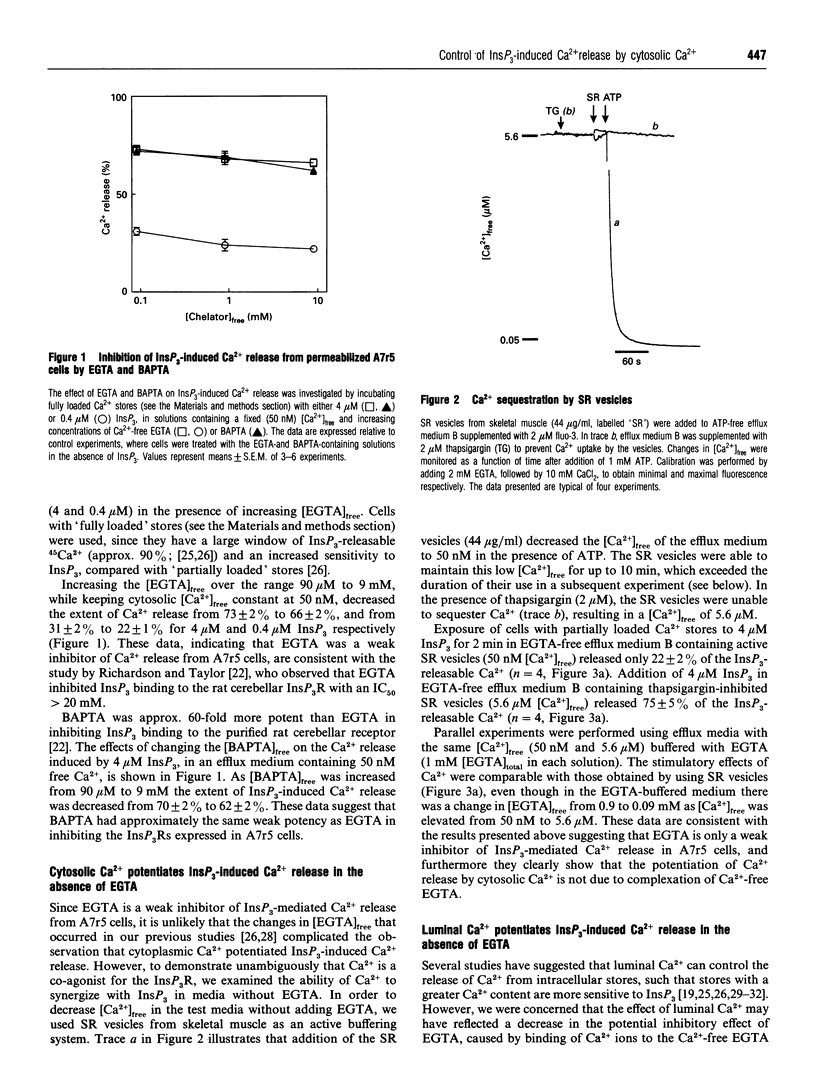
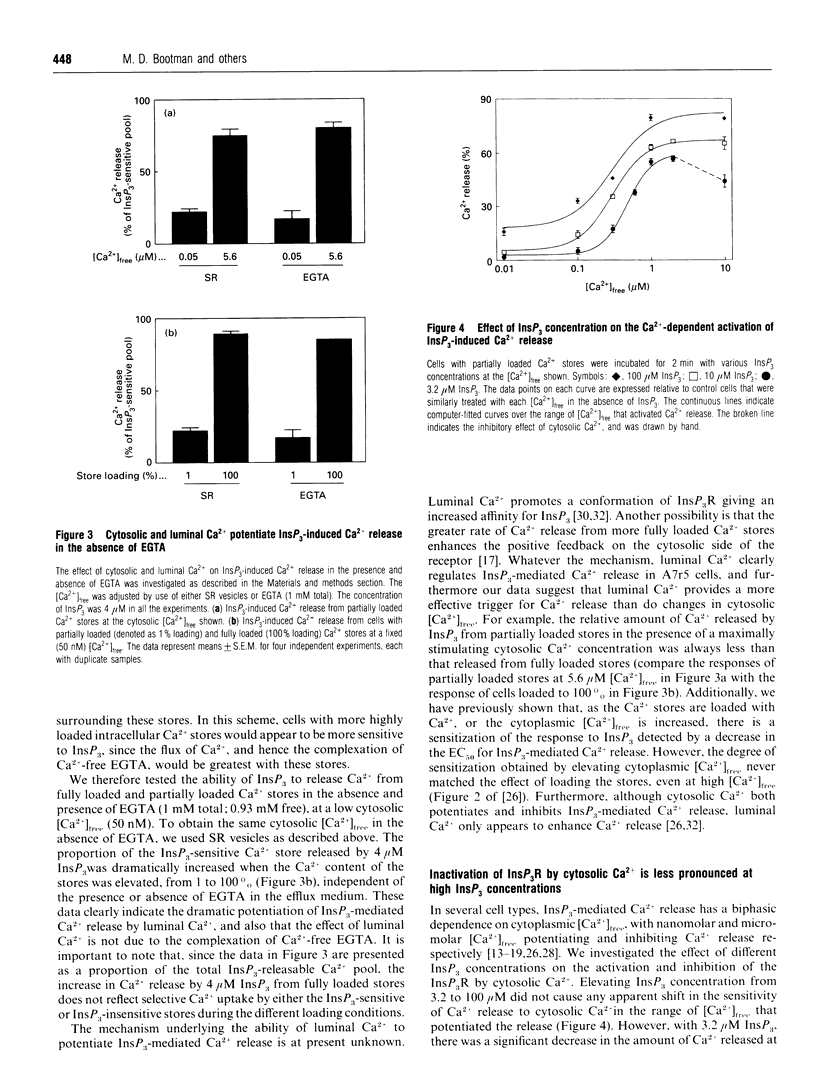
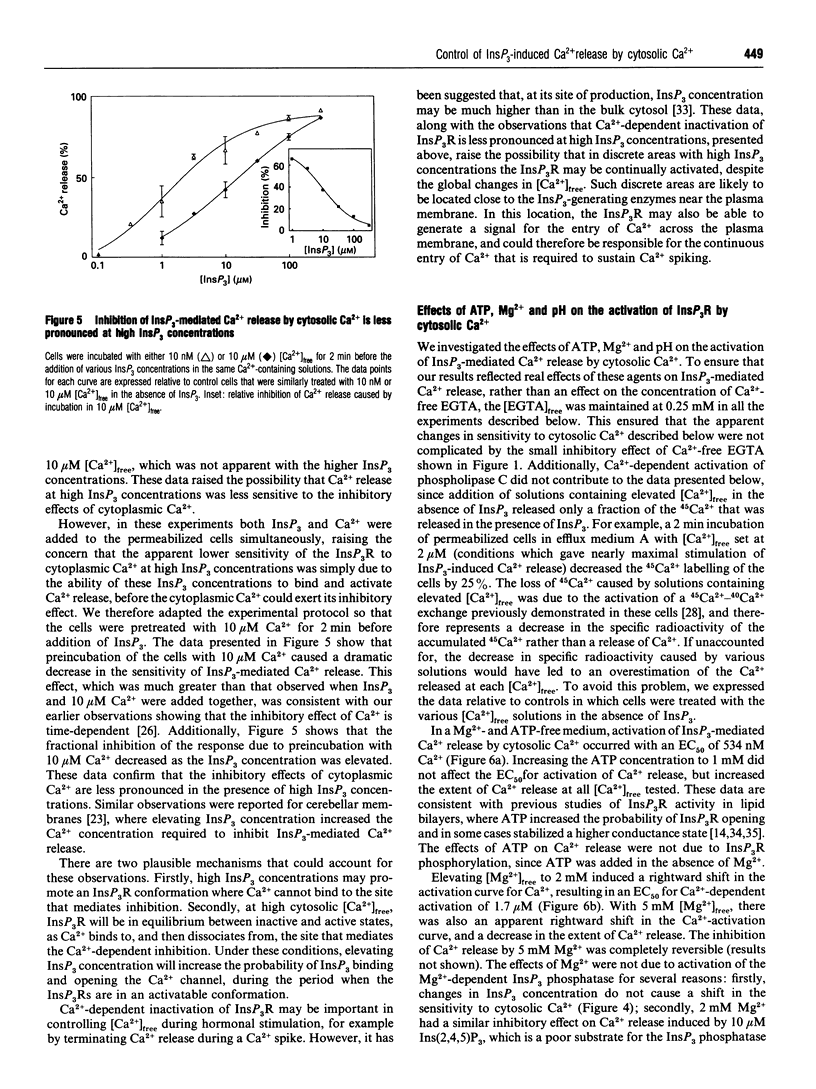
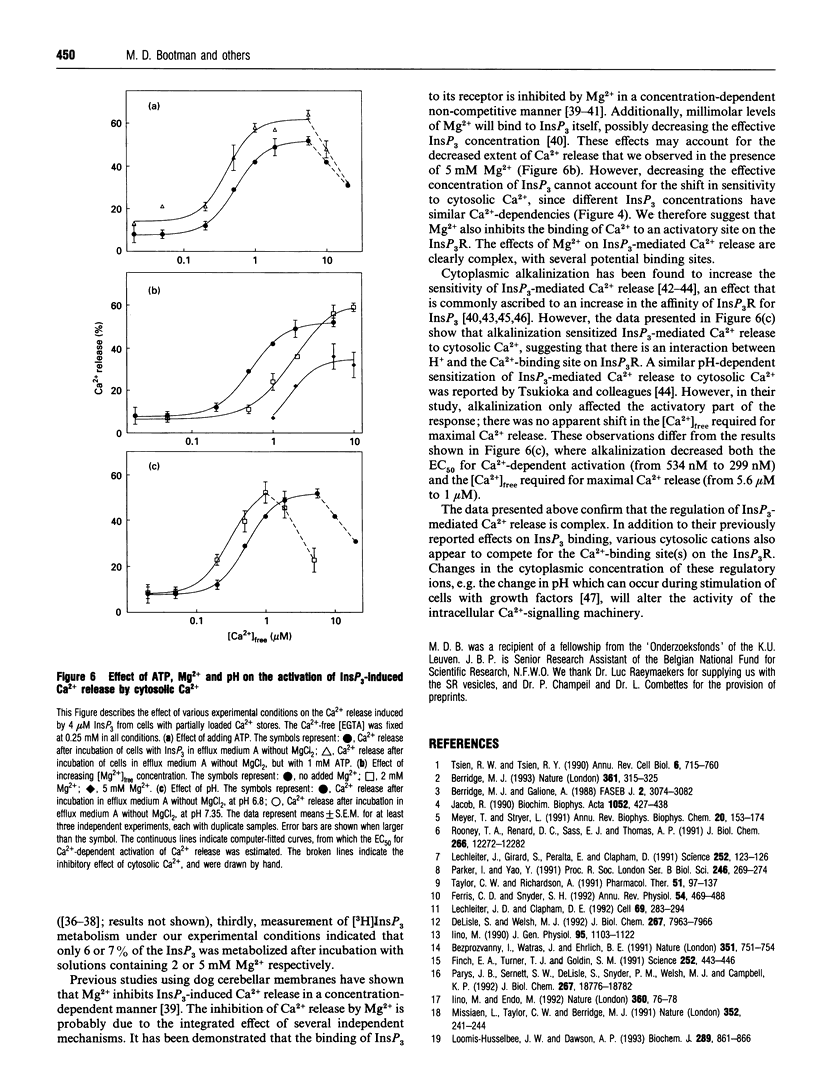
Abstract
The synergistic action of cytosolic Ca2+ and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) in releasing intracellular Ca2+ stores has been suggested to be responsible for the complex intracellular Ca2 signals observed during hormonal stimulation of many cell types. However, the ability of cytosolic Ca2+ to potentiate Ca2+ release has recently been questioned because of the observed inhibitory effects of Ca2+ chelators used in previous studies. In the present study, EGTA and BAPTA [1,2-bis-(2-amino-phenoxy)ethane- NNN'N'-tetra-acetic acid] poorly inhibited InsP3-induced Ca2+ release from permeabilized A7r5 smooth-muscle cells. Additionally, stimulatory effects of cytosolic and luminal Ca2+ were observed either in the complete absence of Ca2+ chelator or at constant Ca(2+)-free chelator concentration. These data suggest that potentiation of InsP3-induced Ca2+ release by Ca2+ in A7r5 cells reflects an interaction between Ca2+ and InsP3 receptors, rather than a decrease in chelator-dependent inhibition. The EC50 for activation of InsP3-induced Ca2+ release by cytosolic Ca2+ was unaffected by ATP, or by changing InsP3 concentration, although InsP3-induced Ca2+ release became less sensitive to the inhibitory effects of cytosolic Ca2+ as the InsP3 concentration was elevated. Increasing H+ or Mg2+ concentration shifted the Ca(2+)-activation curve towards higher Ca2+ concentrations. These data suggest that, in addition to the InsP3-binding site, the affinity of the Ca(2+)-binding site(s) on InsP3 receptors can be modulated by intracellular cations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Galione A. Cytosolic calcium oscillators. FASEB J. 1988 Dec;2(15):3074–3082. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.15.2847949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezprozvanny I., Ehrlich B. E. ATP modulates the function of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-gated channels at two sites. Neuron. 1993 Jun;10(6):1175–1184. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90065-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezprozvanny I., Watras J., Ehrlich B. E. Bell-shaped calcium-response curves of Ins(1,4,5)P3- and calcium-gated channels from endoplasmic reticulum of cerebellum. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):751–754. doi: 10.1038/351751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird G. S., Rossier M. F., Hughes A. R., Shears S. B., Armstrong D. L., Putney J. W., Jr Activation of Ca2+ entry into acinar cells by a non-phosphorylatable inositol trisphosphate. Nature. 