Full text
PDF

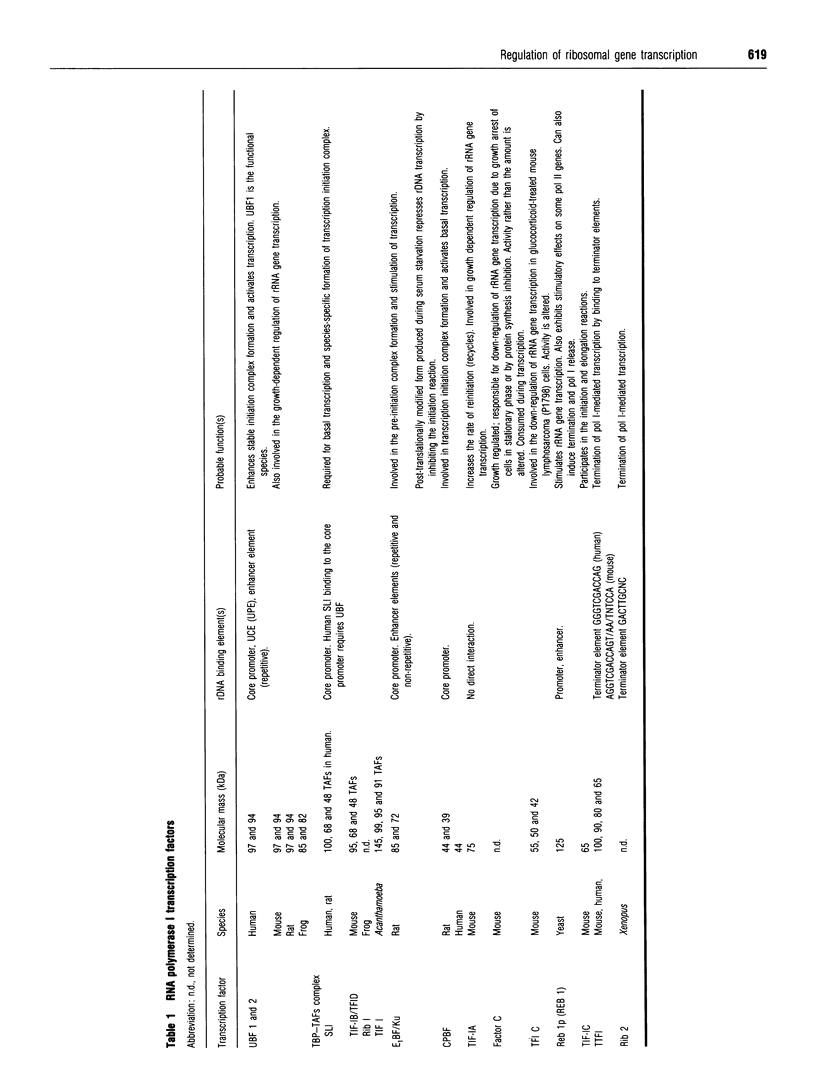







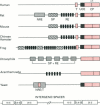
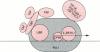
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachvarov D., Moss T. The RNA polymerase I transcription factor xUBF contains 5 tandemly repeated HMG homology boxes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2331–2335. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartsch I., Schoneberg C., Grummt I. Purification and characterization of TTFI, a factor that mediates termination of mouse ribosomal DNA transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3891–3897. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateman E., Paule M. R. Promoter occlusion during ribosomal RNA transcription. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):985–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90113-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazett-Jones D. P., Leblanc B., Herfort M., Moss T. Short-range DNA looping by the Xenopus HMG-box transcription factor, xUBF. Science. 1994 May 20;264(5162):1134–1137. doi: 10.1126/science.8178172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Jantzen H. M., Tjian R. Assembly of alternative multiprotein complexes directs rRNA promoter selectivity. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):943–954. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Learned R. M., Jantzen H. M., Tjian R. Functional cooperativity between transcription factors UBF1 and SL1 mediates human ribosomal RNA synthesis. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1192–1197. doi: 10.1126/science.3413483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill S. J., DiNardo S., Voelkel-Meiman K., Sternglanz R. Need for DNA topoisomerase activity as a swivel for DNA replication for transcription of ribosomal RNA. 1987 Mar 26-Apr 1Nature. 326(6111):414–416. doi: 10.1038/326414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brou C., Kuhn A., Staub A., Chaudhary S., Grummt I., Davidson I., Tora L. Sequence-specific transactivators counteract topoisomerase II-mediated inhibition of in vitro transcription by RNA polymerases I and II. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Aug 25;21(17):4011–4018. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.17.4011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun R. P., Ryan K., Sollner-Webb B. Factor C*, the specific initiation component of the mouse RNA polymerase I holoenzyme, is inactivated early in the transcription process. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):5010–5021. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.5010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S. J., Reeder R. H. Spacer sequences regulate transcription of ribosomal gene plasmids injected into Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):989–996. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90556-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttgereit D., Pflugfelder G., Grummt I. Growth-dependent regulation of rRNA synthesis is mediated by a transcription initiation factor (TIF-IA). Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8165–8180. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy B. G., Yang-Yen H. F., Rothblum L. I. Transcriptional role for the nontranscribed spacer of rat ribosomal DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2766–2773. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavannaugh A. H., Thompson E. A., Jr Hormonal regulation of transcription of rDNA. Inhibition of transcription during glucocorticoid-mediated inhibition of proliferation of lymphosarcoma P1798 cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9768–9773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao Y., Pellegrini M. In vitro transcription of Drosophila rRNA genes shows stimulation by a phorbol ester and serum. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):934–941. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comai L., Tanese N., Tjian R. The TATA-binding protein and associated factors are integral components of the RNA polymerase I transcription factor, SL1. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):965–976. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90039-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comai L., Zomerdijk J. C., Beckmann H., Zhou S., Admon A., Tjian R. Reconstitution of transcription factor SL1: exclusive binding of TBP by SL1 or TFIID subunits. Science. 1994 Dec 23;266(5193):1966–1972. doi: 10.1126/science.7801123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway J. W., Conaway R. C. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor shares functional properties with Escherichia coli sigma 70. Science. 1990 Jun 22;248(4962):1550–1553. doi: 10.1126/science.2193400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copenhaver G. P., Putnam C. D., Denton M. L., Pikaard C. S. The RNA polymerase I transcription factor UBF is a sequence-tolerant HMG-box protein that can recognize structured nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jul 11;22(13):2651–2657. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.13.2651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croston G. E., Kerrigan L. A., Lira L. M., Marshak D. R., Kadonaga J. T. Sequence-specific antirepression of histone H1-mediated inhibition of basal RNA polymerase II transcription. