Abstract
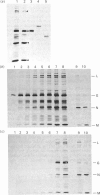
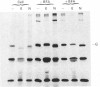
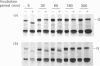
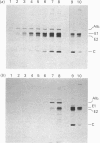
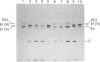
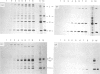
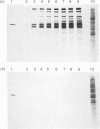
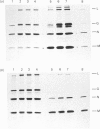
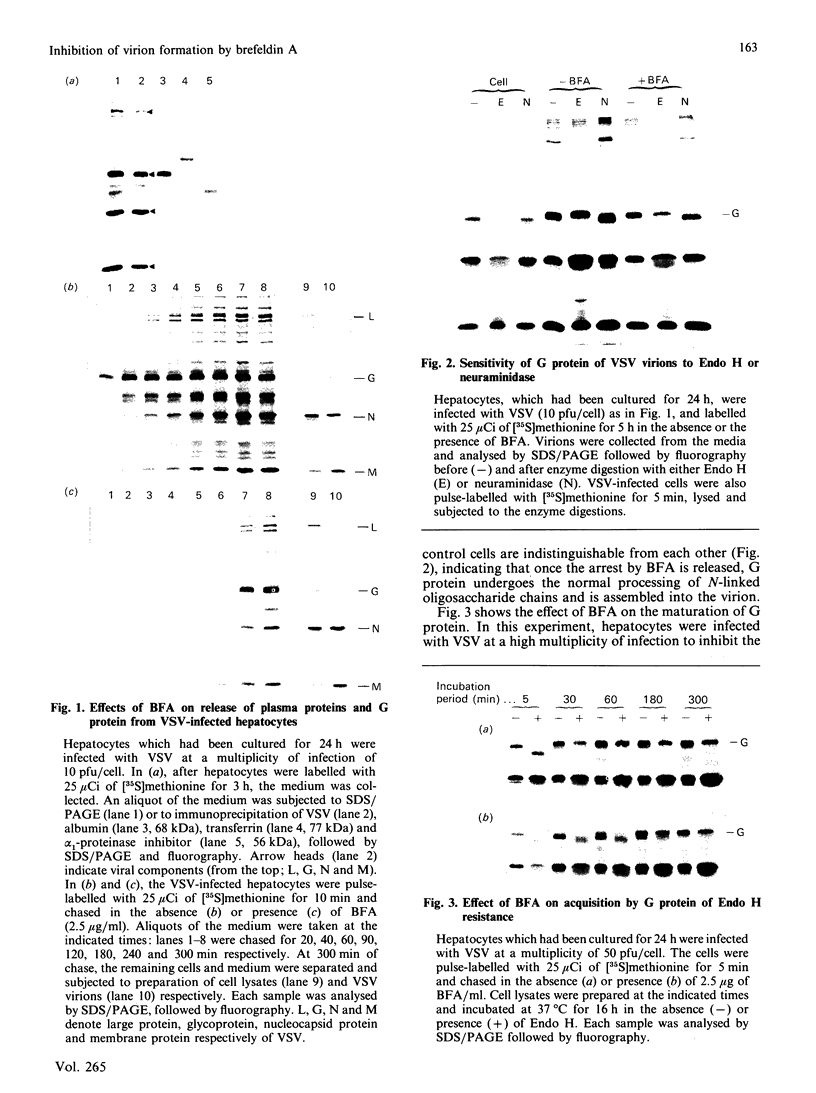
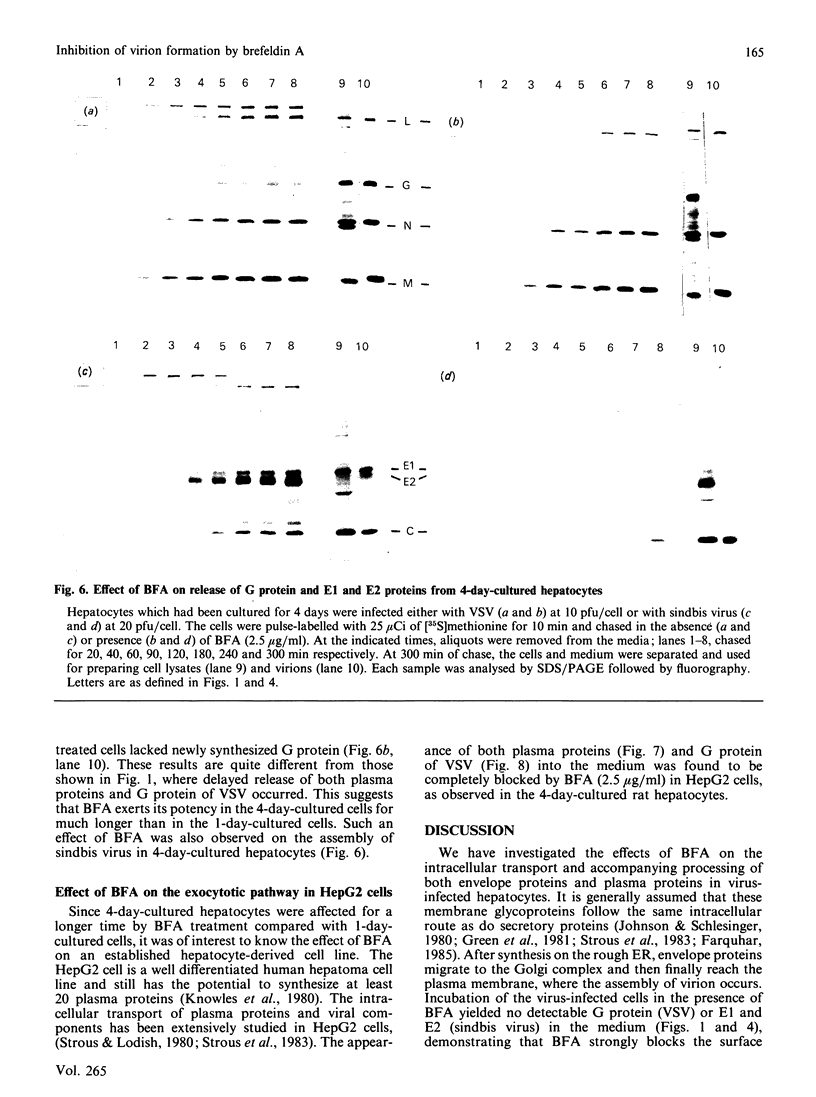
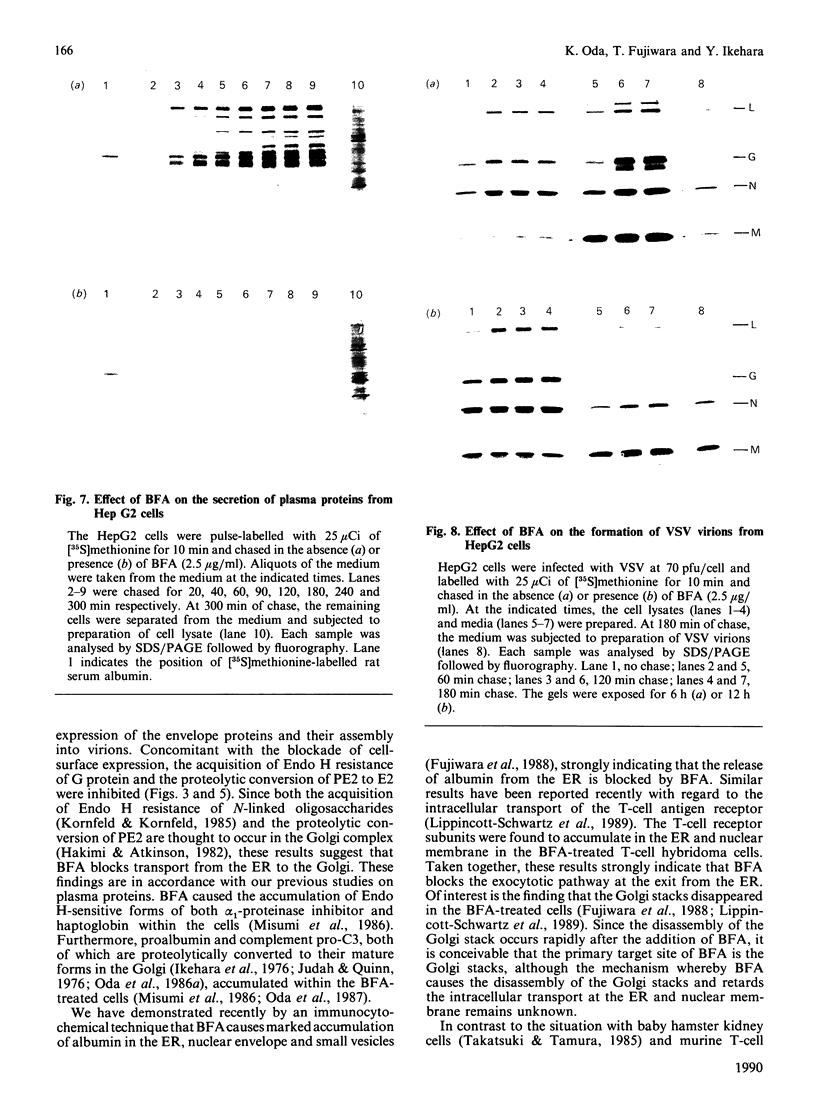
We have studied the effect of brefeldin A (BFA) on the intracellular transport of the envelope proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) and sindbis virus in primary cultured rat hepatocytes. BFA (2.5 micrograms/ml) inhibited not only the secretion of plasma proteins into the medium, but also the assembly of both G protein of VSV and E1 and E2 proteins (envelope proteins) of sindbis virus into respective virions. Concomitantly, both the acquisition of endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H resistance by the G protein and the proteolytic conversion of PE2 to E2 were found to be inhibited in the BFA-treated cells, suggesting that the intracellular transport of the envelope proteins was arrested in the endoplasmic reticulum. Such inhibitory effects of the drug were variable depending upon the culture conditions of the hepatocytes. In the 1-day-cultured cells, even in the presence of the drug, newly synthesized envelope proteins were assembled into the virions after a 3 h chase period, at the same time as secretion of plasma proteins into the medium resumes. In contrast, in 4-day-cultured hepatocytes, BFA continuously blocked the entry of the envelope proteins into the virions and the release of plasma proteins into the medium for at least 5 h. BFA also completely inhibited the exocytotic pathway in HepG2 cells. These results indicate that the duration time of the effect of BFA is different from one cell to another and may change depending upon the culture conditions of the cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Farquhar M. G. Progress in unraveling pathways of Golgi traffic. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:447–488. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Oda K., Yokota S., Takatsuki A., Ikehara Y. Brefeldin A causes disassembly of the Golgi complex and accumulation of secretory proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18545–18552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J., Griffiths G., Louvard D., Quinn P., Warren G. Passage of viral membrane proteins through the Golgi complex. J Mol Biol. 1981 Nov 15;152(4):663–698. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90122-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakimi J., Atkinson P. H. Glycosylation of intracellular Sindbis virus glycoproteins. Biochemistry. 1982 Apr 27;21(9):2140–2145. doi: 10.1021/bi00538a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikehara Y., Miyasato M., Ogata S., Oda K. Multiple forms of rat-serum alpha 1-protease inhibitor. Involvement of sialic acid in the multiplicity of three original forms. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(2):253–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05231.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikehara Y., Oda K., Kato K. An improved method for the purification of rat serum albumin: removal of contaminants by concanavalin A-Sepharose. J Biochem. 1977 May;81(5):1293–1297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikehara Y., Oda K., Kato K. Conversion of proalbumin into serum albumin in the secretory vesicles of rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Sep 7;72(1):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90996-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Schlesinger M. J. Vesicular stomatitis virus and sindbis virus glycoprotein transport to the cell surface is inhibited by ionophores. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):407–424. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Howe C. C., Aden D. P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.6248960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano M., Tabuki T., Akiyama S., Mifune K., Takatsuki A., Tamura G., Ikehara Y. Isolation and characterization of Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants with altered sensitivity to high doses of tunicamycin. Somatic Cell Genet. 1981 Sep;7(5):507–521. doi: 10.1007/BF01549655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Yuan L. C., Bonifacino J. S., Klausner R. D. Rapid redistribution of Golgi proteins into the ER in cells treated with brefeldin A: evidence for membrane cycling from Golgi to ER. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):801–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90685-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misumi Y., Misumi Y., Miki K., Takatsuki A., Tamura G., Ikehara Y. Novel blockade by brefeldin A of intracellular transport of secretory proteins in cultured rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11398–11403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda K., Hirose S., Takami N., Misumi Y., Takatsuki A., Ikehara Y. Brefeldin A arrests the intracellular transport of a precursor of complement C3 before its conversion site in rat hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1987 Apr 6;214(1):135–138. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda K., Koriyama Y., Yamada E., Ikehara Y. Effects of weakly basic amines on proteolytic processing and terminal glycosylation of secretory proteins in cultured rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):739–745. doi: 10.1042/bj2400739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda K., Miki K., Hirose S., Takami N., Misumi Y., Ikehara Y. Immunoblotting analysis of plasma protein processing in the secretory pathway of rat liver: identification of proteolytic conversion sites of complement pro-C3 and prohaptoglobin. J Biochem. 1986 Dec;100(6):1669–1675. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda K., Misumi Y., Ikehara Y. Disparate effects of monensin and colchicine on intracellular processing of secretory proteins in cultured rat hepatocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Sep 15;135(2):209–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07639.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda K., Ogata S., Koriyama Y., Yamada E., Mifune K., Ikehara Y. Tris inhibits both proteolytic and oligosaccharide processing occurring in the Golgi complex in primary cultured rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12576–12583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Preparation of isolated rat liver cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1976;13:29–83. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61797-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strous G. J., Lodish H. F. Intracellular transport of secretory and membrane proteins in hepatoma cells infected by vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90547-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strous G. J., Willemsen R., van Kerkhof P., Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Lodish H. F. Vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein, albumin, and transferrin are transported to the cell surface via the same Golgi vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1815–1822. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takami N., Ogata S., Oda K., Misumi Y., Ikehara Y. Biosynthesis of placental alkaline phosphatase and its post-translational modification by glycophospholipid for membrane-anchoring. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):3016–3021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura G., Ando K., Suzuki S., Takatsuki A., Arima K. Antiviral activity of brefeldin A and verrucarin A. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Feb;21(2):160–161. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]