Abstract
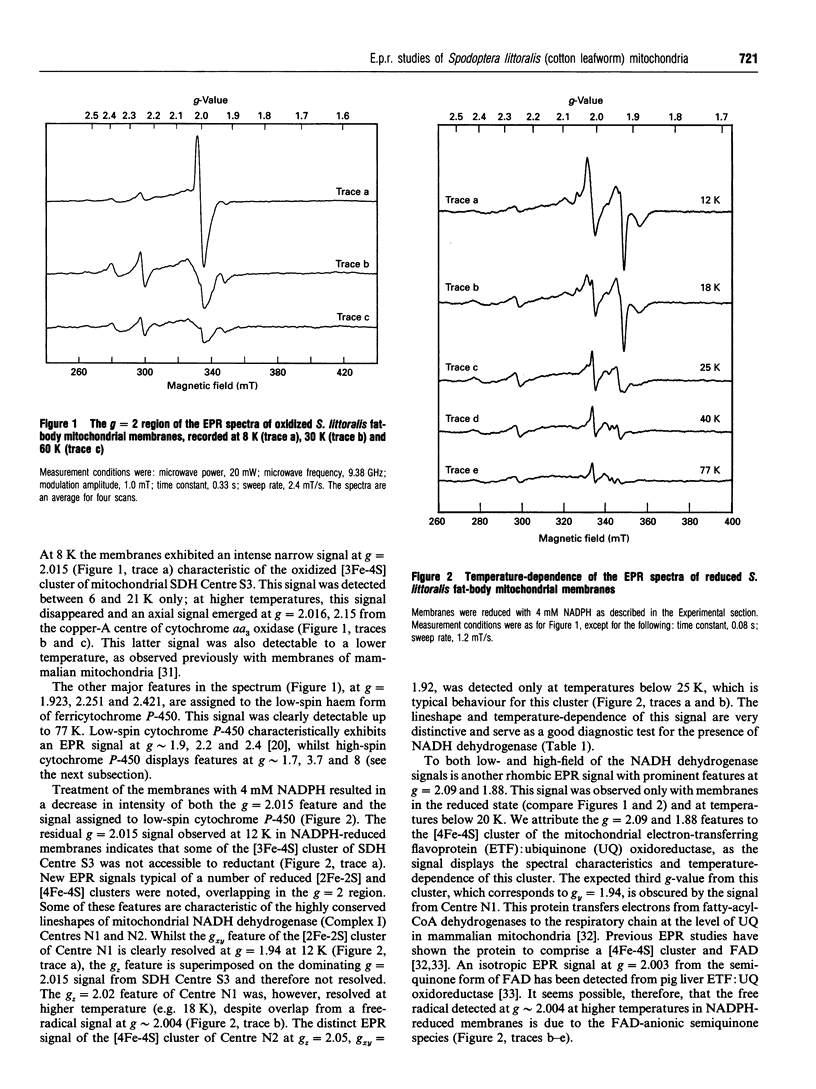
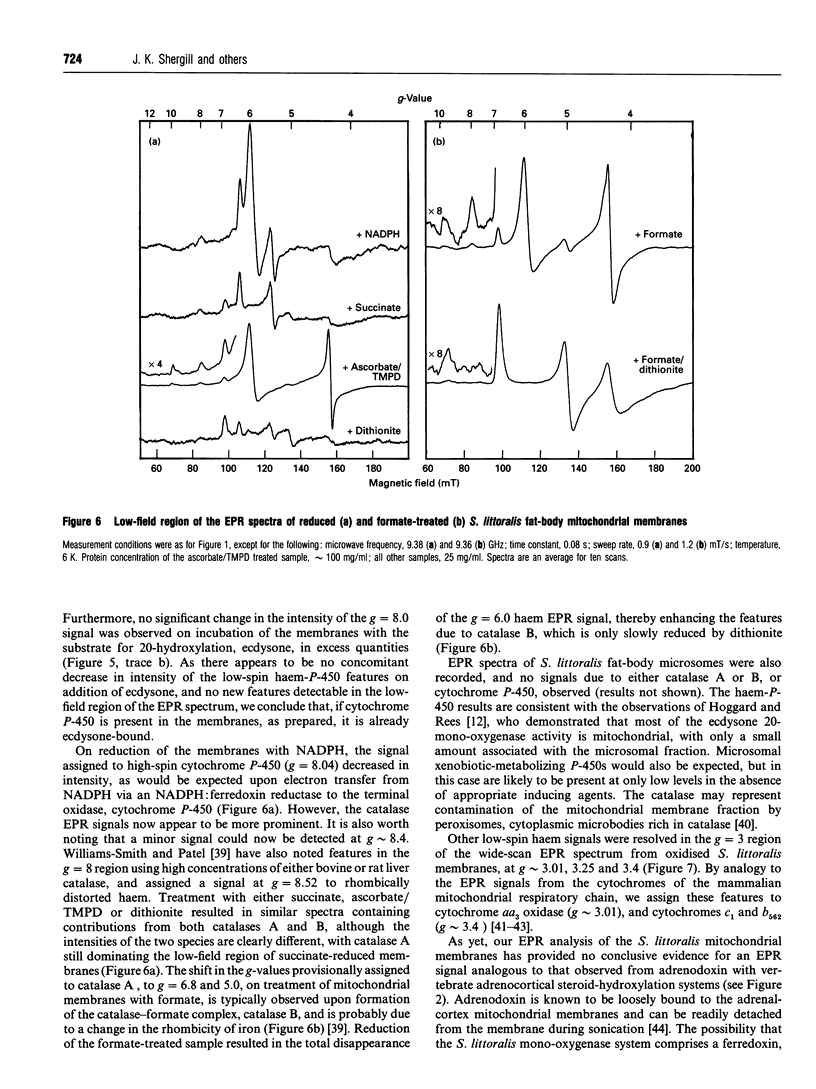
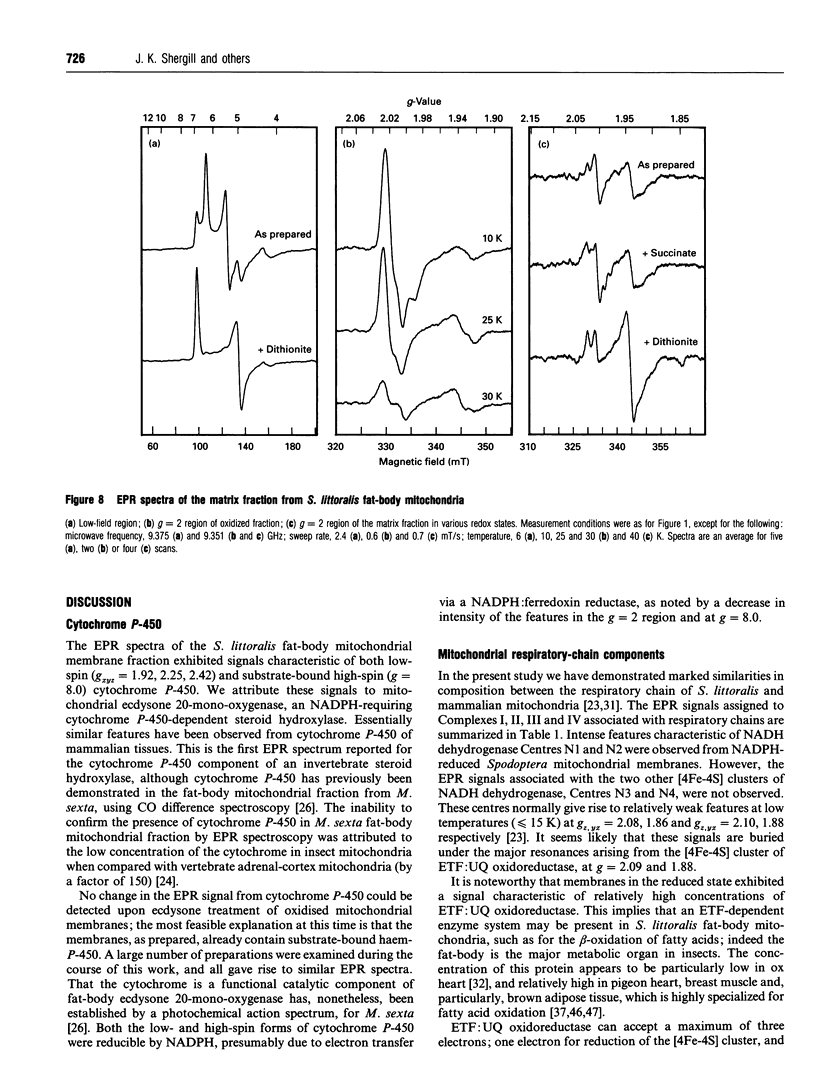
EPR spectroscopy was used to investigate the cytochrome P-450-dependent steroid hydroxylase ecdysone 20-mono-oxygenase of the cotton leafworm (Spodoptera littoralis) and the redox centres associated with membranes from the fat-body mitochondrial fraction. Intense features at g = 2.42, 2.25 and 1.92 from oxidized mitochondrial membranes have been assigned to the low-spin haem form of ferricytochrome P-450, probably of ecdysone 20-mono-oxygenase. High-spin cytochrome P-450 (substrate-bound) was tentatively assigned to a signal at g = 8.0, which was detectable from membranes as prepared. An EPR signal characteristic of a [2Fe-2S] cluster detected from the soluble mitochondrial matrix fraction has been shown to be distinct from the signals associated with mitochondrial NADH dehydrogenase and succinate dehydrogenase, and has therefore been attributed to a ferredoxin. We conclude that the S. littoralis fat-body mitochondrial electron-transport system involved in steroid 20-hydroxylation comprises both ferredoxin and cytochrome P-450 components, and thus resembles the enzyme systems of adrenocortical mitochondria. EPR signals characteristic of the respiratory chain were also observed from fat-body mitochondria and assigned to the iron-sulphur clusters associated with Complex I (Centres N1, N2), Complex II (Centres S1, S3), Complex III (the Rieske centre), and the copper centre of Complex IV, demonstrating similarities to mammalian mitochondria. The reduced membrane fraction also yielded a major resonance at g = 2.09 and 1.88 characteristic of the [4Fe-4S] cluster of electron-transferring flavoprotein: ubiquinone oxidoreductase. As the fat-body is the major metabolic organ of insects, this protein is presumably required for the beta-oxidation of fatty acids in mitochondria. High-spin haem signals in the low-field region of spectra also demonstrated that the mitochondrial fraction contains relatively high concentrations of catalase.