1991 Jul 11;352(6331):162–165. doi: 10.1038/352162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bootman M. D., Berridge M. J., Taylor C. W. All-or-nothing Ca2+ mobilization from the intracellular stores of single histamine-stimulated HeLa cells. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:163–178. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Joseph S. K. A role for inositol triphosphate in intracellular Ca2+ mobilization and granule secretion in platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15172–15179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combettes L., Claret M., Champeil P. Calcium control on InsP3-induced discharge of calcium from permeabilised hepatocyte pools. Cell Calcium. 1993 Apr;14(4):279–292. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(93)90049-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combettes L., Hannaert-Merah Z., Coquil J. F., Rousseau C., Claret M., Swillens S., Champeil P. Rapid filtration studies of the effect of cytosolic Ca2+ on inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced 45Ca2+ release from cerebellar microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 1;269(26):17561–17571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisle S., Welsh M. J. Inositol trisphosphate is required for the propagation of calcium waves in Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):7963–7966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris C. D., Snyder S. H. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-activated calcium channels. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:469–488. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.002345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch E. A., Turner T. J., Goldin S. M. Calcium as a coagonist of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced calcium release. Science. 1991 Apr 19;252(5004):443–446. doi: 10.1126/science.2017683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemette G., Segui J. A. Effects of pH, reducing and alkylating reagents on the binding and Ca2+ release activities of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate in the bovine adrenal cortex. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1249–1255. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. D., Dean N. M., Boynton A. L. Inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate induces Ca2+ sequestration in rat liver cells. Science. 