Abstract
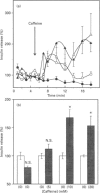
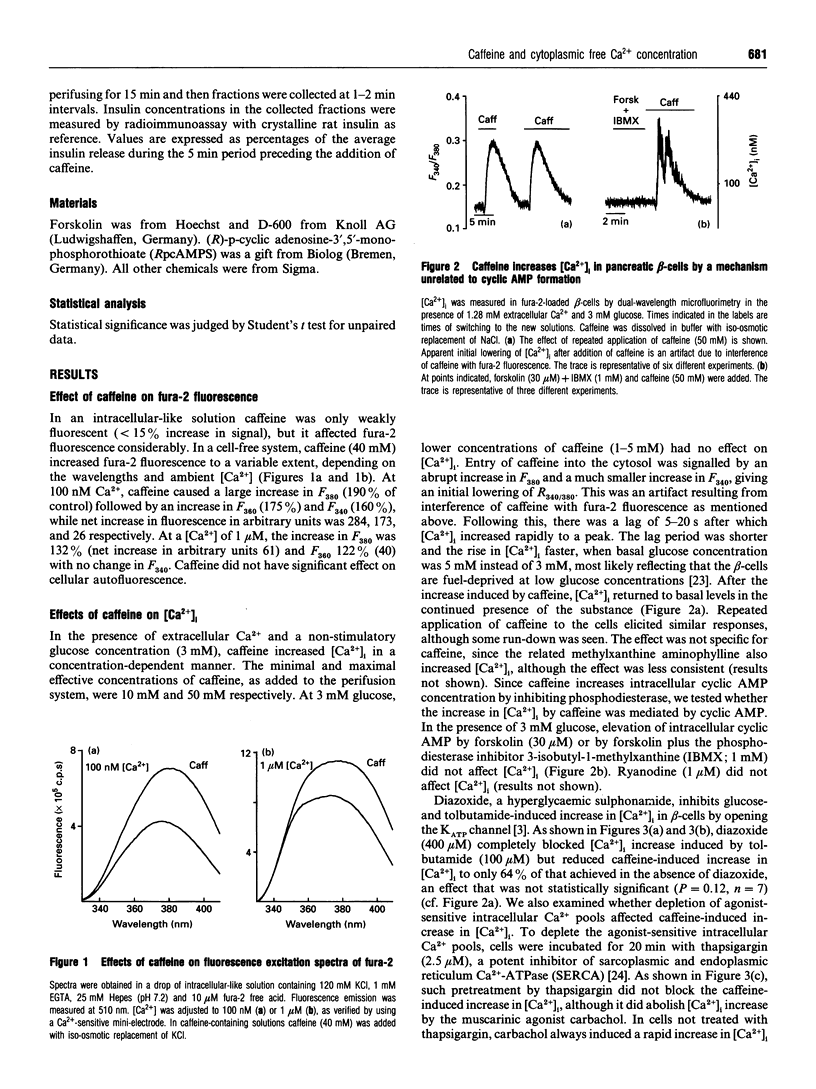
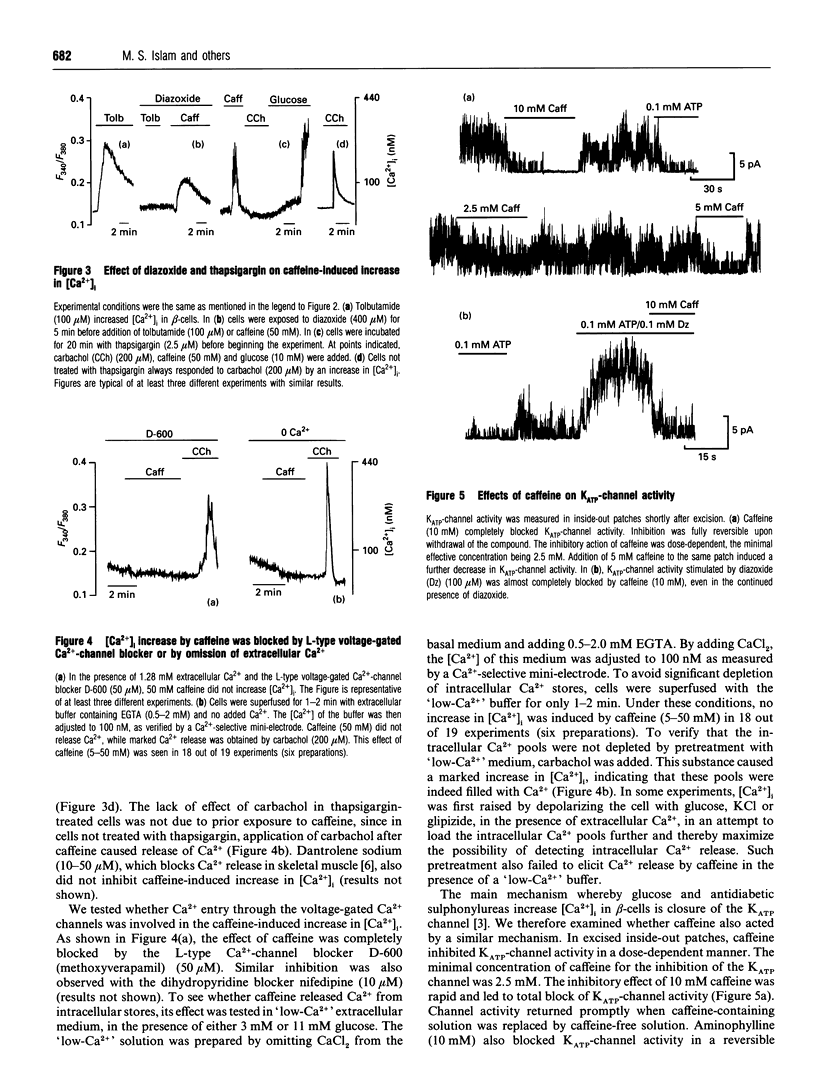
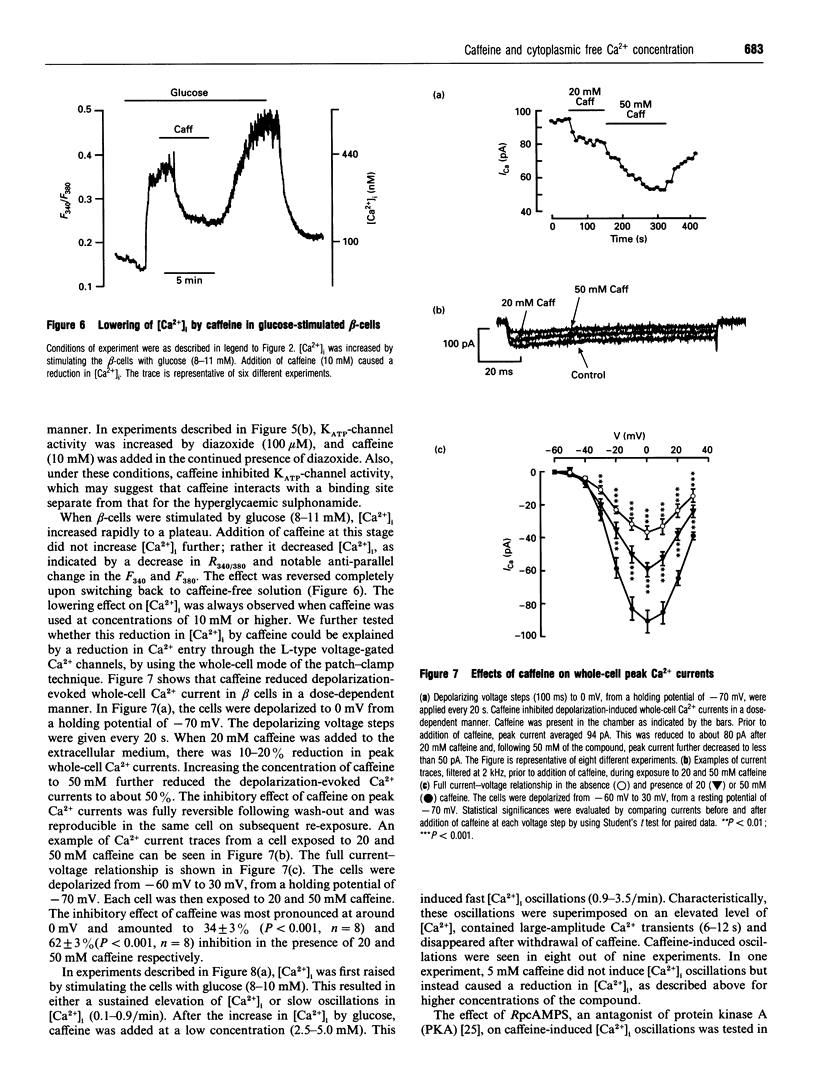
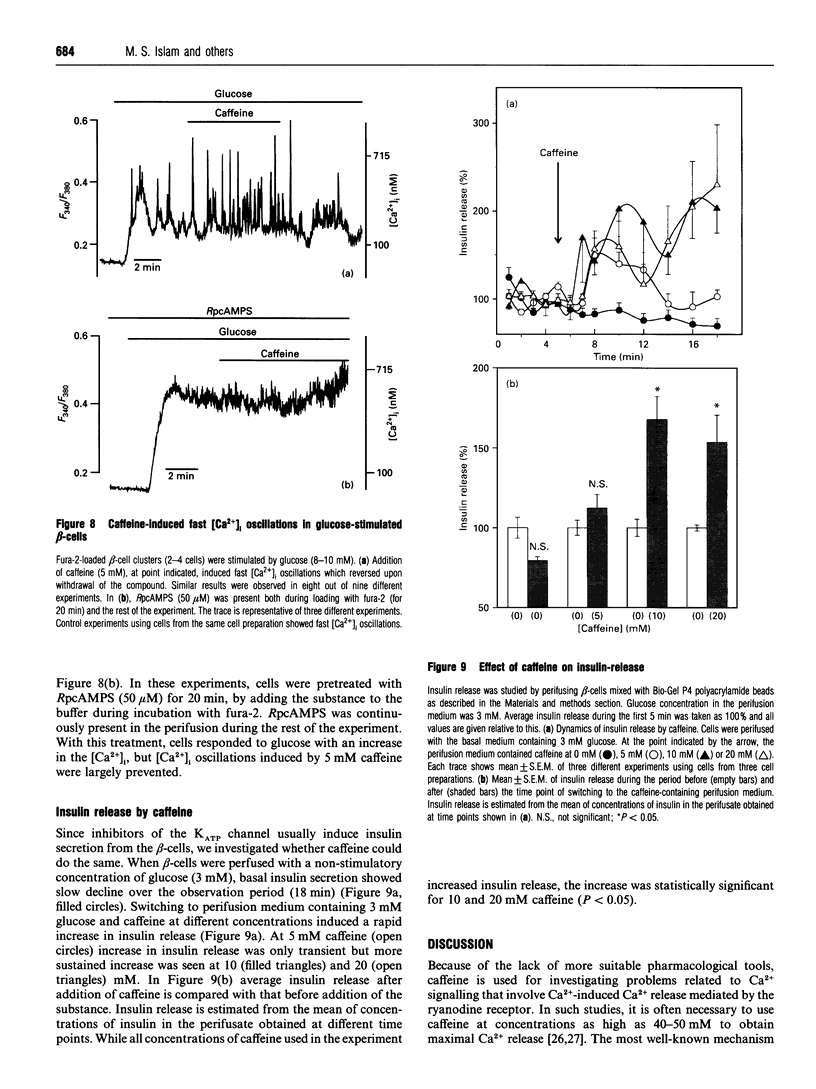
In the pancreatic beta-cell, an increase in the cytoplasmic free Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) by caffeine is believed to indicate mobilization of Ca2+ from intracellular stores, through activation of a ryanodine receptor-like channel. It is not known whether other mechanisms, as well, underlie caffeine-induced changes in [Ca2+]i. We studied the effects of caffeine on [Ca2+]i by using dual-wavelength excitation microfluorimetry in fura-2-loaded beta-cells. In the presence of a non-stimulatory concentration of glucose, caffeine (10-50 mM) consistently increased [Ca2+]i. The effect was completely blocked by omission of extracellular Ca2+ and by blockers of the L-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channel, such as D-600 or nifedipine. Depletion of agonist-sensitive intracellular Ca2+ pools by thapsigargin did not inhibit the stimulatory effect of caffeine on [Ca2+]i. Moreover, this effect of caffeine was not due to an increase in cyclic AMP, since forskolin and 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX) failed to raise [Ca2+]i in unstimulated beta-cells. In beta-cells, glucose and sulphonylureas increase [Ca2+]i by causing closure of ATP-sensitive K+ channels (KATP channels). Caffeine also caused inhibition of KATP channel activity, as measured in excised inside-out patches. Accordingly, caffeine (> 10 mM) induced insulin release from beta-cells in the presence of a non-stimulatory concentration of glucose (3 mM). Hence, membrane depolarization and opening of voltage-gated L-type Ca2+ channels were the underlying mechanisms whereby the xanthine drug increased [Ca2+]i and induced insulin release. Paradoxically, in glucose-stimulated beta-cells, caffeine (> 10 mM) lowered [Ca2+]i. This effect was due to the fact that caffeine reduced depolarization-induced whole-cell Ca2+ current through the L-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channel in a dose-dependent manner. Lower concentrations of caffeine (2.5-5.0 mM), when added after glucose-stimulated increase in [Ca2+]i, induced fast oscillations in [Ca2+]i. The latter effect was likely to be attributable to the cyclic AMP-elevating action of caffeine, leading to phosphorylation of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Hence, in beta-cells, caffeine-induced changes in [Ca2+]i are not due to any interaction with intracellular Ca2+ pools. In these cells, a direct interference with KATP channel- and L-type voltage-gated Ca(2+)-channel activity is the underlying mechanism by which caffeine increases or decreases [Ca2+]i.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammälä C., Ashcroft F. M., Rorsman P. Calcium-independent potentiation of insulin release by cyclic AMP in single beta-cells. Nature. 