Full text
PDF


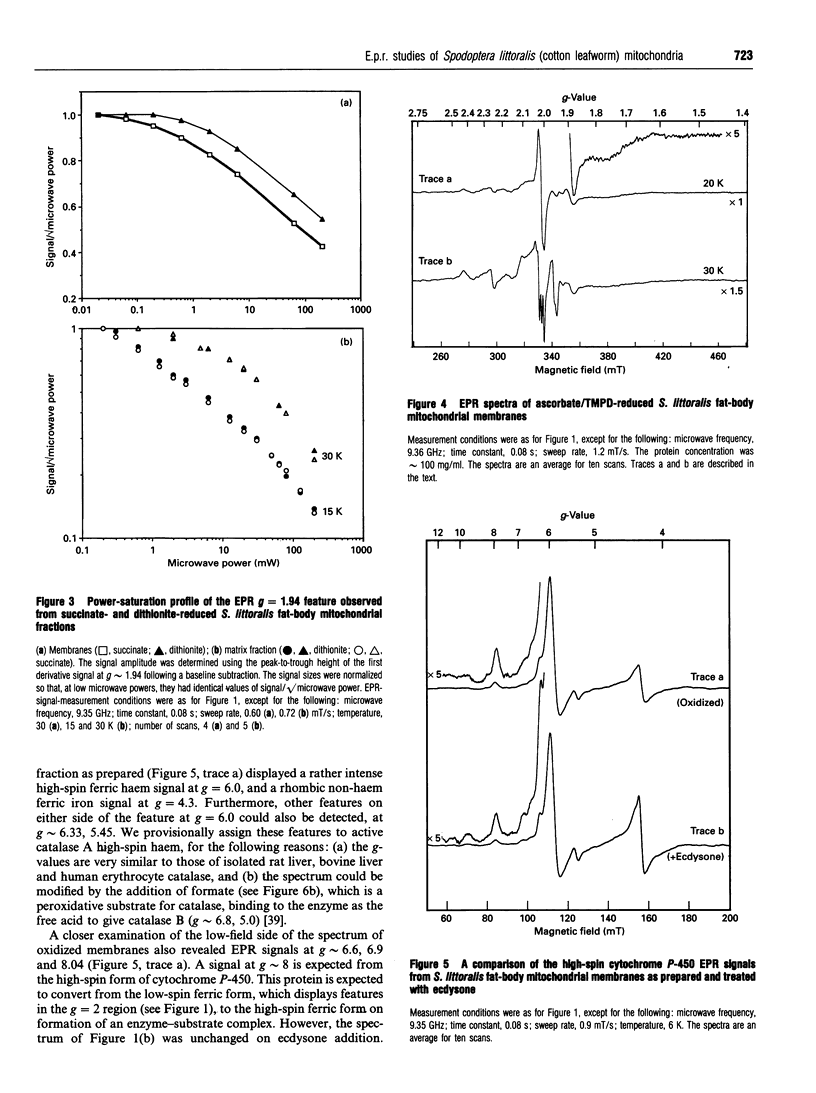


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aasa R., Albracht P. J., Falk K. E., Lanne B., Vänngard T. EPR signals from cytochrome c oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 13;422(2):260–272. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90137-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albracht S. P. Some new paramagnetic centers in submitochondrial particles detectable by EPR spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 22;347(2):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(74)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albracht S. P., van Verseveld H. W., Hagen W. R., Kalkman M. L. A comparison of the respiratory chain in particles from Paracoccus denitrificans and bovine heart mitochondria by EPR spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 3;593(2):173–186. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(80)90055-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beinert H. EPR spectroscopy of components of the mitochondrial electron-transfer system. Methods Enzymol. 1978;54:133–150. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)54014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. H., Hara T., Fisher M. J., Rees H. H. Immunological analysis of developmental changes in ecdysone 20-mono-oxygenase expression in the cotton leafworm, Spodoptera littoralis. Biochem J. 1994 May 1;299(Pt 3):711–717. doi: 10.1042/bj2990711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatmark T., Ruzicka F. J., Beinert H. The pattern of iron--sulfur centers in brown adipose tissue mitochondria: preponderance of ETF dehydrogenase and invariance with the thermogenic state. FEBS Lett. 1976 Mar 15;63(1):51–55. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80192-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunsalus I. C., Pederson T. C., Sligar S. G. Oxygenase-catalyzed biological hydroxylations. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:377–407. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.002113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HATEFI Y., HAAVIK A. G., GRIFFITHS D. E. Studies on the electron transfer system. XL. Preparation and properties of mitochondrial DPNH-coenzyme Q reductase. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1676–1680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. K., Morningstar J. E., Oliver M., Frerman F. E. Electron paramagnetic resonance and magnetic circular dichroism studies of electron-transfer flavoprotein-ubiquinone oxidoreductase from pig liver. FEBS Lett. 1987 Dec 21;226(1):129–133. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80565-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katagiri M., Ganguli B. N., Gunsalus I. C. A soluble cytochrome P-450 functional in methylene hydroxylation. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3543–3546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney K. B., Ackrell B. A., Mayr M., Singer T. P. Activation of succinate dehydrogenase by anions and pH. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2016–2020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura T., Parcells J. H., Wang H. P. Purification of adrenodoxin reductase, adrenodoxin, and cytochrome P-450 from adrenal cortex. Methods Enzymol. 1978;52:132–142. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)52015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura T., Suzuki K. Components of the electron transport system in adrenal steroid hydroxylase. Isolation and properties of non-heme iron protein (adrenodoxin). J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 10;242(3):485–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A. Y., Levin W. The resolution and reconstitution of the liver microsomal hydroxylation system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Sep 16;344(2):205–240. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(74)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire J. J., Johnson M. K., Morningstar J. E., Ackrell B. A., Kearney E. B. Electron paramagnetic resonance studies of mammalian succinate dehydrogenase. Detection of the tetranuclear cluster S2. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):10909–10912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitani F. Cytochrome P450 in adrenocortical mitochondria. Mol Cell Biochem. 