Abstract
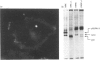
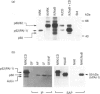
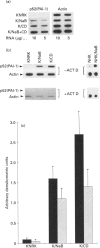
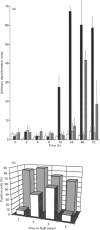
Expression of the rat p52(PAI-1) gene is positively regulated by agents that influence cellular microfilament organization and/or cell-to-substrate adhesion [e.g. cytochalasin D (CD) and sodium n-butyrate (NaB)] [Higgins, Chaudhari and Ryan (1991) Biochem. J. 273, 651-658; Higgins, Ryan and Providence (1994) J. Cell. Physiol. 159, 187-195]. As shape-responsive genes may be subject to inducer-specific controls, the biochemical mechanisms underlying the shape-dependent pathway of p52(PAI-1) gene regulation were examined in v-ras-transformed rat kidney (KNRK) cells. NaB and/or CD effectively stimulated p52(PAI-1) run-off transcription and augmented de novo p52(PAI-1) mRNA and protein synthesis in KNRK cells; induction at both the mRNA and protein levels was inhibited by actinomycin D. Pretreatment with cycloheximide (CX) markedly attenuated NaB- and/or CD-stimulated p52(PAI-1) expression. CX alone, however, induced low levels of p52(PAI-1) mRNA; increased p52(PAI-1) protein synthesis was evident after release of KNRK cells from CX blockade. Such CX-mediated induction was also sensitive to actinomycin D. Full stimulation of p52(PAI-1) expression in KNRK cells in response to the shape modulators NaB and/or CD involves transcriptional activation of the p52(PAI-1) gene, requires de novo RNA synthesis and occurs through a secondary-response (i.e. protein-synthesis-dependent) pathway.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altenburg B. C., Via D. P., Steiner S. H. Modification of the phenotype of murine sarcoma virus-transformed cells by sodium butyrate. Effects on morphology and cytoskeletal elements. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Oct 15;102(2):223–231. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ze'ev A. Cytoarchitecture and signal transduction. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1992;2(3):265–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma P. J., Kooistra T. Different induction of two plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 mRNA species by phorbol ester in human hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):17845–17849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruzdzinski C. J., Riordan-Johnson M., Nordby E. C., Suter S. M., Gelehrter T. D. Isolation and characterization of the rat plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2078–2085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciambrone G. J., McKeown-Longo P. J. Plasminogen activator inhibitor type I stabilizes vitronectin-dependent adhesions in HT-1080 cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;111(5 Pt 1):2183–2195. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.5.2183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton D. F., Harrelson A. L., Darnell J. E., Jr Dependence of liver-specific transcription on tissue organization. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2623–2632. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. L., Niclas J., Lee W. M., Wun T. C., Crowley C. W., Levinson A. D., Sadler J. E., Shuman M. A. Effects of cellular transformation on expression of plasminogen activator inhibitors 1 and 2. Evidence for independent regulation. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8375–8383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frégeau C. J., Helgason C. D., Bleackley R. C. Two cytotoxic cell proteinase genes are differentially sensitive to sodium butyrate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 25;20(12):3113–3119. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.12.3113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill R. K., Christakos S. Identification of sequence elements in mouse calbindin-D28k gene that confer 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3- and butyrate-inducible responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2984–2988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis P., Malter J. S. The adenosine-uridine binding factor recognizes the AU-rich elements of cytokine, lymphokine, and oncogene mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3172–3177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins P. J., Chaudhari P., Ryan M. P. Cell-shape regulation and matrix protein p52 content in phenotypic variants of ras-transformed rat kidney fibroblasts. Functional analysis and biochemical comparison of p52 with proteins implicated in cell-shape determination. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 1;273(Pt 3):651–658. doi: 10.1042/bj2730651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins P. J., Ryan M. P., Ahmed A. Cell-shape-associated transcriptional activation of the p52(PAI-1) gene in rat kidney cells. Biochem J. 1992 Dec 15;288(Pt 3):1017–1024. doi: 10.1042/bj2881017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins P. J., Ryan M. P. Biochemical localization of the transformation-sensitive 52 kDa (p52) protein to the substratum contact regions of cultured rat fibroblasts. Butyrate induction, characterization, and quantification of p52 in v-ras transformed cells. Biochem J. 1989 Jan 1;257(1):173–182. doi: 10.1042/bj2570173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins P. J., Ryan M. P., Chaudhari P. Cytochalasin D-mediated hyperinduction of the substrate-associated 52-kilodalton protein p52 in rat kidney fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1989 May;139(2):407–417. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041390225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins P. J., Ryan M. P. Identification of the 52 kDa cytoskeletal-like protein of cytochalasin D-stimulated normal rat kidney (NRK/CD) cells as substrate-associated glycoprotein p52 [plasminogen-activator inhibitor type-1 (PAI-1)]. Expression of p52 (PAI-1) in NRK/CD cells is regulated at the level of mRNA abundance. Biochem J. 1992 Jun 1;284(Pt 2):433–439. doi: 10.1042/bj2840433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins P. J., Ryan M. P., Providence K. M. Induced expression of p52(PAI-1) in normal rat kidney cells by the microfilament-disrupting agent cytochalasin D. J Cell Physiol. 1994 Apr;159(1):187–195. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041590123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins P. J., Ryan M. P. Redistribution of p52(PAI-1) mRNA to the cytoskeletal framework accompanies increased p52(PAI-1) expression in cytochalasin D-stimulated rat kidney cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1994;358:191–203. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-2578-3_18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins P. J., Ryan M. P., Zeheb R., Gelehrter T. D., Chaudhari P. p52 induction by cytochalasin D in rat kidney fibroblasts: homologies between p52 and plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1. J Cell Physiol. 1990 May;143(2):321–329. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041430216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins P. J., Ryan M. P. p52(PAI-1) and actin expression in butyrate-induced flat revertants of v-ras-transformed rat kidney cells. Biochem J. 1991 Nov 1;279(Pt 3):883–890. doi: 10.1042/bj2790883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins P. J., Smith T. J. Pleotrophic action of interferon gamma in human orbital fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Mar 24;1181(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(93)90085-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins W. E., Westerhausen D. R., Jr, Sobel B. E., Billadello J. J. Transcriptional regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 mRNA in Hep G2 cells by epidermal growth factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):163–168. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg L. J., Earp H. S., Turner C. E., Prockop C., Juliano R. L. Signal transduction by integrins: increased protein tyrosine phosphorylation caused by clustering of beta 1 integrins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8392–8396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruh J., Defer N., Tichonicky L. Action moléculaire et cellulaire du butyrate. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1992;186(1-2):12–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., Keski-Oja J. Growth factors in the regulation of pericellular proteolysis: a review. Cancer Res. 1989 May 15;49(10):2533–2553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., Saksela O., Keski-Oja J. Transforming growth factor-beta induction of type-1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. Pericellular deposition and sensitivity to exogenous urokinase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17467–17474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malter J. S., Hong Y. A redox switch and phosphorylation are involved in the post-translational up-regulation of the adenosine-uridine binding factor by phorbol ester and ionophore. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3167–3171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollinedo F., Gajate C., Tugores A., Flores I., Naranjo J. R. Differences in expression of transcription factor AP-1 in human promyelocytic HL-60 cells during differentiation towards macrophages versus granulocytes. Biochem J. 1993 Aug 15;294(Pt 1):137–144. doi: 10.1042/bj2940137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naranjo J. R., Mellström B., Auwerx J., Mollinedo F., Sassone-Corsi P. Unusual c-fos induction upon chromaffin PC12 differentiation by sodium butyrate: loss of fos autoregulatory function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3605–3610. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. J., Lane E. A., Iannotti A. M., Nugent M. A., Pepinsky R. B., Keski-Oja J. Characterization and purification of a secreted plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) induced by transforming growth factor-beta 1 in normal rat kidney (NRK) cells: decreased PAI-1 expression in transformed NRK cells. Endocrinology. 1990 Jun;126(6):2936–2946. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-6-2936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöllänen J., Hedman K., Nielsen L. S., Danø K., Vaheri A. Ultrastructural localization of plasma membrane-associated urokinase-type plasminogen activator at focal contacts. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;106(1):87–95. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöllänen J., Saksela O., Salonen E. M., Andreasen P., Nielsen L., Danø K., Vaheri A. Distinct localizations of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its type 1 inhibitor under cultured human fibroblasts and sarcoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):1085–1096. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder J. A., Dickinson J. L., Chenevix-Trench G., Antalis T. M. Sodium butyrate differentially modulates plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1, urokinase plasminogen activator, and its receptor in a human colon carcinoma cell. Teratog Carcinog Mutagen. 