Abstract
Several hydrophobic glycosides of N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) served as primers for polylactosamine synthesis when added to Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells. The modified glycosides, containing one to six lactosamine repeats in linear array, were sialylated and secreted into the culture medium. The relative efficiencies of the glycosides to serve as primers were dependent on the nature of the aglycone and on the anomeric configuration of the GlcNAc residue. The same compounds were tested for their effects on glycolipid synthesis in CHO cells. All of the beta-glycosides significantly inhibited the synthesis of the lactoseries glycolipid GM3 whereas the alpha-glycoside was inactive. The compound GlcNAc alpha 1-O-benzyl- was the most efficient primer of polylactosamine synthesis and had no effect on glycolipid synthesis. This compound may have potential for the assay of the polylactosamine synthetic capacity of living cells.
Full text
PDF
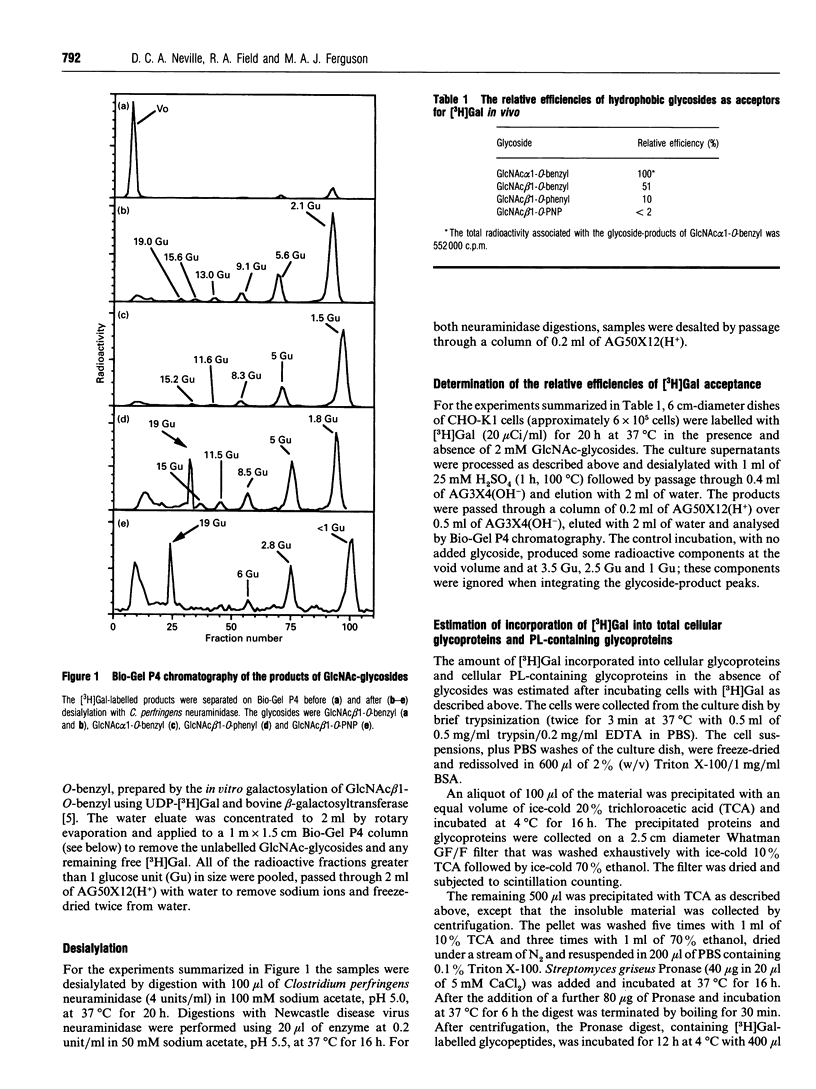

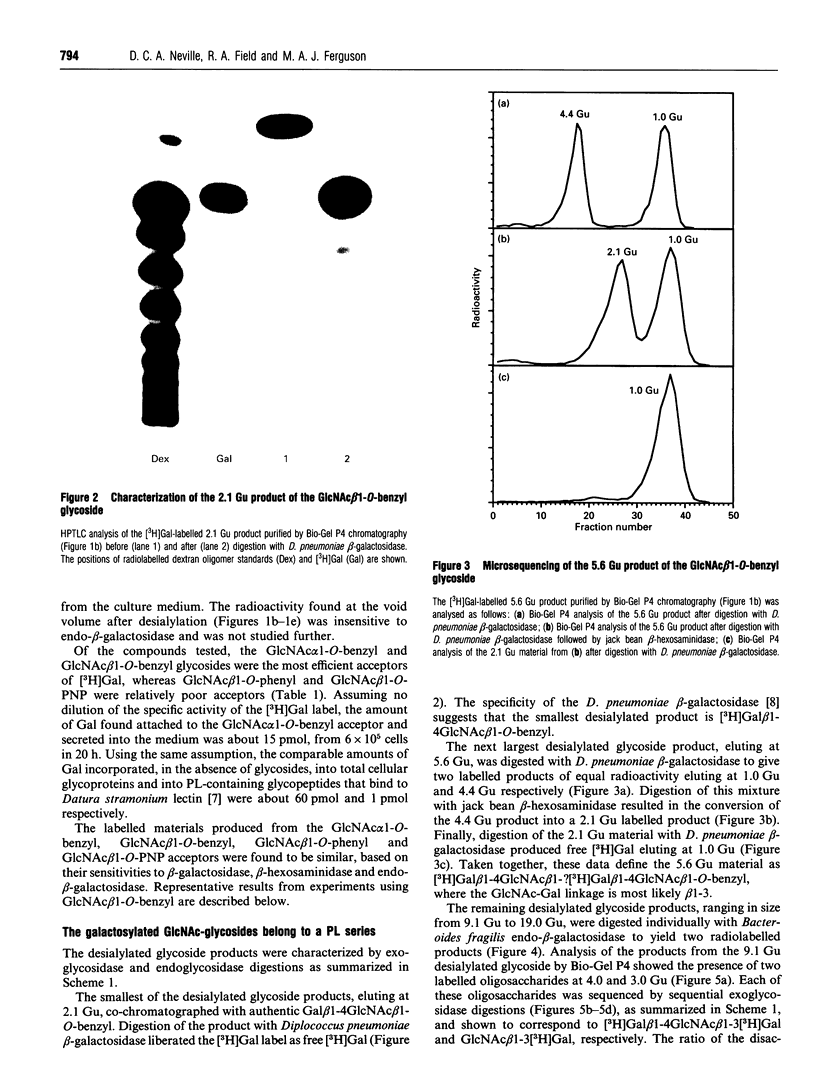


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bierhuizen M. F., Fukuda M. Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding UDP-GlcNAc:Gal beta 1-3-GalNAc-R (GlcNAc to GalNAc) beta 1-6GlcNAc transferase by gene transfer into CHO cells expressing polyoma large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9326–9330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson S. R., Fukuda M. The polylactosaminoglycans of human lysosomal membrane glycoproteins lamp-1 and lamp-2. Localization on the peptide backbones. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20488–20495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs R. A., Kapadia A., Feizi T. Expression of blood group I and i active carbohydrate sequences on cultured human and animal cell lines assessed by radioimmunoassays with monoclonal cold agglutinins. Eur J Immunol. 1980 May;10(5):379–384. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corfield A. P., Veh R. W., Wember M., Michalski J. C., Schauer R. The release of N-acetyl- and N-glycolloyl-neuraminic acid from soluble complex carbohydrates and erythrocytes by bacterial, viral and mammalian sialidases. Biochem J. 1981 Aug 1;197(2):293–299. doi: 10.1042/bj1970293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Do K. Y., Cummings R. D. 2,6-branched mannose and the regulation of poly-N-acetyllactosamine biosynthesis in N-linked oligosaccharides of Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):22028–22035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Do K. Y., Smith D. F., Cummings R. D. LAMP-1 in CHO cells is a primary carrier of poly-N-acetyllactosamine chains and is bound preferentially by a mammalian S-type lectin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 31;173(3):1123–1128. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80902-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elices M. J., Goldstein I. J. Initiation of poly-N-acetyllactosamine chain biosynthesis occurs preferentially on complex multiantennary asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Carbohydr Res. 1990 Aug 1;203(1):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(90)80050-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feizi T., Childs R. A. Carbohydrates as antigenic determinants of glycoproteins. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 1;245(1):1–11. doi: 10.1042/bj2450001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeze H. H., Sampath D., Varki A. Alpha- and beta-xylosides alter glycolipid synthesis in human melanoma and Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1618–1627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz T. A., Lugemwa F. N., Sarkar A. K., Esko J. D. Biosynthesis of heparan sulfate on beta-D-xylosides depends on aglycone structure. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):300–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuan S. F., Byrd J. C., Basbaum C., Kim Y. S. Inhibition of mucin glycosylation by aryl-N-acetyl-alpha-galactosaminides in human colon cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19271–19277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li E., Gibson R., Kornfeld S. Structure of an unusual complex-type oligosaccharide isolated from Chinese hamster ovary cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Feb;199(2):393–399. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90295-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Fambrough D. M. Lysosomal membrane dynamics: structure and interorganellar movement of a major lysosomal membrane glycoprotein. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1593–1605. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugemwa F. N., Esko J. D. Estradiol beta-D-xyloside, an efficient primer for heparan sulfate biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):6674–6677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mane S. M., Marzella L., Bainton D. F., Holt V. K., Cha Y., Hildreth J. E., August J. T. Purification and characterization of human lysosomal membrane glycoproteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Jan;268(1):360–378. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90597-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson J. C., Prieels J. P., Glasgow L. R., Hill R. L. Sialyl- and fucosyltransferases in the biosynthesis of asparaginyl-linked oligosaccharides in glycoproteins. Mutually exclusive glycosylation by beta-galactoside alpha2 goes to 6 sialyltransferase and N-acetylglucosaminide alpha1 goes to 3 fucosyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5617–5624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ram B. P., Munjal D. D. Galactosyltransferases: physical, chemical, and biological aspects. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;17(3):257–311. doi: 10.3109/10409238509113606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seguchi T., Merkle R. K., Ono M., Kuwano M., Cummings R. D. The dysfunctional LDL receptor in a monensin-resistant mutant of Chinese hamster ovary cells lacks selected O-linked oligosaccharides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Feb 1;284(2):245–256. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90292-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi M., Kobata A. Structures and functional roles of the sugar chains of human erythropoietins. Glycobiology. 1991 Sep;1(4):337–346. doi: 10.1093/glycob/1.4.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland F. T., Gleason M. L., Serafini T. A., Rothman J. E. The rate of bulk flow from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cell surface. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90224-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]