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):643–649. doi: 10.1126/science.1899487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croston G. E., Laybourn P. J., Paranjape S. M., Kadonaga J. T. Mechanism of transcriptional antirepression by GAL4-VP16. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2270–2281. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Winter R. F., Moss T. A complex array of sequences enhances ribosomal transcription in Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):813–827. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90407-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov S. I., Bachvarov D., Moss T. Mapping of a sequence essential for the nuclear transport of the Xenopus ribosomal transcription factor xUBF using a simple coupled translation-transport and acid extraction approach. DNA Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;12(3):275–281. doi: 10.1089/dna.1993.12.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixit A., Garg L. C., Chao W., Jacob S. T. An enhancer element in the far upstream spacer region of rat ribosomal RNA gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11616–11622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duceman B. W., Rose K. M., Jacob S. T. Activation of purified hepatoma RNA polymerase I by homologous protein kinase NII. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10755–10758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunaway M. Inhibition of topoisomerase II does not inhibit transcription of RNA polymerase I and II genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2893–2900. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Warner J. R. An RNA polymerase I enhancer in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2089–2097. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firek S., Read C., Smith D. R., Moss T. Point mutation analysis of the Xenopus laevis RNA polymerase I core promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):105–109. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Lu H., Killeen M., Greenblatt J., Burton Z. F., Reinberg D. The small subunit of transcription factor IIF recruits RNA polymerase II into the preinitiation complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):9999–10003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.9999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg L. C., Dixit A., Jacob S. T. A 37-base pair element in the far upstream spacer region can enhance transcription of rat rDNA in vitro and can bind to the core promoter-binding factor(s). J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):220–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh A. K., Hoff C. M., Jacob S. T. Characterization of the 130-bp repeat enhancer element of the rat ribosomal gene: functional interaction with transcription factor E1BF. Gene. 1993 Mar 30;125(2):217–222. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90332-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh A. K., Kermekchiev M., Jacob S. T. Effects of repetitive and non-repetitive rat rDNA enhancer elements on in vivo transcription by RNA polymerases I and II. Gene. 1994 Apr 20;141(2):271–275. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90584-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J. M., Wolf V. J., Dang T., Forbes D. J., Hartl P. Mitotic repression of RNA polymerase III transcription in vitro mediated by phosphorylation of a TFIIIB component. Science. 1994 Jan 7;263(5143):81–84. doi: 10.1126/science.8272869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govoni M., Farabegoli F., Pession A., Novello F. Inhibition of topoisomerase II activity and its effect on nucleolar structure and function. Exp Cell Res. 1994 Mar;211(1):36–41. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith A. J., Blier P. R., Mimori T., Hardin J. A. Ku polypeptides synthesized in vitro assemble into complexes which recognize ends of double-stranded DNA. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):331–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Roth E., Paule M. R. Ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro is species specific. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):173–174. doi: 10.1038/296173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunderson S. I., Knuth M. W., Burgess R. R. The human U1 snRNA promoter correctly initiates transcription in vitro and is activated by PSE1. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2048–2060. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S. The Yin and the Yang of mammalian transcription. Curr Biol. 1992 Mar;2(3):152–154. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(92)90268-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltiner M. M., Smale S. T., Tjian R. Two distinct promoter elements in the human rRNA gene identified by linker scanning mutagenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):227–235. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington C. A., Chikaraishi D. M. Transcription of spacer sequences flanking the rat 45S ribosomal DNA gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):314–325. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S. L., Ryan K., Sollner-Webb B. The promoter-proximal rDNA terminator augments initiation by preventing disruption of the stable transcription complex caused by polymerase read-in. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):212–223. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N. TBP, a universal eukaryotic transcription factor? Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1291–1308. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff C. M., Ghosh A. K., Prabhakar B. S., Jacob S. T. Enhancer 1 binding factor, a Ku-related protein, is a positive regulator of RNA polymerase I transcription initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):762–766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff C. M., Jacob S. T. Characterization of the factor E1BF from a rat hepatoma that modulates ribosomal RNA gene transcription and its relationship to the human Ku autoantigen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Feb 15;190(3):747–753. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inostroza J. A., Mermelstein F. H., Ha I., Lane W. S., Reinberg D. Dr1, a TATA-binding protein-associated phosphoprotein and inhibitor of class II gene transcription. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):477–489. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob S. T., Muecke W., Sajdel E. M., Munro H. N. Evidence for extranucleolar control of RNA synthesis in the nucleolus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jul 27;40(2):334–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob S. T., Sajdel E. M., Munro H. N. Regulation of nucleolar RNA metabolism by hydrocortisone. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Feb;7(4):449–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb19630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob S. T. Transcription of eukaryotic ribosomal RNA gene. Mol Cell Biochem. 1986 Apr;70(1):11–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00233800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob S. T., Zhang J., Garg L. C., Book C. B. Multiple functional enhancer motifs of rat ribosomal gene. 1991 May 29-Jun 12Mol Cell Biochem. 104(1-2):155–162. doi: 10.1007/BF00229815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs F. A., Bird R. C., Sells B. H. Differentiation of rat myoblasts. Regulation of turnover of ribosomal proteins and their mRNAs. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jul 15;150(2):255–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Admon A., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Nucleolar transcription factor hUBF contains a DNA-binding motif with homology to HMG proteins. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):830–836. doi: 10.1038/344830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Chow A. M., King D. S., Tjian R. Multiple domains of the RNA polymerase I activator hUBF interact with the TATA-binding protein complex hSL1 to mediate transcription. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1950–1963. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju Q. D., Morrow B. E., Warner J. R. REB1, a yeast DNA-binding protein with many targets, is essential for growth and bears some resemblance to the oncogene myb. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5226–5234. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jänne O., Bullock L. P., Bardin C. W., Jacob S. T. Early androgen action in kidney of normal and androgen-insensitive (tfm/y) mice. Changes in RNA polymerase and chromatin template activities. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 5;418(3):330–343. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90295-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karagyozov L. K., Stoyanova B. B., Hadjiolov A. A. Effect of cycloheximide on the in vivo and in vitro synthesis of ribosomal RNA in rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 30;607(2):295–303. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kermekchiev M., Muramatsu M. Presence of an inhibitor of RNA polymerase I mediated transcription in extracts from growth arrested mouse cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 11;21(3):447–453. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.3.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Kane C. M. RNA polymerase: regulation of transcript elongation and termination. FASEB J. 1991 Oct;5(13):2833–2842. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.13.1916107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knuth M. W., Gunderson S. I., Thompson N. E., Strasheim L. A., Burgess R. R. Purification and characterization of proximal sequence element-binding protein 1, a transcription activating protein related to Ku and TREF that binds the proximal sequence element of the human U1 promoter. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17911–17920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller H. T., Frondorf K. A., Maschner P. D., Vaughn J. C. In vivo transcription from multiple spacer rRNA gene promoters during early development and evolution of the intergenic spacer in the brine shrimp Artemia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5391–5411. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauter K. S., Soeiro R., Nadal-Ginard B. Transcriptional regulation of ribosomal RNA accumulation during L6E9 myoblast differentiation. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 15;134(4):727–741. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90482-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Bartsch I., Grummt I. Specific interaction of the murine transcription termination factor TTF I with class-I RNA polymerases. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):559–562. doi: 10.1038/344559a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Deppert U., Grummt I. A 140-base-pair repetitive sequence element in the mouse rRNA gene spacer enhances transcription by RNA polymerase I in a cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7527–7531. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Stefanovsky V., Grummt I. The nucleolar transcription activator UBF relieves Ku antigen-mediated repression of mouse ribosomal gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 11;21(9):2057–2063. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.9.2057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Voit R., Stefanovsky V., Evers R., Bianchi M., Grummt I. Functional differences between the two splice variants of the nucleolar transcription factor UBF: the second HMG box determines specificity of DNA binding and transcriptional activity. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 15;13(2):416–424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. A point mutation uncouples RNA 3'-end formation and termination during ribosomal gene transcription in Xenopus laevis. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):269–276. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Heat shock stabilizes highly unstable transcripts of the Xenopus ribosomal gene spacer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):56–60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalo D., Carles C., Sentenac A., Thuriaux P. Interactions between three common subunits of yeast RNA polymerases I and III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5524–5528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang W. H., Morrow B. E., Ju Q., Warner J. R., Reeder R. H. A model for transcription termination by RNA polymerase I. Cell. 1994 Nov 4;79(3):527–534. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90261-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang W. H., Reeder R. H. The REB1 site is an essential component of a terminator for RNA polymerase I in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):649–658. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson D. E., Xie W., Glibetic M., O'Mahony D., Sells B. H., Rothblum L. I. Coordinated decreases in rRNA gene transcription factors and rRNA synthesis during muscle cell differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):7933–7936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.7933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laybourn P. J., Kadonaga J. T. Role of nucleosomal cores and histone H1 in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Science. 1991 Oct 11;254(5029):238–245. doi: 10.1126/science.254.5029.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Smale S. T., Haltiner M. M., Tjian R. Regulation of human ribosomal RNA transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3558–3562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. C., Bullock L. P., Bardin C. W., Jacob S. T. Effect of medroxyprogesterone acetate and testosterone on solubilized RNA polymerases and chromatin template activity in kidney from normal and androgen-insensitive (Tfm/Y) mice. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4833–4838. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X., Miller C. W., Koeffler P. H., Berk A. J. The p53 activation domain binds the TATA box-binding polypeptide in Holo-TFIID, and a neighboring p53 domain inhibits transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3291–3300. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z., Jacob S. T. Characterization of a protein that interacts with the rat ribosomal gene promoter and modulates RNA polymerase I transcription. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 17;269(24):16618–16625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorch Y., Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. Interchangeable RNA polymerase I and II enhancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8202–8206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchini R., Sogo J. M. Different chromatin structures along the spacers flanking active and inactive Xenopus rRNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4288–4296. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda Y., Hisatake K., Kondo T., Hanada K., Song C. Z., Nishimura T., Muramatsu M. Mouse rRNA gene transcription factor mUBF requires both HMG-box1 and an acidic tail for nucleolar accumulation: molecular analysis of the nucleolar targeting mechanism. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3695–3704. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05454.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan P. B., Thompson E. A. Hormonal regulation of transcription of rDNA. Purification and characterization of the hormone-regulated transcription factor IC. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16225–16233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Hu C. H., Pikaard C. S., Reeder R. H. xUBF and Rib 1 are both required for formation of a stable polymerase I promoter complex in X. laevis. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2297–2303. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07766.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Reeder R. H. A DNA-binding protein is required for termination of transcription by RNA polymerase I in Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2793–2800. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merino A., Madden K. R., Lane W. S., Champoux J. J., Reinberg D. DNA topoisomerase I is involved in both repression and activation of transcription. Nature. 1993 Sep 16;365(6443):227–232. doi: 10.1038/365227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. R., Hayward D. C., Glover D. M. Transcription of the 'non-transcribed' spacer of Drosophila melanogaster rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):11–19. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Tower J., Sollner-Webb B. A complex control region of the mouse rRNA gene directs accurate initiation by RNA polymerase I. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):554–562. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. L., Jr, Beatty B. R. Visualization of nucleolar genes. Science. 1969 May 23;164(3882):955–957. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3882.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Financsek I., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Fractionation and reconstitution of factors required for accurate transcription of mammalian ribosomal RNA genes: identification of a species-dependent initiation factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6659–6670. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misseyanni A., Scheidereit C., Kalff M., Beato M. Neither the endogenous nor a functional steroid hormone receptor binding site transactivate the ribosomal RNA gene promoter in vitro. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1991 Oct;39(4A):409–418. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(91)90234-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow B. E., Ju Q., Warner J. R. Purification and characterization of the yeast rDNA binding protein REB1. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):20778–20783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T. A transcriptional function for the repetitive ribosomal spacer in Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):223–228. doi: 10.1038/302223a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Stefanovsky V. Y. Promotion and regulation of ribosomal transcription in eukaryotes by RNA polymerase I. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1995;50:25–66. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60810-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolov D. B., Hu S. H., Lin J., Gasch A., Hoffmann A., Horikoshi M., Chua N. H., Roeder R. G., Burley S. K. Crystal structure of TFIID TATA-box binding protein. Nature. 1992 Nov 5;360(6399):40–46. doi: 10.1038/360040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niu H., Jacob S. T. Enhancer 1 binding factor (E1BF), a Ku-related protein, is a growth-regulated RNA polymerase I transcription factor: association of a repressor activity with purified E1BF from serum-deprived cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):9101–9105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.9101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niu H., Zhang J., Jacob S. T. E1BF/Ku interacts physically and functionally with the core promoter binding factor CPBF and promotes the basal transcription of rat and human ribosomal RNA genes. Gene Expr. 1995;4(3):111–124. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Mahony D. J., Rothblum L. I. Identification of two forms of the RNA polymerase I transcription factor UBF. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3180–3184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Mahony D. J., Xie W. Q., Smith S. D., Singer H. A., Rothblum L. I. Differential phosphorylation and localization of the transcription factor UBF in vivo in response to serum deprivation. In vitro dephosphorylation of UBF reduces its transactivation properties. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):35–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape L. K., Windle J. J., Sollner-Webb B. Half helical turn spacing changes convert a frog into a mouse rDNA promoter: a distant upstream domain determines the helix face of the initiation site. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):52–62. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker K. A., Bond U. Analysis of pre-rRNAs in heat-shocked HeLa cells allows identification of the upstream termination site of human polymerase I transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2500–2512. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paule M. R., Iida C. T., Perna P. J., Harris G. H., Knoll D. A., D'Alessio J. M. In vitro evidence that eukaryotic ribosomal RNA transcription is regulated by modification of RNA polymerase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):8161–8180. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.8161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paule M. R. Polymerase I transcription, termination, and processing. Gene Expr. 1993;3(1):1–9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikaard C. S., Pape L. K., Henderson S. L., Ryan K., Paalman M. H., Lopata M. A., Reeder R. H., Sollner-Webb B. Enhancers for RNA polymerase I in mouse ribosomal DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4816–4825. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnam C. D., Copenhaver G. P., Denton M. L., Pikaard C. S. The RNA polymerase I transactivator upstream binding factor requires its dimerization domain and high-mobility-group (HMG) box 1 to bend, wrap, and positively supercoil enhancer DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6476–6488. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radebaugh C. A., Matthews J. L., Geiss G. K., Liu F., Wong J. M., Bateman E., Camier S., Sentenac A., Paule M. R. TATA box-binding protein (TBP) is a constituent of the polymerase I-specific transcription initiation factor TIF-IB (SL1) bound to the rRNA promoter and shows differential sensitivity to TBP-directed reagents in polymerase I, II, and III transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):597–605. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W. Three in one and one in three: it all depends on TBP. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):7–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90042-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose K. M., Bell L. E., Siefken D. A., Jacob S. T. A heparin-sensitive nuclear protein kinase. Purification, properties, and increased activity in rat hepatoma relative to liver. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7468–7477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose K. M., Stetler D. A., Jacob S. T. Protein kinase activity of RNA polymerase I purified from a rat hepatoma: probable function of Mr 42,000 and 24,600 polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2833–2837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein S. J., Dasgupta A. Inhibition of rRNA synthesis by poliovirus: specific inactivation of transcription factors. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4689–4696. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4689-4696.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudenko G., Chung H. M., Pham V. P., Van der Ploeg L. H. RNA polymerase I can mediate expression of CAT and neo protein-coding genes in Trypanosoma brucei. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3387–3397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04903.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudenko G., Lee M. G., Van der Ploeg L. H. The PARP and VSG genes of Trypanosoma brucei do not resemble RNA polymerase II transcription units in sensitivity to Sarkosyl in nuclear run-on assays. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):303–306. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudloff U., Eberhard D., Tora L., Stunnenberg H., Grummt I. TBP-associated factors interact with DNA and govern species specificity of RNA polymerase I transcription. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 1;13(11):2611–2616. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudloff U., Stunnenberg H. G., Keaveney M., Grummt I. Yeast TBP can replace its human homologue in the RNA polymerase I-specific multisubunit factor SL1. J Mol Biol. 1994 Nov 11;243(5):840–845. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadis S., Hickey E., Weber L. A. Effect of heat shock on RNA metabolism in HeLa cells. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Jun;135(3):377–386. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041350304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajdel E. M., Jacob S. T. Mechanism of early effect of hydrocortisone on the transcriptional process: stimulation of the activities of purified rat liver nucleolar RNA polymerases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Nov 5;45(3):707–715. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90474-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon C., Türler H., Weil R. Polyoma-induced stimulation of cellular RNA synthesis is paralleled by changed expression of the viral genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1483–1503. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp A., Grummt I. Transcription complex formation at the mouse rDNA promoter involves the stepwise association of four transcription factors and RNA polymerase I. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24588–24595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp A., Pfleiderer C., Rosenbauer H., Grummt I. A growth-dependent transcription initiation factor (TIF-IA) interacting with RNA polymerase I regulates mouse ribosomal RNA synthesis. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2857–2863. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07475.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp A., Schnapp G., Erny B., Grummt I. Function of the growth-regulated transcription initiation factor TIF-IA in initiation complex formation at the murine ribosomal gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):6723–6732. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.6723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp G., Schnapp A., Rosenbauer H., Grummt I. TIF-IC, a factor involved in both transcription initiation and elongation of RNA polymerase I. EMBO J. 1994 Sep 1;13(17):4028–4035. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06719.