Abstract
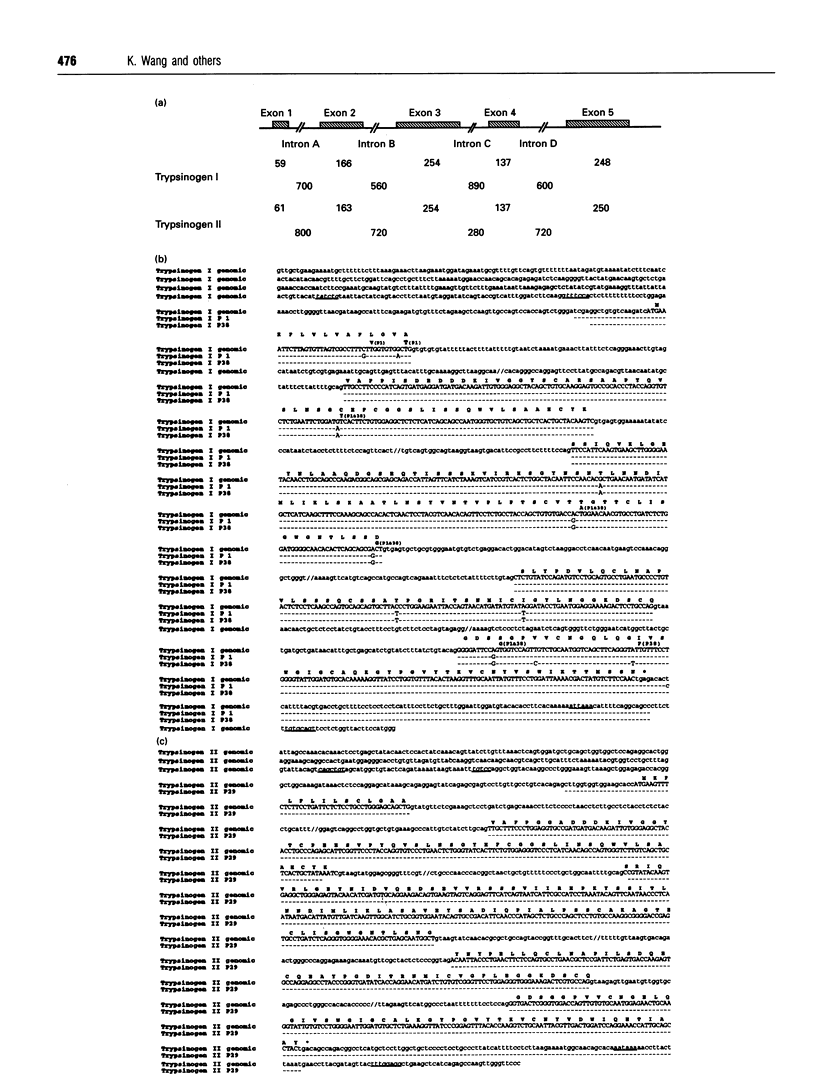
Based on genomic Southern hybridizations and cDNA sequence analyses, the chicken trypsinogen gene family can be divided into two multi-member subfamilies, a six-member trypsinogen I subfamily which encodes the cationic trypsin isoenzymes and a three-member trypsinogen II subfamily which encodes the anionic trypsin isoenzymes. The chicken cDNA and genomic clones containing these two subfamilies were isolated and characterized by DNA sequence analysis. The results indicated that the chicken trypsinogen genes encoded a signal peptide of 15 to 16 amino acid residues, an activation peptide of 9 to 10 residues and a trypsin of 223 amino acid residues. The chicken trypsinogens contain all the common catalytic and structural features for trypsins, including the catalytic triad His, Asp and Ser and the six disulphide bonds. The trypsinogen I and II subfamilies share approximately 70% sequence identity at the nucleotide and amino acid level. The sequence comparison among chicken trypsinogen subfamily members and trypsin sequences from other species suggested that the chicken trypsinogen genes may have evolved in coincidental or concerted fashion.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell G. I., Quinto C., Quiroga M., Valenzuela P., Craik C. S., Rutter W. J. Isolation and sequence of a rat chymotrypsin B gene. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14265–14270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson L. M., McCormack W. T., Postema C. E., Humphries E. H., Thompson C. B. Templated insertions in the rearranged chicken IgL V gene segment arise by intrachromosomal gene conversion. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):536–547. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craik C. S., Choo Q. L., Swift G. H., Quinto C., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Structure of two related rat pancreatic trypsin genes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14255–14264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. P., Hammer R. E., Messing A., MacDonald R. J. Selective expression of trypsin fusion genes in acinar cells of the pancreas and stomach of transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):26070–26077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E. The structures of cytochrome c and the rates of molecular evolution. J Mol Evol. 1971;1(1):26–45. doi: 10.1007/BF01659392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emi M., Nakamura Y., Ogawa M., Yamamoto T., Nishide T., Mori T., Matsubara K. Cloning, characterization and nucleotide sequences of two cDNAs encoding human pancreatic trypsinogens. Gene. 1986;41(2-3):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher T. S., Alhadeff M., Craik C. S., Largman C. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding rat cationic trypsinogen. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 2;26(11):3081–3086. doi: 10.1021/bi00385a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudmundsdóttir A., Gudmundsdóttir E., Oskarsson S., Bjarnason J. B., Eakin A. K., Craik C. S. Isolation and characterization of cDNAs from Atlantic cod encoding two different forms of trypsinogen. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Nov 1;217(3):1091–1097. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18341.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermodson M. A., Ericsson L. H., Neurath H., Walsh K. A. Determination of the amino acid sequence of porcine trypsin by sequenator aalysis. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 14;12(17):3146–3153. doi: 10.1021/bi00741a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Campbell J. H., Elgin S. C. The organization, expression, and evolution of antibody genes and other multigene families. Annu Rev Genet. 1975;9:305–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.09.120175.001513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida Y. Quantification analysis of 5'-splice signal sequences in mRNA precursors. Mutations in 5'-splice signal sequence of human beta-globin gene and beta-thalassemia. J Theor Biol. 1990 Aug 23;145(4):523–533. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(05)80486-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman D. L. The disulphide bridges of trypsin. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):929–932. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80340-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraut J. Serine proteases: structure and mechanism of catalysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:331–358. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.001555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Huerou I., Wicker C., Guilloteau P., Toullec R., Puigserver A. Isolation and nucleotide sequence of cDNA clone for bovine pancreatic anionic trypsinogen. Structural identity within the trypsin family. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 13;193(3):767–773. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19398.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louvard M. N., Puigserver A. On bovine and porcine anionic trypsinogens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 5;371(1):177–185. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütcke H., Rausch U., Vasiloudes P., Scheele G. A., Kern H. F. A fourth trypsinogen (P23) in the rat pancreas induced by CCK. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6736–6736. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. J., Stary S. J., Swift G. H. Two similar but nonallelic rat pancreatic trypsinogens. Nucleotide sequences of the cloned cDNAs. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9724–9732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A., Weinrich S. L., Nelson C., Rutter W. J. The chymotrypsin enhancer core. Specific factor binding and biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20744–20751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinsky S. D., LaForge K. S., Scheele G. Differential regulation of trypsinogen mRNA translation: full-length mRNA sequences encoding two oppositely charged trypsinogen isoenzymes in the dog pancreas. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2669–2676. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y. B., Brown D. D. Developmental and thyroid hormone-dependent regulation of pancreatic genes in Xenopus laevis. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1107–1113. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson B. J., Hagenbüchle O., Wellauer P. K. Sequence organisation and transcriptional regulation of the mouse elastase II and trypsin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8307–8330. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani T., Kawashima I., Mita K., Takiguchi Y. Nucleotide sequence of the human pancreatic trypsinogen III cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 25;18(6):1631–1631. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.6.1631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Ericsson L. H., Neurath H., Walsh K. A. Amino acid sequence of dogfish trypsin. Biochemistry. 1975 Apr 8;14(7):1358–1366. doi: 10.1021/bi00678a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALSH K. A., NEURATH H. TRYPSINOGEN AND CHYMOTRYPSINOGEN AS HOMOLOGOUS PROTEINS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:884–889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K., Klotz J. L., Kiser G., Bristol G., Hays E., Lai E., Gese E., Kronenberg M., Hood L. Organization of the V gene segments in mouse T-cell antigen receptor alpha/delta locus. Genomics. 1994 Apr;20(3):419–428. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. E. Compilation of published signal sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5145–5164. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegand U., Corbach S., Minn A., Kang J., Müller-Hill B. Cloning of the cDNA encoding human brain trypsinogen and characterization of its product. Gene. 1993 Dec 22;136(1-2):167–175. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90460-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer E. A., Martin S. L., Beverley S. M., Kan Y. W., Wilson A. C. Rapid duplication and loss of genes coding for the alpha chains of hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2158–2162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]