1993 May 27;363(6427):356–358. doi: 10.1038/363356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammälä C., Larsson O., Berggren P. O., Bokvist K., Juntti-Berggren L., Kindmark H., Rorsman P. Inositol trisphosphate-dependent periodic activation of a Ca(2+)-activated K+ conductance in glucose-stimulated pancreatic beta-cells. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):849–852. doi: 10.1038/353849a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arkhammar P., Nilsson T., Rorsman P., Berggren P. O. Inhibition of ATP-regulated K+ channels precedes depolarization-induced increase in cytoplasmic free Ca2+ concentration in pancreatic beta-cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5448–5454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Harrison D. E., Ashcroft S. J. Glucose induces closure of single potassium channels in isolated rat pancreatic beta-cells. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):446–448. doi: 10.1038/312446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Weerasinghe L. C., Bassett J. M., Randle P. J. The pentose cycle and insulin release in mouse pancreatic islets. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(3):525–532. doi: 10.1042/bj1260525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTCHER R. W., SUTHERLAND E. W. Adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in biological materials. I. Purification and properties of cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase and use of this enzyme to characterize adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in human urine. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1244–1250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berggren P. O., Arkhammar P., Islam M. S., Juntti-Berggren L., Khan A., Kindmark H., Köhler M., Larsson K., Larsson O., Nilsson T. Regulation of cytoplasmic free Ca2+ in insulin-secreting cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1993;334:25–45. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-2910-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheek T. R., Barry V. A., Berridge M. J., Missiaen L. Bovine adrenal chromaffin cells contain an inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-insensitive but caffeine-sensitive Ca2+ store that can be regulated by intraluminal free Ca2+. Biochem J. 1991 May 1;275(Pt 3):697–701. doi: 10.1042/bj2750697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehlinger-Kremer M., Zeuzem S., Schulz I. Interaction of caffeine-, IP3- and vanadate-sensitive Ca2+ pools in acinar cells of the exocrine pancreas. J Membr Biol. 1991 Jan;119(1):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF01868543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J., Petersen O. H. Intracellular ADP activates K+ channels that are inhibited by ATP in an insulin-secreting cell line. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 10;208(1):59–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81532-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M. Calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jan;57(1):71–108. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flockerzi V., Oeken H. J., Hofmann F., Pelzer D., Cavalié A., Trautwein W. Purified dihydropyridine-binding site from skeletal muscle t-tubules is a functional calcium channel. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):66–68. doi: 10.1038/323066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foskett J. K., Wong D. Free cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration oscillations in thapsigargin-treated parotid acinar cells are caffeine- and ryanodine-sensitive. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14535–14538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannini G., Clementi E., Ceci R., Marziali G., Sorrentino V. Expression of a ryanodine receptor-Ca2+ channel that is regulated by TGF-beta. Science. 1992 Jul 3;257(5066):91–94. doi: 10.1126/science.1320290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant A. M., Christie M. R., Ashcroft S. J. Insulin release from human pancreatic islets in vitro. Diabetologia. 1980 Aug;19(2):114–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00421856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. Metabolic control of potassium permeability in pancreatic islet cells. Biochem J. 1980 Feb 15;186(2):541–550. doi: 10.1042/bj1860541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Schmeer W., Meissner H. P. Forskolin, an activator of adenylate cyclase, increases CA2+-dependent electrical activity induced by glucose in mouse pancreatic B cells. Endocrinology. 1983 Jun;112(6):2218–2220. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-6-2218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herchuelz A., Lebrun P. A role for Na/Ca exchange in the pancreatic B cell. Studies with thapsigargin and caffeine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Jan 7;45(1):7–11. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90370-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M. Biphasic Ca2+ dependence of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca release in smooth muscle cells of the guinea pig taenia caeci. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Jun;95(6):1103–1122. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.6.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Islam M. S., Berggren P. O., Larsson O. Sulfhydryl oxidation induces rapid and reversible closure of the ATP-regulated K+ channel in the pancreatic beta-cell. FEBS Lett. 1993 Mar 15;319(1-2):128–132. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80051-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Islam M. S., Berggren P. O. Mobilization of Ca2+ by thapsigargin and 2,5-di-(t-butyl)-1,4-benzohydroquinone in permeabilized insulin-secreting RINm5F cells: evidence for separate uptake and release compartments in inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive Ca2+ pool. Biochem J. 1993 Jul 15;293(Pt 2):423–429. doi: 10.1042/bj2930423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Islam M. S., Larsson O., Berggren P. O. Cyclic ADP-ribose in beta cells. Science. 1993 Oct 22;262(5133):584–586. doi: 10.1126/science.8211188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Islam M. S., Rorsman P., Berggren P. O. Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ release in insulin-secreting cells. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jan 27;296(3):287–291. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80306-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscombe D., Madison D. V., Poenie M., Reuter H., Tsien R. W., Tsien R. Y. Imaging of cytosolic Ca2+ transients arising from Ca2+ stores and Ca2+ channels in sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1988 Jul;1(5):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90185-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin C., Dacquet C., Mironneau C., Mironneau J. Caffeine-induced inhibition of calcium channel current in cultured smooth cells from pregnant rat myometrium. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;98(2):493–498. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12622.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mészáros L. G., Bak J., Chu A. Cyclic ADP-ribose as an endogenous regulator of the non-skeletal type ryanodine receptor Ca2+ channel. Nature. 1993 Jul 1;364(6432):76–79. doi: 10.1038/364076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Arkhammar P., Berggren P. O. Dual effect of glucose on cytoplasmic free Ca2+ concentration and insulin release reflects the beta-cell being deprived of fuel. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 30;153(3):984–991. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81325-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Arkhammar P., Hallberg A., Hellman B., Berggren P. O. Characterization of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ release in pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 1;248(2):329–336. doi: 10.1042/bj2480329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Glennon M. C., Geschwind J. F., Matschinsky F. M., Corkey B. E. Cyclic AMP raises cytosolic Ca2+ and promotes Ca2+ influx in a clonal pancreatic beta-cell line (HIT T-15). FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 10;220(1):103–107. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80884-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roe M. W., Lancaster M. E., Mertz R. J., Worley J. F., 3rd, Dukes I. D. Voltage-dependent intracellular calcium release from mouse islets stimulated by glucose. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):9953–9956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Abrahamsson H. Cyclic AMP potentiates glucose-induced insulin release from mouse pancreatic islets without increasing cytosolic free Ca2+. Acta Physiol Scand. 