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz M. C., Brill S. J., Ju Q., Sternglanz R., Reeder R. H. Topoisomerases and yeast rRNA transcription: negative supercoiling stimulates initiation and topoisomerase activity is required for elongation. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1332–1341. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentenac A. Eukaryotic RNA polymerases. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;18(1):31–90. doi: 10.3109/10409238509082539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. TATA-binding protein is a classless factor. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):819–821. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. D., O'Mahony D. J., Kinsella B. T., Rothblum L. I. Transcription from the rat 45S ribosomal DNA promoter does not require the factor UBF. Gene Expr. 1993;3(3):229–236. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. D., Oriahi E., Lowe D., Yang-Yen H. F., O'Mahony D., Rose K., Chen K., Rothblum L. I. Characterization of factors that direct transcription of rat ribosomal DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3105–3116. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Tower J. Transcription of cloned eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:801–830. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song C. Z., Hanada K., Yano K., Maeda Y., Yamamoto K., Muramatsu M. High conservation of subunit composition of RNA polymerase I(A) between yeast and mouse and the molecular cloning of mouse RNA polymerase I 40-kDa subunit RPA40. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 28;269(43):26976–26981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soprano K. J., Dev V. G., Croce C. M., Baserga R. Reactivation of silent rRNA genes by simian virus 40 in human-mouse hybrid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3885–3889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soprano K. J., Jonak G. J., Galanti N., Floros J., Baserga R. Identification of an SV40 DNA sequence related to the reactivation of silent rRNA genes in human greater than mouse hybrid cells. Virology. 1981 Feb;109(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90477-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Duality of TBP, the universal transcription factor. Science. 1994 Feb 25;263(5150):1103–1104. doi: 10.1126/science.8108728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tower J., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of mouse rDNA is regulated by an activated subform of RNA polymerase I. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):873–883. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90514-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treiber D. K., Zhai X., Jantzen H. M., Essigmann J. M. Cisplatin-DNA adducts are molecular decoys for the ribosomal RNA transcription factor hUBF (human upstream binding factor). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5672–5676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallett S. M., Brudnak M., Pellegrini M., Weber H. W. In vivo regulation of rRNA transcription occurs rapidly in nondividing and dividing Drosophila cells in response to a phorbol ester and serum. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):928–933. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voit R., Schnapp A., Kuhn A., Rosenbauer H., Hirschmann P., Stunnenberg H. G., Grummt I. The nucleolar transcription factor mUBF is phosphorylated by casein kinase II in the C-terminal hyperacidic tail which is essential for transactivation. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2211–2218. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05280.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb M. L., Mealey-Cavender J. F., Jacob S. T. Glucocorticoid-induced stimulation of ribosomal gene transcription in rat hepatoma cells is mediated by modification of RNA polymerase I or an associated factor. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Nov;3(11):1861–1868. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-11-1861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik N. A., Liao S. M., Kolodziej P. A., Young R. A. Subunits shared by eukaryotic nuclear RNA polymerases. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):313–323. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie W. Q., Rothblum L. I. Domains of the rat rDNA promoter must be aligned stereospecifically. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1266–1275. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi M., Nomura M. Deficiency in both type I and type II DNA topoisomerase activities differentially affect rRNA and ribosomal protein synthesis in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Curr Genet. 1988 Apr;13(4):305–314. doi: 10.1007/BF00424424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawel L., Reinberg D. Initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II: a multi-step process. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1993;44:67–108. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60217-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Jacob S. T. Purification and characterization of a novel factor which stimulates rat ribosomal gene transcription in vitro by interacting with enhancer and core promoter elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5177–5186. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]