effects of secondary interactions on the kinetics of peptide and peptide ester hydrolysis by tissue kallikrein and trypsin. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Mar 2;163(2):303–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10801.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler F. Enzymology of porcine tissue kallikrein. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1983;156:263–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler F., Müller B., Werle E. Active site titration of pig pancreatic kallikrein with p-nitrophenyl p'-guanidinobenzoate. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jul 15;24(1):41–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80821-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giusti E. P., Sampaio C. A., Michelacci Y. M., Stella R. C., Oliveira L., Prado E. S. Horse urinary kallikrein, I. Complete purification and characterization. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1988 May;369(5):387–396. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1988.369.1.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E. Strukturaufklärung kininliefernder Peptide aus Rinderserum-Kininogen. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1966;253(4):474–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han Y. N., Kato H., Iwanaga S., Suzuki T. Bovine plasma high molecular weight kininogen: the amino acid sequence of fragment 1 (glycopeptide) released by the action of plasma kallikrein and its location in the precursor protein. FEBS Lett. 1976 Mar 15;63(1):197–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80225-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juliano M. A., Juliano L. Synthesis and kinetic parameters of hydrolysis by trypsin of some acyl-arginyl-p-nitroanilides and peptides containing arginyl-p-nitroanilide. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1985;18(4):435–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Enjyoji K., Miyata T., Hayashi I., Oh-ishi S., Iwanaga S. Demonstration of arginyl-bradykinin moiety in rat HMW kininogen: direct evidence for liberation of bradykinin by rat glandular kallikreins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 28;127(1):289–295. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80157-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettner C., Shaw E. Inactivation of trypsin-like enzymes with peptides of arginine chloromethyl ketone. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):826–842. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80065-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lottspeich F., Kellermann J., Henschen A., Rauth G., Müller-Esterl W. Human low-molecular-mass kininogen. Amino-acid sequence of the light chain; homology with other protein sequences. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jul 16;142(2):227–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira L., Araujo-Viel M. S., Juliano L., Prado E. S. Substrate activation of porcine pancreatic kallikrein by N alpha derivatives of arginine 4-nitroanilides. Biochemistry. 1987 Aug 11;26(16):5032–5035. doi: 10.1021/bi00390a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polosa R. Role of the kinin-kallikrein pathway in allergic diseases. Allergy. 1993 May;48(4):217–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1993.tb00719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers C. A. Anterior pituitary glandular kallikrein: a putative prolactin processing protease. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1993 Jan;90(2):C15–C20. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(93)90146-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prado E. S., Araújo-Viel M. S., Juliano M. A., Juliano L., Stella R. C., Sampaio C. A. Tetrapeptide substrates for the discrimination among kallikreins and other trypsin-like serine proteinases. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1986 Mar;367(3):199–205. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1986.367.1.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prado E. S., Prado de Carvalho L., Araujo-Viel M. S., Ling N., Rossier J. A Met-enkephalin-containing-peptide, BAM 22P, as a novel substrate for glandular kallikreins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Apr 29;112(2):366–371. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91472-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampaio C. A., Sampaio M. U., Prado E. S. Active-site titration of horse urinary kallikrein. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1984 Mar;365(3):297–302. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1984.365.1.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I., Berger A. On the size of the active site in proteases. I. Papain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Apr 20;27(2):157–162. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(67)80055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey J. E., Atlas S. A., Laragh J. H. Linking the kallikrein and renin systems via activation of inactive renin: new data and a hypothesis. Am J Med. 1978 Dec;65(6):994–1000. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90752-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimamoto K., Chao J., Margolius H. S. The radioimmunoassay of human urinary kallikrein and comparisons with kallikrein activity measurements. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Oct;51(4):840–848. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-4-840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugo T., Kato H., Iwanaga S., Fujii S. High-molecular-weight kininogen from horse plasma. Isolation, characterization and comparison with bovine high-Mr kininogen. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(3):439–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Cohen S., Mitchell W. M. Epidermal growth factor: high and low molecular weight forms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):164–171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. A., Baglan N. C., Bradshaw R. A. The amino acid sequence of the gamma-subunit of mouse submaxillary gland 7 S nerve growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9156–9166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokosawa N., Takahashi N., Inagami T., Page D. L. Isolation of completely inactive plasma prorenin and its activation by kallikreins. A possible new link between renin and kallikrein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 15;569(2):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