1985 Dec;125(4):639–647. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1985.tb07766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothermel J. D., Parker Botelho L. H. A mechanistic and kinetic analysis of the interactions of the diastereoisomers of adenosine 3',5'-(cyclic)phosphorothioate with purified cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochem J. 1988 May 1;251(3):757–762. doi: 10.1042/bj2510757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau E., Meissner G. Single cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-release channel: activation by caffeine. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 2):H328–H333. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.256.2.H328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sculptoreanu A., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. Voltage-dependent potentiation of L-type Ca2+ channels due to phosphorylation by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Nature. 1993 Jul 15;364(6434):240–243. doi: 10.1038/364240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakui M., Osipchuk Y. V., Petersen O. H. Receptor-activated cytoplasmic Ca2+ spiking mediated by inositol trisphosphate is due to Ca2(+)-induced Ca2+ release. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90505-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weik R., Neumcke B. ATP-sensitive potassium channels in adult mouse skeletal muscle: characterization of the ATP-binding site. J Membr Biol. 1989 Sep;110(3):217–226. doi: 10.1007/BF01869152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Ullrich S., Pozzan T. Glyceraldehyde, but not cyclic AMP-stimulated insulin release is preceded by a rise in cytosolic free Ca2+. FEBS Lett. 1984 Nov 5;177(1):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80972-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazawa T., Iino M., Endo M. Presence of functionally different compartments of the Ca2+ store in single intestinal smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1992 Apr 20;301(2):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81243-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacchetti D., Clementi E., Fasolato C., Lorenzon P., Zottini M., Grohovaz F., Fumagalli G., Pozzan T., Meldolesi J. Intracellular Ca2+ pools in PC12 cells. A unique, rapidly exchanging pool is sensitive to both inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and caffeine-ryanodine. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20152–20158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zholos A. V., Baidan L. V., Shuba M. F. The inhibitory action of caffeine on calcium currents in isolated intestinal smooth muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 1991 Oct;419(3-4):267–273. doi: 10.1007/BF00371106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]