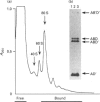
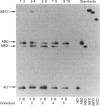
Abstract
Transcripts of human SP-A genes, SP-A1 and SP-A2, undergo alternative splicing of 5' untranslated-region exons. We reverse-transcribed and amplified free cytoplasmic and polysome-bound RNA and showed that (a) all splice variants of both genes are translated in vivo, (b) the relative translatability of splice variants can differ among individuals, and (c) the relative levels of different SP-A splice variants differ among individuals.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dobbs L. G., Wright J. R., Hawgood S., Gonzalez R., Venstrom K., Nellenbogen J. Pulmonary surfactant and its components inhibit secretion of phosphatidylcholine from cultured rat alveolar type II cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1010–1014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floros J., Karinch A. M. Human SP-A: then and now. Am J Physiol. 1995 Feb;268(2 Pt 1):L162–L165. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1995.268.2.L162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floros J., Phelps D. S., Harding H. P., Church S., Ware J. Postnatal stimulation of rat surfactant protein A synthesis by dexamethasone. Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 1):L137–L143. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1989.257.2.L137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floros J., Steinbrink R., Jacobs K., Phelps D., Kriz R., Recny M., Sultzman L., Jones S., Taeusch H. W., Frank H. A. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for the 35-kDa pulmonary surfactant-associated protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):9029–9033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foyt H. L., Lanau F., Woloschak M., LeRoith D., Roberts C. T., Jr Effect of growth hormone on levels of differentially processed insulin-like growth factor I mRNAs in total and polysomal mRNA populations. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Nov;6(11):1881–1888. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.11.1282673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foyt H. L., LeRoith D., Roberts C. T., Jr Differential association of insulin-like growth factor I mRNA variants with polysomes in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):7300–7305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory T. J., Longmore W. J., Moxley M. A., Whitsett J. A., Reed C. R., Fowler A. A., 3rd, Hudson L. D., Maunder R. J., Crim C., Hyers T. M. Surfactant chemical composition and biophysical activity in acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1991 Dec;88(6):1976–1981. doi: 10.1172/JCI115523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallman M., Merritt T. A., Akino T., Bry K. Surfactant protein A, phosphatidylcholine, and surfactant inhibitors in epithelial lining fluid. Correlation with surface activity, severity of respiratory distress syndrome, and outcome in small premature infants. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Dec;144(6):1376–1384. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/144.6.1376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karinch A. M., Floros J. 5' splicing and allelic variants of the human pulmonary surfactant protein A genes. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1995 Jan;12(1):77–88. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.12.1.7811473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katyal S. L., Amenta J. S., Singh G., Silverman J. A. Deficient lung surfactant apoproteins in amniotic fluid with mature phospholipid profile from diabetic pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1984 Jan 1;148(1):48–53. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(84)80031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katyal S. L., Singh G., Locker J. Characterization of a second human pulmonary surfactant-associated protein SP-A gene. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1992 Apr;6(4):446–452. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/6.4.446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Simon D., Horowitz P. M. Aspects of secondary and quaternary structure of surfactant protein A from canine lung. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 20;1001(3):294–301. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krizkova L., Sakthivel R., Olowe S. A., Rogan P. K., Floros J. Human SP-A: genotype and single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis. Am J Physiol. 1994 May;266(5 Pt 1):L519–L527. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1994.266.5.L519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. F., Jobe A. H. Surfactant and the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Jan;147(1):218–233. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/147.1.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick S. M., Boggaram V., Mendelson C. R. Characterization of mRNA transcripts and organization of human SP-A1 and SP-A2 genes. Am J Physiol. 1994 Apr;266(4 Pt 1):L354–L366. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1994.266.4.L354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick S. M., Mendelson C. R. Human SP-A1 and SP-A2 genes are differentially regulated during development and by cAMP and glucocorticoids. Am J Physiol. 1994 Apr;266(4 Pt 1):L367–L374. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1994.266.4.L367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moya F. R., Montes H. F., Thomas V. L., Mouzinho A. M., Smith J. F., Rosenfeld C. R. Surfactant protein A and saturated phosphatidylcholine in respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Dec;150(6 Pt 1):1672–1677. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.150.6.7952631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B. Structure/function relationships in the collectins (mammalian lectins containing collagen-like regions). Biochem Soc Trans. 1993 May;21(2):464–468. doi: 10.1042/bst0210464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rishi A., Hatzis D., McAlmon K., Floros J. An allelic variant of the 6A gene for human surfactant protein A. Am J Physiol. 1992 May;262(5 Pt 1):L566–L573. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.262.5.L566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAEHELIN T., WETTSTEIN F. O., OURA H., NOLL H. DETERMINATION OF THE CODING RATIO BASED ON MOLECULAR WEIGHT OF MESSENGER RIBONUCLEIC ACID ASSOCIATED WITH ERGOSOMES OF DIFFERENT AGGREGATE SIZE. Nature. 1964 Jan 18;201:264–270. doi: 10.1038/201264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Fujita Y., Kogishi K. Reconstitution of tubular myelin from synthetic lipids and proteins associated with pig pulmonary surfactant. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Jul;140(1):75–81. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vary T. C., Jurasinski C. V., Karinch A. M., Kimball S. R. Regulation of eukaryotic initiation factor-2 expression during sepsis. Am J Physiol. 1994 Feb;266(2 Pt 1):E193–E201. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1994.266.2.E193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss T., Melchers K., Scheirle G., Schäfer K. P. Structural comparison of recombinant pulmonary surfactant protein SP-A derived from two human coding sequences: implications for the chain composition of natural human SP-A. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Jan;4(1):88–94. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/4.1.88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. T., Damm D., Miller J., Spratt K., Schilling J., Hawgood S., Benson B., Cordell B. Isolation and characterization of the human pulmonary surfactant apoprotein gene. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):361–363. doi: 10.1038/317361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. C., Hawgood S., Hamilton R. L. Changes in lipid structure produced by surfactant proteins SP-A, SP-B, and SP-C. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Jul;5(1):41–50. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deMello D. E., Heyman S., Phelps D. S., Floros J. Immunogold localization of SP-A in lungs of infants dying from respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1993 May;142(5):1631–1640. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]