1993;13(2):75–88. doi: 10.1002/tcm.1770130204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rius C., Zorrilla A., Mata F., Aller P. Comparative effects of butyrate and N6, 2'-O-dibutyryladenosine-3':5'-cyclic monophosphate on growth, differentiation and gene expression in U937 human monoblastoid cells. Biochem Int. 1991 Feb;23(3):555–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan M. P., Borenfreund E., Higgins P. J. Cytoarchitectural analysis of epithelial sheets formed in vitro by hepatic tumor cells possessing defined intermediate-sized filament cytoskeletal abnormalities. Am J Pathol. 1989 Feb;134(2):447–456. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan M. P., Higgins P. J. Control of p52(PAI-1) gene expression in normal and transformed rat kidney cells: relationship between p52(PAI-1) induction and actin cytoarchitecture. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1994;358:215–230. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-2578-3_20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan M. P., Higgins P. J. Cytoarchitecture of Kirsten sarcoma virus-transformed rat kidney fibroblasts: butyrate-induced reorganization within the actin microfilament network. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Oct;137(1):25–34. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041370104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan M. P., Higgins P. J. Growth state-regulated expression of p52(PAI-1) in normal rat kidney cells. J Cell Physiol. 1993 May;155(2):376–384. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041550219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. J., Doherty D. E., Ritter A. G., Benedict S. H., Clark R. A. Adherence-dependent increase in human monocyte PDGF(B) mRNA is associated with increases in c-fos, c-jun, and EGR2 mRNA. J Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;111(5 Pt 1):2139–2148. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.5.2139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. J., Ahmed A., Hogg M. G., Higgins P. J. Interferon-gamma is an inducer of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 in human orbital fibroblasts. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jul;263(1 Pt 1):C24–C29. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.1.C24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. J., Higgins P. J. Bidimensional gel electrophoretic analysis of protein synthesis and response to interferon-gamma in cultured human dermal fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jun 19;1181(3):300–306. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(93)90036-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souleimani A., Asselin C. Regulation of C-fos expression by sodium butyrate in the human colon carcinoma cell line Caco-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 May 28;193(1):330–336. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staiano-Coico L., Higgins P. J. Cell shape changes during transition of basal keratinocytes to mature enucleate-cornified envelopes: modulation of terminal differentiation by fibronectin. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Jul;201(1):126–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90356-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staiano-Coico L., Higgins P. J., Darzynkiewicz Z., Kimmel M., Gottlieb A. B., Pagan-Charry I., Madden M. R., Finkelstein J. L., Hefton J. M. Human keratinocyte culture. Identification and staging of epidermal cell subpopulations. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):396–404. doi: 10.1172/JCI112317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang S. J., Ko L. W., Lee Y. H., Wang F. F. Induction of fos and sis proto-oncogenes and genes of the extracellular matrix proteins during butyrate induced glioma differentiation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jan 30;1048(1):59–65. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90022-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tichonicky L., Kruh J., Defer N. Sodium butyrate inhibits c-myc and stimulates c-fos expression in all the steps of the cell-cycle in hepatoma tissue cultured cells. Biol Cell. 1990;69(1):65–67. doi: 10.1016/0248-4900(90)90329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Via D. P., Sramek S., Larriba G., Steiner S. Effects of sodium butyrate on the membrane glycoconjugates of murine sarcoma virus-transformed rat cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):225–234. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Tremble P. M., Behrendtsen O., Crowley E., Damsky C. H. Signal transduction through the fibronectin receptor induces collagenase and stromelysin gene expression. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):877–889. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada A., Nikaido T., Nojima Y., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Activation of human CD4 T lymphocytes. Interaction of fibronectin with VLA-5 receptor on CD4 cells induces the AP-1 transcription factor. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):53–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambetti G., Ramsey-Ewing A., Bortell R., Stein G., Stein J. Disruption of the cytoskeleton with cytochalasin D induces c-fos gene expression. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Jan;192(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90162-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeheb R., Gelehrter T. D. Cloning and sequencing of cDNA for the rat plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Gene. 1988 Dec 20;73(2):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90510-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]