1988 Nov 25;242(4882):1176–1178. doi: 10.1126/science.2847317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M. Biphasic Ca2+ dependence of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca release in smooth muscle cells of the guinea pig taenia caeci. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Jun;95(6):1103–1122. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.6.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M., Endo M. Calcium-dependent immediate feedback control of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate-induced Ca2+ release. Nature. 1992 Nov 5;360(6399):76–78. doi: 10.1038/360076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. 'Quantal' Ca2+ release and the control of Ca2+ entry by inositol phosphates--a possible mechanism. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 9;263(1):5–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80692-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob R. Calcium oscillations in electrically non-excitable cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 22;1052(3):427–438. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90152-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechleiter J. D., Clapham D. E. Molecular mechanisms of intracellular calcium excitability in X. laevis oocytes. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):283–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90409-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechleiter J., Girard S., Peralta E., Clapham D. Spiral calcium wave propagation and annihilation in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Science. 1991 Apr 5;252(5002):123–126. doi: 10.1126/science.2011747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis-Husselbee J. W., Dawson A. P. A steady-state mechanism can account for the properties of inositol 2,4,5-trisphosphate-stimulated Ca2+ release from permeabilized L1210 cells. Biochem J. 1993 Feb 1;289(Pt 3):861–866. doi: 10.1042/bj2890861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Kawasaki T., Nakade S., Yokota N., Taguchi T., Kasai M., Mikoshiba K. Structural and functional characterization of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor channel from mouse cerebellum. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1109–1116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Stryer L. Calcium spiking. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:153–174. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.001101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Stryer L. Transient calcium release induced by successive increments of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3841–3845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Missiaen L., De Smedt H., Droogmans G., Casteels R. Ca2+ release induced by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate is a steady-state phenomenon controlled by luminal Ca2+ in permeabilized cells. Nature. 1992 Jun 18;357(6379):599–602. doi: 10.1038/357599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Missiaen L., De Smedt H., Droogmans G., Casteels R. Luminal Ca2+ controls the activation of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor by cytosolic Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):22961–22966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Missiaen L., De Smedt H., Parys J. B., Casteels R. Co-activation of inositol trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ release by cytosolic Ca2+ is loading-dependent. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7238–7242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Missiaen L., Taylor C. W., Berridge M. J. Spontaneous calcium release from inositol trisphosphate-sensitive calcium stores. Nature. 1991 Jul 18;352(6332):241–244. doi: 10.1038/352241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. J., Murray K. J., England P. J., Downes C. P., Michell R. H. Partial purification and some properties of rat brain inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 1;251(1):157–163. doi: 10.1042/bj2510157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn D. L., Taylor C. W. Luminal Ca2+ increases the sensitivity of Ca2+ stores to inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Jan;41(1):115–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldershaw K. A., Taylor C. W. Luminal Ca2+ increases the affinity of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate for its receptor. Biochem J. 1993 Jun 15;292(Pt 3):631–633. doi: 10.1042/bj2920631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker I., Yao Y. Regenerative release of calcium from functionally discrete subcellular stores by inositol trisphosphate. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 Dec 23;246(1317):269–274. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parys J. B., Missiaen L., De Smedt H., Casteels R. Loading dependence of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ release in the clonal cell line A7r5. Implications for the mechanism of quantal Ca2+ release. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):25206–25212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parys J. B., Sernett S. W., DeLisle S., Snyder P. M., Welsh M. J., Campbell K. P. Isolation, characterization, and localization of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor protein in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18776–18782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson A., Taylor C. W. Effects of Ca2+ chelators on purified inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) receptors and InsP3-stimulated Ca2+ mobilization. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11528–11533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney T. A., Renard D. C., Sass E. J., Thomas A. P. Oscillatory cytosolic calcium waves independent of stimulated inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate formation in hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12272–12282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. W., Richardson A. Structure and function of inositol trisphosphate receptors. Pharmacol Ther. 1991;51(1):97–137. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(91)90043-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Tsien R. Y. Calcium channels, stores, and oscillations. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:715–760. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukioka M., Iino M., Endo M. pH dependence of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ release in permeabilized smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1994 Mar 15;475(3):369–375. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Delden C., Foti M., Lew D. P., Krause K. H. Ca2+ and Mg2+ regulation of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate binding in myeloid cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12443–12448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varney M. A., Rivera J., Lopez Bernal A., Watson S. P. Are there subtypes of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor? Biochem J. 1990 Jul 1;269(1):211–216. doi: 10.1042/bj2690211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White A. M., Varney M. A., Watson S. P., Rigby S., Liu C. S., Ward J. G., Reese C. B., Graham H. C., Williams R. J. Influence of Mg2+ and pH on n.m.r. spectra and radioligand binding of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Biochem J. 1991 Sep 15;278(Pt 3):759–764. doi: 10.1042/bj2780759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Supattapone S., Wilson V. S., Snyder S. H. Characterization of inositol trisphosphate receptor binding in brain. Regulation by pH and calcium. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12132–12136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