1979 Mar 5;24(1):21–43. doi: 10.1007/BF00220191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami K., Mason H. S. An electron spin resonance study of microsomal Fe. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 25;242(6):1102–1110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi T., Lim J., Winter D. B., King T. E. Thermodynamic and EPR characteristics of a HiPIP-type iron-sulfur center in the succinate dehydrogenase of the respiratory chain. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):2105–2109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi T., Schägger H., Meinhardt S. W., LoBrutto R., Link T. A., von Jagow G. Spatial organization of redox active centers in the bovine heart ubiquinol-cytochrome c oxidoreductase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):735–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi T., Wilson D. F., Asakura T., Chance B. Studies on iron-sulfur proteins in the site I region of the respiratory chain in pigeon heart mitochondria and submitochondrial particles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Feb 25;46(4):1631–1638. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90796-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme-Johnson N. R., Hansen R. E., Beinert H. Electron paramagnetic resonance-detectable electron acceptors in beef heart mitochondria. Ubihydroquinone-cytochrome c reductase segment of the electron transfer system and complex mitochondrial fragments. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 25;249(6):1928–1939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruzicka F. J., Beinert H. A new iron-sulfur flavoprotein of the respiratory chain. A component of the fatty acid beta oxidation pathway. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8440–8445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruzicka F. J., Beinert H. The soluble "high potential" type iron-sulfur protein from mitochondria is aconitase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2514–2517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salerno J. C. Cytochrome electron spin resonance line shapes, ligand fields, and components stoichiometry in ubiquinol-cytochrome c oxidoreductase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2331–2336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shergill J. K., Cammack R. ESEEM studies of the iron-sulphur clusters of succinate dehydrogenase in Arum maculatum spadix mitochondrial membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Mar 29;1185(1):43–49. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(94)90191-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sih C. J. Enzymatic mechanism of steroid hydroxylation. Science. 1969 Mar 21;163(3873):1297–1300. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3873.1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. L., Bollenbacher W. E., Cooper D. Y., Schleyer H., Wielgus J. J., Gilbert L. I. Ecdysone 20-monooxygenase: characterization of an insect cytochrome p-450 dependent steroid hydroxylase. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1979 Sep;15(3):111–133. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(79)90033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trumpower B. L. New concepts on the role of ubiquinone in the mitochondrial respiratory chain. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1981 Apr;13(1-2):1–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00744743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai R., Yu C. A., Gunsalus I. C., Peisach J., Blumberg W., Orme-Johnson W. H., Beinert H. Spin-state changes in cytochrome P-450cam on binding of specific substrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1157–1163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermilion J. L., Coon M. J. Identification of the high and low potential flavins of liver microsomal NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8812–8819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams-Smith D. L., Patel K. Induced changes in the electron paramagnetic resonance spectra of mammalian catalases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 20;405(2):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Duve C. Microbodies in the living cell. Sci Am. 1983 May;248(5):74–84. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0583-74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


