Abstract
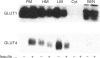
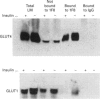
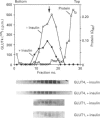
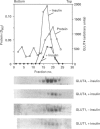
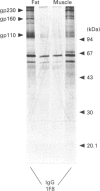
Insulin-sensitive tissues (fat and muscle) express a specific isoform of glucose-transporter protein, GLUT4, which normally resides in intracellular vesicular structures and is translocated to the cell surface in response to insulin. Here we provide a biochemical comparison of GLUT4-containing structures from fat and muscle cells. We demonstrate that, in spite of totally different protocols for cell homogenization and fractionation used for adipocytes as compared with skeletal-muscle tissue, GLUT4-containing vesicles from both sources have identical buoyant densities, sedimentation coefficients, and a very similar, if not identical, protein composition. The individual proteins first identified in GLUT4-containing vesicles from adipocytes (GTV3/SCAMPs proteins and aminopeptidase gp160) are also present in the analogous vesicles from muscle. Intracellular microsomes from rat adipocytes also contain GLUT1, a ubiquitously expressed glucose-transporter isoform. GLUT1 has not been detected in intracellular vesicular pool(s) from skeletal-muscle cells, probably because of its low abundance there. GLUT1 in adipocytes is excluded from GLUT4-containing vesicles, but is found in membrane structures which are indistinguishable from the former by all methods tested and demonstrate the same type of regulation by insulin. That is, the GLUT1- and GLUT4-containing vesicles have identical densities and sedimentation coefficients in sucrose gradients, and translocate to the cell surface in response to hormonal exposure. Also, we describe a simple procedure for the purification of native glucose-transporter vesicles from rat adipocytes. Overall, our data suggest the existence of a unique endosomal compartment in fat and muscle cells which is functionally and compositionally different from other microsomal vesicles and which is responsible for insulin-sensitive glucose transport in these tissues.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett M. K., Scheller R. H. The molecular machinery for secretion is conserved from yeast to neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2559–2563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J. The insulin-sensitive glucose transporter. Int Rev Cytol. 1992;137:239–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. J., Gould G. W., Davies A., Baldwin S. A., Lienhard G. E., Gibbs E. M. Characterization of vesicles containing insulin-responsive intracellular glucose transporters isolated from 3T3-L1 adipocytes by an improved procedure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Oct 7;971(3):339–350. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90150-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain C. C., Trimble W. S., Lienhard G. E. Members of the VAMP family of synaptic vesicle proteins are components of glucose transporter-containing vesicles from rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11681–11684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P., Buxton J. M. Insulin action on the internalization of the GLUT4 glucose transporter in isolated rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9187–9190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Jacot E., Jequier E., Maeder E., Wahren J., Felber J. P. The effect of insulin on the disposal of intravenous glucose. Results from indirect calorimetry and hepatic and femoral venous catheterization. Diabetes. 1981 Dec;30(12):1000–1007. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.12.1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J. E., Dudek R. W., Whitehead D. S., Downes D. L., Frisell W. R., Caro J. F., Dohm G. L. Immunolocalization of glucose transporter GLUT4 within human skeletal muscle. Diabetes. 1991 Jan;40(1):150–154. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.1.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haney P. M., Slot J. W., Piper R. C., James D. E., Mueckler M. Intracellular targeting of the insulin-regulatable glucose transporter (GLUT4) is isoform specific and independent of cell type. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(4):689–699. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.4.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris H. W., Jr, Strange K., Zeidel M. L. Current understanding of the cellular biology and molecular structure of the antidiuretic hormone-stimulated water transport pathway. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):1–8. doi: 10.1172/JCI115263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirshman M. F., Goodyear L. J., Wardzala L. J., Horton E. D., Horton E. S. Identification of an intracellular pool of glucose transporters from basal and insulin-stimulated rat skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):987–991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman G. D., Kozka I. J., Clark A. E., Flower C. J., Saltis J., Habberfield A. D., Simpson I. A., Cushman S. W. Cell surface labeling of glucose transporter isoform GLUT4 by bis-mannose photolabel. Correlation with stimulation of glucose transport in rat adipose cells by insulin and phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18172–18179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Brown R., Navarro J., Pilch P. F. Insulin-regulatable tissues express a unique insulin-sensitive glucose transport protein. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):183–185. doi: 10.1038/333183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Jenkins A. B., Kraegen E. W. Heterogeneity of insulin action in individual muscles in vivo: euglycemic clamp studies in rats. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):E567–E574. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.5.E567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Lederman L., Pilch P. F. Purification of insulin-dependent exocytic vesicles containing the glucose transporter. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11817–11824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jhun B. H., Rampal A. L., Liu H., Lachaal M., Jung C. Y. Effects of insulin on steady state kinetics of GLUT4 subcellular distribution in rat adipocytes. Evidence of constitutive GLUT4 recycling. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17710–17715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandror K. V., Yu L., Pilch P. F. The major protein of GLUT4-containing vesicles, gp160, has aminopeptidase activity. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 9;269(49):30777–30780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandror K., Pilch P. F. Identification and isolation of glycoproteins that translocate to the cell surface from GLUT4-enriched vesicles in an insulin-dependent fashion. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):138–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Ramlal T., Young D. A., Holloszy J. O. Insulin-induced translocation of glucose transporters in rat hindlimb muscles. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 16;224(1):224–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80452-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraegen E. W., James D. E., Jenkins A. B., Chisholm D. J. Dose-response curves for in vivo insulin sensitivity in individual tissues in rats. Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 1):E353–E362. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.3.E353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie S. M., Cain C. C., Lienhard G. E., Castle J. D. The glucose transporter GluT4 and secretory carrier membrane proteins (SCAMPs) colocalize in rat adipocytes and partially segregate during insulin stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):19110–19117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marette A., Burdett E., Douen A., Vranic M., Klip A. Insulin induces the translocation of GLUT4 from a unique intracellular organelle to transverse tubules in rat skeletal muscle. Diabetes. 1992 Dec;41(12):1562–1569. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.12.1562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastick C. C., Aebersold R., Lienhard G. E. Characterization of a major protein in GLUT4 vesicles. Concentration in the vesicles and insulin-stimulated translocation to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 25;269(8):6089–6092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka Y., Asano T., Shibasaki Y., Kasuga M., Kanazawa Y., Takaku F. Studies with antipeptide antibody suggest the presence of at least two types of glucose transporter in rat brain and adipocyte. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13432–13439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M., SCOW R. O., CHERNICK S. S. REMOVAL AND METABOLISM OF TRIGLYCERIDES BY PERFUSED LIVER. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:385–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson L. J., James D. E. Insulin-regulated sorting of glucose transporters in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Am J Physiol. 1992 Aug;263(2 Pt 1):E383–E393. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1992.263.2.E383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodnick K. J., Slot J. W., Studelska D. R., Hanpeter D. E., Robinson L. J., Geuze H. J., James D. E. Immunocytochemical and biochemical studies of GLUT4 in rat skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6278–6285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Orci L. Molecular dissection of the secretory pathway. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):409–415. doi: 10.1038/355409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh S., Nishimura H., Clark A. E., Kozka I. J., Vannucci S. J., Simpson I. A., Quon M. J., Cushman S. W., Holman G. D. Use of bismannose photolabel to elucidate insulin-regulated GLUT4 subcellular trafficking kinetics in rat adipose cells. Evidence that exocytosis is a critical site of hormone action. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):17820–17829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd P. R., Gnudi L., Tozzo E., Yang H., Leach F., Kahn B. B. Adipose cell hyperplasia and enhanced glucose disposal in transgenic mice overexpressing GLUT4 selectively in adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22243–22246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Cushman S. W. Hormonal regulation of mammalian glucose transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1059–1089. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Yver D. R., Hissin P. J., Wardzala L. J., Karnieli E., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. Insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transporters in the isolated rat adipose cells: characterization of subcellular fractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 19;763(4):393–407. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(83)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha M. K., Raineri-Maldonado C., Buchanan C., Pories W. J., Carter-Su C., Pilch P. F., Caro J. F. Adipose tissue glucose transporters in NIDDM. Decreased levels of muscle/fat isoform. Diabetes. 1991 Apr;40(4):472–477. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.4.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Gigengack S., James D. E., Lienhard G. E. Translocation of the glucose transporter GLUT4 in cardiac myocytes of the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7815–7819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Gigengack S., Lienhard G. E., James D. E. Immuno-localization of the insulin regulatable glucose transporter in brown adipose tissue of the rat. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(1):123–135. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. M., Charron M. J., Shah N., Lodish H. F., Jarett L. Immunoelectron microscopic demonstration of insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transporters to the plasma membrane of isolated rat adipocytes and masking of the carboxyl-terminal epitope of intracellular GLUT4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6893–6897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söllner T., Whiteheart S. W., Brunner M., Erdjument-Bromage H., Geromanos S., Tempst P., Rothman J. E. SNAP receptors implicated in vesicle targeting and fusion. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):318–324. doi: 10.1038/362318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoidis G., Kotliar N., Pilch P. F. Immunological analysis of GLUT4-enriched vesicles. Identification of novel proteins regulated by insulin and diabetes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11691–11696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Clark A. E., Harrison R., Kozka I. J., Holman G. D. Trafficking of glucose transporters in 3T3-L1 cells. Inhibition of trafficking by phenylarsine oxide implicates a slow dissociation of transporters from trafficking proteins. Biochem J. 1992 Feb 1;281(Pt 3):809–817. doi: 10.1042/bj2810809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Holman G. D. Comparison of GLUT4 and GLUT1 subcellular trafficking in basal and insulin-stimulated 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):4600–4603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzano A., Wilkinson W., Kotliar N., Thoidis G., Wadzinkski B. E., Ruoho A. E., Pilch P. F. Insulin-regulated glucose uptake in rat adipocytes is mediated by two transporter isoforms present in at least two vesicle populations. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12358–12363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]