Abstract
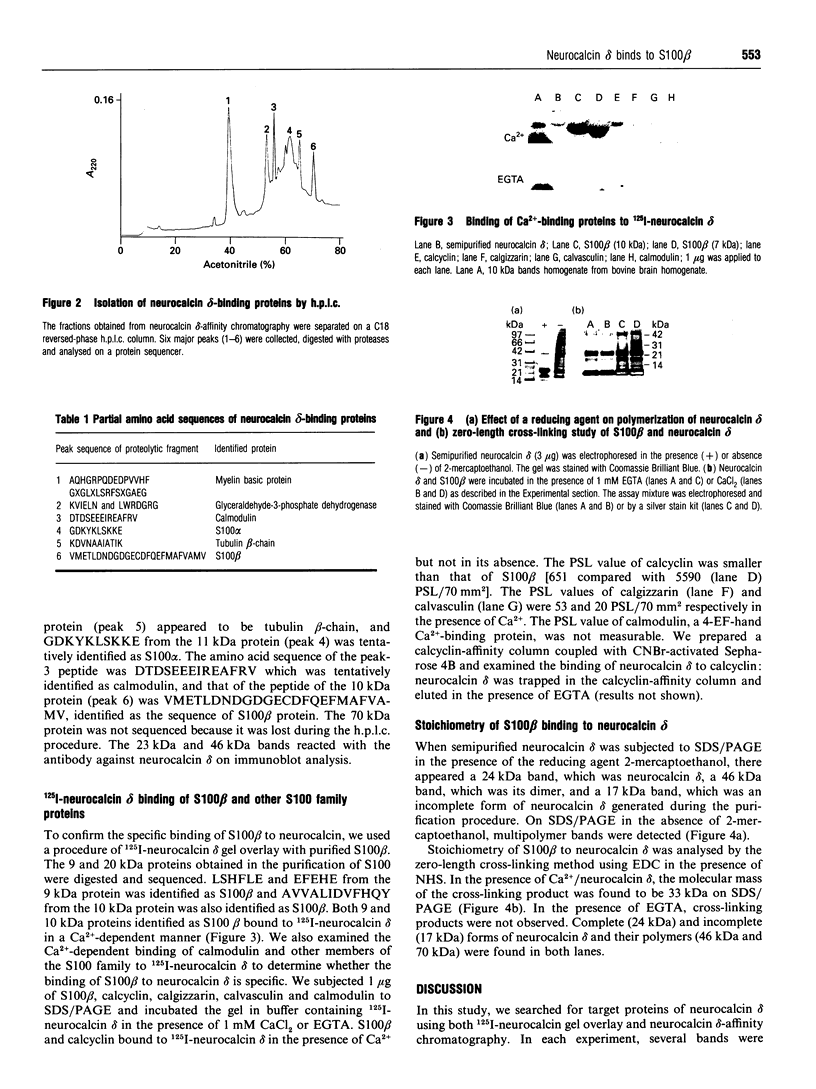
To clarify the function of neurocalcin delta, an isoform found abundantly in glial cells, we attempted to find its target proteins by using neurocalcin delta-affinity chromatography and the 125I-neurocalcin delta gel-overlay method. The 10, 14, 27, 36 and 50 kDa bands found on SDS/PAGE bound to 125I-neurocalcin delta, and 10, 11, 19, 24, 26, 50 and 70 kDa proteins were eluted from a neurocalcin delta-affinity column in a Ca(2+)-dependent manner. Sequence analysis of proteolytic peptides revealed the following identities: S100 beta (10 kDa), S100 alpha (11 kDa), myelin basic protein (19 kDa), glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (36 kDa) and tubulin beta-chain (50 kDa). A zero-length cross-linking study indicated that 1 mol of S100 beta bound to 1 mol of neurocalcin delta. With the gel-overlay method, purified S100 beta protein and calcyclin bound to 125I-neurocalcin delta whereas calgizarrin and calvasculin, other members of the S100 family, did not. These findings suggest that S100 beta is one of the target proteins of neurocalcin delta, and the neurocalcin delta-S100 beta complex may be involved in Ca(2+)-signalling in the glial cell.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bastianelli E., Okazaki K., Hidaka H., Pochet R. Neurocalcin immunoreactivity in rat olfactory bulb. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Oct 29;161(2):165–168. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90285-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipek A., Gerke V., Weber K., Kuźnicki J. Characterization of the cell-cycle-regulated protein calcyclin from Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Identification of two binding proteins obtained by Ca2(+)-dependent affinity chromatography. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Feb 14;195(3):795–800. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Weber K. Calmodulin-binding proteins of the microfilaments present in isolated brush borders and microvilli of intestinal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10551–10554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabarek Z., Gergely J. Zero-length crosslinking procedure with the use of active esters. Anal Biochem. 1990 Feb 15;185(1):131–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90267-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Okazaki K. Neurocalcin family: a novel calcium-binding protein abundant in bovine central nervous system. Neurosci Res. 1993 Feb;16(2):73–77. doi: 10.1016/0168-0102(93)90074-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isobe T., Nakajima T., Okuyama T. Reinvestigation of extremely acidic proteins in bovine brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 27;494(1):222–232. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90150-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrand C., Clos J., Legrand J., Langley O. K., Ghandour M. S., Labourdette G., Gombos G., Vincendon G. Localization of S100 protein in the rat cerebellum: an immunoelectron microscope study. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1981 Jul-Aug;7(4):299–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1981.tb00101.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano A., Terasawa M., Watanabe M., Okazaki K., Inoue S., Kato M., Nimura Y., Usuda N., Morita T., Hidaka H. Distinct regional localization of neurocalcin, a Ca(2+)-binding protein, in the bovine adrenal gland. J Endocrinol. 1993 Aug;138(2):283–290. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1380283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano A., Terasawa M., Watanabe M., Usuda N., Morita T., Hidaka H. Neurocalcin, a novel calcium binding protein with three EF-hand domains, expressed in retinal amacrine cells and ganglion cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Aug 14;186(3):1207–1211. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81534-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki K., Iino S., Inoue S., Kobayashi S., Hidaka H. Differential distribution of neurocalcin isoforms in rat spinal cord, dorsal root ganglia and muscle spindle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Sep 29;1223(3):311–317. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(94)90089-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki K., Watanabe M., Ando Y., Hagiwara M., Terasawa M., Hidaka H. Full sequence of neurocalcin, a novel calcium-binding protein abundant in central nervous system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 29;185(1):147–153. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80968-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terasawa M., Nakano A., Kobayashi R., Hidaka H. Neurocalcin: a novel calcium-binding protein from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19596–19599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokumitsu H., Kobayashi R., Hidaka H. A calcium-binding protein from rabbit lung cytosol identified as the product of growth-regulated gene (2A9) and its binding proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Jul;288(1):202–207. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90184-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Ando Y., Todoroki H., Minami H., Hidaka H. Molecular cloning and sequencing of a cDNA clone encoding a new calcium binding protein, named calgizzarin, from rabbit lung. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 16;181(2):644–649. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91239-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Kobayashi R., Ishikawa T., Hidaka H. Isolation and characterization of a calcium-binding protein derived from mRNA termed p9Ka, pEL-98, 18A2, or 42A by the newly synthesized vasorelaxant W-66 affinity chromatography. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Feb 1;292(2):563–569. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90031-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]