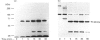Abstract
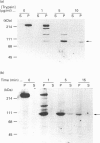
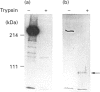
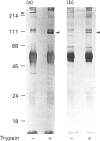
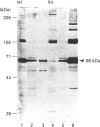
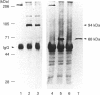
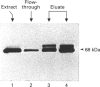
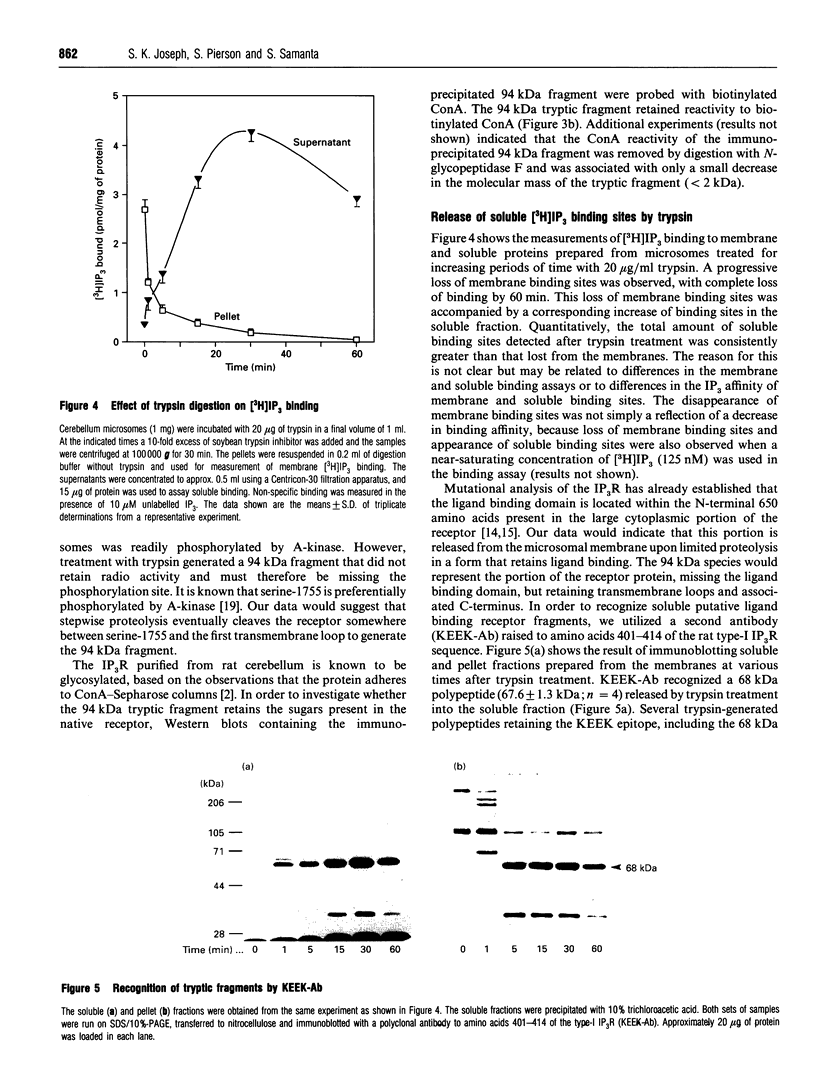
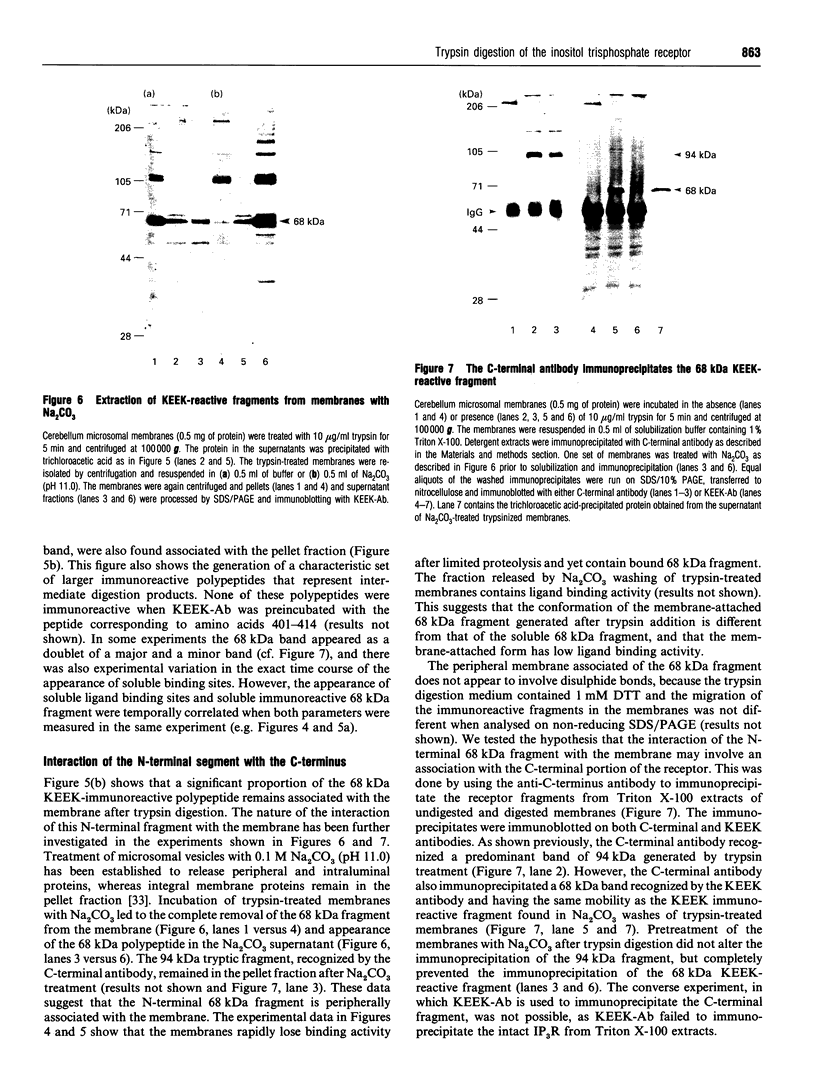
Limited digestion of rat cerebellum microsomal vesicles with trypsin resulted in the proteolysis of the 240 kDa inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor (IP3R) and the formation of a 94 kDa species that remained membrane-bound and retained immunoreactivity to an antibody raised against the C-terminal sequence of this protein. The appearance of the 94 kDa species was associated with a loss of [3H]IP3 binding sites in the membrane and the appearance of [3H]IP3 binding sites in the soluble fraction. The 94 kDa fragment retained reactivity to biotinylated concanavalin A. In vitro phosphorylation of the IP3R in membranes with cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase and [gamma-32P]ATP produced an unlabelled 94 kDa fragment after tryptic digestion. According to current models of the cerebellar IP3R this would place the proteolytic site between the phosphorylation site at serine-1755 and the first transmembrane segment of the IP3R. A second antibody raised to amino acids 401-414 in the N-terminal region of the receptor recognizes a 68 kDa fragment released into the soluble fraction after trypsin treatment. The time course of release of the 68 kDa fragment was correlated with the appearance of soluble binding sites, and the fragment was bound by IP3-Affigel resin. A large proportion of the 68 kDa fragment remained associated with the membrane fraction and could be specifically immunoprecipitated from detergent extracts of digested membranes by anti-C-terminus antibody. Our results provide experimental evidence to further localize the ligand binding domain and suggest that regions of the N-terminus and C-terminus may be non-covalently associated.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blondel O., Takeda J., Janssen H., Seino S., Bell G. I. Sequence and functional characterization of a third inositol trisphosphate receptor subtype, IP3R-3, expressed in pancreatic islets, kidney, gastrointestinal tract, and other tissues. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11356–11363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J., Drevin H., Axén R. Protein thiolation and reversible protein-protein conjugation. N-Succinimidyl 3-(2-pyridyldithio)propionate, a new heterobifunctional reagent. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 1;173(3):723–737. doi: 10.1042/bj1730723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. R., Airey J. A., MacLennan D. H. Positioning of major tryptic fragments in the Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) resulting from partial digestion of rabbit skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22642–22649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danoff S. K., Ferris C. D., Donath C., Fischer G. A., Munemitsu S., Ullrich A., Snyder S. H., Ross C. A. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors: distinct neuronal and nonneuronal forms derived by alternative splicing differ in phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2951–2955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Takei K., Mignery G. A., Südhof T. C. InsP3 receptor turnaround. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):495–495. doi: 10.1038/344495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris C. D., Cameron A. M., Bredt D. S., Huganir R. L., Snyder S. H. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor is phosphorylated by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase at serines 1755 and 1589. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Feb 28;175(1):192–198. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris C. D., Huganir R. L., Bredt D. S., Cameron A. M., Snyder S. H. Inositol trisphosphate receptor: phosphorylation by protein kinase C and calcium calmodulin-dependent protein kinases in reconstituted lipid vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2232–2235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris C. D., Huganir R. L., Snyder S. H. Calcium flux mediated by purified inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor in reconstituted lipid vesicles is allosterically regulated by adenine nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2147–2151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris C. D., Huganir R. L., Supattapone S., Snyder S. H. Purified inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor mediates calcium flux in reconstituted lipid vesicles. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):87–89. doi: 10.1038/342087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi T., Yoshikawa S., Miyawaki A., Wada K., Maeda N., Mikoshiba K. Primary structure and functional expression of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-binding protein P400. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):32–38. doi: 10.1038/342032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell K. E., Palade G. E. Hepatic Golgi fractions resolved into membrane and content subfractions. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):822–832. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Rice H. L., Williamson J. R. The effect of external calcium and pH on inositol trisphosphate-mediated calcium release from cerebellum microsomal fractions. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 15;258(1):261–265. doi: 10.1042/bj2580261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Samanta S. Detergent solubility of the inositol trisphosphate receptor in rat brain membranes. Evidence for association of the receptor with ankyrin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6477–6486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Braell W. A., Schwartz A. L., Strous G. J., Zilberstein A. Synthesis and assembly of membrane and organelle proteins. Int Rev Cytol Suppl. 1981;12:247–307. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-364373-5.50016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Kawasaki T., Nakade S., Yokota N., Taguchi T., Kasai M., Mikoshiba K. Structural and functional characterization of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor channel from mouse cerebellum. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1109–1116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Niinobe M., Mikoshiba K. A cerebellar Purkinje cell marker P400 protein is an inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) receptor protein. Purification and characterization of InsP3 receptor complex. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):61–67. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08080.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maranto A. R. Primary structure, ligand binding, and localization of the human type 3 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor expressed in intestinal epithelium. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1222–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michikawa T., Hamanaka H., Otsu H., Yamamoto A., Miyawaki A., Furuichi T., Tashiro Y., Mikoshiba K. Transmembrane topology and sites of N-glycosylation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 25;269(12):9184–9189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignery G. A., Newton C. L., Archer B. T., 3rd, Südhof T. C. Structure and expression of the rat inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12679–12685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignery G. A., Südhof T. C. The ligand binding site and transduction mechanism in the inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate receptor. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3893–3898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07609.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikoshiba K. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Mar;14(3):86–89. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90069-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyawaki A., Furuichi T., Ryou Y., Yoshikawa S., Nakagawa T., Saitoh T., Mikoshiba K. Structure-function relationships of the mouse inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4911–4915. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mourey R. J., Estevez V. A., Marecek J. F., Barrow R. K., Prestwich G. D., Snyder S. H. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors: labeling the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate binding site with photoaffinity ligands. Biochemistry. 1993 Feb 23;32(7):1719–1726. doi: 10.1021/bi00058a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mourey R. J., Verma A., Supattapone S., Snyder S. H. Purification and characterization of the inositol 1,4,5- trisphosphate receptor protein from rat vas deferens. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 1;272(2):383–389. doi: 10.1042/bj2720383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakade S., Maeda N., Mikoshiba K. Involvement of the C-terminus of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor in Ca2+ release analysed using region-specific monoclonal antibodies. Biochem J. 1991 Jul 1;277(Pt 1):125–131. doi: 10.1042/bj2770125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa T., Okano H., Furuichi T., Aruga J., Mikoshiba K. The subtypes of the mouse inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor are expressed in a tissue-specific and developmentally specific manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6244–6248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parys J. B., Sernett S. W., DeLisle S., Snyder P. M., Welsh M. J., Campbell K. P. Isolation, characterization, and localization of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor protein in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18776–18782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., Danoff S. K., Schell M. J., Snyder S. H., Ullrich A. Three additional inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors: molecular cloning and differential localization in brain and peripheral tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4265–4269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusakov D. A., Podini P., Villa A., Meldolesi J. Tridimensional organization of Purkinje neuron cisternal stacks, a specialized endoplasmic reticulum subcompartment rich in inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors. J Neurocytol. 1993 Apr;22(4):273–282. doi: 10.1007/BF01187126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supattapone S., Danoff S. K., Theibert A., Joseph S. K., Steiner J., Snyder S. H. Cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation of a brain inositol trisphosphate receptor decreases its release of calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8747–8750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supattapone S., Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Snyder S. H. Solubilization, purification, and characterization of an inositol trisphosphate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1530–1534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Newton C. L., Archer B. T., 3rd, Ushkaryov Y. A., Mignery G. A. Structure of a novel InsP3 receptor. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3199–3206. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04882.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takei K., Mignery G. A., Mugnaini E., Südhof T. C., De Camilli P. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor causes formation of ER cisternal stacks in transfected fibroblasts and in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neuron. 1994 Feb;12(2):327–342. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90275-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Supattapone S., Wilson V. S., Snyder S. H. Characterization of inositol trisphosphate receptor binding in brain. Regulation by pH and calcium. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12132–12136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa S., Tanimura T., Miyawaki A., Nakamura M., Yuzaki M., Furuichi T., Mikoshiba K. Molecular cloning and characterization of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor in Drosophila melanogaster. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16613–16619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]